Содержание
- 2. Classification of liver diseases, their ethiology and pathogenesis Hepatoses: definition, ethiology, pathogenesis, pathological anatomy, complications and
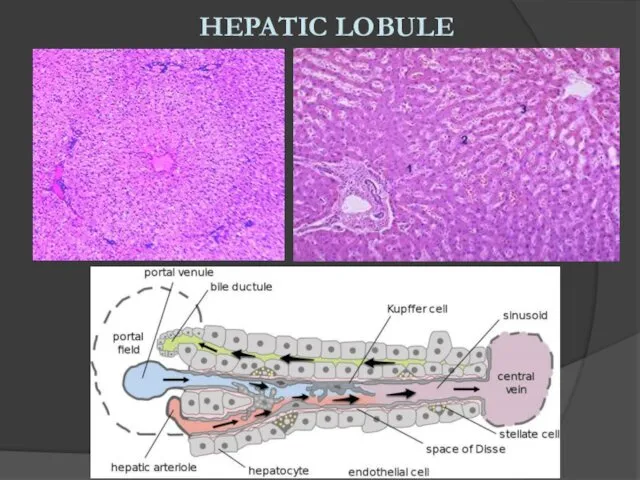
- 3. HEPATIC LOBULE
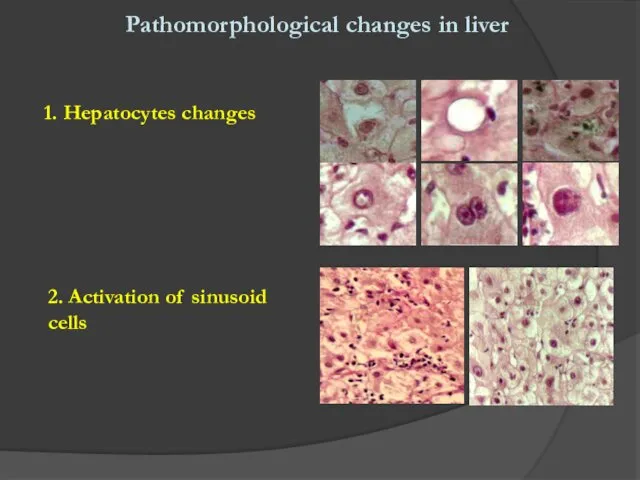
- 4. Pathomorphological changes in liver 1. Hepatocytes changes 2. Activation of sinusoid cells
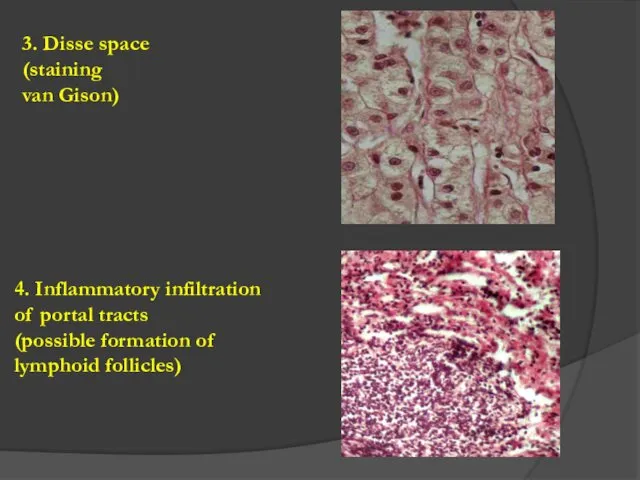
- 5. 3. Disse space (staining van Gison) 4. Inflammatory infiltration of portal tracts (possible formation of lymphoid
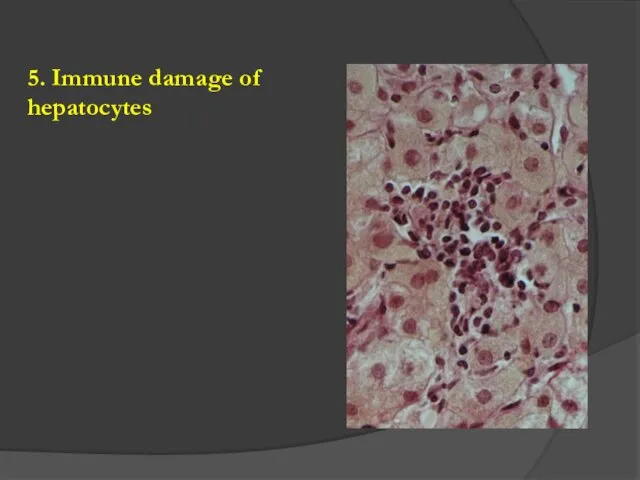
- 6. 5. Immune damage of hepatocytes
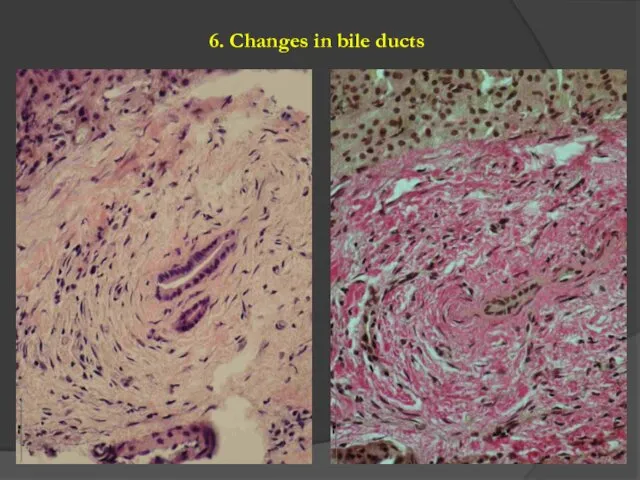
- 7. 6. Changes in bile ducts
- 8. CLASSIFICATION OF LIVER DISEASES Congenital abnormalies Hepatoses (lipid, pigment, etc.) Hepatitis (alcoholic, viral, etc.) Liver cirrhosis
- 9. HEPATOSES Hepatosis is a disease of the liver with dystrophy and necrosis of hepatocytes Poisoning (phosphorus,
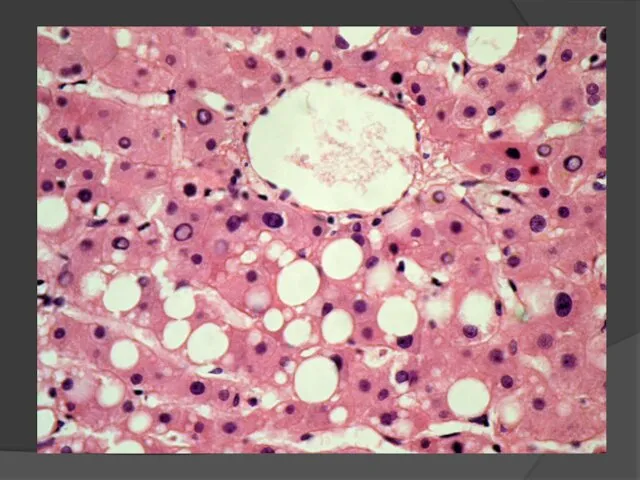
- 10. HEPATOSES Macroscopic: liver is enlarged, compact or loose, bright yellow color. Then it decreases, becomes flabby
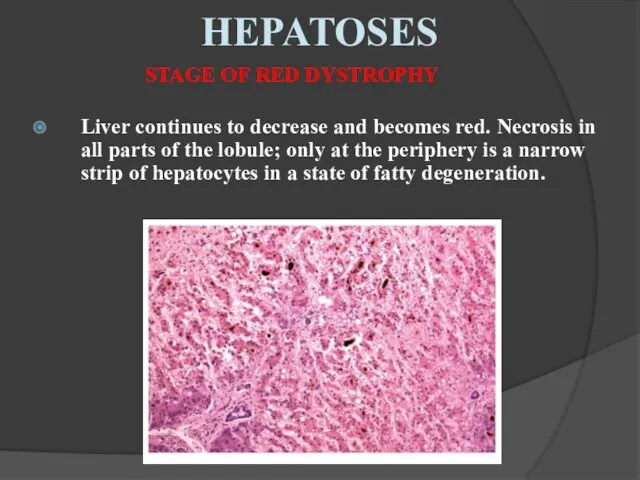
- 13. Liver continues to decrease and becomes red. Necrosis in all parts of the lobule; only at
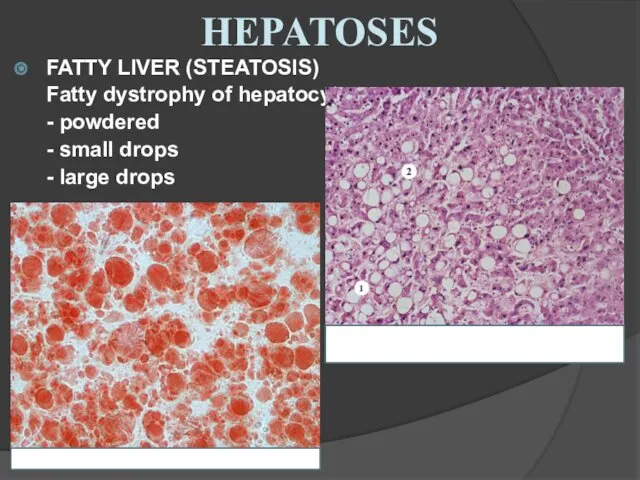
- 14. FATTY LIVER (STEATOSIS) Fatty dystrophy of hepatocytes - powdered - small drops - large drops HEPATOSES
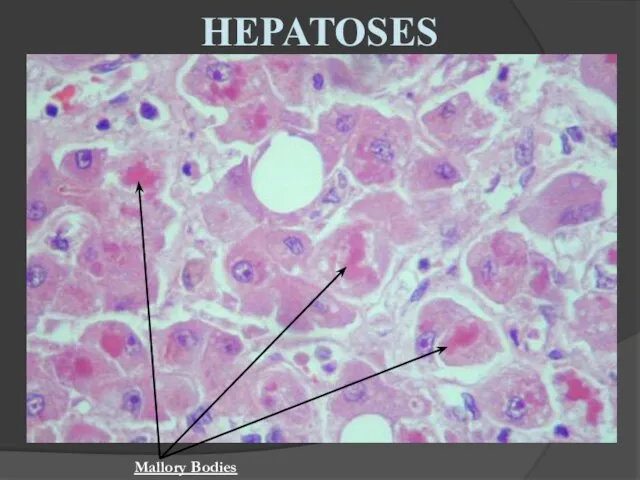
- 15. HEPATOSES Mallory Bodies
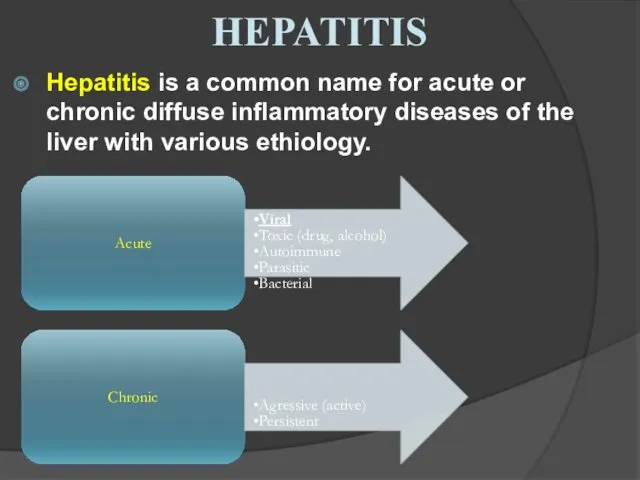
- 16. HEPATITIS Hepatitis is a common name for acute or chronic diffuse inflammatory diseases of the liver
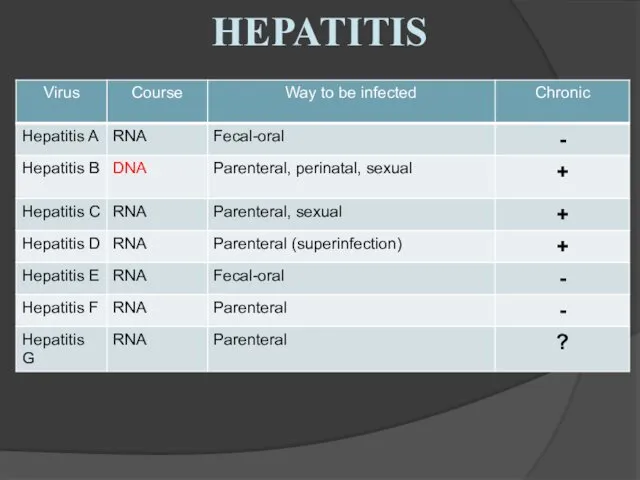
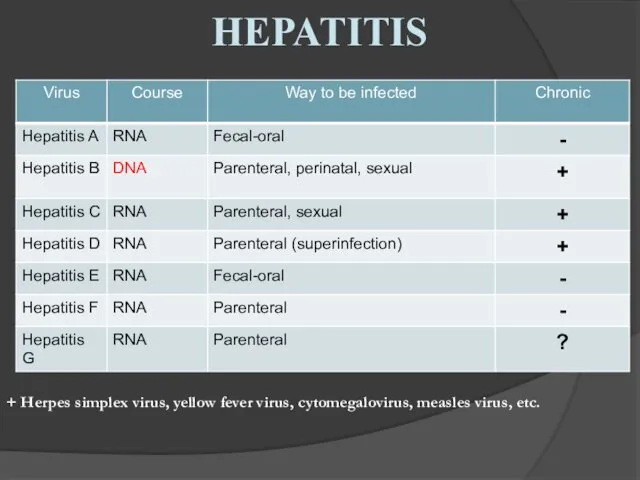
- 17. HEPATITIS
- 18. HEPATITIS + Herpes simplex virus, yellow fever virus, cytomegalovirus, measles virus, etc.
- 19. PATHOGENESIS Damage of the hepatic cells by hepatotropic viruses is based on two possible mechanisms: Direct
- 20. There are several forms due to course and clinical symptoms: 1. Carrier state (subclinical course) –
- 21. There are 4 stages in course of the acute hepatitis: Incubation period; Pre-jaundice; Jaundice; Recovery. Hepatitis
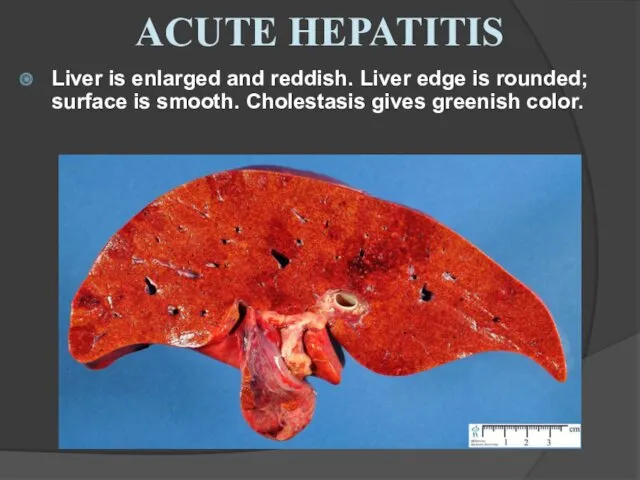
- 22. Liver is enlarged and reddish. Liver edge is rounded; surface is smooth. Cholestasis gives greenish color.
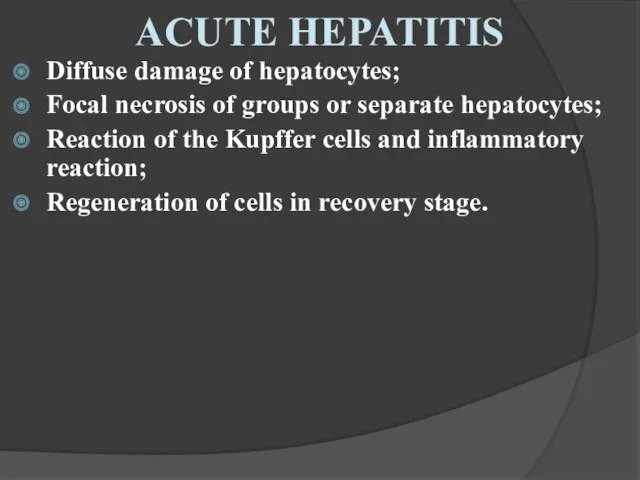
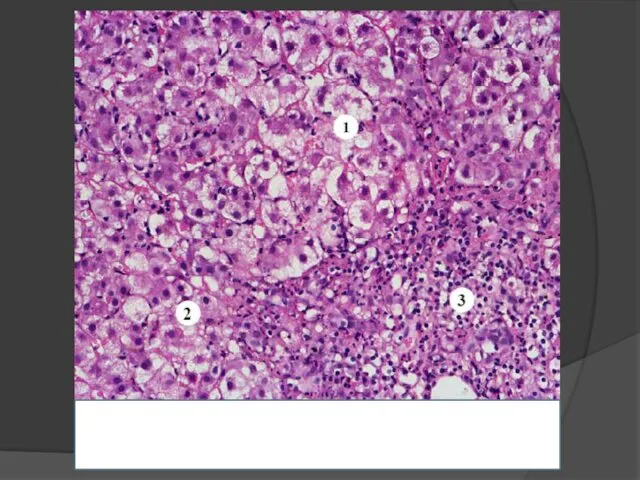
- 23. Diffuse damage of hepatocytes; Focal necrosis of groups or separate hepatocytes; Reaction of the Kupffer cells
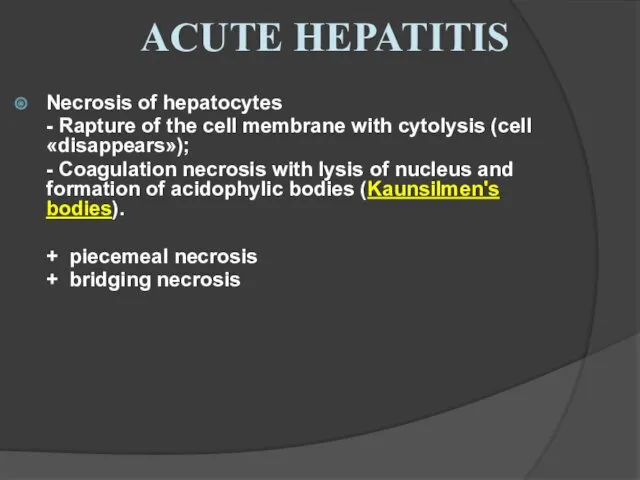
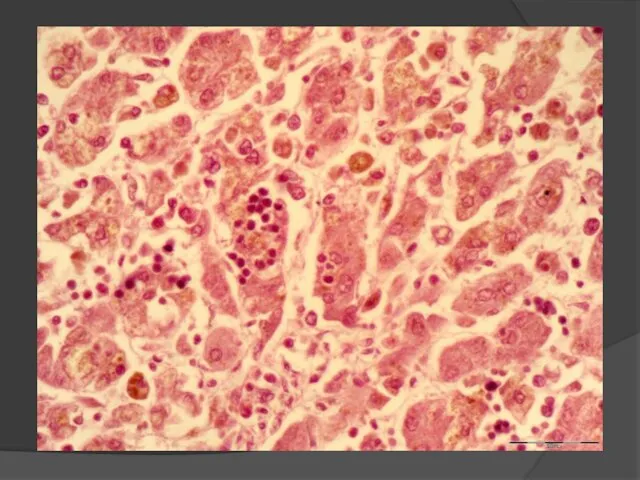
- 24. Necrosis of hepatocytes - Rapture of the cell membrane with cytolysis (cell «disappears»); - Coagulation necrosis
- 27. Chronic persistent hepatitis Relapsing course, with NO observed progressive liver injury with NO outcome in cirrhosis
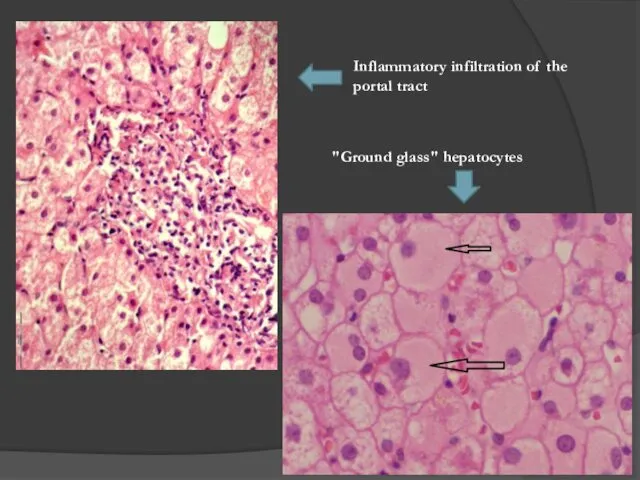
- 28. Inflammatory infiltration of the portal tract "Ground glass" hepatocytes
- 29. Chronic active hepatitis is characterized by progressive destruction of hepatocytes and development of cirrhosis. Viral Hepatitis
- 30. Poratal and periportal infiltration with lymphocytes, plasmocytes and macrophages; Active destruction of hepatocytes in zone between
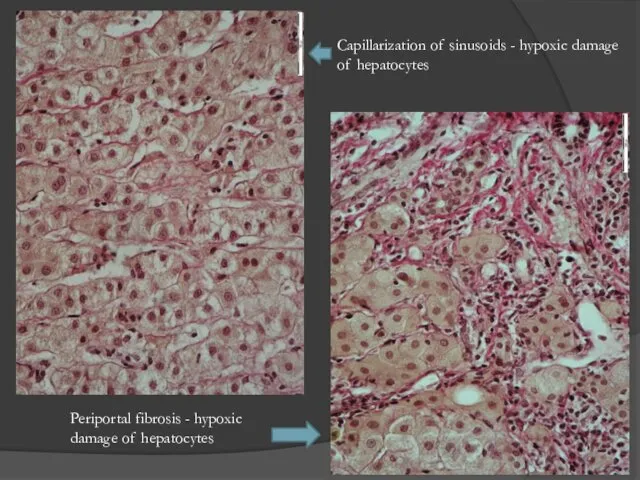
- 31. Capillarization of sinusoids - hypoxic damage of hepatocytes Periportal fibrosis - hypoxic damage of hepatocytes
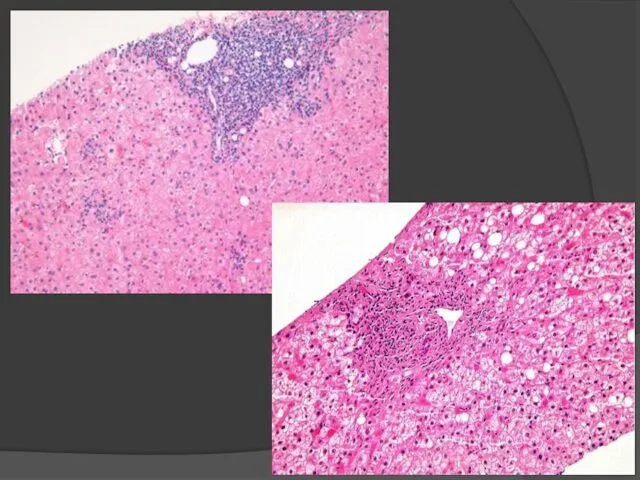
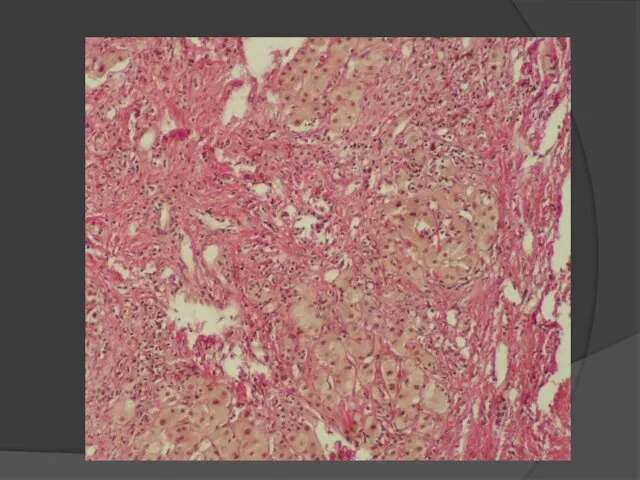
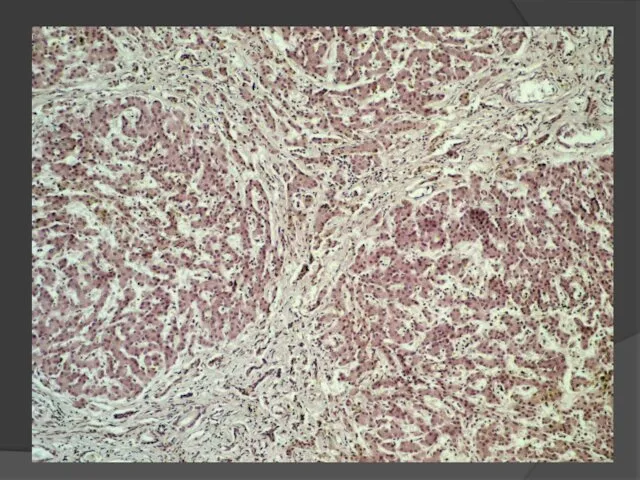
- 33. Liver cirrhosis is characterized by the following sings: Dystrophy anв necrosis of hepatocytes Fibrosis; Compensatory hyperplasia
- 34. CLASSIFICATION Morphological : Micronodular liver cirrhosis Macronodular liver cirrhosis Mixed liver cirrhosis LIVER CIRRHOSIS
- 35. Ethiological: 1. Acquired forms Toxic cirrhosis (such as alcoholic) Postinfectious Circulatory Cryptogenic cirrhosis Biliary cirrhosis (primary,
- 36. Pathogenetic: Portal Postnecrotic Biliary Mixed
- 37. 1. Liver failure (acute or chronic, up to hepatic coma) Hepatic encephalopathy Jaundice Renal failure Ascites
- 38. 2. Portal hypertension Varicose changes in portocaval extrahepatic anastomoses Ascites Splenomegaly 3. Cancer of the liver
- 43. Скачать презентацию













 Экстрагенитальные заболевания, вызывающие клинику острого живота
Экстрагенитальные заболевания, вызывающие клинику острого живота Подход к пациенту с политравмой
Подход к пациенту с политравмой Врожденный и приобретенный иммунитет. Клеточные и гуморальные механизмы
Врожденный и приобретенный иммунитет. Клеточные и гуморальные механизмы Antigeny
Antigeny Маңызды класс аурулары деп. Туберкулез
Маңызды класс аурулары деп. Туберкулез Боковой амиотрофический склероз
Боковой амиотрофический склероз Гигиенические требования к рентгенологическим и радиологическим отделениям больниц
Гигиенические требования к рентгенологическим и радиологическим отделениям больниц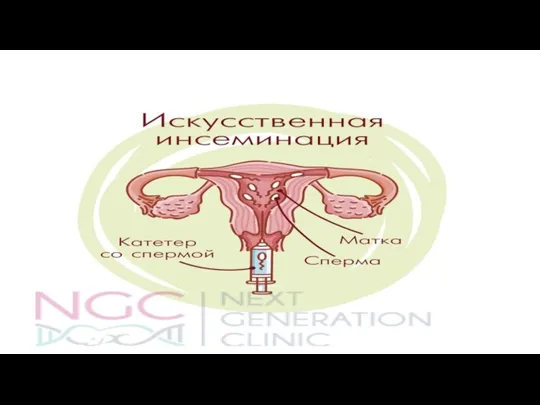 Искусственная инсеминация
Искусственная инсеминация Синдром серцевої та судинної недостатності при захворюваннях серцево–судинної системи
Синдром серцевої та судинної недостатності при захворюваннях серцево–судинної системи Патофизиология ожоговой болезни. Интенсивная терапия ожоговой болезни и ожогового шока у детей
Патофизиология ожоговой болезни. Интенсивная терапия ожоговой болезни и ожогового шока у детей Көмекей, кеңірдек, бронхылар. Өкпенің құрылымы мен функциялары. Плевра қойнаулары
Көмекей, кеңірдек, бронхылар. Өкпенің құрылымы мен функциялары. Плевра қойнаулары Профессиональные компетенции медсестры при заболеваниях органов дыхания у детей
Профессиональные компетенции медсестры при заболеваниях органов дыхания у детей Модуль 2. Оказание первой помощи при отсутствии сознания, остановке дыхания и кровообращения
Модуль 2. Оказание первой помощи при отсутствии сознания, остановке дыхания и кровообращения Диагностика ишемической болезни сердца
Диагностика ишемической болезни сердца Подагра
Подагра Боль. Местная анестезия, блокады и общее обезболивание
Боль. Местная анестезия, блокады и общее обезболивание Рак пищевода
Рак пищевода Просветление. Рентгенопульмонология
Просветление. Рентгенопульмонология Нові підходи до лікування гострої респіраторної вірусної інфекції у дітей
Нові підходи до лікування гострої респіраторної вірусної інфекції у дітей Система комп’ютерного моделювання процесів життєдіяльності органів та систем організму СКІФ
Система комп’ютерного моделювання процесів життєдіяльності органів та систем організму СКІФ Жедел холецистит. Жіктемесі, диагностикасы, саралау диагностикасы. Аурудың асқынулары,асқынуларды диагностикалау
Жедел холецистит. Жіктемесі, диагностикасы, саралау диагностикасы. Аурудың асқынулары,асқынуларды диагностикалау Первая помощь при ранениях и кровотечениях. СОЦМК
Первая помощь при ранениях и кровотечениях. СОЦМК Наследственные атаксии Пьера-Мари, Фридрейха
Наследственные атаксии Пьера-Мари, Фридрейха 20231031_zhiznennyy_tsikl_virusov
20231031_zhiznennyy_tsikl_virusov Тірек-қимыл жүйесінің аурулары
Тірек-қимыл жүйесінің аурулары Галактоземия
Галактоземия Қан тобын анықтау
Қан тобын анықтау Азбука СПИДа
Азбука СПИДа