Содержание
- 2. Multiple Myeloma Definition: B-cell malignancy characterised by abnormal proliferation of plasma cells able to produce a
- 3. Multiple Myeloma = M-CRAB Monoclonal protein Calcium Renal failure Anemia Bone pain with lytic lesions
- 4. Disorders Associated with M- Protein Neoplastic cell proliferation multiple myeloma solitary plasmacytoma Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia, CLL heavy
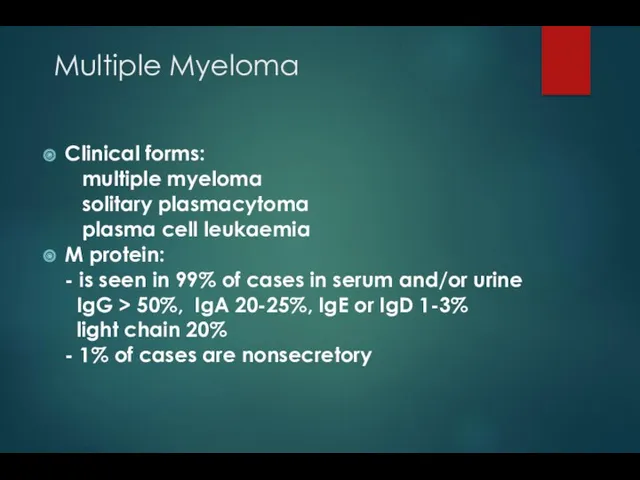
- 5. Multiple Myeloma Clinical forms: multiple myeloma solitary plasmacytoma plasma cell leukaemia M protein: - is seen
- 6. Multiple Myeloma Clinical manifestations are related to malignant behaviour of plasma cells and abnormalities produced by
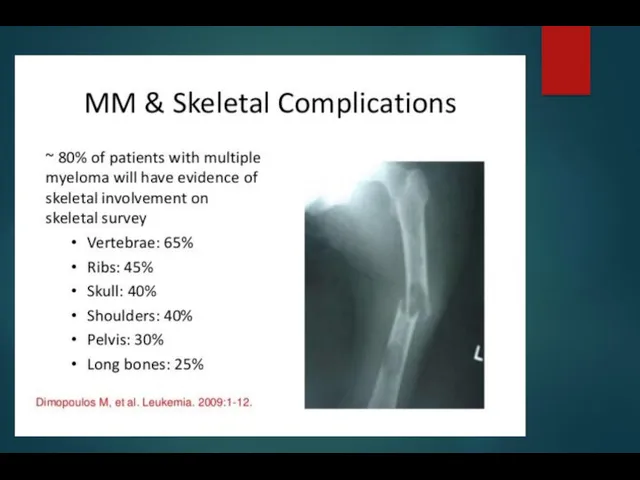
- 7. Multiple Myeloma Clinical symptoms: bone pain, pathologic fractures weakness and fatigue serious infection renal failure bleeding
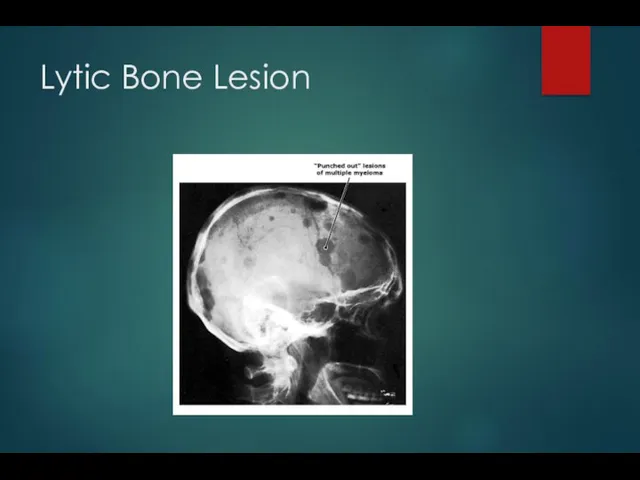
- 8. Lytic Bone Lesion
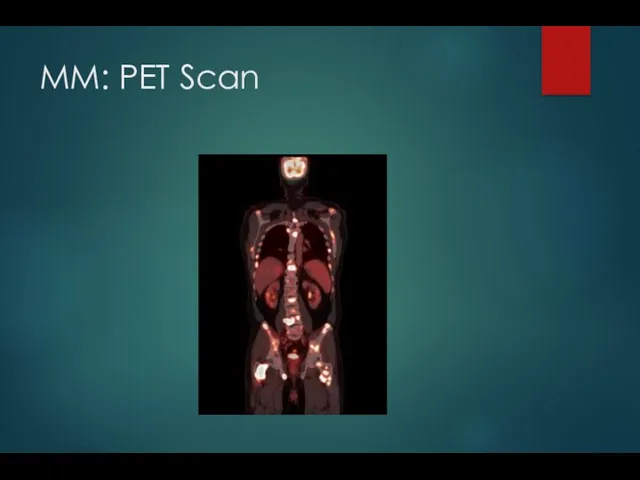
- 10. MM: PET Scan
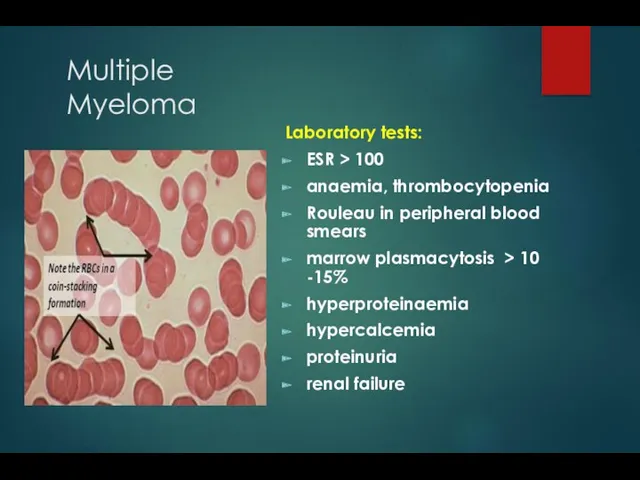
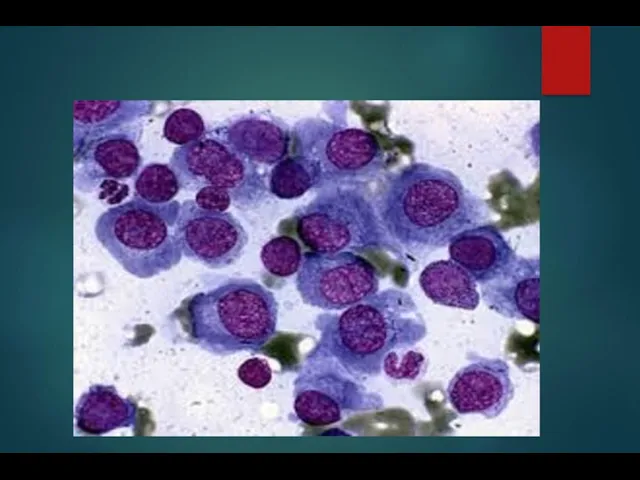
- 11. Multiple Myeloma Laboratory tests: ESR > 100 anaemia, thrombocytopenia Rouleau in peripheral blood smears marrow plasmacytosis
- 13. Diagnostic Criteria for Multiple Myeloma Major criteria I. Plasmacytoma on tissue biopsy II. Bone marrow plasma
- 14. Multiple Myeloma All 3 criteria must be met (except unsecretory): Presence of a serum or urinary
- 15. Smoldering Multiple Myeloma SMM, Asymptomatic Both criteria must be met: Serum monoclonal protein ≥3 g/dL and/or
- 16. Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance (MGUS) All 3 criteria must be met: Serum monoclonal protein Bone
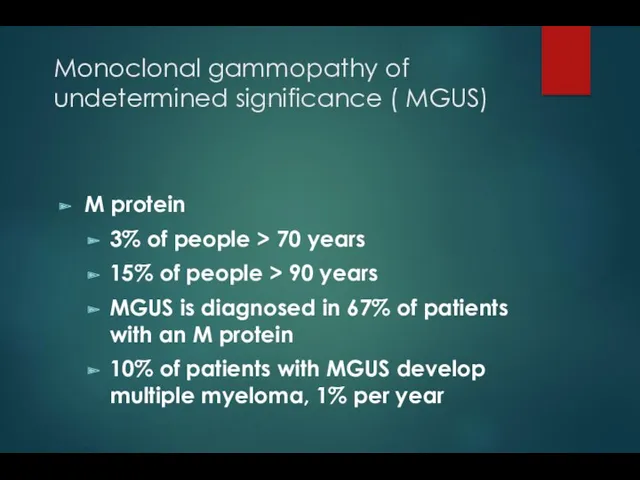
- 17. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance ( MGUS) M protein 3% of people > 70 years 15%
- 18. POEMS Syndrome Osteosclerotic myeloma Polyneuropathy Organomegaly Endocrinopathy Monoclonal protein Skin changes
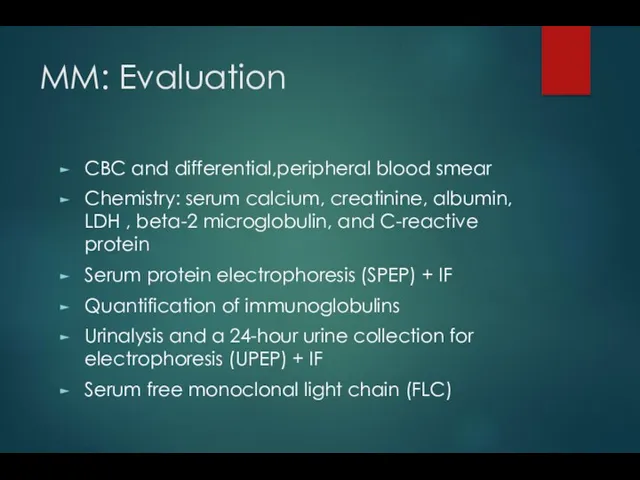
- 19. MM: Evaluation CBC and differential,peripheral blood smear Chemistry: serum calcium, creatinine, albumin, LDH , beta-2 microglobulin,
- 20. MM Evaluation Serum viscosity should be measured if the M-protein concentration is high Bone marrow aspiration
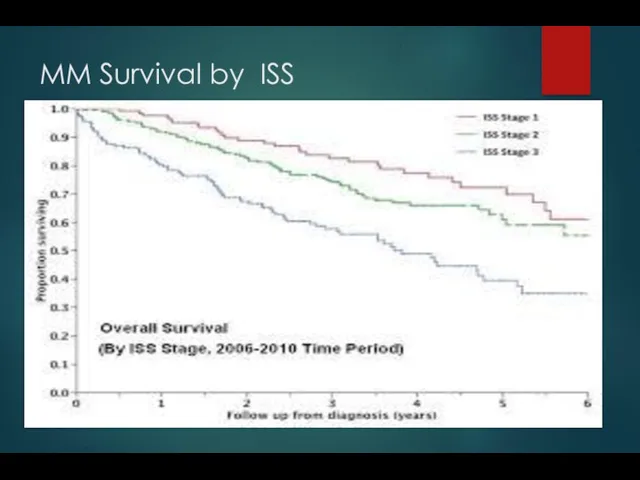
- 21. Staging for MM International staging system (ISS) Stage I — B2M Stage II — neither stage
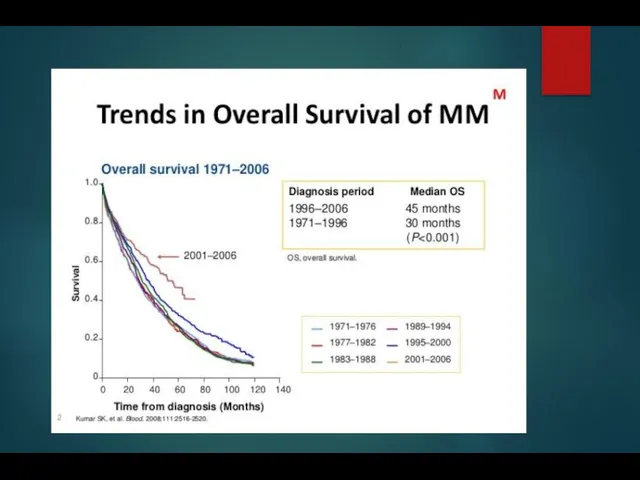
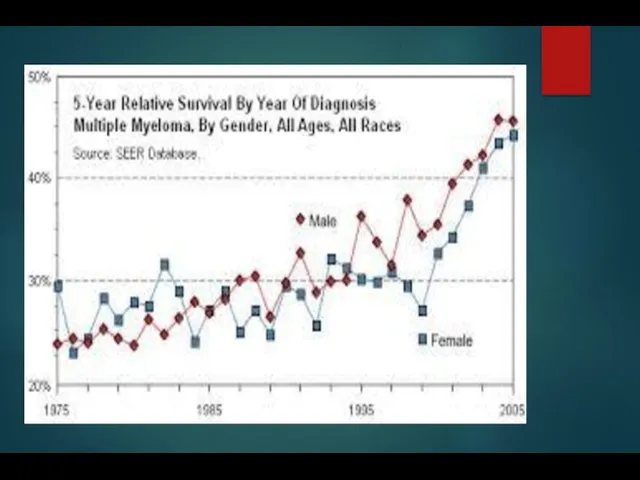
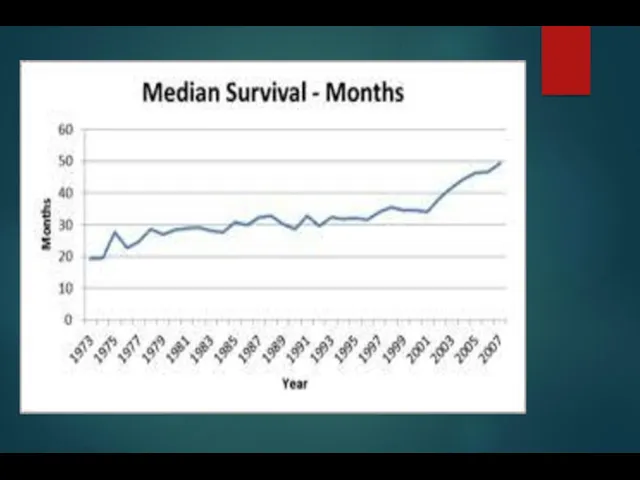
- 22. MM Survival by ISS
- 23. Cytogenenetics, Interphase FISH Poor prognosis (median survival 25 months): t(4;14)(p16;q32), t(14;16)(q32;q23), and -17p13 Intermediate prognosis (median
- 27. MM: RISK STRATIFICATION FISH for detection of t(4;14), t(14;16), and del17p13 Conventional cytogenetics (karyotyping) for detection
- 28. Multiple Myeloma Poor prognosis factors cytogenetic abnormalities High β-2 microglobulin Advanced stage Hypercalcemia Renal failure Plasma
- 29. MM: Indications for Treatment Anemia (hemoglobin Hypercalcemia (serum calcium >11.5 mg/dL) Renal insufficiency (serum creatinine>2 mg/dL)
- 30. Treatment of Multiple Myeloma Patients fit induction with combination of IMIDS, cyclophosphamide, dexamethasone and velcade High
- 31. Treatment of Multiple Myeloma Conventional chemotherapy Melphlan + Prednisone M2 ( Vincristine, Melphalan, Cyclophosphamid, BCNU, Prednisone)
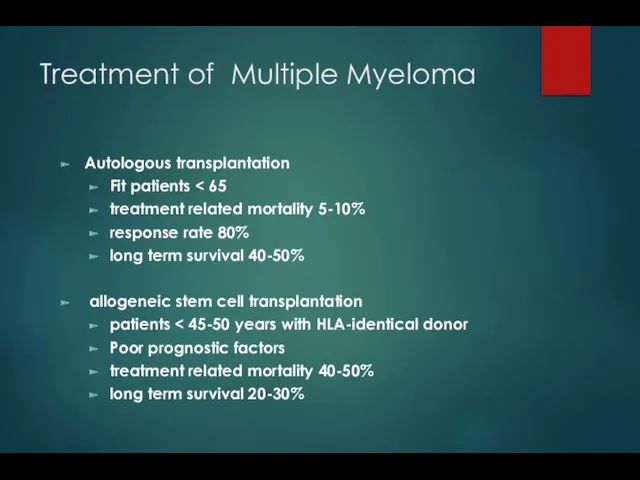
- 32. Treatment of Multiple Myeloma Autologous transplantation Fit patients treatment related mortality 5-10% response rate 80% long
- 33. Treatment of Multiple Myeloma New methods Reduced intensity allogeneic transplantation Thalidomide, Revlimid, Pomalidomide Proteasome inhibitors –
- 34. Treatment of Multiple Myeloma Supportive treatment biphosphonates, calcitonin recombinant erythropoietin immunoglobulins plasmapheresis radiation therapy
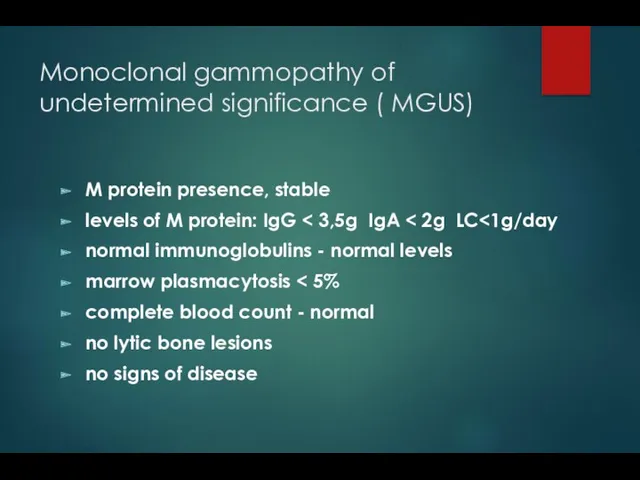
- 35. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance ( MGUS) M protein presence, stable levels of M protein: IgG
- 37. Скачать презентацию



















 План курса Общая нейрофизиология
План курса Общая нейрофизиология Анемии. Эритроцитопоэз
Анемии. Эритроцитопоэз Симптоматические артериальные гипертензии
Симптоматические артериальные гипертензии Cardiogenic shock
Cardiogenic shock Лекарственные растения обладающие мочегонными свойствами
Лекарственные растения обладающие мочегонными свойствами Паталогия печени
Паталогия печени Патогенез речевых нарушений
Патогенез речевых нарушений Фибрилляция предсердий
Фибрилляция предсердий Транквилизаторы
Транквилизаторы Зубные пасты. Жевательные резинки. Жевательные таблетки. Ополаскиватель для полости рта
Зубные пасты. Жевательные резинки. Жевательные таблетки. Ополаскиватель для полости рта Ожоги органа зрения
Ожоги органа зрения Факторы свертывающей и противосвертывающей системы крови. Геморрагические диатезы и синдромы. Тромбофилии
Факторы свертывающей и противосвертывающей системы крови. Геморрагические диатезы и синдромы. Тромбофилии Зоонозы. Туляремия
Зоонозы. Туляремия Систематизация и диагностика васкулитов
Систематизация и диагностика васкулитов Травматический шок
Травматический шок Иммунопрофилактика. Национальный календарь
Иммунопрофилактика. Национальный календарь Адам ағзасының иммундық жүйесі
Адам ағзасының иммундық жүйесі Биоэнергомассажер Fohow
Биоэнергомассажер Fohow Развитие медицины в России XIX век
Развитие медицины в России XIX век Жұқпалы үрдіс патофизиологиясы. Сепсис және сепсистік сілейменің патогенезі
Жұқпалы үрдіс патофизиологиясы. Сепсис және сепсистік сілейменің патогенезі Респираторлық дистресс синдромының клинико-лабораторлық зерттеу көріністері
Респираторлық дистресс синдромының клинико-лабораторлық зерттеу көріністері Питание как стиль жизни. Основные правила и принципы
Питание как стиль жизни. Основные правила и принципы Физическое развитие. Основные показатели физического развития в различных возрастно-половых группах, их особенности и тенденции
Физическое развитие. Основные показатели физического развития в различных возрастно-половых группах, их особенности и тенденции Гельминтозы. Диагностика. Лечение
Гельминтозы. Диагностика. Лечение Синдром Дауна
Синдром Дауна Сүт бездерінің дисормональды аурулары туралы не білеміз?
Сүт бездерінің дисормональды аурулары туралы не білеміз? Жүктілік кезіндегі гипертензия
Жүктілік кезіндегі гипертензия Возможности медикаментозного обезболивания во время хирургических вмешательств
Возможности медикаментозного обезболивания во время хирургических вмешательств