Содержание
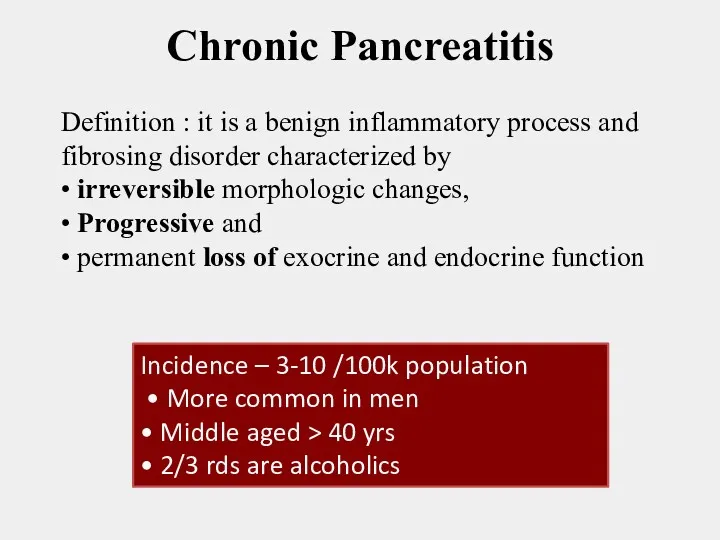
- 2. Chronic Pancreatitis Definition : it is a benign inflammatory process and fibrosing disorder characterized by •
- 3. Pathophysiology Etiology
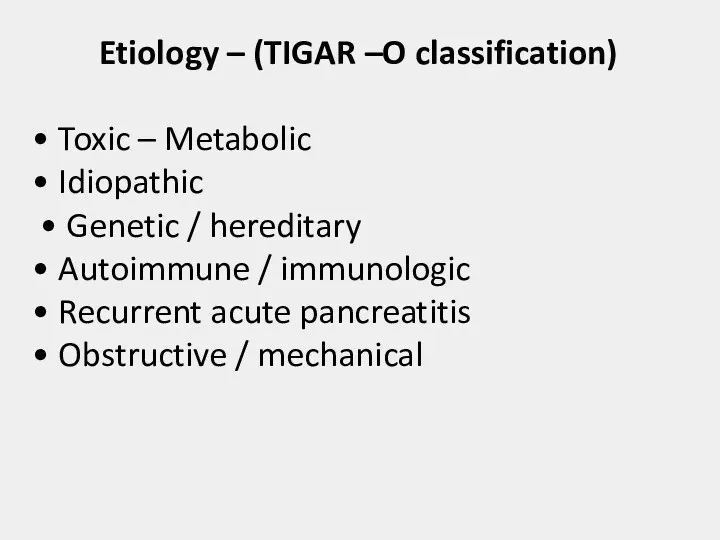
- 4. Etiology – (TIGAR –O classification) • Toxic – Metabolic • Idiopathic • Genetic / hereditary •
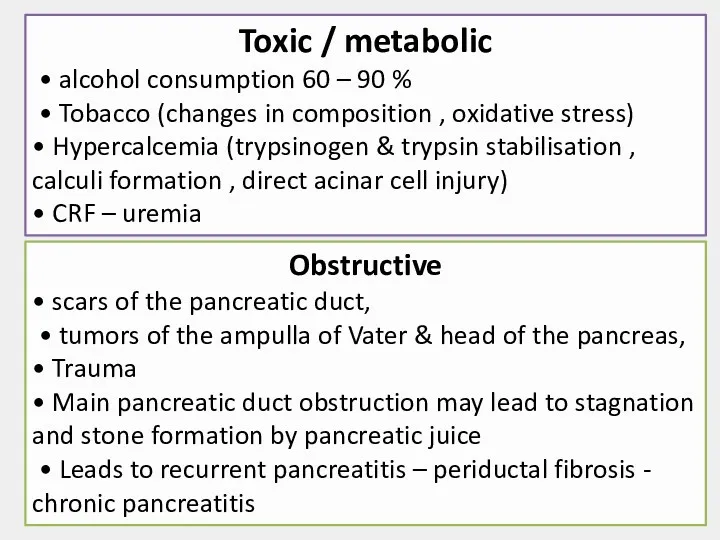
- 5. Toxic / metabolic • alcohol consumption 60 – 90 % • Tobacco (changes in composition ,
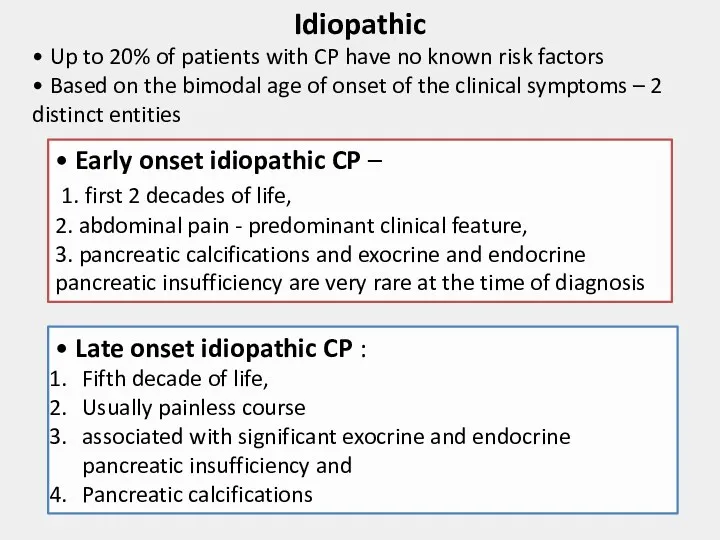
- 6. Idiopathic • Up to 20% of patients with CP have no known risk factors • Based
- 7. Auto immune / immunological rare but distinct form of CP characterized by specific histopathologic an immunologic
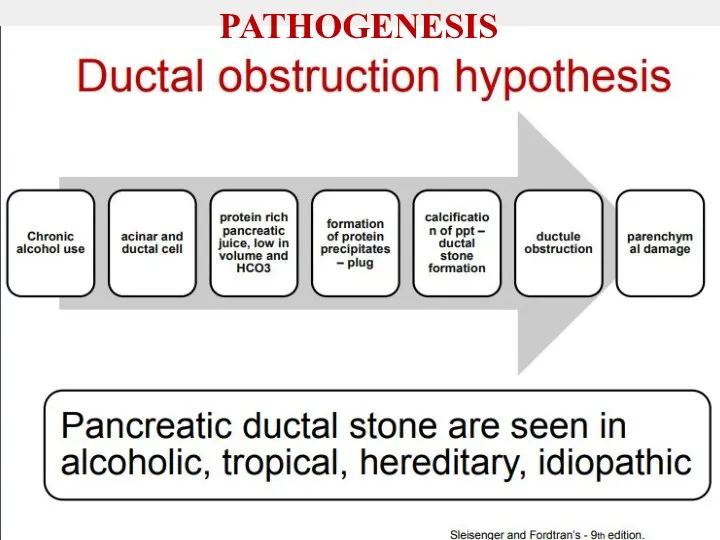
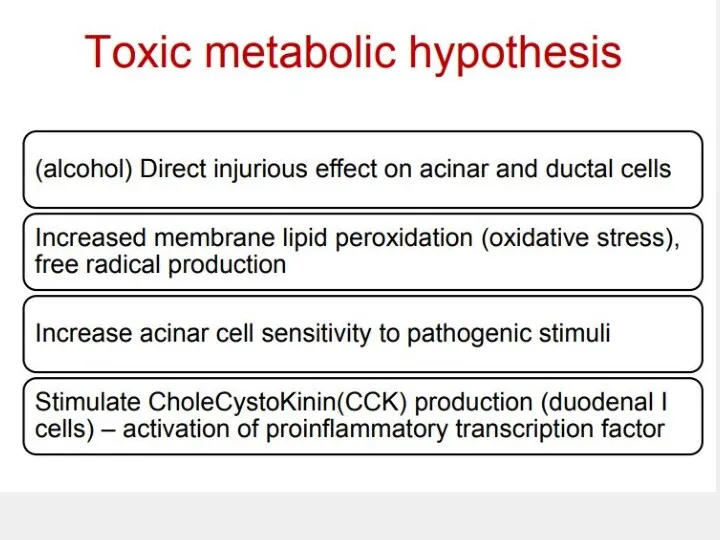
- 8. PATHOGENESIS
- 11. Clinical features • Abdominal Pain • Exocrine insufficiency occurs in 80% to 90% • steatorrhea, •
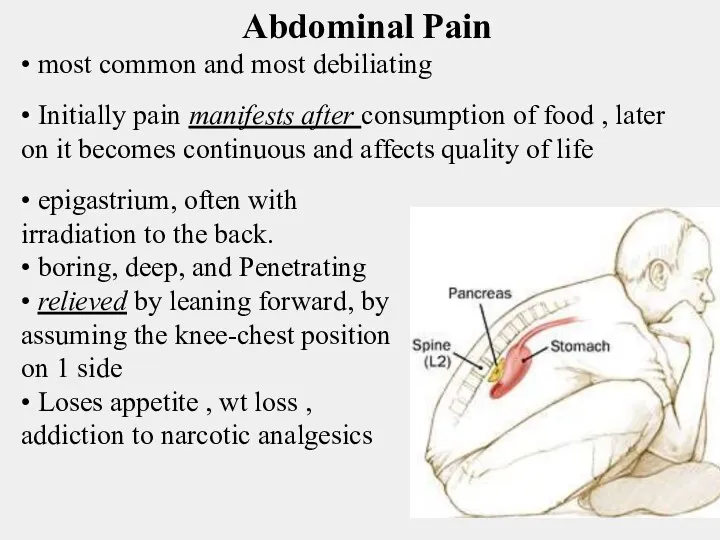
- 12. Abdominal Pain • most common and most debiliating • Initially pain manifests after consumption of food
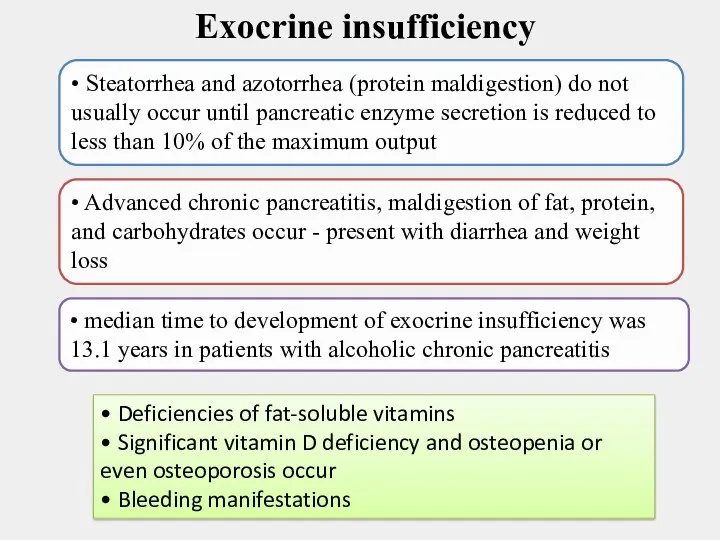
- 13. Exocrine insufficiency • Steatorrhea and azotorrhea (protein maldigestion) do not usually occur until pancreatic enzyme secretion
- 14. Endocrine insufficiency : • Chronic pancreatitis also affects islet cell populations - 40% to 80% of
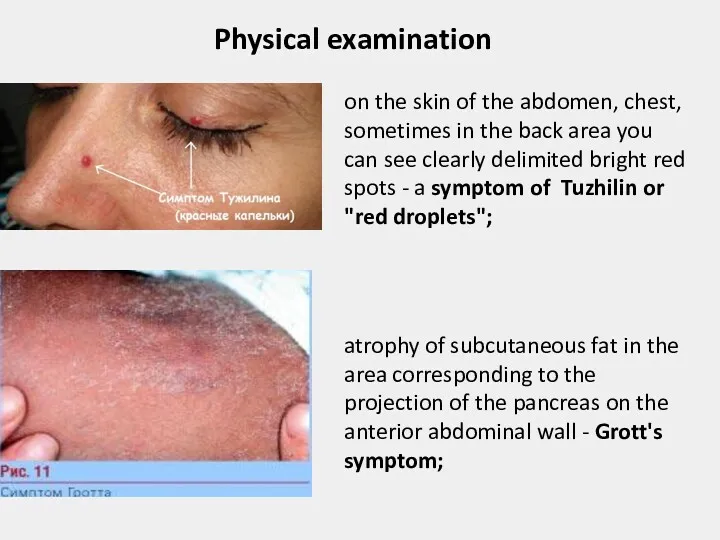
- 15. Physical examination on the skin of the abdomen, chest, sometimes in the back area you can
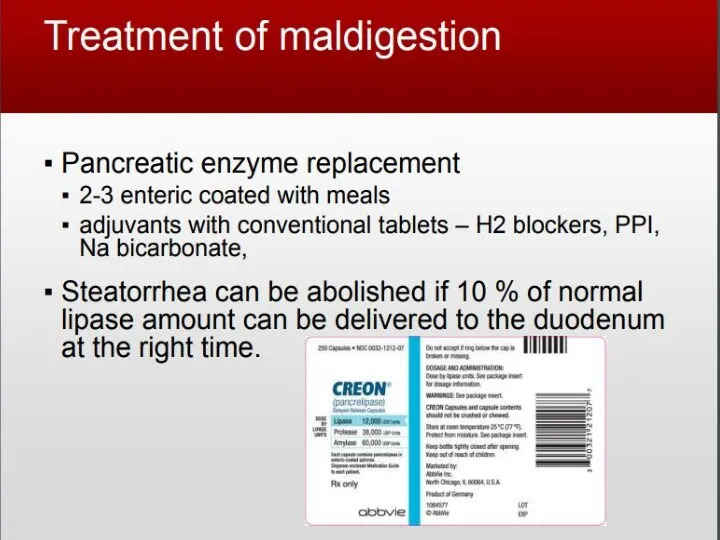
- 26. 75000-80000ME for food intake
- 31. Скачать презентацию







 Профилактика нарушений зрения у школьников
Профилактика нарушений зрения у школьников Сестринский уход при хроническом панкреатите
Сестринский уход при хроническом панкреатите Оказание первой медицинской помощи при ушибах, переломах
Оказание первой медицинской помощи при ушибах, переломах Балалардағы асқазан ойық жара ауруы
Балалардағы асқазан ойық жара ауруы Общие правила оказания первой медицинской помощи
Общие правила оказания первой медицинской помощи Тазовое предлежание. Многоплодная беременность
Тазовое предлежание. Многоплодная беременность Общая характеристика основных этапов исследования качества лекарственных средств
Общая характеристика основных этапов исследования качества лекарственных средств Санитарно-гигиеническое обучение
Санитарно-гигиеническое обучение Healthy lifestyle. Your choice
Healthy lifestyle. Your choice Заболевания щитовидной железы. Синдром тиреотоксикоза. ДТЗ. Синдром гипотиреоза. ЙДЗ
Заболевания щитовидной железы. Синдром тиреотоксикоза. ДТЗ. Синдром гипотиреоза. ЙДЗ Лимфопролиферативные заболевания
Лимфопролиферативные заболевания Қазақстан Республикасында сібір жарасы ауруының таралу корсеткіштері
Қазақстан Республикасында сібір жарасы ауруының таралу корсеткіштері Полное обследование новорожденного. (Модуль 1)
Полное обследование новорожденного. (Модуль 1) Ревматоидный артрит
Ревматоидный артрит Магнитно-резонансная томография (МРТ)
Магнитно-резонансная томография (МРТ) Здоровьесберегающие технологии на уроках физической культуры
Здоровьесберегающие технологии на уроках физической культуры Технология мягких лекарственных форм
Технология мягких лекарственных форм Сложный путь между полипрагмазией и нигилизмом в нейрореаниматологии
Сложный путь между полипрагмазией и нигилизмом в нейрореаниматологии Противовоспалительные, противоаллергические средства
Противовоспалительные, противоаллергические средства Сердечные гликозиды. Общая характеристика, методы выделения, анализ. (Тема 7)
Сердечные гликозиды. Общая характеристика, методы выделения, анализ. (Тема 7) Определение групп крови
Определение групп крови HELLP-синдромы, диагностикасы, интенсивті емі
HELLP-синдромы, диагностикасы, интенсивті емі Осторожно, клещи
Осторожно, клещи Инсулин. Современная классификация инсулинов
Инсулин. Современная классификация инсулинов Вирустық аурулардың спецификалық алдын алу. Вакцина дайындау принциптері. Адьюванттар, иммуномодуляторлар
Вирустық аурулардың спецификалық алдын алу. Вакцина дайындау принциптері. Адьюванттар, иммуномодуляторлар Инфекции, передающиеся клещами и комарами
Инфекции, передающиеся клещами и комарами Физиология органов, сочетающих неэндокринную функцию с эндокринной и их влияние на деятельность организма
Физиология органов, сочетающих неэндокринную функцию с эндокринной и их влияние на деятельность организма Отруєння речовинами, що є хімічною зброєю. Заходи безпеки під час надання домедичної допомоги
Отруєння речовинами, що є хімічною зброєю. Заходи безпеки під час надання домедичної допомоги