Содержание
- 2. Plan of the lecture 1. Definition of peptic ulcer disease 2. Etiologic factors 3. Classification 4.
- 3. Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) - - is polygene inherited chronic recurrent disease, manifested by formation of
- 4. PUD morbidity is 1 case for 1000 healthy children. Before puberty PUD morbidity is the same
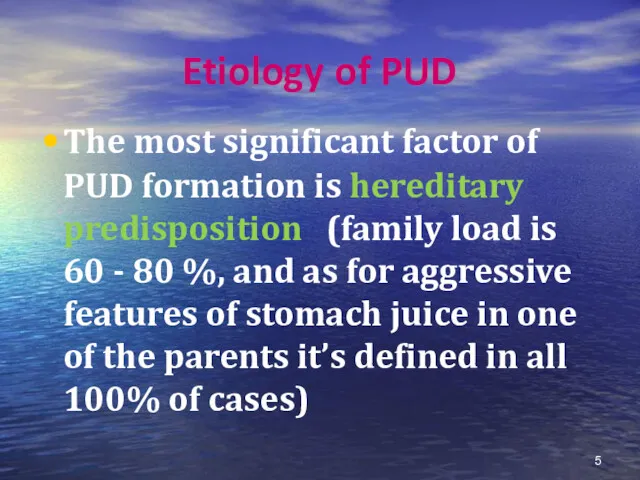
- 5. Etiology of PUD The most significant factor of PUD formation is hereditary predisposition (family load is
- 6. Predisposing factors HP contamination Early formula feeding (it can induce activation of gastrin produced cells and
- 7. Environment factors Can change ratio of some regulatory system compartments, actively influence to peptic acid factor,
- 8. HP strains of the first type has the highest cytolytic activity so this strain is 4
- 9. Pathogenesis Hereditary predisposition in PUD has such features: Hereditary determined peculiarities of mucous membranes structure –
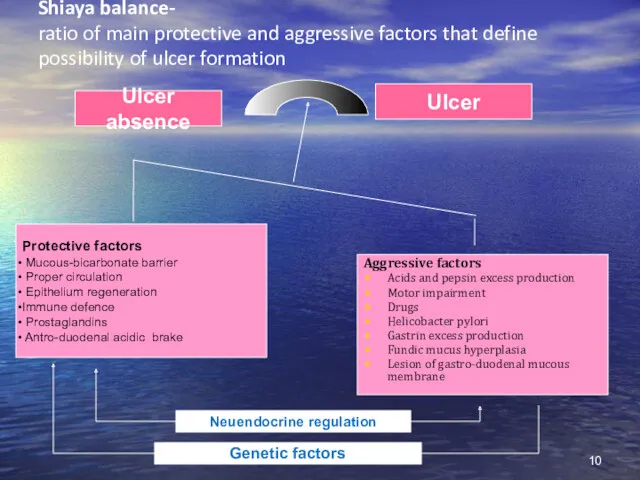
- 10. Shiaya balance- ratio of main protective and aggressive factors that define possibility of ulcer formation Protective
- 11. Classic clinics of typical pain syndrome in PUD was described at the beginning of 20 century
- 12. Clinics Pain syndrome Fasting pain appearance or 1,5-2 hours after feeding ( Moinigan rythm) Nocturnal pain
- 13. PUD peculiarities in children Classic clinics can be seen less than in 50% patients In 15%
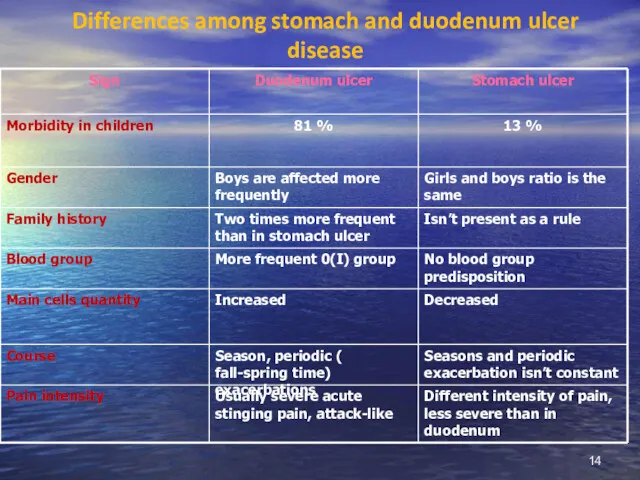
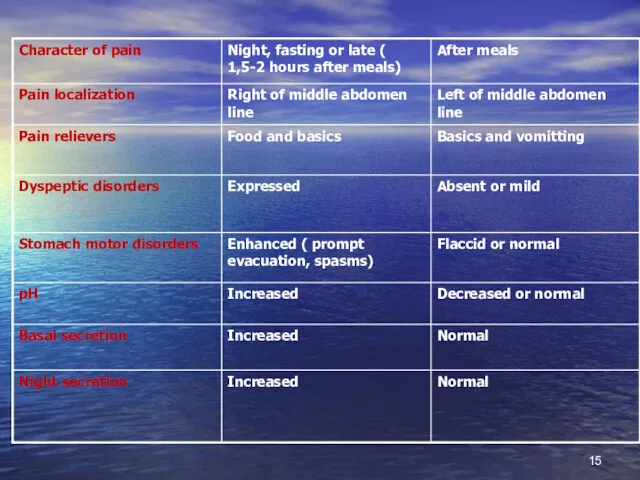
- 14. Differences among stomach and duodenum ulcer disease
- 16. Most helpful diagnostic examining Endoscopy . X-ray (not obedient for non-complicated cases). Examining of secretory function
- 17. PUD classification Severity (first defined, mild-recurrence once per year and less , moderate – relapse 2
- 18. PUD complications BLEEDING – most frequent (80%) complication. Clinics: emesis, melena, symptoms of acute blood loss
- 19. Diagnostics approach algorithm in the case of PUD bleeding Taking history and patient inspection Blood group
- 20. Perforation (8 %) – sudden knife-like pain in epigastrium, nausea, defans of anterior abdomen wall ,
- 21. Differential diagnosis Must be performed with acute symptomatic ulcers. STRESS -ulcers They can appear in burnings,
- 22. Endocrine. Very rare development in diabetes, hypothyroidism. Course of this ulcer disease id similar to severe
- 23. Clinics of symptomatic ulcers Diagnostic difficulties Absence of typical pain syndrome and dyspeptic symptoms Absence of
- 24. Treatment goals To reduce PUD symptoms and provide reparation of ulcer defect Eradicate contamination of H.P.
- 25. PUD treatment PUD treatment is directed to suppress aggression factors like acidic –peptic factor and contamination
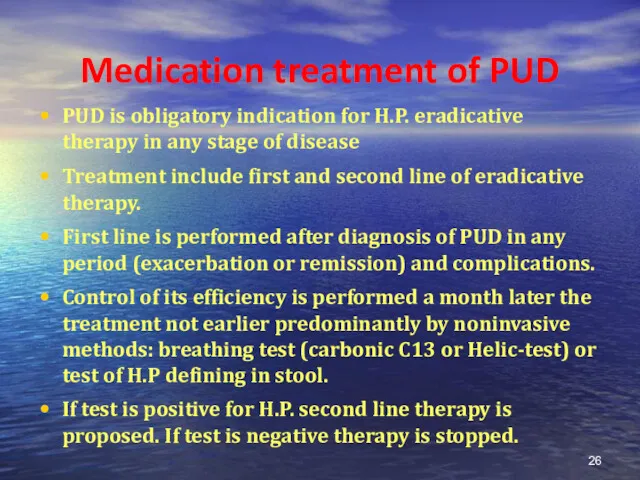
- 26. Medication treatment of PUD PUD is obligatory indication for H.P. eradicative therapy in any stage of
- 27. HELICOBACTER PYLORI eradication provides regression of inflammatory and dystrophic changes and restitutes protective properties of stomach
- 28. Regulations for antihelicobacter therapy If usage of the eradication scheme doesn’t provide complete H.pylori eradication you
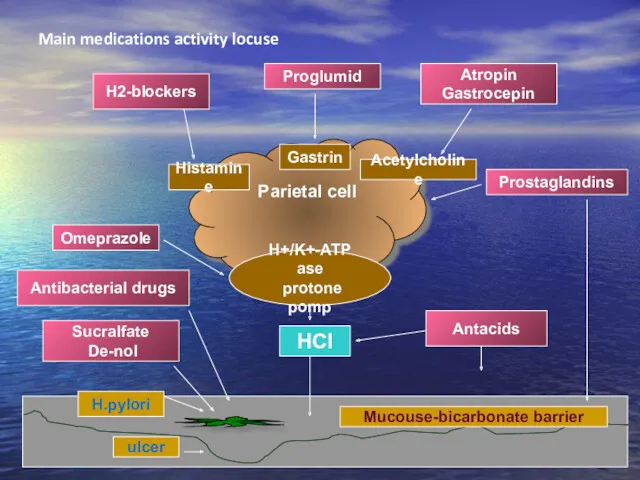
- 29. Main medications activity locuse Parietal cell Н+/K+-АТP ase protone pomp Histamine Gastrin Acetylcholine ulcer H.pylori Mucouse-bicarbonate
- 30. Antisecretory medications Selective M-cholinolytics (pirenzepim, gastrocepin) Н2-histamine receptor blockers (ranitidin, famotidin) Protone pomp inhibitors – blockers
- 31. Antisecretory therapy 1. Н2-histamine receptor blockers Selectively block secretion of HCl Decrease volume of gastric juice
- 32. 2. Peripheral M- choline receptors blockers (gastrocepin, pyrenzepin, gastrozem, gastril, pyren) Suppress HCL and pepsin production
- 33. Cytoprotectors 1. Film-forming medications(decrease backward diffusion of Hydrogen ion): Colloid Bismuthi subcytrate, De-nol (Tribimol, Ventrixol). Increase
- 34. 2. PROSTOGLANDINS – increase bicarbonates and mucus production, increase protective layer thickness, improve microcirculation. It’s mesoprostol
- 35. If accompanied dysmotility is present (duodeno-gastral reflux, gastro-esophageal reflux) DOPA-receptor blockers (cerucal, motilium) 1mg/kg TID or
- 36. Bleeding treatment Urgent hospitalization to provide endoscopic treatment (diathermo coagulation, laser coagulation). Intravenous infusion of haemostatic
- 37. Duration of hospitalization in the case of Duodenum PUD is 28 days, in Stomach PUD –
- 38. Efficacy criteria of therapy is clinic and endoscopic remission, exacerbation symptoms absence, healing of ulcer defect
- 39. Dispensary Doctor’s examination must be performed 2-4 times per year depending on severity of disease. If
- 40. During complete remission period diet № 1 is taken for 4-6 mo. Child is freed from
- 42. Скачать презентацию

































 Воспаление. Классификация воспаления
Воспаление. Классификация воспаления Антропометриялық көрсеткіштерді анықтау
Антропометриялық көрсеткіштерді анықтау Осложнения инфаркта миокарда
Осложнения инфаркта миокарда Оспа (variola)
Оспа (variola) Микроклимат помещений
Микроклимат помещений Нәрестелердегі іріңді қабыну ауруы
Нәрестелердегі іріңді қабыну ауруы Vital amputatsiya o`tkazish
Vital amputatsiya o`tkazish Ветеринарно-санитарная экспертиза туш и органов животных при инвазионных заболеваниях, передающихся и не передающихся человеку
Ветеринарно-санитарная экспертиза туш и органов животных при инвазионных заболеваниях, передающихся и не передающихся человеку Миксоматоз кроликов
Миксоматоз кроликов Хирургические инструменты
Хирургические инструменты Общие понятия об иммунитете
Общие понятия об иммунитете Здоровье человека и окружающая среда. Раздел 2
Здоровье человека и окружающая среда. Раздел 2 Переливание крови
Переливание крови Наркотики. Героиновая наркомания
Наркотики. Героиновая наркомания Неотложные состояния у детей
Неотложные состояния у детей Клинический диагноз: сибирская язва
Клинический диагноз: сибирская язва Травмы позвоночника и таза
Травмы позвоночника и таза Алгоритм действий при обнаружении пострадавшего человека
Алгоритм действий при обнаружении пострадавшего человека Правила личной гигиены и здоровья
Правила личной гигиены и здоровья Дұрыс тамақтану
Дұрыс тамақтану История ухода за зубами
История ухода за зубами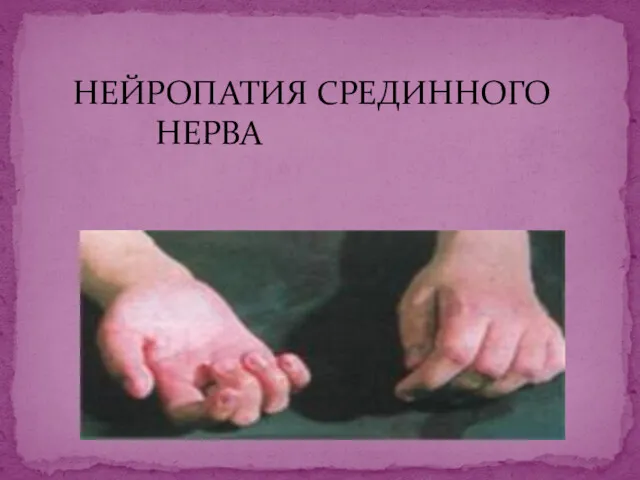 Нейропатия срединного нерва
Нейропатия срединного нерва Понятие о трансплантационном иммунитете. Тканевая несовместимость и пути ее преодоления
Понятие о трансплантационном иммунитете. Тканевая несовместимость и пути ее преодоления Классификация, сбор и удаление отходов в ЛПУ. Медицинские отходы
Классификация, сбор и удаление отходов в ЛПУ. Медицинские отходы Субъективные и объективные методы обследования в клинике внутренних болезней
Субъективные и объективные методы обследования в клинике внутренних болезней Классификация психических и поведенческих расстройств, вызванных употреблением психоактивных веществ
Классификация психических и поведенческих расстройств, вызванных употреблением психоактивных веществ Цитология в дерматологии
Цитология в дерматологии Трахома в Чувашской Республике
Трахома в Чувашской Республике