Содержание
- 2. Plan of the lecture 1. Definition of glomerulonephritis 2. Risk factors and etiology 3. Pathogenesis 4.
- 3. Glomerulonephritis (Gn): definition Gn is heterogeneous group of inflammatory immune-complex diseases predominantly of kidney glomerular apparatus
- 4. Epidemiology Glomerulonephritis take 3-4 place among all urinary tract diseases; Morbidity is more frequent in 3-12
- 5. Etiology Any diseases that are caused by Streptococcal infections of group A : 4, 6, 12,
- 6. Pathogenesis Main mechanism is immunopathologic reactions; There are 2 main mechanisms: immunocomplex (in 80-85%) and autoimmune;
- 7. Immuncomplex glomerulonephritis factors Disturbances of immune complexes clearance from circulation; Compliment system pathology that leads to
- 8. Autoimmune mechanism of glomerulonephritis development differs from immunocomplex process only by its initial steps. Effector process
- 9. The only necessary condition for glomerulonephritis development due to autoimmune mechanism is specific immunodefficiancy with decreased
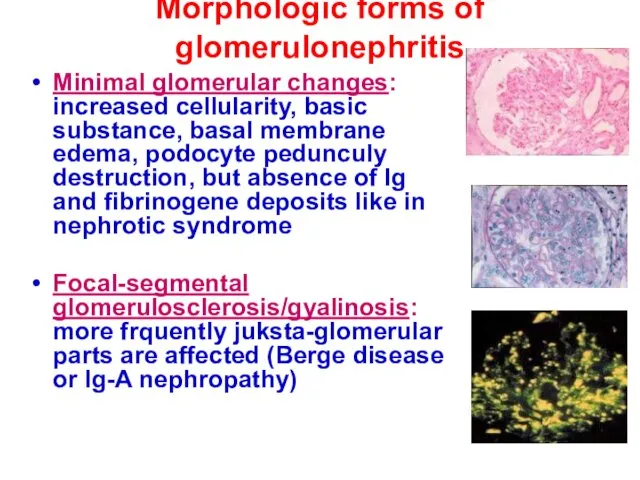
- 10. Morphologic forms of glomerulonephritis Minimal glomerular changes: increased cellularity, basic substance, basal membrane edema, podocyte pedunculy
- 11. Diffuse Gn (80% and more glomerulus are affected) Membranous Gn: diffuse uniform capillary walls thickening in
- 12. Classification of primary glomerulonephritis ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS: Nephritic syndrome; Isolated urinary syndrome; Nephrotic syndrome; Nephrotic with hypertension
- 13. CHRONIC GLOMERULONEPHRITIS: Hematuric form; Nephrotic form; Mixed form. SUBACUTE (MALIGNANT) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
- 14. Process course activity Acute Gn Initial manifestation; Swing period (2-4 weeks); Period of clinical regression (2-3
- 15. Kidney functioning condition Acute Gn Without impairment; With kidney functioning impairment; Acute kidney failure. Chronic Gn
- 16. NEPHRITIC SYNDROME Morbidity is frequent at 5-12 y old; Streptococcal diseases of oral cavity and skin
- 17. Paleness of skin (due to angiospasm) Loin pains ( due to kidney capsule distention because of
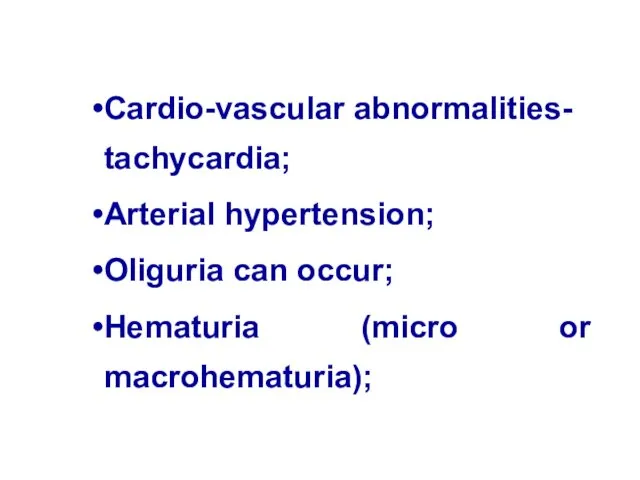
- 18. Cardio-vascular abnormalities- tachycardia; Arterial hypertension; Oliguria can occur; Hematuria (micro or macrohematuria);
- 19. Proteinuria not more than 1-2 g/l per day; Frequently moderate anemia, ESR elevation, leucocytosis ( if
- 20. Isolated urine syndrome Onset is steady without any subjective symptoms and extrarenal signs. There are only
- 21. NEPHROTIC SYNDROME Typical for preschools (1,5-5 y old) Frequently family history has allergologic anamnesis;
- 22. Onset is steady with edema development that can be excessive. Edema can be peripheral, cavitary, and
- 23. Olyguria Significant proteinuria more than 3 g/l per day.; Blood tests – hypoproteinemia predominantly due to
- 24. NВ ! BP is normal, hematuria isn’t present, kidney function failure isn’t typical
- 25. Standards of lab testing Obligatory lab studies Common blood test +thrombocyte count; Biochemical tests (proteinogram, cholesterol,
- 26. Specifying tests (if necessary)) Blood electrolites ( in stimulated urination, corticosteroid treatment) Liver tests (especially in
- 27. Additional lab tests Of blood Antibodies to glomerular basal membrane and neutrophyl cytoplasm (ANCA); Lipidogram; Acidic-basic
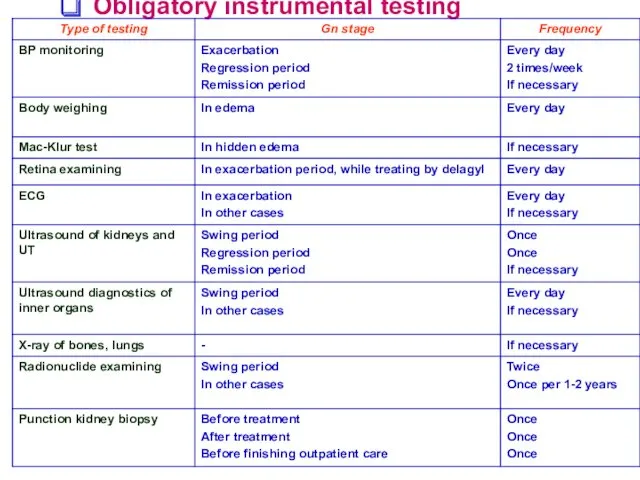
- 28. Obligatory instrumental testing
- 29. Glomerulonephritis treatment Regimen is strictly bed type only if extrarenal symptoms are present like edema, hypertension,
- 30. Diet Is dependant on edema arterial hypertension and functional kidney capacity. During acute period salt (NaCl)
- 31. Medications: а) etiologic (if infection as initializing factor is proved or chronic focus of infection is
- 32. b) pathogenic (the main goal is to eradicate antigen from organism and supress antibody production) Plasmopheresis
- 33. disaggregants (curantil, ticlid) for 3-4 weeks 2-5 mg/kg per day, than 1/2 of this dosage for
- 34. Corticosteroids 1,5-2mg/kg per day, prednisolon for 8 weeks than cyclic treatment with 1/2 of initial dosage
- 35. Antihypertension, antiproteinuric, antisclerotic drugs : Angitensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI) –enalapril, lysinopril – 5-40 mg/day; Angiotensin
- 36. Outpatient care After acute glomerulonephritis clinical-laboratory remision children must be for 5 years under outpatient medical
- 37. Subacute rapidly progressive (crescentic) GN Crescentic GN is severe form of glomeruli injury with presence of
- 38. Chronic kidney diseases From 2003 concept “Chronic kidney disease” was introduced to children nephrology Criteria of
- 39. CKD can be independent diagnose or summerized one; Like: CKD CKD: chronic glomerulonephritis, hematuric form, clinic-lab
- 40. Risk factors for CKD development CKD induced factors Diabetes mellitus 1, 2 type; Arterial hypertension; Autoimmune
- 41. Factors induced CKD progression High level of proteinurea or arterial hypertension; Insufficient glycemia level control; Smoking.
- 42. Glomerular filtration rate GFR less than 60 ml/min – can be developed due to CKF without
- 43. Formula for GFR calculation * - in online regimen calculations of GFR according Schwartz formua is
- 44. Hystologic types of CKD Proliferative GN ( mesangial prolifirative GN, crescentic GN, membranoproliferative GN) Focal segmental
- 45. CKD treatment There is no specific treatment for chronic GN. Steroids and immunosuppressive drugs can only
- 46. Chronic kidney failure is stable irreversible progressive kidney function disorder due to different diseases manifested by
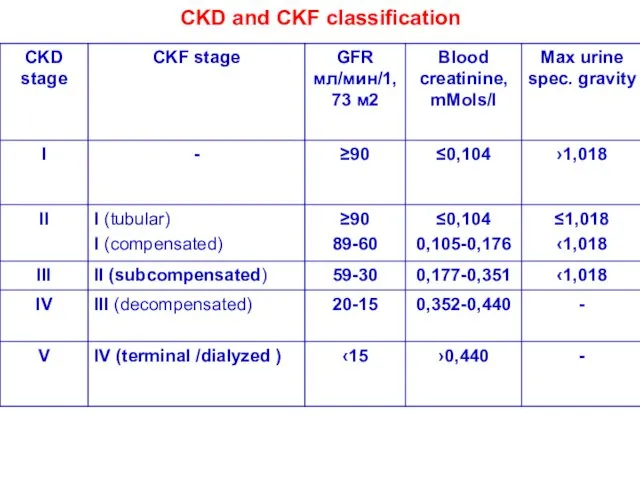
- 47. CKD and CKF classification
- 48. 2.Total kidney failure Serum createnine content 0,17 –0,44 mmols/l: Glomerulopathies: Hypertension, hemorrhagic syndrome, acidosis, decreasing of
- 49. Chronic kidney failure (CKF) etiology Glomerulopathies: Primary glomerular dieases, immuneglobuline A nephropathies, membrane-proliferative glomerulonephritis Glomerulopathies associated
- 50. CKF syndromes and reasons of their development Failure to growth and development – hypostature, malnutrition, sexual
- 51. Arterial hypertension - head ache, hypertonic crises, retinopathy due to enhanced Pg production and water –electrolyte
- 52. Diet in CKF Diet N 7 : moderate limitation in protein, salt (not more than 0,4
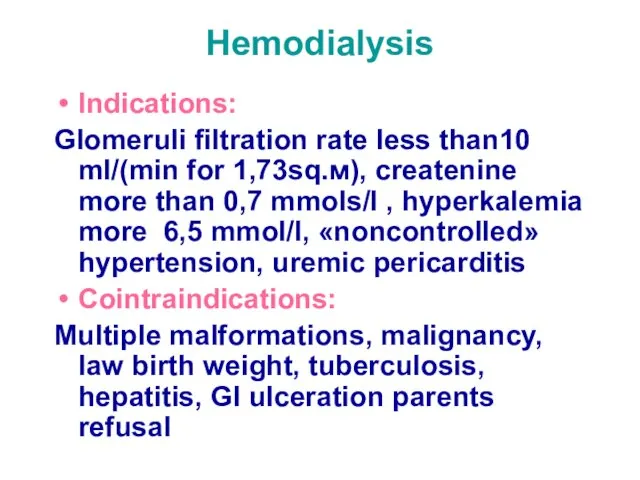
- 53. Hemodialysis Indications: Glomeruli filtration rate less than10 ml/(min for 1,73sq.м), createnine more than 0,7 mmols/l ,
- 54. Indications for kidney transplantation terminal kidney failure stage Contraindications : mental diseases, malignancies, sepsis, chronic purulent
- 56. Скачать презентацию















































 Стоматологиядағы кірісулер кезіндегі шұғыл көмек
Стоматологиядағы кірісулер кезіндегі шұғыл көмек Половое воспитание. Инфекции, передаваемые половым путём. 9 класс
Половое воспитание. Инфекции, передаваемые половым путём. 9 класс Көпіршікті дерматоздар (пемфигус)
Көпіршікті дерматоздар (пемфигус) Этапы обработки медицинских изделий. Тема 5
Этапы обработки медицинских изделий. Тема 5 Гиперкинетический синдром у детей
Гиперкинетический синдром у детей Бауме бойынша тістесу түрлері
Бауме бойынша тістесу түрлері Жас стоматолог
Жас стоматолог Шизофрения. Признаки шизофрении
Шизофрения. Признаки шизофрении Полуколичественный метод определения ДНК онкогенных типов ВПЧ-Digene-тест, онкоцитологическое исследование ASC-US
Полуколичественный метод определения ДНК онкогенных типов ВПЧ-Digene-тест, онкоцитологическое исследование ASC-US Surgical revascularization of myocardium
Surgical revascularization of myocardium Haemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn. Rh isoimmunization
Haemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn. Rh isoimmunization Рак щитовидной железы
Рак щитовидной железы Відмороження. Визначення поняття “відмороження”
Відмороження. Визначення поняття “відмороження” Артерия гистологиясы
Артерия гистологиясы Трансплантация почки
Трансплантация почки Теория медицинского диагноза и клинико-анатомический анализ летальных исходов. Теория и практика
Теория медицинского диагноза и клинико-анатомический анализ летальных исходов. Теория и практика Современные проблемы диагностики сепсиса
Современные проблемы диагностики сепсиса Искусственное кровообращение
Искусственное кровообращение Острый тонзиллит
Острый тонзиллит Кариес зуба
Кариес зуба Ноотропные препараты
Ноотропные препараты Первая помощь при ожогах и обморожениях
Первая помощь при ожогах и обморожениях Основные приемы классического массажа
Основные приемы классического массажа Зәр шығару жүйесінің сәулелік диагностика әдістері
Зәр шығару жүйесінің сәулелік диагностика әдістері Зерттеу сұрағы мен ақпаратты іздеу
Зерттеу сұрағы мен ақпаратты іздеу Ламбдацизм и методы его исправления
Ламбдацизм и методы его исправления Определение содержания гемоглобина по методу Сали. Лабораторная работа № 3
Определение содержания гемоглобина по методу Сали. Лабораторная работа № 3 Хроническая лучевая болезнь
Хроническая лучевая болезнь