Содержание
- 2. Methods of respiratory organs examination: Radiography Radioscopy Bronchography Angiopulmonography Ultrasound diagnostics CT scan Magnetic resonance imaging
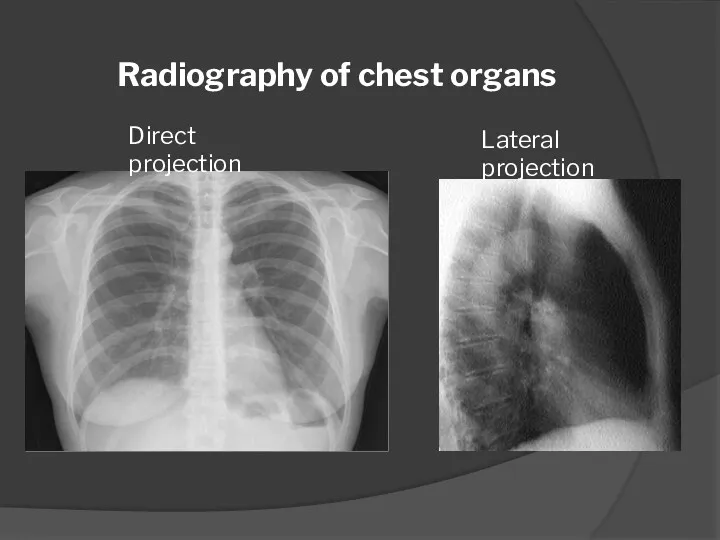
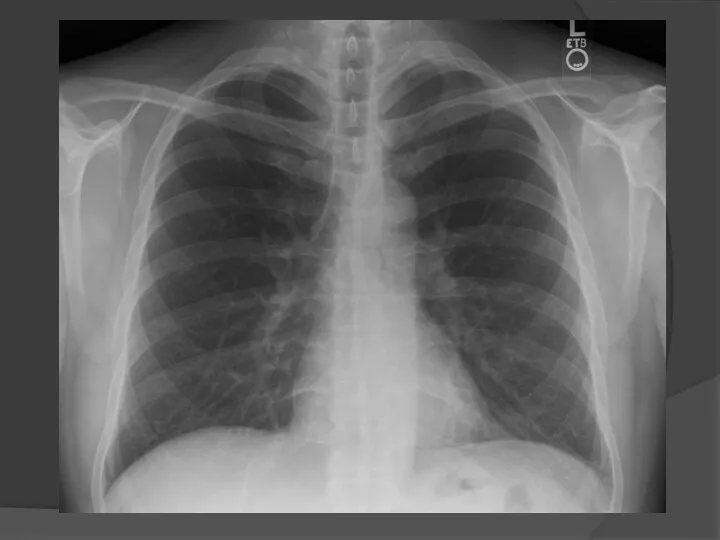
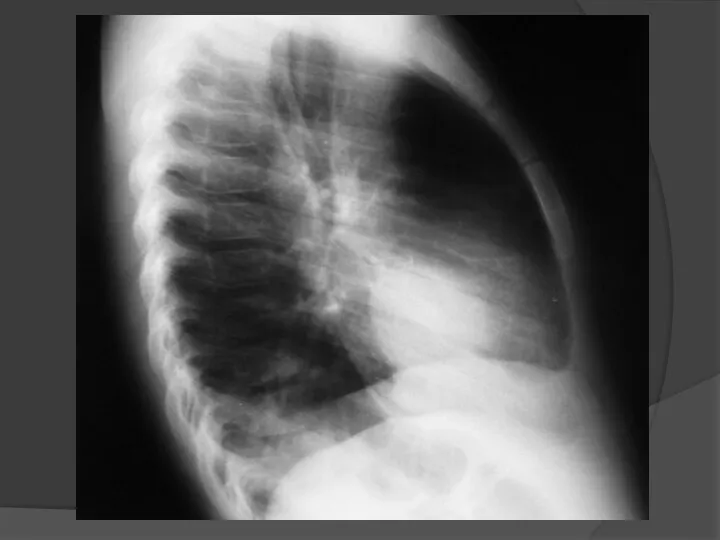
- 3. Direct projection Lateral projection Radiography of chest organs
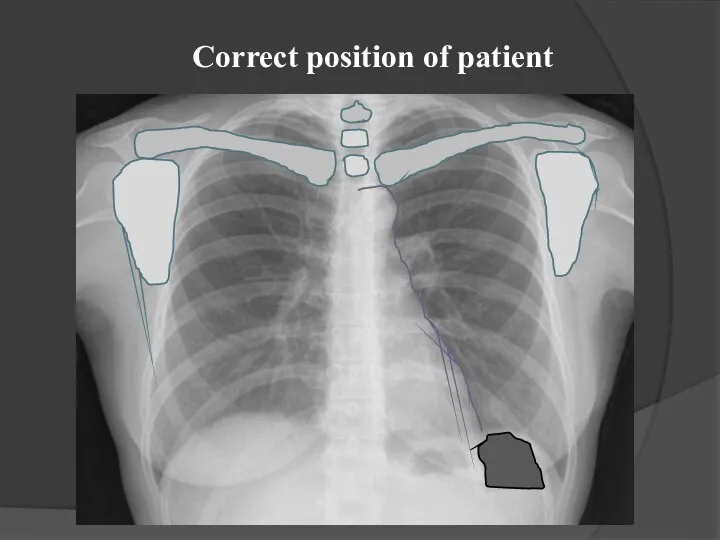
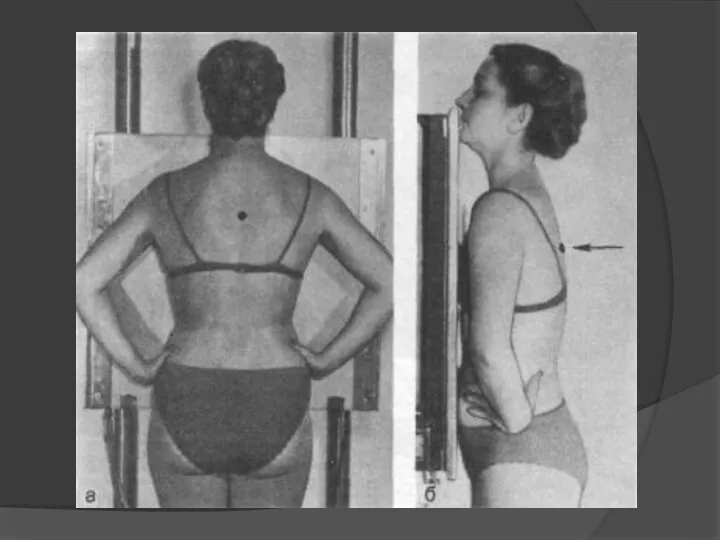
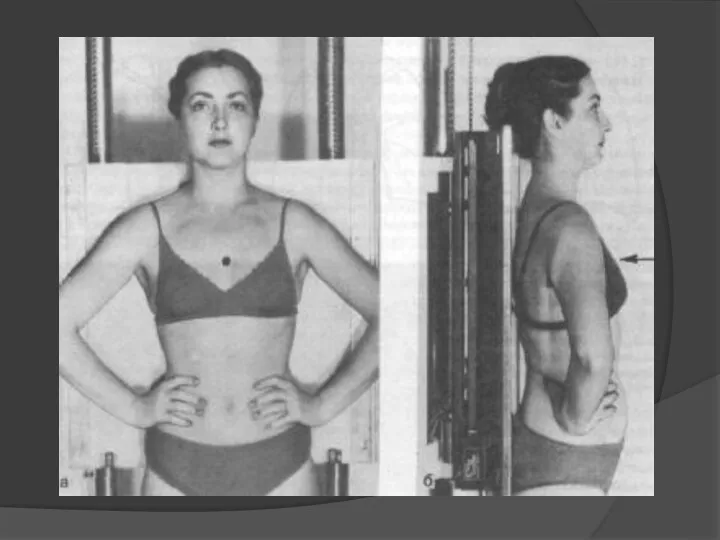
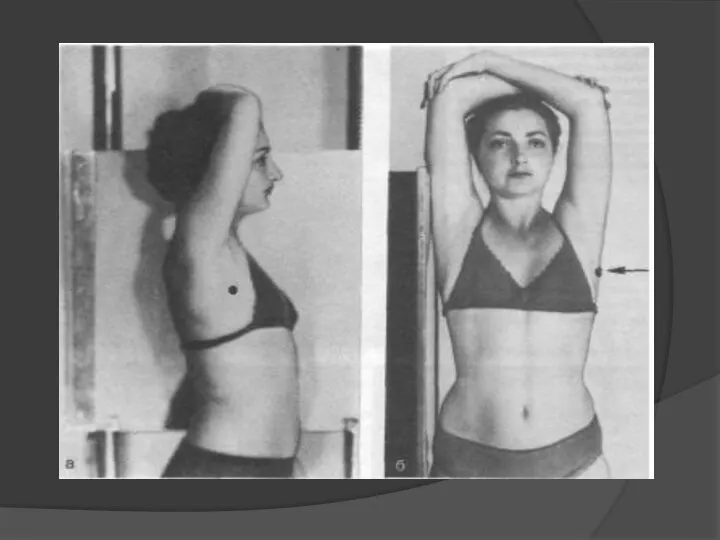
- 4. Correct position of patient
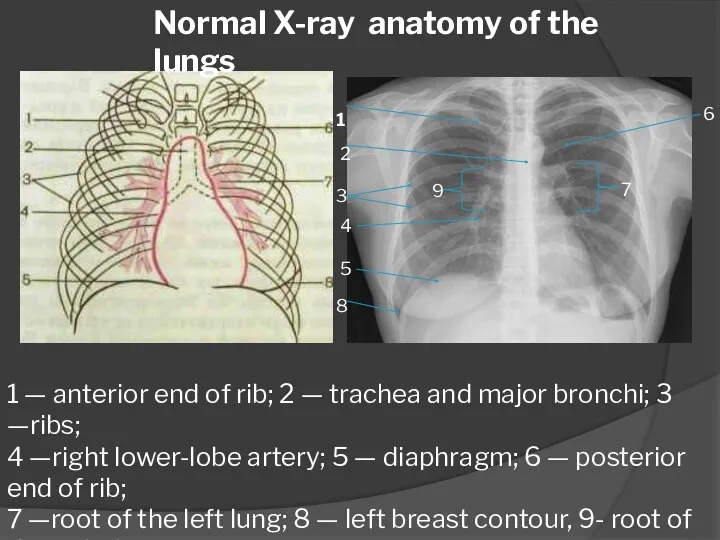
- 5. 1 — anterior end of rib; 2 — trachea and major bronchi; 3 —ribs; 4 —right
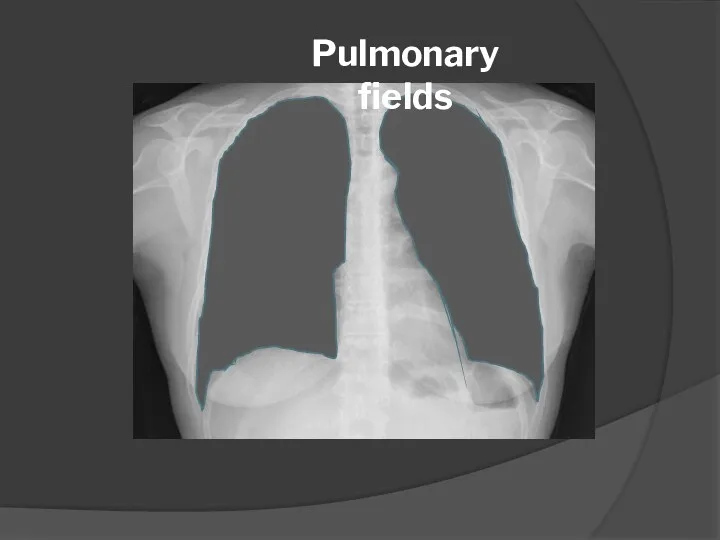
- 6. Pulmonary fields
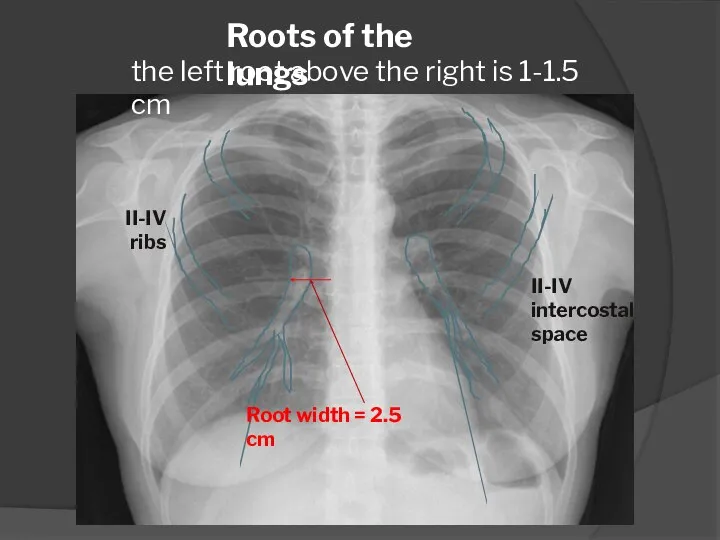
- 7. Roots of the lungs II-IV intercostal space II-IV ribs the left root above the right is
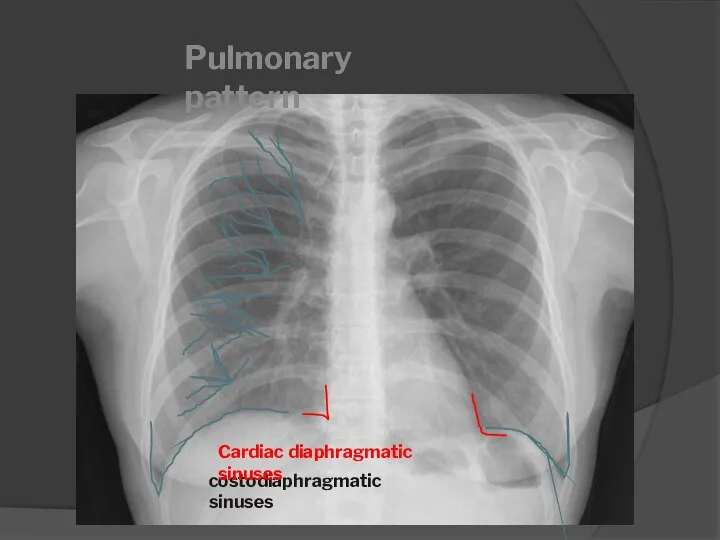
- 8. costodiaphragmatic sinuses Pulmonary pattern Cardiac diaphragmatic sinuses
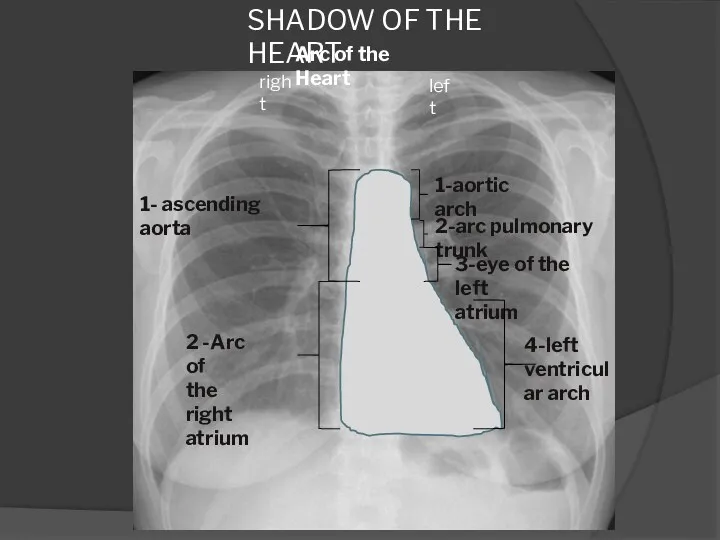
- 9. SHADOW OF THE HEART Arc of the Heart 1- ascending aorta 2 -Arc of the right
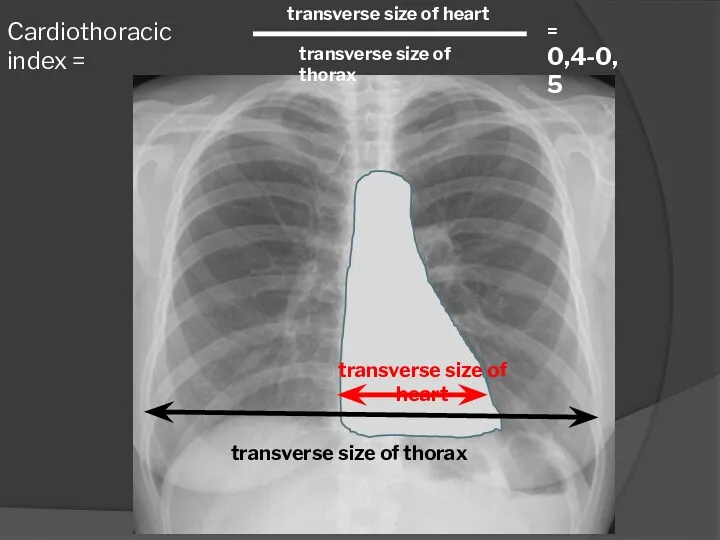
- 10. Cardiothoracic index = transverse size of heart transverse size of thorax transverse size of heart transverse
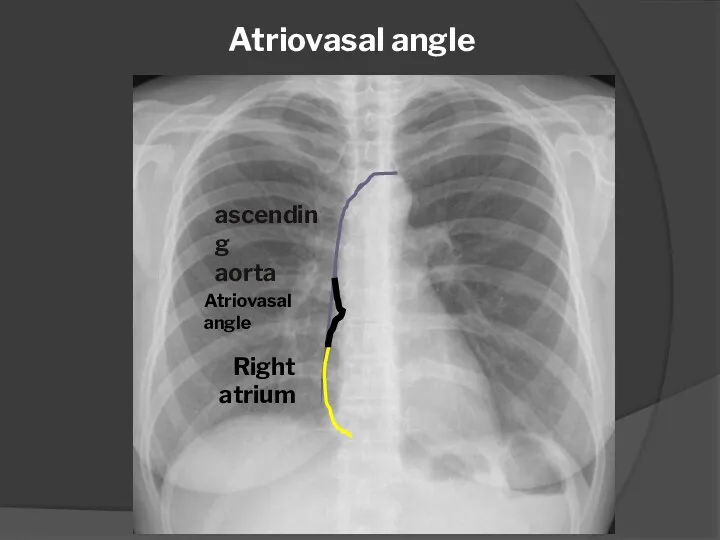
- 11. Atriovasal angle ascending aorta Right atrium Atriovasal angle
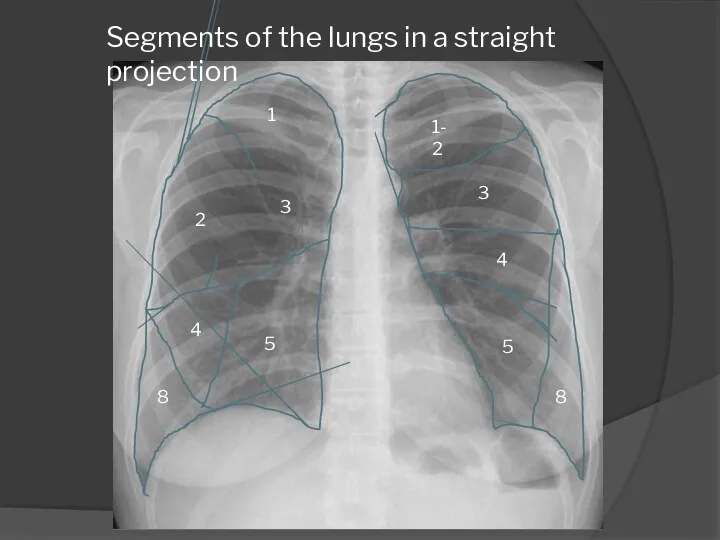
- 12. 1 2 3 4 5 8 Segments of the lungs in a straight projection 1-2 3
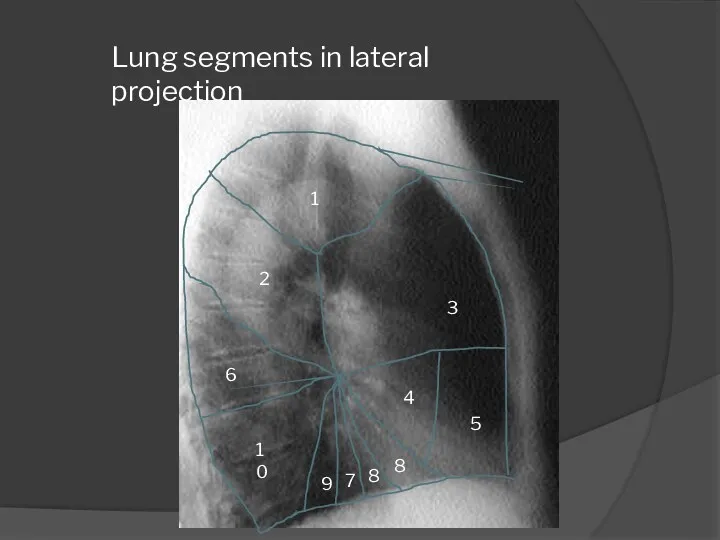
- 13. 1 2 3 6 10 4 5 Lung segments in lateral projection 9 7 8 8
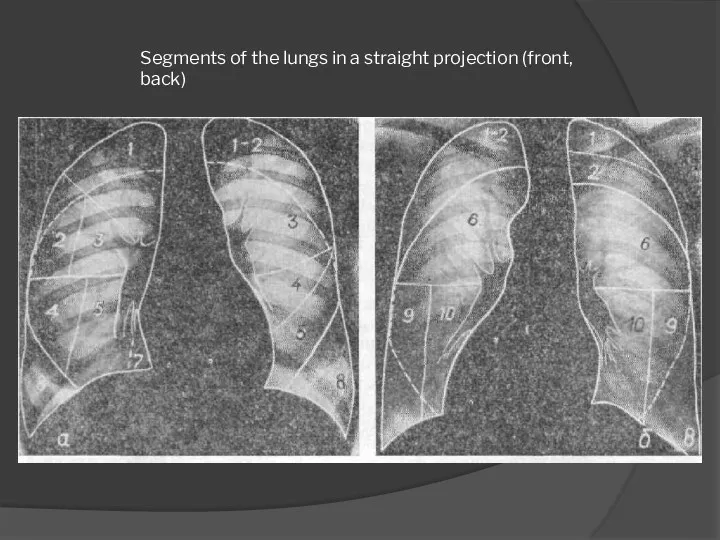
- 14. Segments of the lungs in a straight projection (front, back)
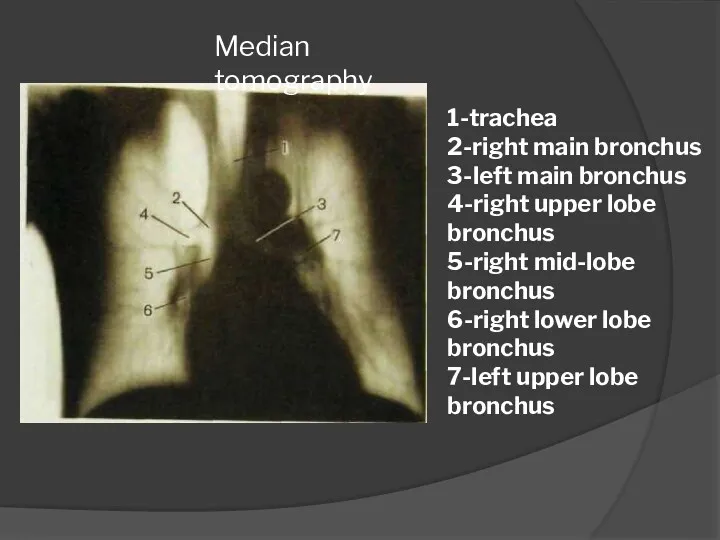
- 15. Median tomography 1-trachea 2-right main bronchus 3-left main bronchus 4-right upper lobe bronchus 5-right mid-lobe bronchus
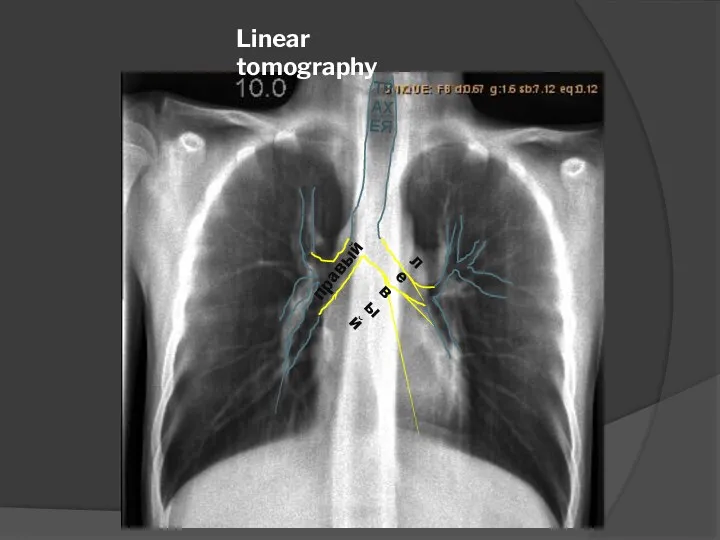
- 16. Linear tomography ТРАХЕЯ правый левый
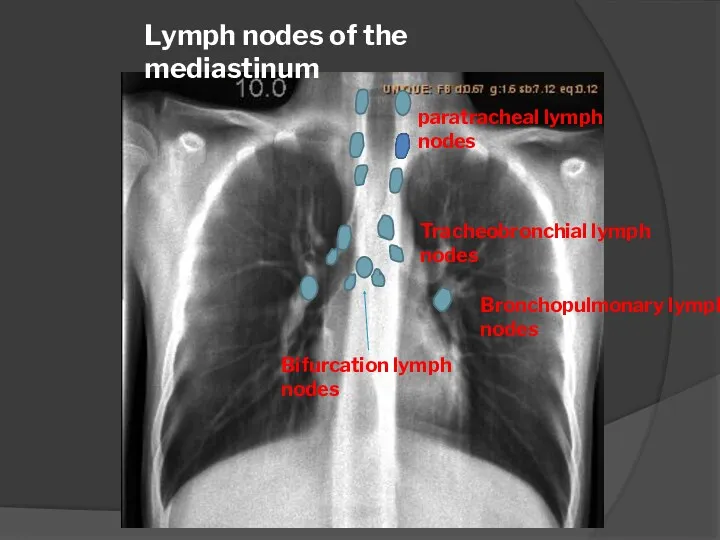
- 17. Lymph nodes of the mediastinum paratracheal lymph nodes Tracheobronchial lymph nodes Bifurcation lymph nodes Bronchopulmonary lymph
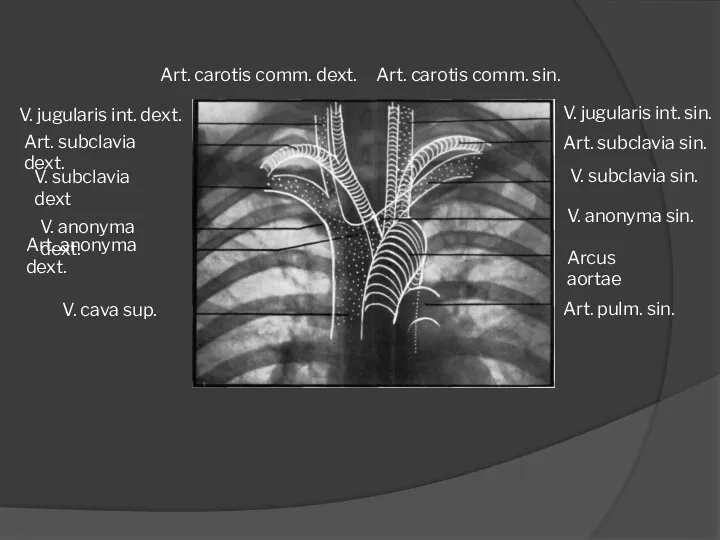
- 18. Art. pulm. sin. Arcus aortae V. anonyma sin. V. subclavia sin. Art. subclavia sin. V. jugularis
- 19. - Radiography - Fluorography - Radioscopy - Linear tomography X-ray examination methods
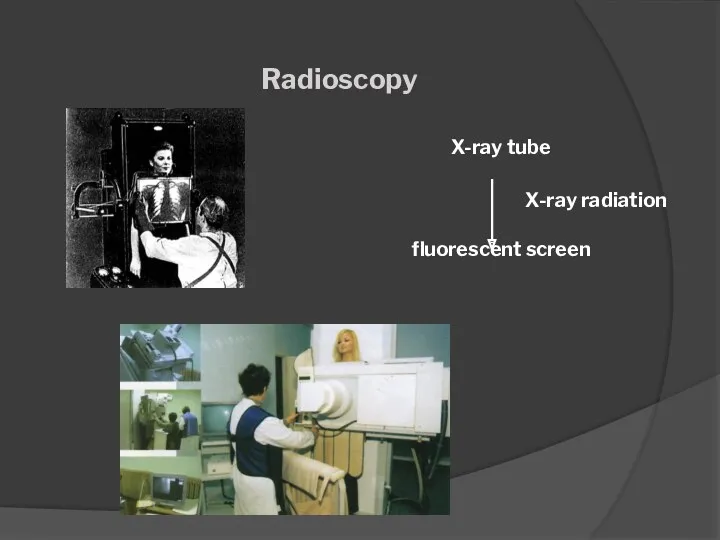
- 20. Radioscopy X-ray examination method in which an X-ray image of an object is obtained on the
- 21. Radioscopy X-ray tube fluorescent screen X-ray radiation
- 22. Indications: - polypositional study - real-time evaluation of the function - conducting the catheterization, angioplasty under
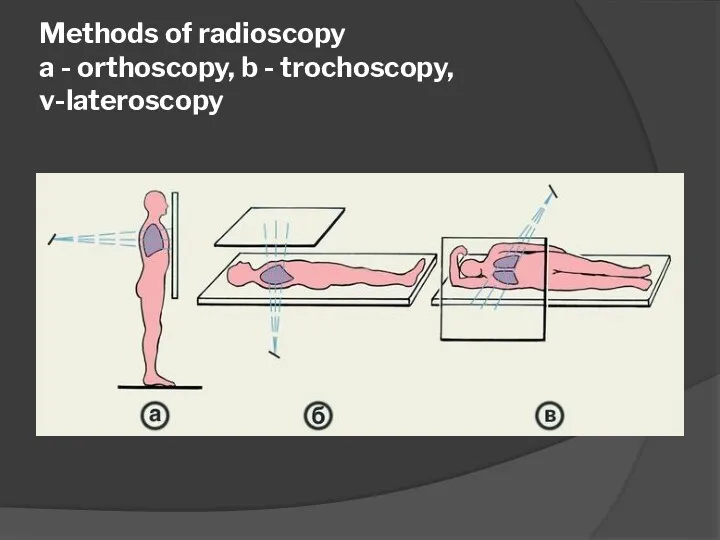
- 23. Methods of radioscopy a - orthoscopy, b - trochoscopy, v-lateroscopy
- 25. Radiography An X-ray examination method in which a fixed X-ray image of an object is obtained
- 26. Advantages of radiography: - better detectability of small parts - less radiation load - the possibility
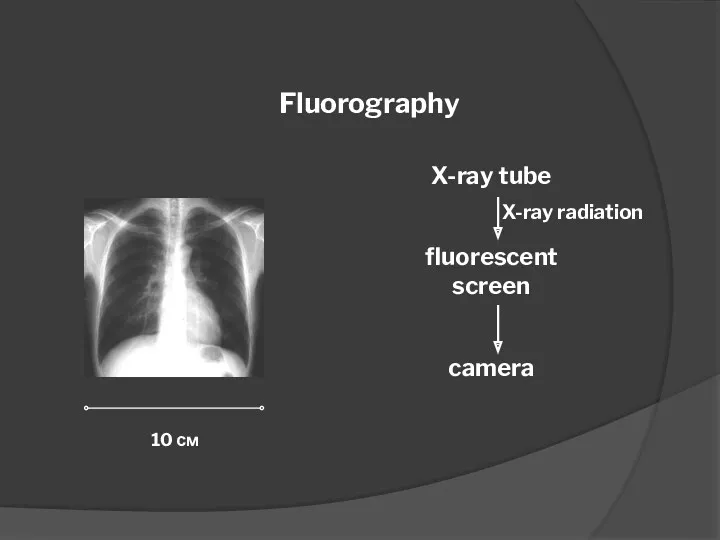
- 32. Fluorography The method of X-ray examination consists in photographing the image from a fluorescent screen, screen
- 33. Fluorography X-ray tube fluorescent screen camera 10 см X-ray radiation
- 34. Advantages of fluorography : - low cost of research - the possibility of conducting mass verification
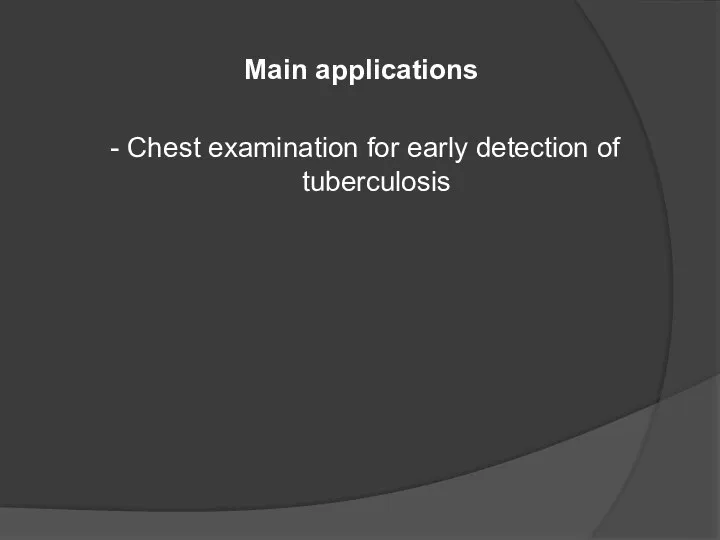
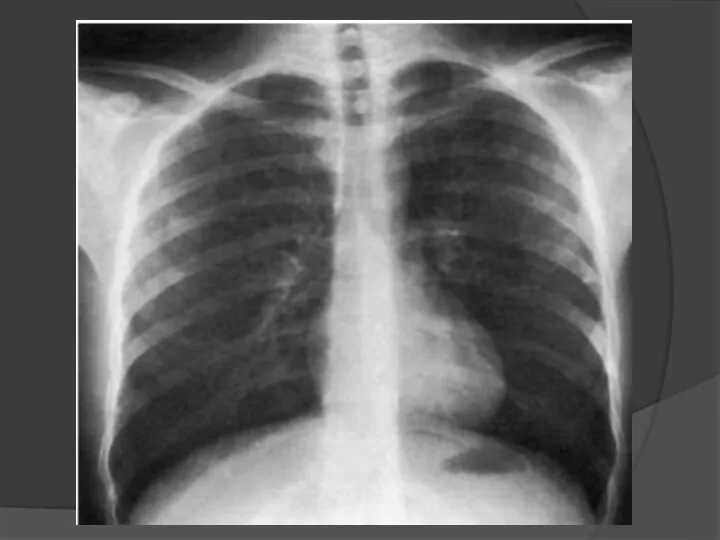
- 35. Main applications - Chest examination for early detection of tuberculosis
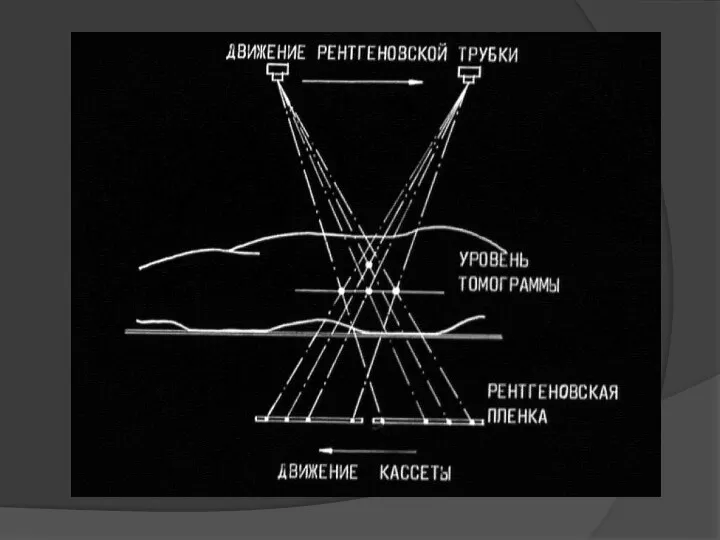
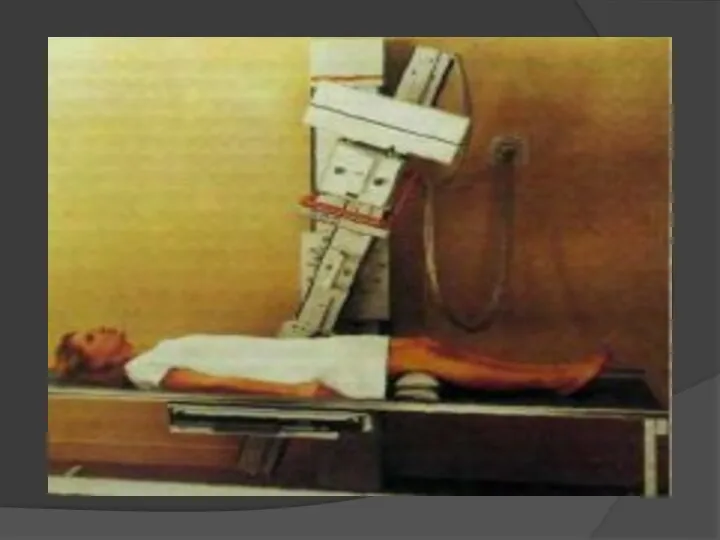
- 37. Linear tomography The method of X-ray examination is to obtain an image of an object at
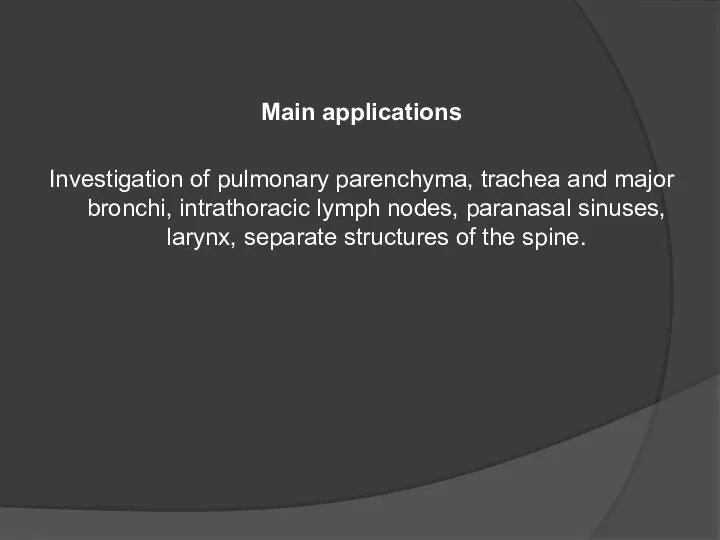
- 40. Main applications Investigation of pulmonary parenchyma, trachea and major bronchi, intrathoracic lymph nodes, paranasal sinuses, larynx,
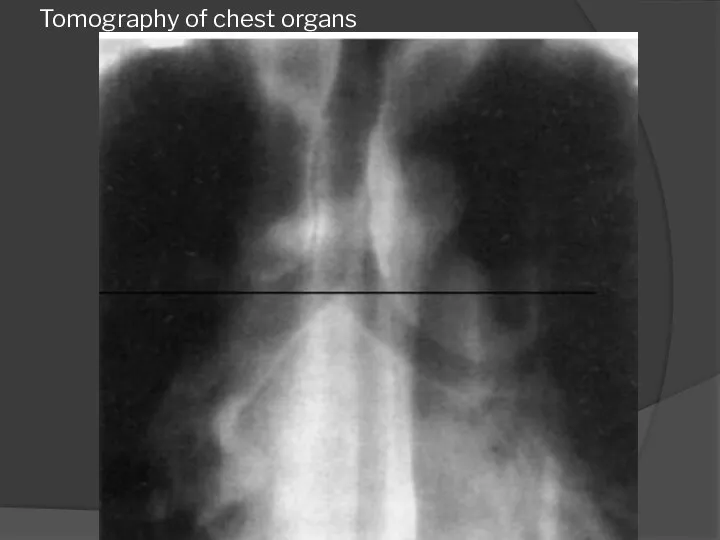
- 41. Tomography of chest organs
- 42. Evaluation of the quality of the radiograph Completeness of volume : the whole chest from the
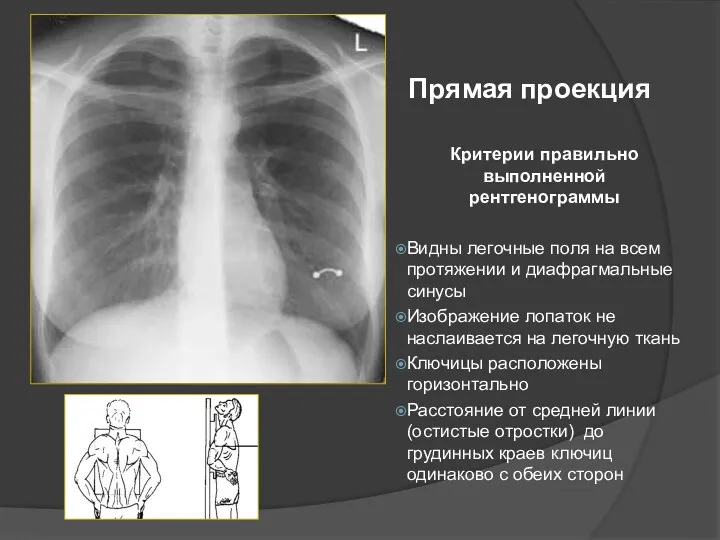
- 43. Прямая проекция Критерии правильно выполненной рентгенограммы Видны легочные поля на всем протяжении и диафрагмальные синусы Изображение
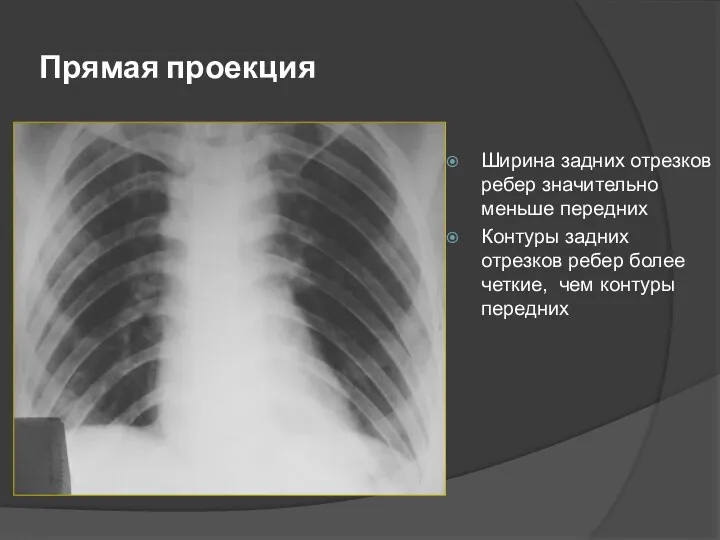
- 44. Прямая проекция Ширина задних отрезков ребер значительно меньше передних Контуры задних отрезков ребер более четкие, чем
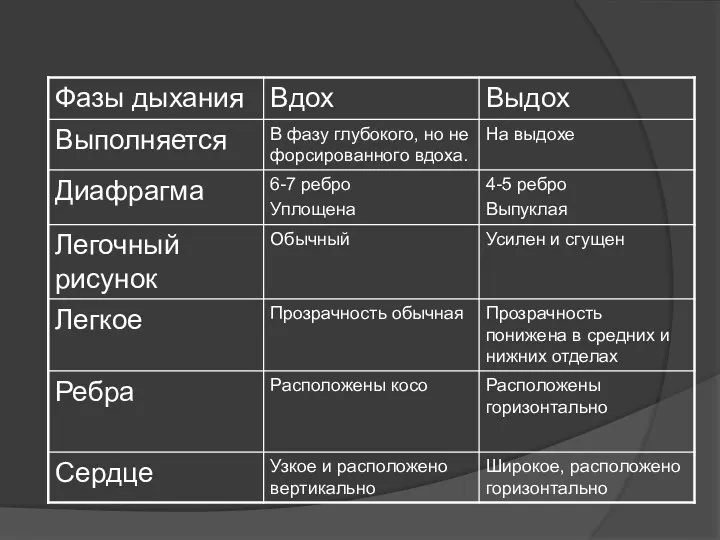
- 45. Исследование на вдохе и выдохе Рентгенография легких производится в фазу глубокого, но не форсированного вдоха. Диафрагма
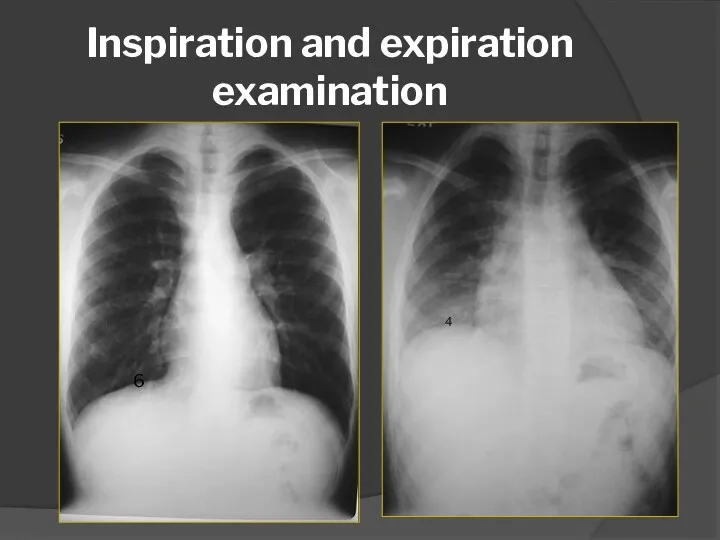
- 47. Inspiration and expiration examination 6 4
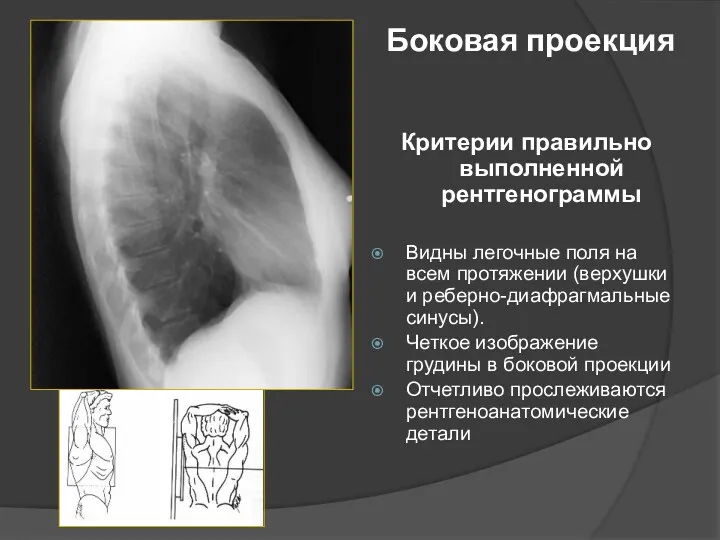
- 48. Боковая проекция Критерии правильно выполненной рентгенограммы Видны легочные поля на всем протяжении (верхушки и реберно-диафрагмальные синусы).
- 50. Скачать презентацию












 План курса Общая нейрофизиология
План курса Общая нейрофизиология Анемии. Эритроцитопоэз
Анемии. Эритроцитопоэз Симптоматические артериальные гипертензии
Симптоматические артериальные гипертензии Cardiogenic shock
Cardiogenic shock Лекарственные растения обладающие мочегонными свойствами
Лекарственные растения обладающие мочегонными свойствами Паталогия печени
Паталогия печени Патогенез речевых нарушений
Патогенез речевых нарушений Фибрилляция предсердий
Фибрилляция предсердий Транквилизаторы
Транквилизаторы Зубные пасты. Жевательные резинки. Жевательные таблетки. Ополаскиватель для полости рта
Зубные пасты. Жевательные резинки. Жевательные таблетки. Ополаскиватель для полости рта Ожоги органа зрения
Ожоги органа зрения Факторы свертывающей и противосвертывающей системы крови. Геморрагические диатезы и синдромы. Тромбофилии
Факторы свертывающей и противосвертывающей системы крови. Геморрагические диатезы и синдромы. Тромбофилии Зоонозы. Туляремия
Зоонозы. Туляремия Систематизация и диагностика васкулитов
Систематизация и диагностика васкулитов Травматический шок
Травматический шок Иммунопрофилактика. Национальный календарь
Иммунопрофилактика. Национальный календарь Адам ағзасының иммундық жүйесі
Адам ағзасының иммундық жүйесі Биоэнергомассажер Fohow
Биоэнергомассажер Fohow Развитие медицины в России XIX век
Развитие медицины в России XIX век Жұқпалы үрдіс патофизиологиясы. Сепсис және сепсистік сілейменің патогенезі
Жұқпалы үрдіс патофизиологиясы. Сепсис және сепсистік сілейменің патогенезі Респираторлық дистресс синдромының клинико-лабораторлық зерттеу көріністері
Респираторлық дистресс синдромының клинико-лабораторлық зерттеу көріністері Питание как стиль жизни. Основные правила и принципы
Питание как стиль жизни. Основные правила и принципы Физическое развитие. Основные показатели физического развития в различных возрастно-половых группах, их особенности и тенденции
Физическое развитие. Основные показатели физического развития в различных возрастно-половых группах, их особенности и тенденции Гельминтозы. Диагностика. Лечение
Гельминтозы. Диагностика. Лечение Синдром Дауна
Синдром Дауна Сүт бездерінің дисормональды аурулары туралы не білеміз?
Сүт бездерінің дисормональды аурулары туралы не білеміз? Жүктілік кезіндегі гипертензия
Жүктілік кезіндегі гипертензия Возможности медикаментозного обезболивания во время хирургических вмешательств
Возможности медикаментозного обезболивания во время хирургических вмешательств