Содержание
- 2. Diuretics excrete excess water and ions from the body. They increase diuresis. Urine formation includes 3
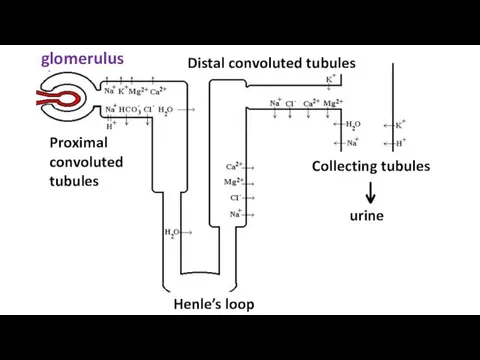
- 3. glomerulus Proximal convoluted tubules Distal convoluted tubules Henle’s loop Collecting tubules urine
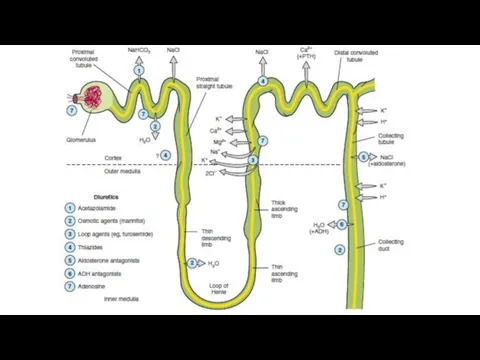
- 4. Mechanisms of reabsorption of Na and H₂O ATP-dependent membrane pump sodium in the proximal and distal
- 5. Classification according to the localization and mechanism of action 1.Drugs that increase glomerular filtration (hydruretics): aminophylline,
- 6. Proximal and distal convoluted tubules: hydrochlorothiazide, clopamide, cyclomethiazidum, indapamide Potassium-sparing diuretics (distal convoluted tubule and collecting
- 8. Classification according the power of action The most active diuretics (reduce the reabsorption of sodium by
- 9. Classification according speed of onset and duration of action: Rapid and short-acting (the effect after a
- 10. Indications for diuretics Emergency: Pulmonary edema, edema of brain, larynx Acute heart failure Acute renal failure
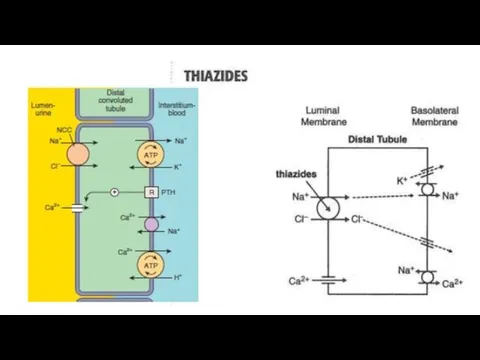
- 11. Hydrochlorothiazide is a derivate of thiazide. It suppresses reabsorption of sodium and chlorine ions mostly in
- 13. The speed of onset of action – 0.5-1 h, duration of action – 8-12 h. The
- 14. Cyclomethiazidum is 50 times as active as hydrochlorothiazide. Clopamide acts slowly but longer. The drug begins
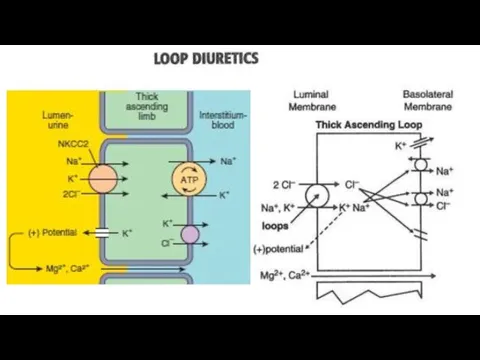
- 15. Furosemide is a very efficacious agent. Its effect begins in glomerulus because it increased the concentration
- 17. When administered intravenously, the drug begins to act in 3-5 min after infusion. The effect lasts
- 18. Torasemide’s effect lasts longer. Maximal effect develops in 2-3 h. The duration of effect is 6-8
- 19. Triamterene is a “potassium-and magnesium-sparing diuretic”. It retain potassium and magnesium in the body. The main
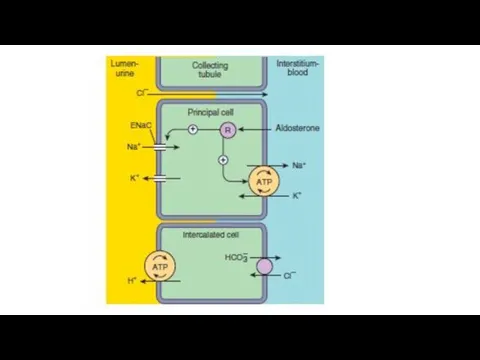
- 20. Spironolactone is a antagonist of mineralocorticoid aldosterone. It eliminates its effects on renal tubular function. Aldosterone
- 22. It is a weak diuretic. It is effective in cases of edema that resulted from aldosterone
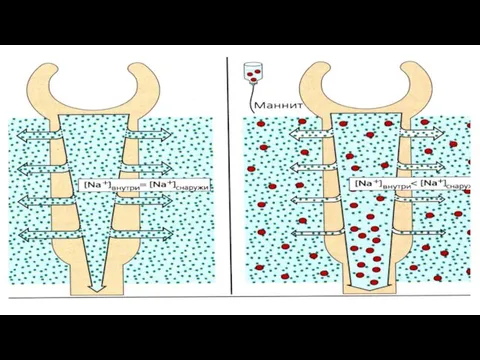
- 23. Mannitol is osmotic diuretic. Its effect begins in blood. It is injected intravenously and it increases
- 24. Mannitol is used as a diuretic, as a dehydrating agent in the treatment of brain edema,
- 26. Euphylline is xanthine derivate. It has a vasodilating effect. It increases renal blood flow and glomerular
- 28. Скачать презентацию



















 Артериальная гипертензия у беременных
Артериальная гипертензия у беременных Проблема качества жизни в контексте современной трансплантологии
Проблема качества жизни в контексте современной трансплантологии Les inlays-onlays esthétiques Procédures d’assemblage
Les inlays-onlays esthétiques Procédures d’assemblage ВКР: Сравнительная характеристика различных видов коронок и мостовидных протезов
ВКР: Сравнительная характеристика различных видов коронок и мостовидных протезов Hemolytic anemia
Hemolytic anemia Эндоскопические методы диагностики онкологических больных
Эндоскопические методы диагностики онкологических больных Leishmaniasis. Department of Infectious Diseases Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis. Department of Infectious Diseases Leishmaniasis ВКР: Деятельность медицинской сестры по уходу и наблюдению за пациентами при ОРВИ
ВКР: Деятельность медицинской сестры по уходу и наблюдению за пациентами при ОРВИ Острые нейроинфекции. Менингиты
Острые нейроинфекции. Менингиты Репродуктивне здоров’я молоді
Репродуктивне здоров’я молоді Оснащение формирований службы медицины катастроф по оказанию медицинской помощи в чрезвычайных ситуациях
Оснащение формирований службы медицины катастроф по оказанию медицинской помощи в чрезвычайных ситуациях Masaje al tejido conectivo
Masaje al tejido conectivo Синдром острой и хронической печеночной недостаточности
Синдром острой и хронической печеночной недостаточности Долікарська допомога
Долікарська допомога Эпилепсия
Эпилепсия Мимические мышцы лица
Мимические мышцы лица Вирусы, друзья и враги
Вирусы, друзья и враги Сестринский уход при различных заболеваниях и состояниях раздел Сестринская помощь в хирургии
Сестринский уход при различных заболеваниях и состояниях раздел Сестринская помощь в хирургии Методы обследования пациентов с патологией органов сердечно-сосудистой системы: пальпация, перкуссия, аускультация
Методы обследования пациентов с патологией органов сердечно-сосудистой системы: пальпация, перкуссия, аускультация Организация и содержание государственного ветеринарного надзора
Организация и содержание государственного ветеринарного надзора Острый живот в гинекологии
Острый живот в гинекологии Питание кормящей матери
Питание кормящей матери Анксиолитики (транквилизаторы)
Анксиолитики (транквилизаторы) Инфекционные болезни собак
Инфекционные болезни собак Токсические поражения печени
Токсические поражения печени Система здравоохранения в России
Система здравоохранения в России Тиреоидиты. Классификация
Тиреоидиты. Классификация Выделительная система
Выделительная система