Содержание
- 2. 1) sanitary legislation in radiation factor sphere; 2) preventive and regular sanitary control at objects, that
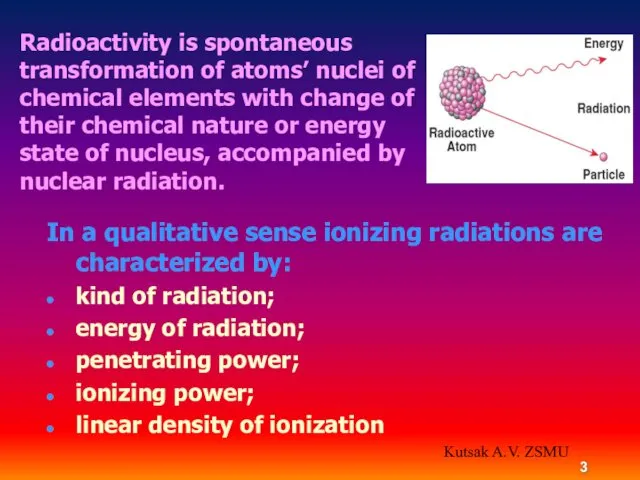
- 3. Radioactivity is spontaneous transformation of atoms’ nuclei of chemical elements with change of their chemical nature
- 4. Qualitative characteristics of ionizing radiation are doses (D): 4 аbsorbed dose; exposure dose; еquivalent dose; еffective
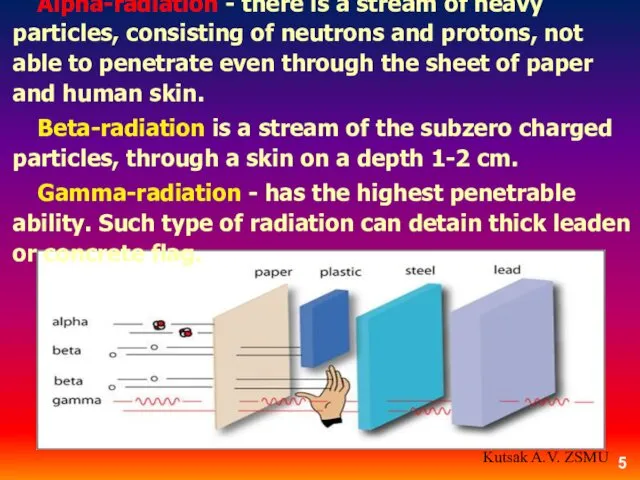
- 5. Alpha-radiation - there is a stream of heavy particles, consisting of neutrons and protons, not able
- 6. From hygienic and choice of method of radioactive waste decontamination points of view, all radioactive nuclides
- 7. EFFECT ON HUMAN BODY Kutsak A.V. ZSMU
- 8. Ionizing radiation sources name materials, radioactive substances, or technical devices which generate ionizing radiation. The sources
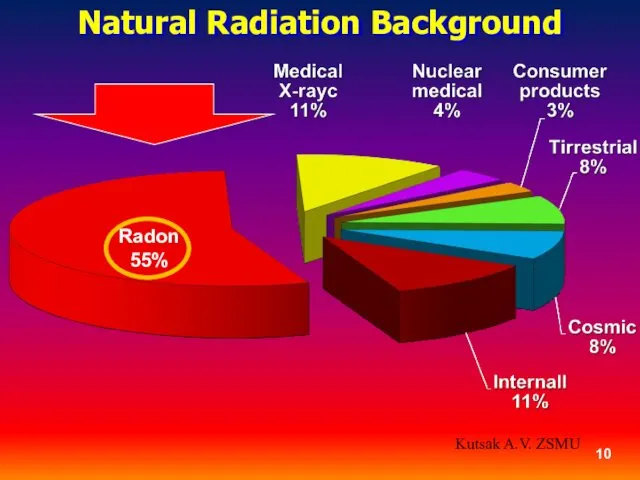
- 9. Natural radiating background - constantly operating factor of environment caused by space radiation, earth crust radiation,
- 10. Natural Radiation Background Radon 55% Kutsak A.V. ZSMU
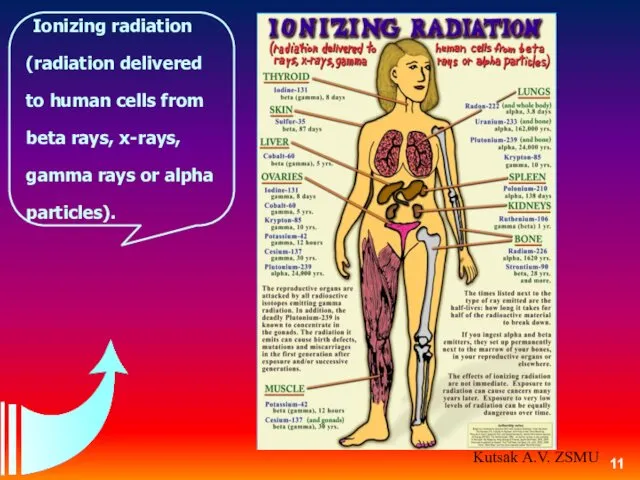
- 11. Ionizing radiation (radiation delivered to human cells from beta rays, x-rays, gamma rays or alpha particles).
- 12. At present universal use of sources of ionizing radiation has found the place in the: industry;
- 13. Distinguish two kinds of influence of ionizing radiation on a sell: A straight line at which
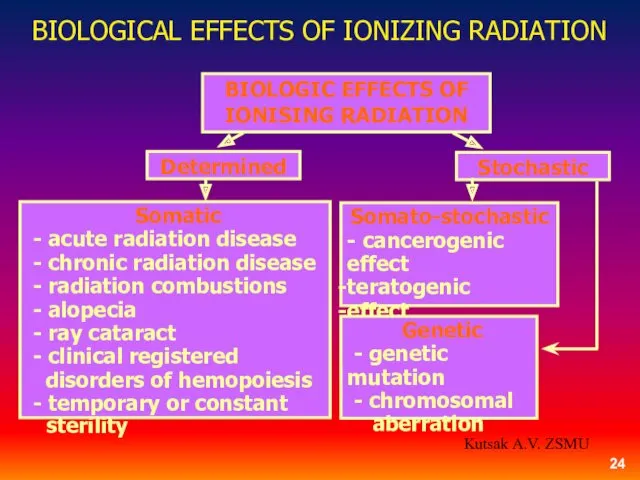
- 14. All harmful consequences of an irradiation share on the determined (direct) and stochastic (possible) effects. The
- 15. Radiation sickness is characteristic display of action of ionizing radiation. Laws of development of radiation sickness
- 16. Radiation illness severity level depends on, whether all organism (the general irradiation) or its separate sites
- 17. Sharp radiation sickness in its typical form develops at the disposable general external rather uniform irradiation
- 18. The consistency of change of separate pathological displays in an organism which sharpness depends on severity
- 19. The phase of the general primary reaction is characterized dispeptition by displays - a nausea, vomiting,
- 20. The phase at the height of illness is characterized by increase leuco - both a lymphocytopenia,
- 21. Chronic radiation illness develops as a result of a long irradiation of an organism small doses
- 22. For chronic radiation illness characteristic there is a slow increase of severity of damages and more
- 23. To stochastic (possible) effects of an irradiation belong without the threshold effects which reliability of occurrence
- 24. BIOLOGIC EFFECTS OF IONISING RADIATION Determined Stochastic Somatic - acute radiation disease - chronic radiation disease
- 25. The international commission of radiating protection (ICRP) at rationing of the radiating factor and an estimation
- 26. There are three main principles of radiating protection: Correctness principle. Any practical activities connected with use
- 27. By Norms of radiating safety operating at present in Ukraine (NRSU-97) it is provided - аll
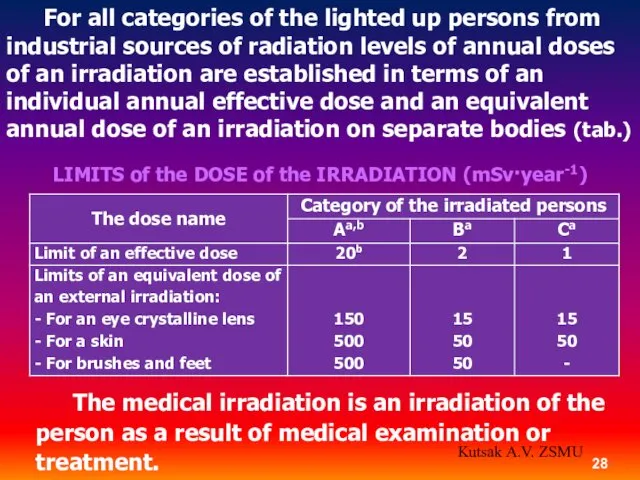
- 28. For all categories of the lighted up persons from industrial sources of radiation levels of annual
- 29. Considering features of this kind of an irradiation, antiradiation protection of patients is based on following
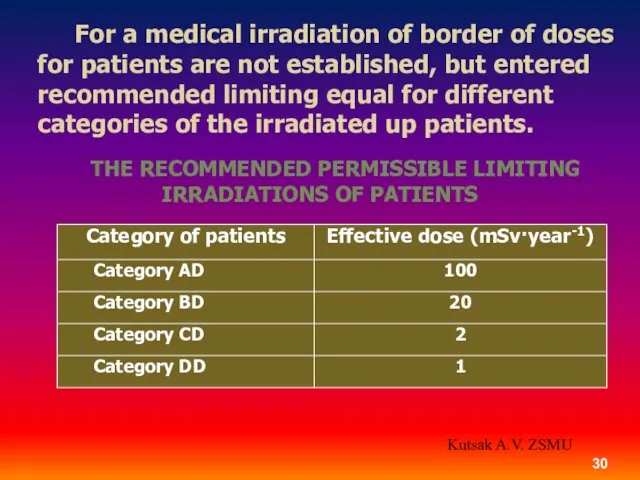
- 30. For a medical irradiation of border of doses for patients are not established, but entered recommended
- 31. Category AD. Patients with oncological and precancer diseases, with a congenital cardiovascular pathology, and also urgention
- 32. For persons of categories the AD and a BD is in addition entered restriction of equivalent
- 33. RADIATING PROTECTION OF THE PERSONNEL AT INDUSTRIAL ACTIVITY Decrease in levels of an external and internal
- 34. The Radioactive waste is determined: On a consistence on liquid and solid. On activity degree -
- 35. MAINTENANCE OF RADIATING SAFETY AT APPLICATION OF SOURCES OF IONIZING RADIATION IN MEDICINE Control of observance
- 36. Main principles on which personnel protection at use of sources of radiation in medicine is based
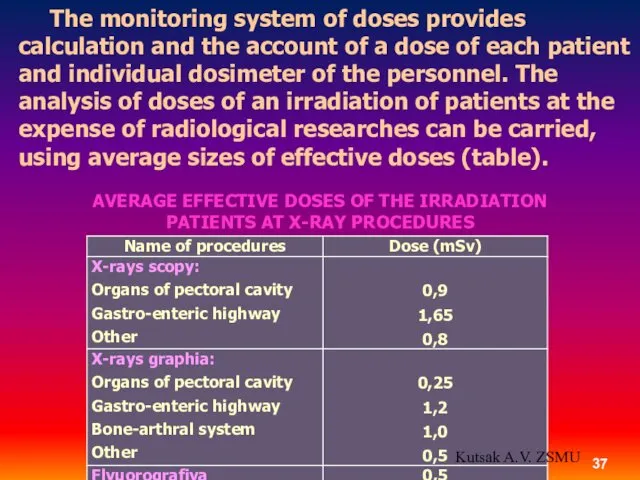
- 37. The monitoring system of doses provides calculation and the account of a dose of each patient
- 38. RADIATING CONTROL The purpose of radiating control are receptions of the information on doses of an
- 39. According to it and all equipment of radiating control according to the destination divide into four
- 41. Скачать презентацию






























 Средства, активирующие холинорецепторы и ингибирующие холинэстеразу
Средства, активирующие холинорецепторы и ингибирующие холинэстеразу Традиционная гигиена в античную эпоху древней Греции и Римской империи
Традиционная гигиена в античную эпоху древней Греции и Римской империи Закаливание холодом
Закаливание холодом Этиология патологии ЖКТ
Этиология патологии ЖКТ Гемостаз
Гемостаз Госпитальная хирургия: Долихосигма
Госпитальная хирургия: Долихосигма Венерические заболевания
Венерические заболевания Маскүнемдік. Салыс тырмалы жастық ерекшеліктер
Маскүнемдік. Салыс тырмалы жастық ерекшеліктер Течение и ведение послеродового периода. Становление лактации. Послеродовая контрацепция
Течение и ведение послеродового периода. Становление лактации. Послеродовая контрацепция Обязанности должностных лиц медицинской службы соединения по медицинскому снабжению
Обязанности должностных лиц медицинской службы соединения по медицинскому снабжению Табиғи және техногенді радияциялық фон. Иондық сәулелену көзінің адам ағзасына әсерінің салдары
Табиғи және техногенді радияциялық фон. Иондық сәулелену көзінің адам ағзасына әсерінің салдары Использование УЗИ при катетеризации центральных вен
Использование УЗИ при катетеризации центральных вен Здоровый образ жизни. Здоровое полноценное питание
Здоровый образ жизни. Здоровое полноценное питание Жасуша патофизиологиясы
Жасуша патофизиологиясы Аурудың денсаулық және ауру кезеңдері. Клиникалық және биологиялық өлімдер
Аурудың денсаулық және ауру кезеңдері. Клиникалық және биологиялық өлімдер Оказание первой помощи себе и пострадавшим в несчастных случаях. (Тема 8)
Оказание первой помощи себе и пострадавшим в несчастных случаях. (Тема 8) Pacienta komforta nodrošinājums un pacienta drošība
Pacienta komforta nodrošinājums un pacienta drošība Гастрит, асқазан ойық жарасы
Гастрит, асқазан ойық жарасы Қанның тамырлар бойымен қан қозғалысы
Қанның тамырлар бойымен қан қозғалысы Методы лабораторной диагностики кровотечений из различных отделов ЖКТ
Методы лабораторной диагностики кровотечений из различных отделов ЖКТ Профилактика тромбоэмболических осложнений. Сравнительная характеристика антикоагулянтов непрямого действия
Профилактика тромбоэмболических осложнений. Сравнительная характеристика антикоагулянтов непрямого действия Т-клеточная лимфома с поражением кожи спины, груди
Т-клеточная лимфома с поражением кожи спины, груди Энпиты и нутриенты. Энтеральное питание
Энпиты и нутриенты. Энтеральное питание Плоскости, оси и области тела
Плоскости, оси и области тела Ауыз қуысы шырышты қабатының анатомо-гистологиялық құрылым ерекшеліктері.терминология, АҚШҚ ауруларының жүйесі
Ауыз қуысы шырышты қабатының анатомо-гистологиялық құрылым ерекшеліктері.терминология, АҚШҚ ауруларының жүйесі Клуб Будущий доктор
Клуб Будущий доктор Tetanus. Distribution
Tetanus. Distribution Интерпретация данных исследований углеводного обмена. Данные исследований гормонального статуса
Интерпретация данных исследований углеводного обмена. Данные исследований гормонального статуса