Содержание
- 2. Definition of GERD (by WHO) It is a chronic relapsing disease which characterized by inflammatory damage
- 3. Epidemiology GERD is a global disease, and evidence suggests that its prevalence is increasing. Prevalence estimates
- 4. Factors contributing development of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Failure of antireflux barrier Reduced motor-evacuation function of
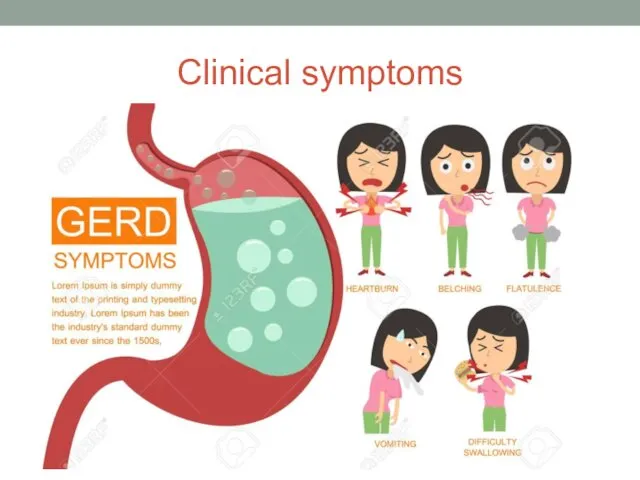
- 6. Clinical symptoms
- 7. Clinical symptoms
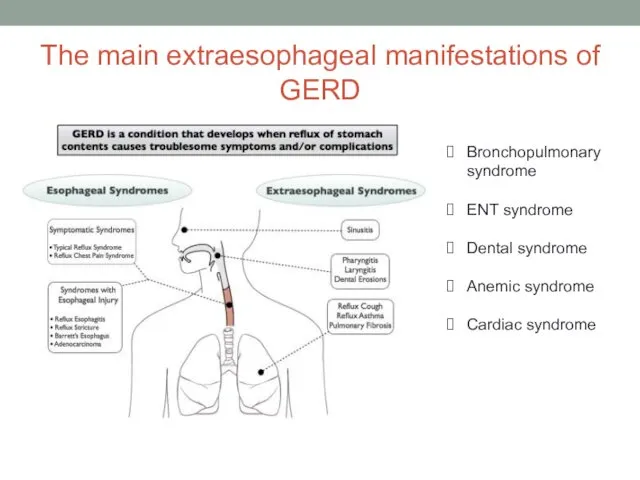
- 8. The main extraesophageal manifestations of GERD Bronchopulmonary syndrome ENT syndrome Dental syndrome Anemic syndrome Cardiac syndrome
- 9. Bronchopulmonary syndrome Chronic cough Paroxysmal sleep apnea Bouts of paroxysmal cough Reflux-induced asthma COPD Less often-the
- 10. Otolaryngological syndrome inflammation of the nasopharynx Pharyngitis, laryngitis, laryngeal croup Ulcers, granulomas, and polyps of the
- 11. Anemic syndrome Manifested by the development of posthemorrhagic hypochromic iron-deficiency anemia. Occurs due to chronic bleeding
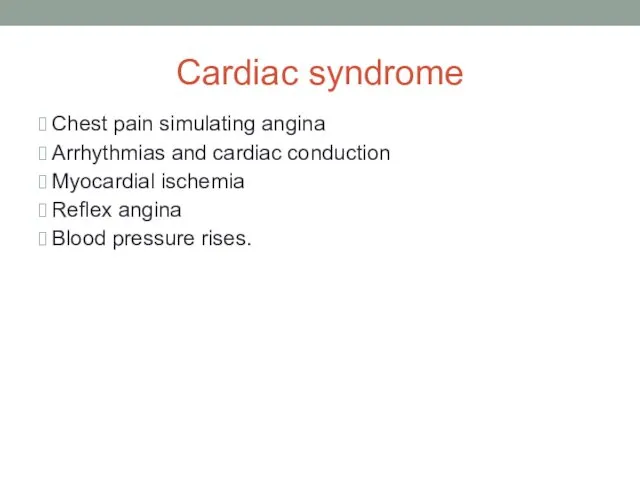
- 12. Cardiac syndrome Chest pain simulating angina Arrhythmias and cardiac conduction Myocardial ischemia Reflex angina Blood pressure
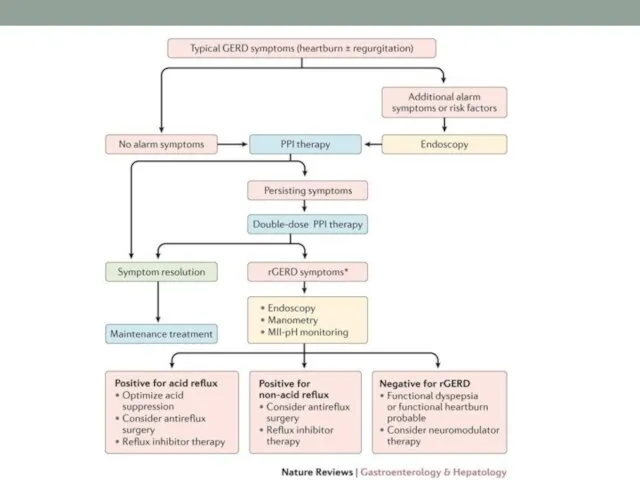
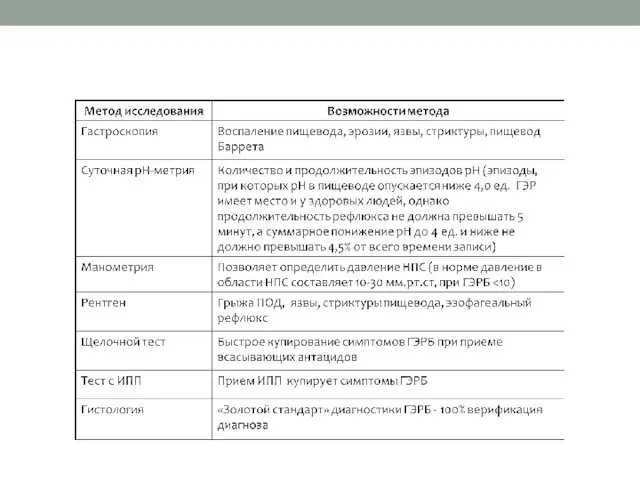
- 15. DIAGNOSING (TESTS) Gastroscopy Manometry Radiology Alkaline test Histology
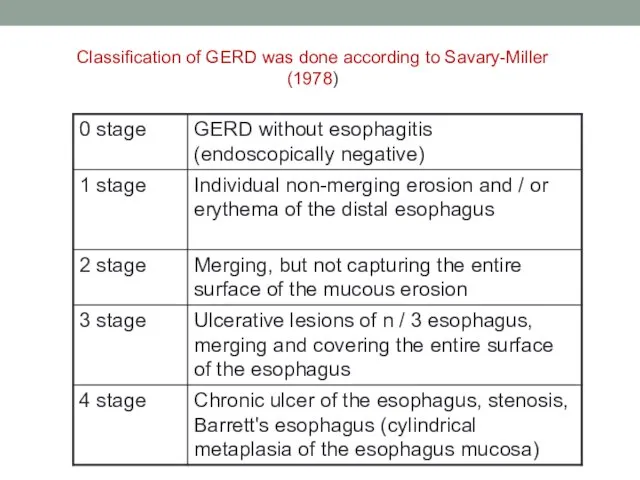
- 17. Classification of GERD was done according to Savary-Miller (1978)
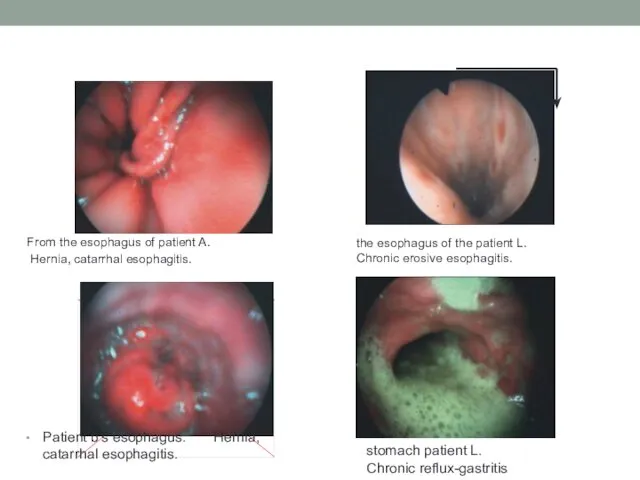
- 18. From the esophagus of patient A. Hernia, catarrhal esophagitis. Patient b's esophagus. Hernia, catarrhal esophagitis. the
- 19. TREATMENT I stage. Lifestyle change Stage II. Medicamental antireflux therapy Stage III. Supporting therapy
- 20. Lifestyle changing Fight against overweight Fractional power Walking for 30 minutes after meals Don't lie down
- 21. Basic antisecretory drugs and their daily doses Inhibitors of the proton pump - the "gold standard"
- 22. Alginates, aluminum-containing antacids Gaviscon 2-4 TB (carefully chew the tablets) or 10-20 ml suspension after a
- 23. Gastroproktektors Misoprostol (cytotec), 200 mcg, 3 times a day immediately after meals and h/night, De Nol,
- 24. Complications of GERD Stricture of the esophagus (7-23%) Esophageal ulcers (5%) Bleeding from erosions and ulcers
- 25. BIBLIOGRAPHY “Internal Diseases” 2nd edition. A.I. Martynov.,N.A. Mukhin.,B.C. Moiseev. Perkins Sherrie L. Normal blood and bone
- 27. Скачать презентацию

















 Первая помощь при ушибах, растяжениях, вывихах и переломах
Первая помощь при ушибах, растяжениях, вывихах и переломах Unsatisfactory progress of labor (parturition)
Unsatisfactory progress of labor (parturition) Система государственных учреждений, обеспечивающих контроль качества лекарственных средств
Система государственных учреждений, обеспечивающих контроль качества лекарственных средств Оказание первой помощи при отсутствии сознания, остановке дыхания и кровообращения
Оказание первой помощи при отсутствии сознания, остановке дыхания и кровообращения Mac-анестезия в эндоскопии и малоинвазивной хирургии
Mac-анестезия в эндоскопии и малоинвазивной хирургии Лифома Ходжкина
Лифома Ходжкина Введение в оперативную гинекологию
Введение в оперативную гинекологию Бауыр циррозы
Бауыр циррозы Профилактика нарушения осанки детей
Профилактика нарушения осанки детей Клиническая фармакология антигипертензивных ЛС. Фармакотерапия артериальной гипертензии
Клиническая фармакология антигипертензивных ЛС. Фармакотерапия артериальной гипертензии Эхокардиография
Эхокардиография Гемостаз
Гемостаз Острая пневмония
Острая пневмония Научные статьи в электронных базах данных о факторе риска крови в развитии лихорадки Эбола
Научные статьи в электронных базах данных о факторе риска крови в развитии лихорадки Эбола Ожоги глаз. Классификация
Ожоги глаз. Классификация Режим дня в дошкольном учреждении
Режим дня в дошкольном учреждении Диадинамотерапия: показания и противопоказания
Диадинамотерапия: показания и противопоказания Красная волчанка
Красная волчанка Проблема бессонницы в структуре соматических заболеваний
Проблема бессонницы в структуре соматических заболеваний Искусственный интеллект в медицине
Искусственный интеллект в медицине Сепсис новорожденных
Сепсис новорожденных Ультразвуковое исследование голеностопного сустава
Ультразвуковое исследование голеностопного сустава Дәрігер мен науқастың тиімді қарым-қатынасына кедергі келтіретін бөгеттер
Дәрігер мен науқастың тиімді қарым-қатынасына кедергі келтіретін бөгеттер Нарушения аффективной сферы
Нарушения аффективной сферы Здоровое питание в школе и дома
Здоровое питание в школе и дома Хирургические лазеры в оториноларингологии
Хирургические лазеры в оториноларингологии Проблемы невынашивания. Современные принципы лечения
Проблемы невынашивания. Современные принципы лечения Постхолецистэктомический синдром
Постхолецистэктомический синдром