Содержание
- 2. Giardiasis Most common causative agent of epidemic & endemic diarrhoea throughout the world Prevalence - 2-5%
- 3. Morphology of Giardia lamblia trophozoite Pear shaped, rounded anterior end, posterior end pointed (looks like monkey
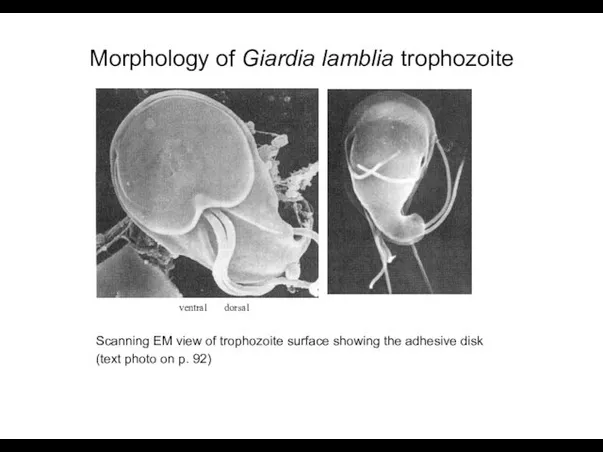
- 4. Morphology of Giardia lamblia trophozoite ventral dorsal Scanning EM view of trophozoite surface showing the adhesive
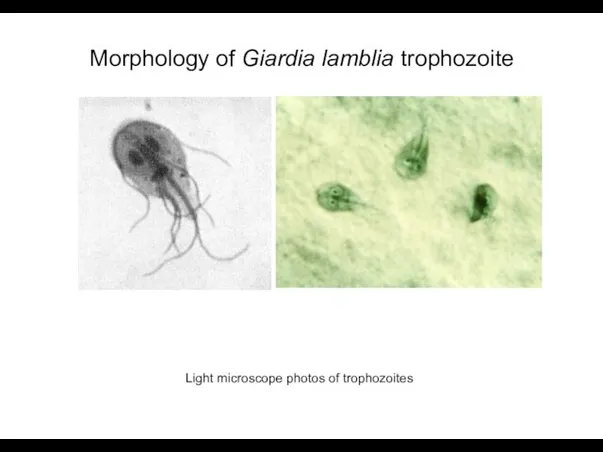
- 5. Morphology of Giardia lamblia trophozoite Light microscope photos of trophozoites
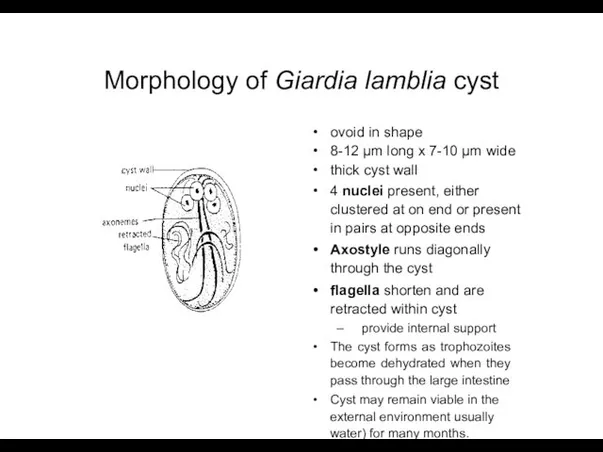
- 6. Morphology of Giardia lamblia cyst ovoid in shape 8-12 µm long x 7-10 µm wide thick
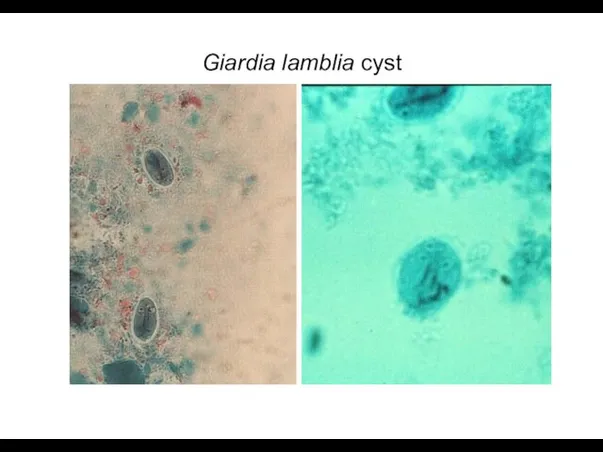
- 7. Giardia lamblia cyst
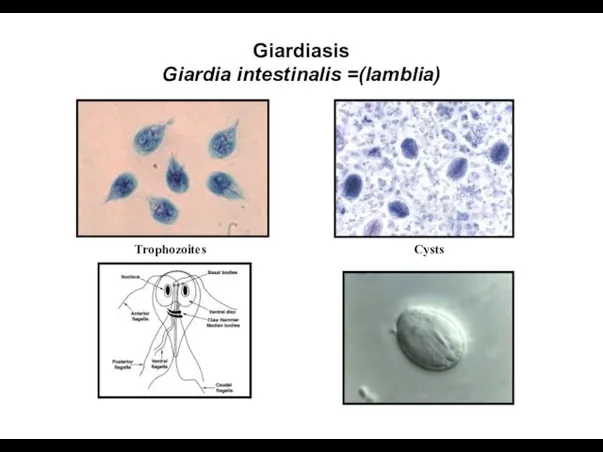
- 8. Giardiasis Giardia intestinalis =(lamblia) Trophozoites Cysts
- 9. Infective form – mature cyst passed in feces of man Routes of transmission Feco-oral ingestion of
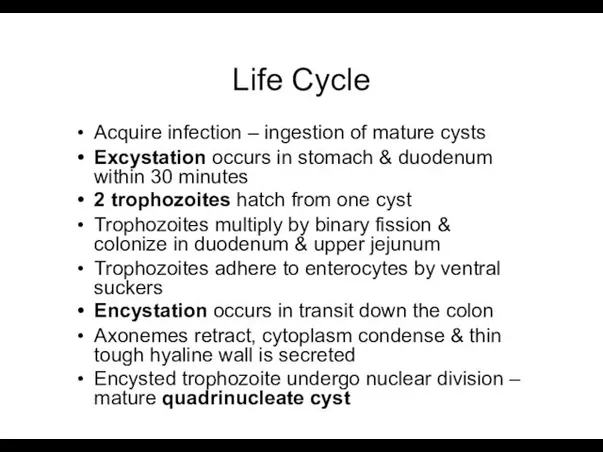
- 10. Life Cycle Acquire infection – ingestion of mature cysts Excystation occurs in stomach & duodenum within
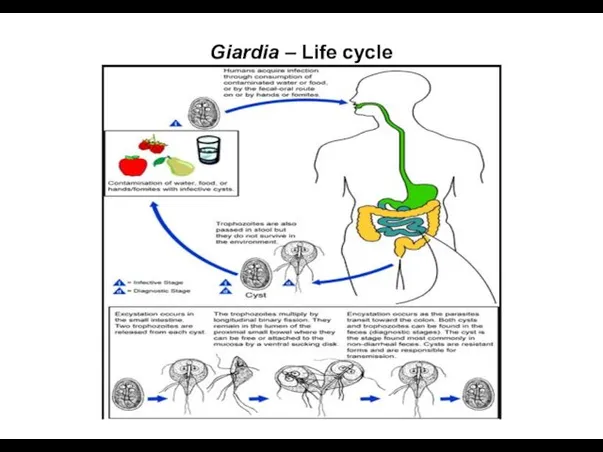
- 11. Giardia – Life cycle
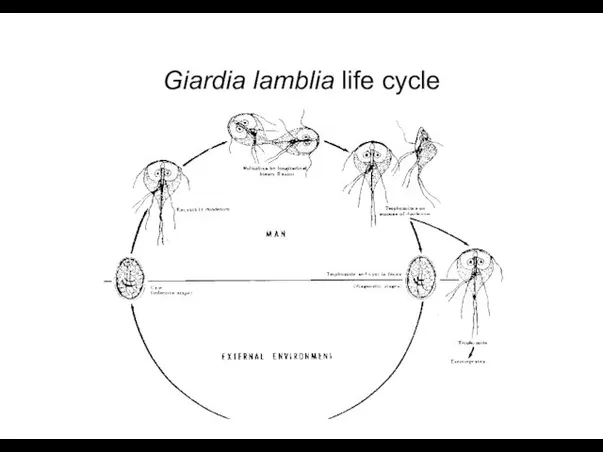
- 12. Giardia lamblia life cycle
- 13. Pathology Do not invade tissues Feed on mucous secretions May localise in biliary tract to avoid
- 14. Giardiasis: The Disease Asymptomatic : largest group Acute : self-limiting infection, acute watery diarrhoea, abdominal cramps,
- 15. Laboratory Diagnosis Parasitic Diagnosis Samples Stool Duodenal contents Duodenal fluid( Entero test ) Duodenal/ jejunal biopsy
- 16. Parasitic Diagnosis Microscopy Microscopy Direct Wet Mount Trophozoite with falling leaf motility in saline mount Cyst
- 17. Laboratory Diagnosis Parasitic Diagnosis Antigen detection ( Coproantigen ) ELISA Sensitivity & specificity high Culture Not
- 18. Laboratory Diagnosis Serodiagnosis ELISA Epidemiological purpose Molecular diagnosis DNA probes & PCR for research purpose
- 19. Prevention Avoid food & water that might be contaminated filtration of water (be sure filter is
- 21. Скачать презентацию










 Епідеміологічний метод дослідження, його структура і зміст. Система епідеміологічного нагляду. Епідеміологія туберкульозу
Епідеміологічний метод дослідження, його структура і зміст. Система епідеміологічного нагляду. Епідеміологія туберкульозу Синдром гострого запалення слизових оболонок дихальних шляхів. Грип
Синдром гострого запалення слизових оболонок дихальних шляхів. Грип Ас қорыту физиологиясы
Ас қорыту физиологиясы Физиология и методы исследования системы гемостаза
Физиология и методы исследования системы гемостаза Родовые повреждения новорожденных
Родовые повреждения новорожденных Ведение нормальных родов. Управление родовым актом
Ведение нормальных родов. Управление родовым актом Трансформация патологии населения. Основные социально-гигиенические проблемы современного общества
Трансформация патологии населения. Основные социально-гигиенические проблемы современного общества Профилактика ВИЧ - инфекций
Профилактика ВИЧ - инфекций Рефракция и аккомодация глаза
Рефракция и аккомодация глаза Негізгі психопатологиялық синдромдар
Негізгі психопатологиялық синдромдар Риски расстройств пищевого поведения у спортсменов
Риски расстройств пищевого поведения у спортсменов Дошкольный и преддошкольный возраст
Дошкольный и преддошкольный возраст Беременность при туберкулезе
Беременность при туберкулезе Введение в иммунологию. Иммунная система
Введение в иммунологию. Иммунная система Гіполіпідемічні лікарські засоби
Гіполіпідемічні лікарські засоби Анатомо-физиологические особенности спинального и эпидурального пространств у детей раннего возраста
Анатомо-физиологические особенности спинального и эпидурального пространств у детей раннего возраста История медицинского халата
История медицинского халата Кровь. Функции и состав крови. Группы крови
Кровь. Функции и состав крови. Группы крови Бронхообструктивный синдром
Бронхообструктивный синдром ВПР мочевыводящей системы
ВПР мочевыводящей системы Пороки развития ЦНС
Пороки развития ЦНС Equipment and instruments of dental clinic
Equipment and instruments of dental clinic Классификация острого панкреатита
Классификация острого панкреатита Виявлення хворих на туберкульоз. (Лекція 2)
Виявлення хворих на туберкульоз. (Лекція 2) Ведение пациентов с болью в спине в практике терапевта и семейного врача
Ведение пациентов с болью в спине в практике терапевта и семейного врача Перикардиты у детей
Перикардиты у детей Инвазивный мониторинг внутричерепного давления
Инвазивный мониторинг внутричерепного давления Несеп жыныс жүйесі
Несеп жыныс жүйесі