Слайд 2
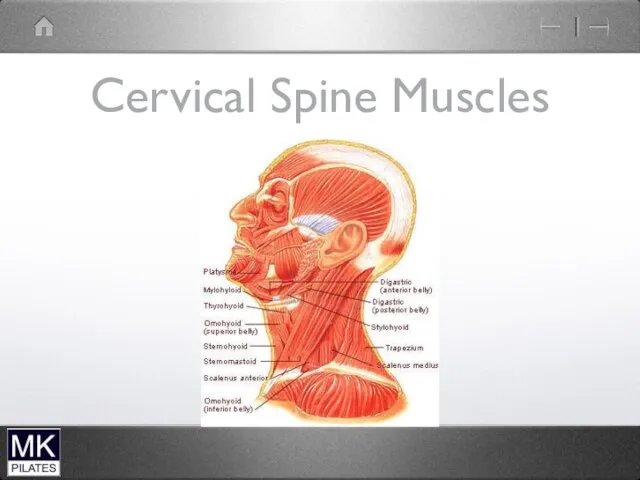
Слайд 3

Neck Flexors
Superficial
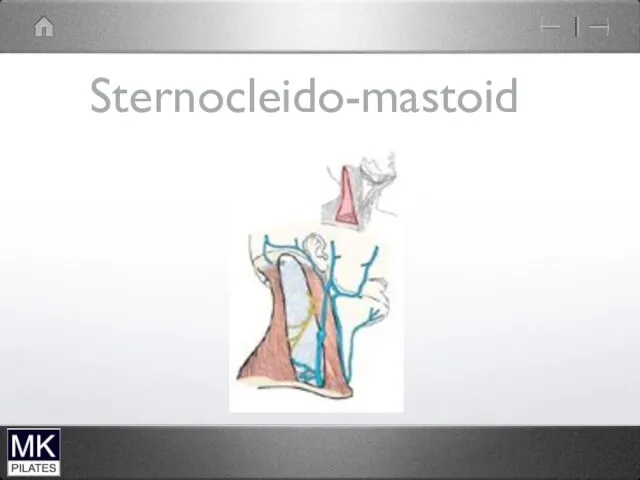
Sternocleidomastoid
Scalenes
Supra-hyoid muscles
Infrahyoid musles
Deep
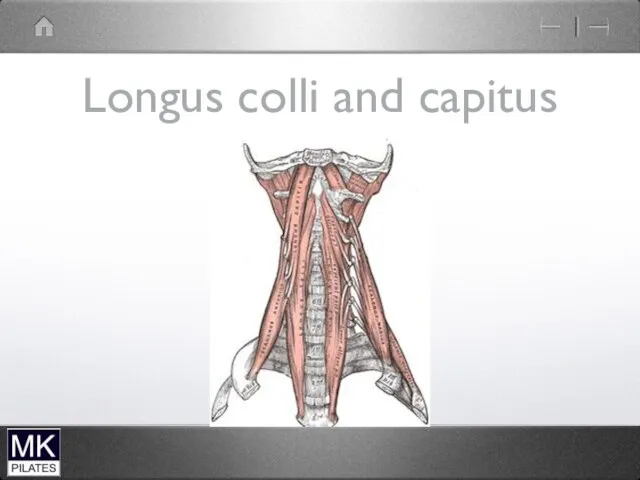
Longus Colli
Longus Capitus
Rectus Capitus Anterior
Rectus Capitus Lateralis
Слайд 4

Deep neck flexors
Deep
Attach directly to the vertebrae
Single segments
Close to axis of
rotation
Tonic activity
Support the spinal curve
Слайд 5
Слайд 6

Слайд 7

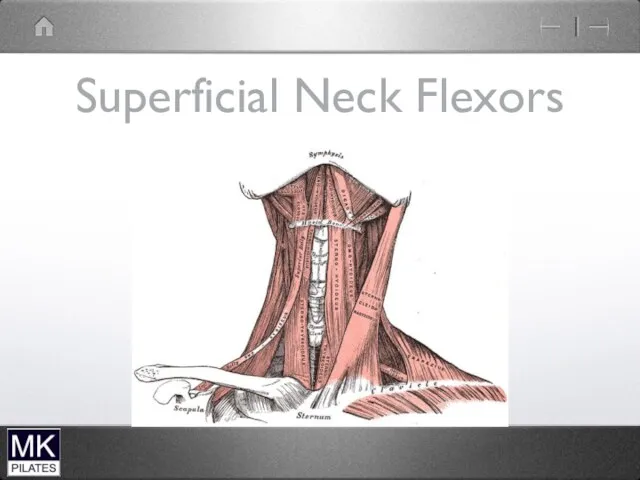
Superficial Neck Flexors
Predominantly Mobilisers
Also lateral flexion and rotation
Hyoid muscles also control
hyoid movement (for speech and swallowing)
therefore only secondary cervical spine mobilisers
Слайд 8
Слайд 9

Слайд 10
Слайд 11
Слайд 12

Слайд 13

Слайд 14

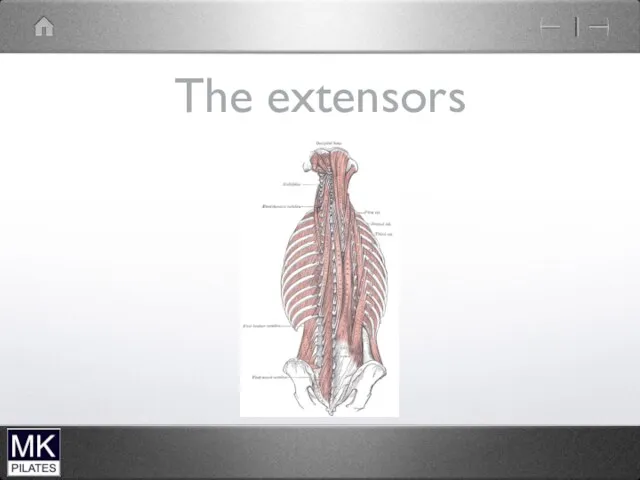
Neck Extensors
Deep Extensors
Spinales
Semispinalis
Rotators
Intertransversarii
Interspinales
Suboccipital extensors
Multifidus
Superficial Extensors
Upper trapezius
Levator scapulae
Splenius
Longisimus
Слайд 15
Слайд 16
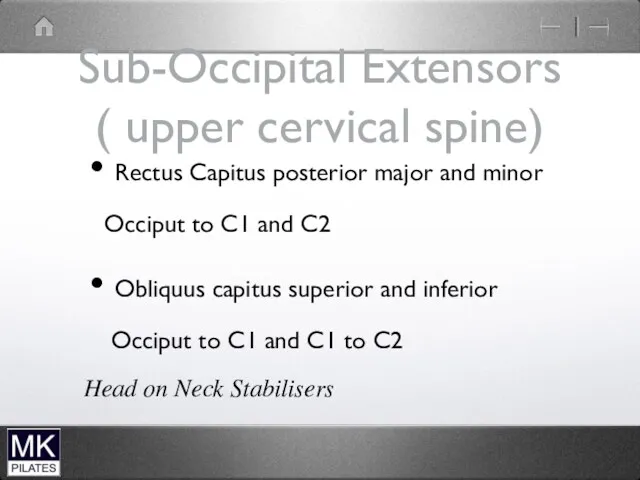
Sub-Occipital Extensors
( upper cervical spine)
Rectus Capitus posterior major and minor
Occiput
to C1 and C2
Obliquus capitus superior and inferior
Occiput to C1 and C1 to C2
Head on Neck Stabilisers
Слайд 17
Upper cervical extensors
Bilaterally upper cervical extension . Mainly work to control
excessive upper cervical flexion.
Control excessive movement
Eccentric activity
Significant proprioceptive function
Слайд 18

Deep neck extensors
( mid to low cervical spine)
Eccentric action to control
movement
Proprioceptive role
Слайд 19

Deep neck extensors
Segmental control of extension mid to lower cervical spine
Limit
and control excessive cervical flexion and shear /translation forces
Unilaterally controls rotation and lateral flexion
Proprioceptive role
Слайд 20

Mobility Muscles
Splenius mastoid to C4-T3
Slenius cervicus TP C1-2 to Sp T4-6
Longissimus
capitus Mastoid to TPC5-6
Iliocostalis cervicus TP C4-6 to ribs 3-6
Levator scapulae TP C1-4 to superiormedial border of scapula
Lets just call them superficial extensors!!!
Слайд 21
Superficial Extensors
Upper and lower cervical extension
Not segmental
Ipsilateral rotation and lateral
flexion without segmental control
Слайд 22
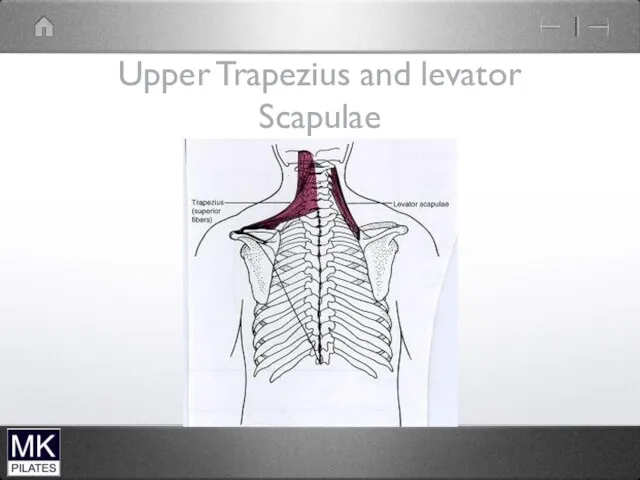
Upper Trapezius and levator Scapulae
Слайд 23

Слайд 24

Levator Scapulae and Upper Trapezius
Mainly mobility of scapula
Can also produce Neck
extension and lateral flexion but not their prime role
No segmental control
problematic if become short and stiff
Слайд 25
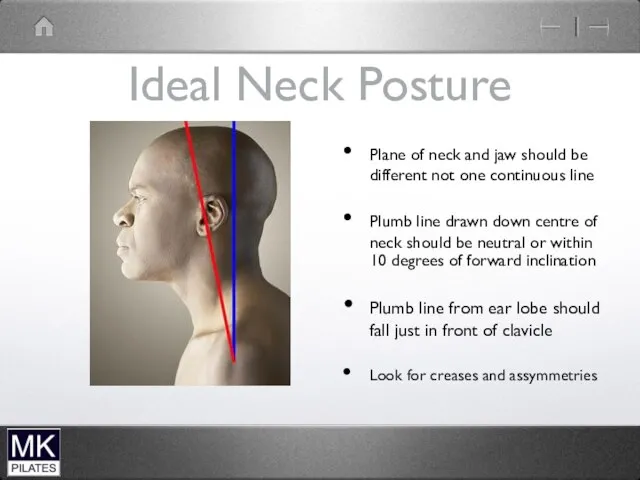
Ideal Neck Posture
Plane of neck and jaw should be different not
one continuous line
Plumb line drawn down centre of neck should be neutral or within 10 degrees of forward inclination
Plumb line from ear lobe should fall just in front of clavicle
Look for creases and assymmetries
Слайд 26
Common Posture types
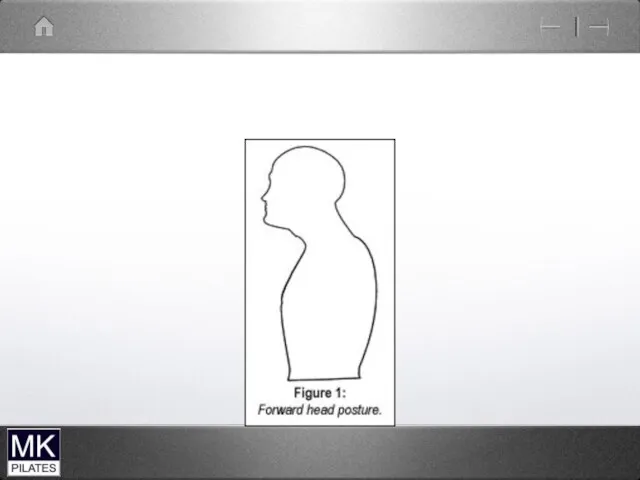
Chin Poke ( upper cervical spine)
Forward head ( lower
cervical spine)
Forward head with chin poke
Can also get a hinge or mid cervical collapse
Слайд 27
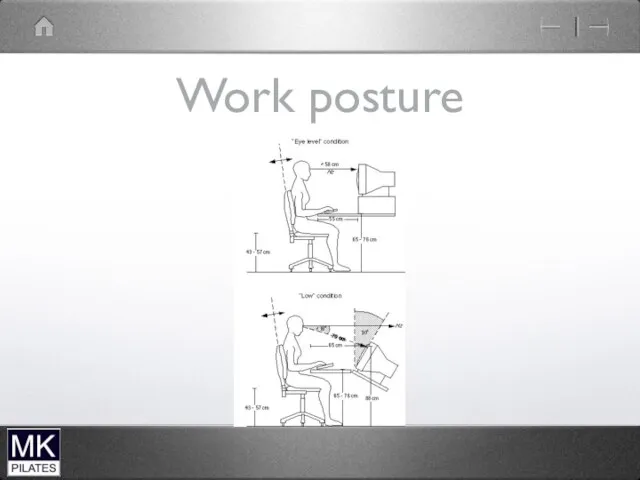
Слайд 28
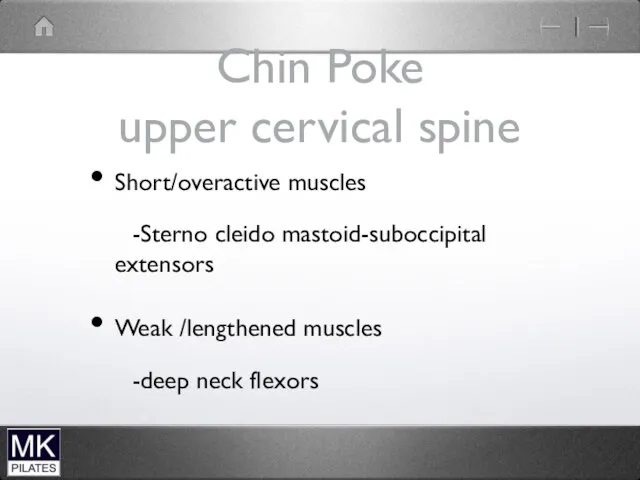
Chin Poke
upper cervical spine
Short/overactive muscles
-Sterno cleido mastoid-suboccipital extensors
Weak /lengthened muscles
-deep neck
flexors
Слайд 29

Слайд 30
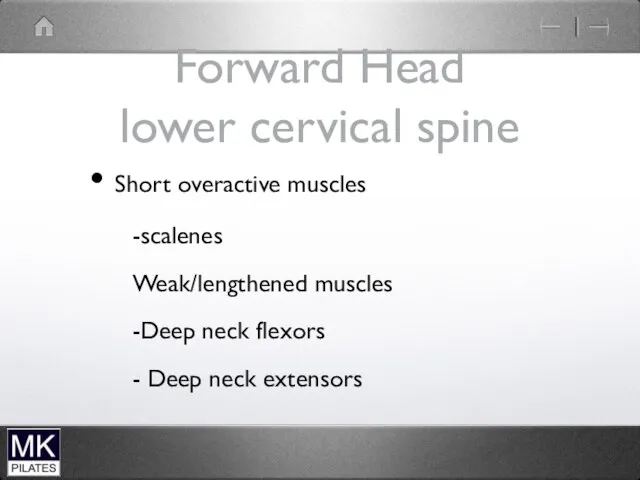
Forward Head
lower cervical spine
Short overactive muscles
-scalenes
Weak/lengthened muscles
-Deep neck flexors
- Deep neck
extensors
Слайд 31
Слайд 32
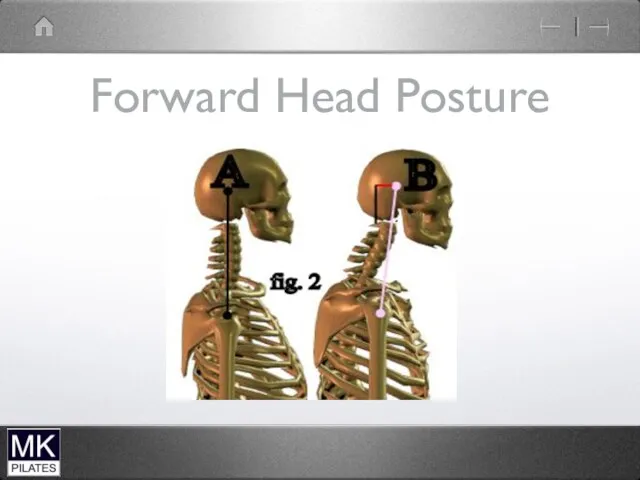
Слайд 33

Слайд 34

Слайд 35

Make best use of office space
Слайд 36

Occupational therapy for patients can be used creatively to ease the
A&C shortages
Слайд 37
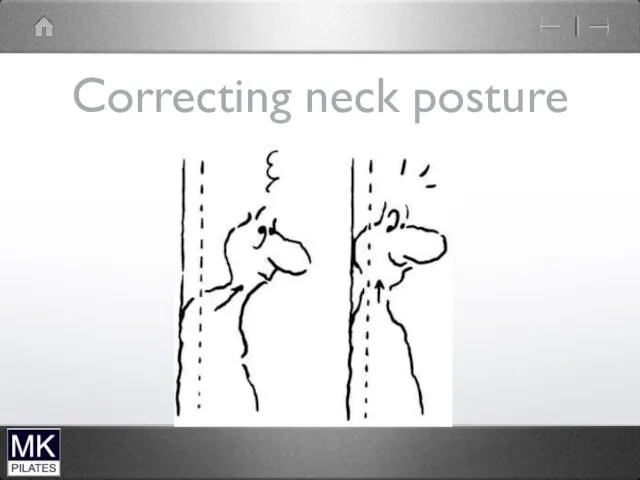
Слайд 38
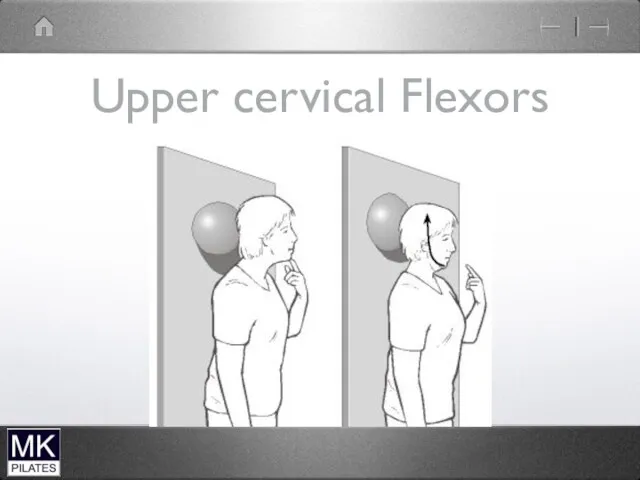
Слайд 39

Слайд 40
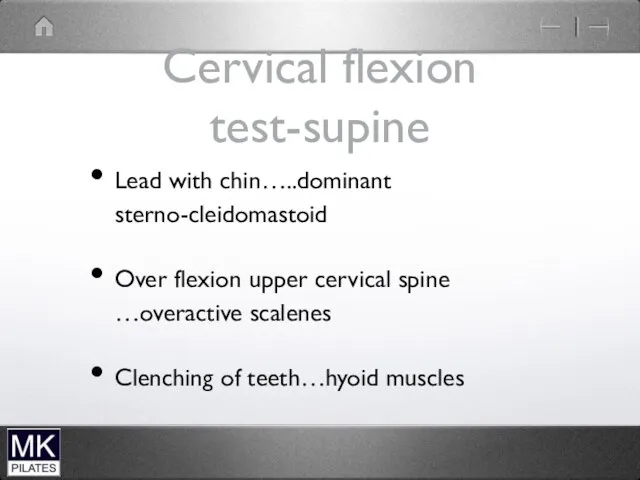
Cervical flexion test-supine
Lead with chin…..dominant sterno-cleidomastoid
Over flexion upper cervical spine …overactive
scalenes
Clenching of teeth…hyoid muscles
Слайд 41

Слайд 42

Слайд 43

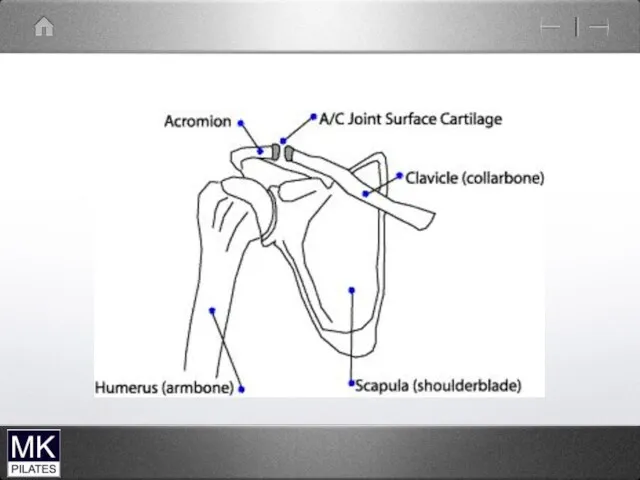
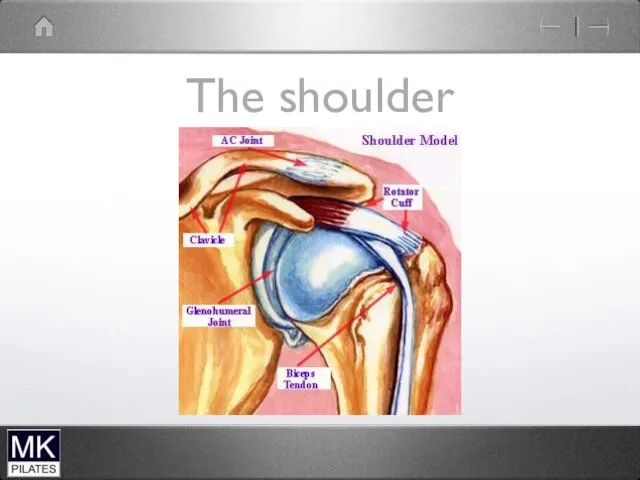
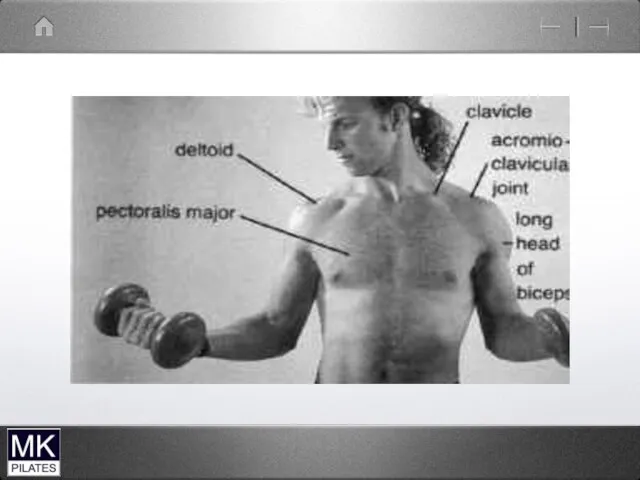
4 joints
The glenohumeral joint
The acromioclavicular joint
The Sternoclavicular joint
The Scapulothoracic articulation
Слайд 44
Слайд 45
Слайд 46
Слайд 47

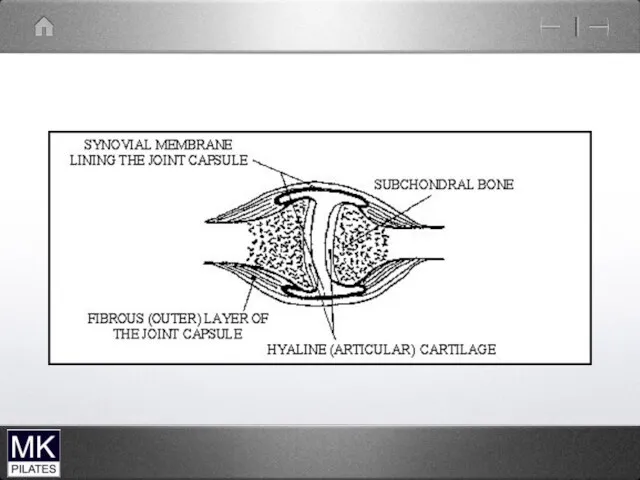
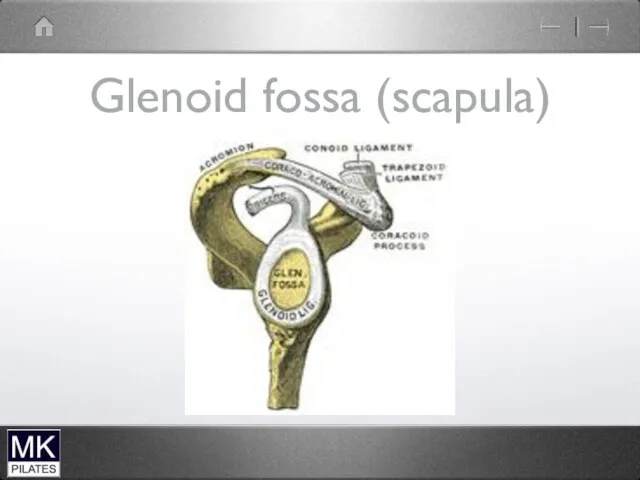
The glenohumeral joint
Ball and socket synovial joint
Large humeral head
Small glenoid fossa
Stability
sacrificed for mobility
Слайд 48
Слайд 49
Слайд 50
Слайд 51

Gleno-humeral movement
Flexion
Extension
Internal (medial) Rotation
External (lateral) Rotation
Abduction
Adduction
Слайд 52

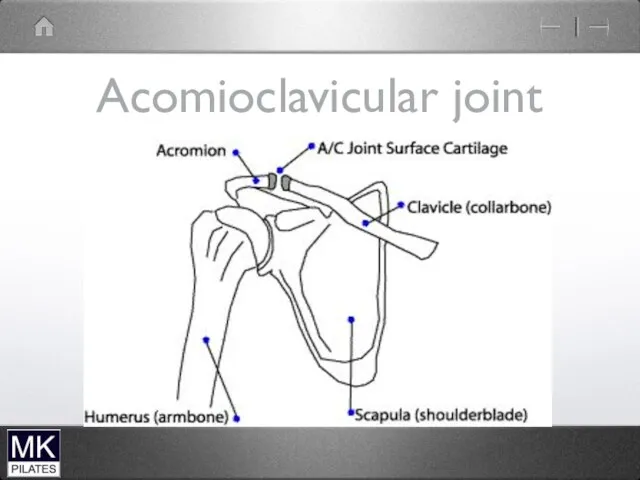
The Acromioclavicular joint
Small plane joint
The lateral end of the clavicle and
the acromion process of the scapula
Joins the scapula to the clavicle
Small gliding movements through shoulder elevation
Rotation of scapular around clavicle
Слайд 53
Слайд 54

Acromioclavicular joint sprain
Fall onto point of shoulder.
Sprain or disruption of the
acromio-clavicular ligaments
Grade 1 to 3
Step deformity with grade 3
Слайд 55

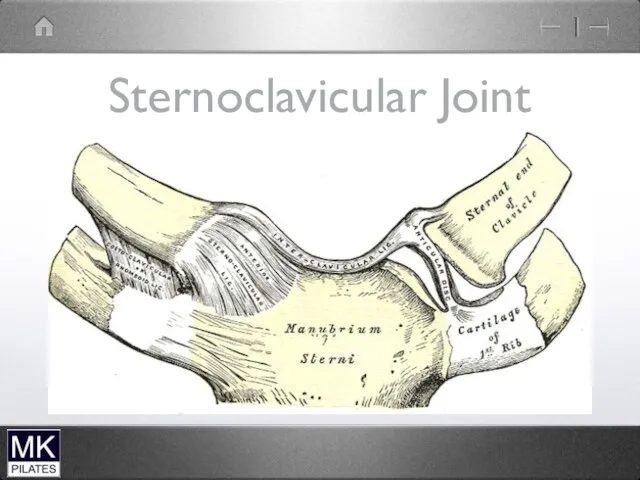
The Sternoclavicular joint
Small fibrous plane joint
Between the medial end of the
clavicle and the sternum
This attaches the shoulder complex to the trunk
Gliding Movements and rotation of the clavicle on the sternum
Allows end range elevation
Слайд 56
Слайд 57

The Scapulothoracic articulation
Not a true synovial joint
Allows the scapula to glide
around the thoracic wall
Keeps the glenoid in contact with the humerus
Supported only by muscles
Слайд 58

Слайд 59
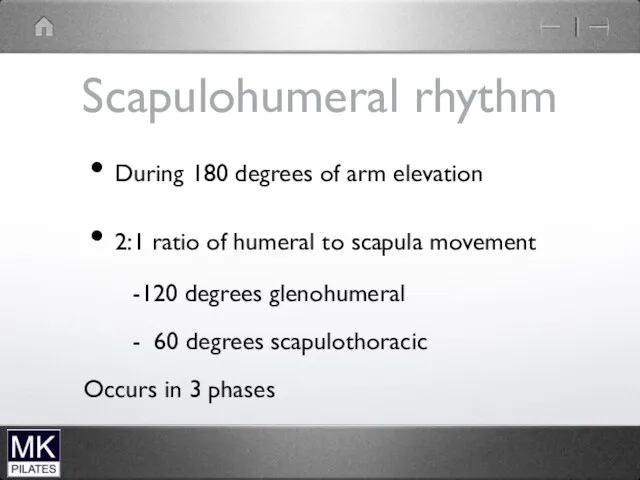
Scapulohumeral rhythm
During 180 degrees of arm elevation
2:1 ratio of humeral to
scapula movement
-120 degrees glenohumeral
- 60 degrees scapulothoracic
Occurs in 3 phases
Слайд 60
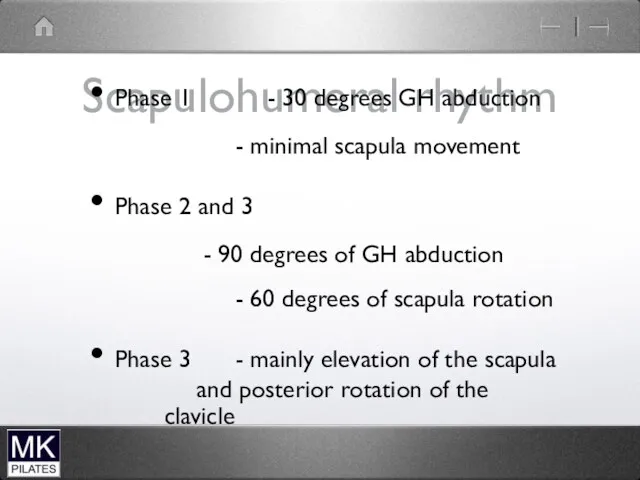
Scapulohumeral rhythm
Phase 1 - 30 degrees GH abduction
- minimal scapula
movement
Phase 2 and 3
- 90 degrees of GH abduction
- 60 degrees of scapula rotation
Phase 3 - mainly elevation of the scapula and posterior rotation of the clavicle
Слайд 61
Слайд 62

Слайд 63
Слайд 64

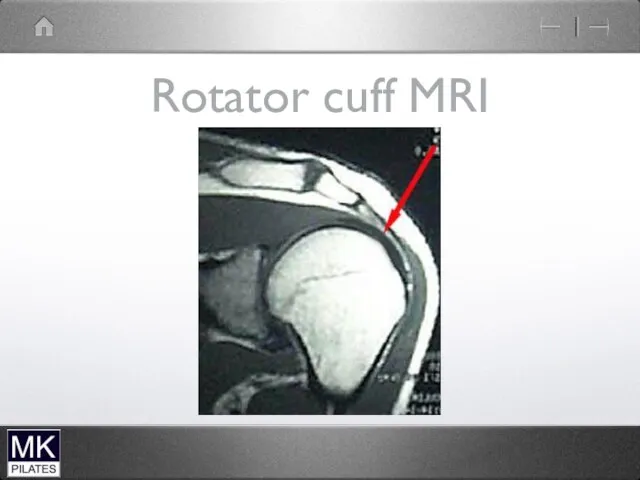
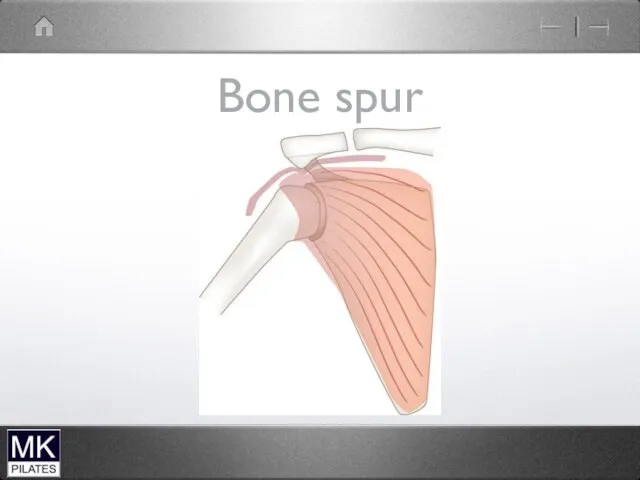
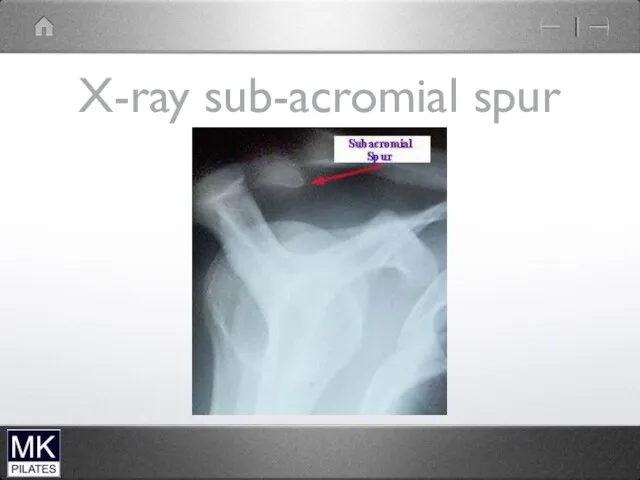
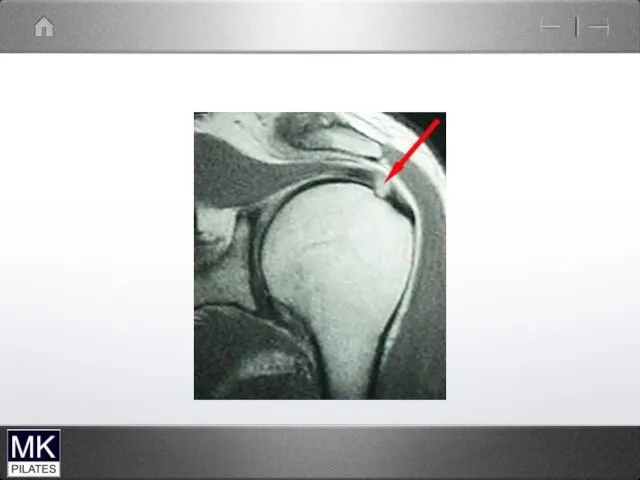
Impingement Syndrome
Structures between the humerus and the acromion can become compressed
and pinched during elevation of the arm. The space is at its narrowest between 70 and 120 degrees.
Supraspinatus tendon
Long head of biceps
Sub-acromial bursa
Слайд 65

Слайд 66

Biomechanical risk factors
Internal rotation of the shoulder during elevation
Secondary impingement due
to reversed scapulohumeral rhythm
Short 2 joint muscles
Слайд 67
Слайд 68
Слайд 69
Слайд 70
Слайд 71

Glenohumeral Instability
Excessive translation of the large humeral head on the relatively
small glenoid due to
- Damaged ligaments
- Poor muscle control
Unidirectional (anterior or posterior)
Multidirectional (global)
Instability tests
Need to improve dynamic control
Слайд 72
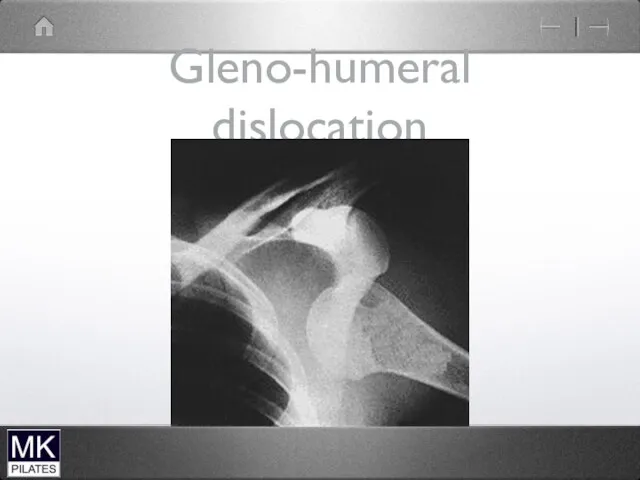
Gleno-humeral dislocation
Слайд 73

Frozen Shoulder
Frozen shoulder is characterised by progressive pain and stiffness in
the glenohumeral joint
Can be idiopathic or following injury
3 stages all lasting about 6 months
Слайд 74

Frozen Shoulder stages
Stage 1 Progressive and severe pain. Little stiffness
Stage 11
Plateau in pain and increasing stiffness
Stage 111 Little pain. Shoulder very stiff
Слайд 75
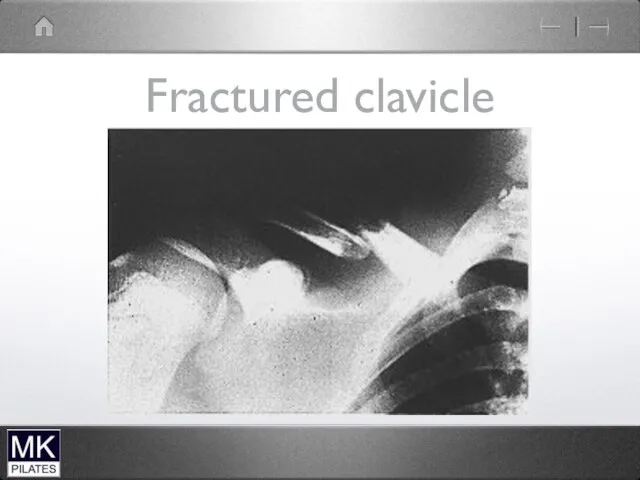
Слайд 76
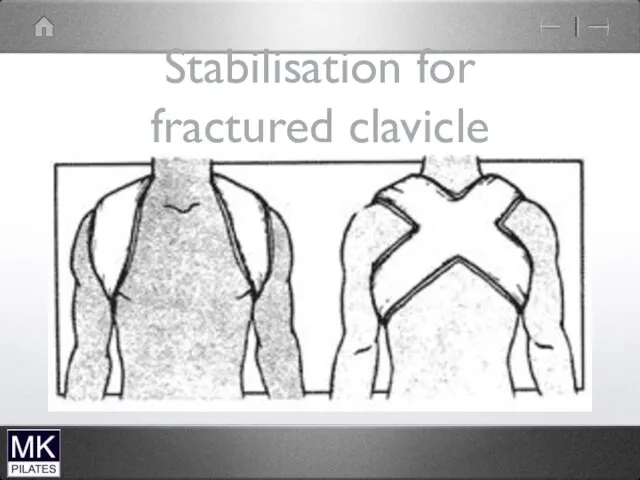
Stabilisation for fractured clavicle
Слайд 77
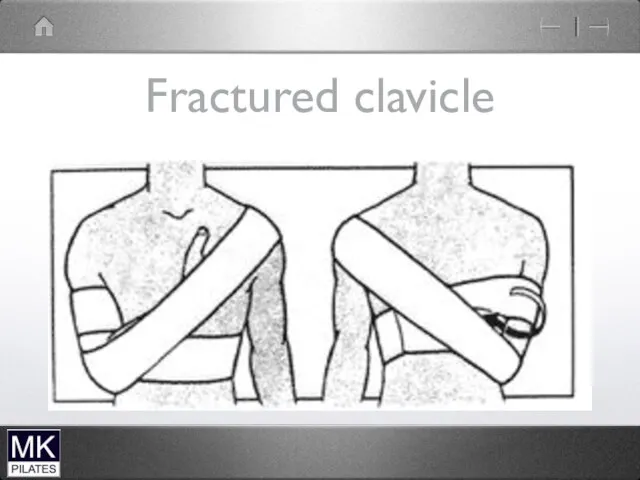
Слайд 78

Слайд 79

Shoulder muscle stability
Слайд 80

Role of The Scapula
Provides base for muscle attachment
Allows the glenoid to
upwardly rotate therefore allowing a greater range of shoulder movement
Elevation/depression
Abduction/adduction
Upward and downward rotation
Слайд 81

Trunk to Humerus
Latissimus Dorsi
Pectoralis Major
Слайд 82
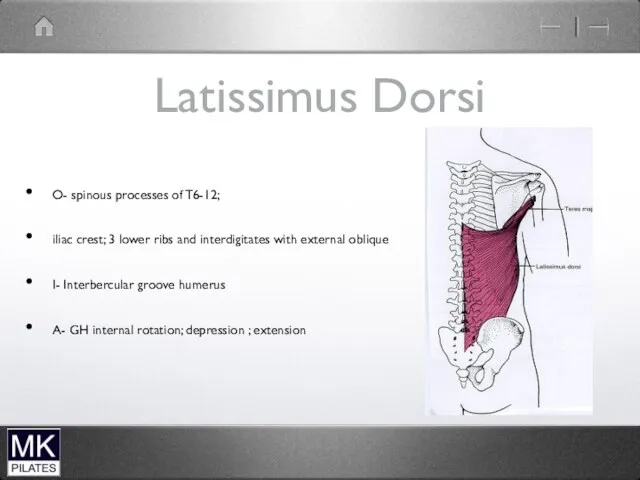
Latissimus Dorsi
O- spinous processes of T6-12;
iliac crest; 3 lower ribs
and interdigitates with external oblique
I- Interbercular groove humerus
A- GH internal rotation; depression ; extension
Слайд 83

Pectoralis Major
O- sternal end of clavicle;
strenum; external oblique;rib cartilages 2-6
I-
greater tubercle of humerus
A- Adducts the abducted arm :
internal rotation ; forward adduction across chest
Слайд 84
Слайд 85

Trunk to Shoulder Complex
Pectoralis Minor
Trapezius
Levator Scapula
Rhomboids
Serratus Anterior
Слайд 86
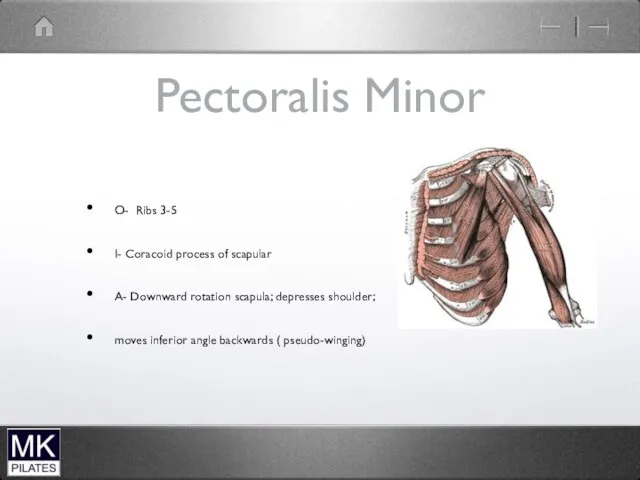
Pectoralis Minor
O- Ribs 3-5
I- Coracoid process of scapular
A- Downward rotation scapula;
depresses shoulder;
moves inferior angle backwards ( pseudo-winging)
Слайд 87
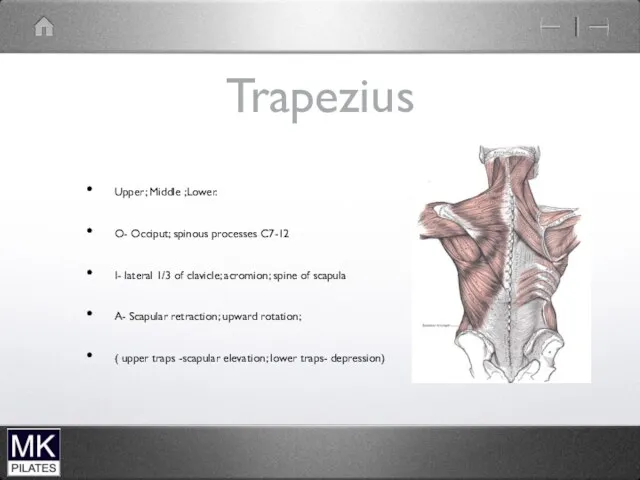
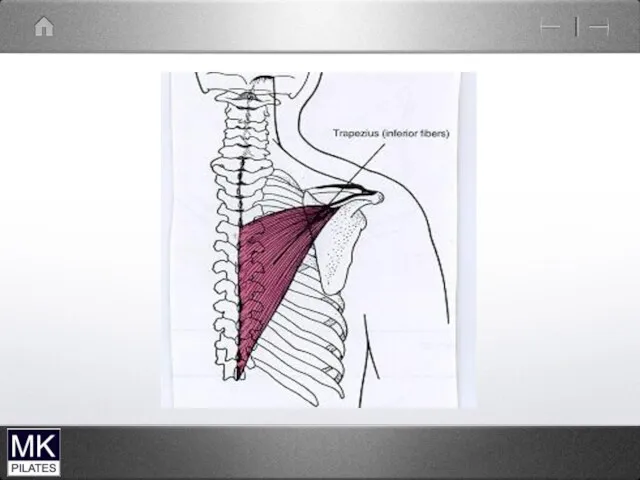
Trapezius
Upper; Middle ;Lower.
O- Occiput; spinous processes C7-12
I- lateral 1/3 of clavicle;
acromion; spine of scapula
A- Scapular retraction; upward rotation;
( upper traps -scapular elevation; lower traps- depression)
Слайд 88
Слайд 89

Слайд 90
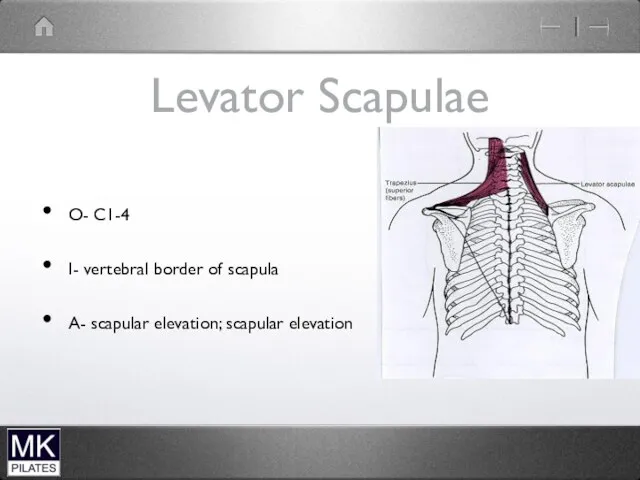
Levator Scapulae
O- C1-4
I- vertebral border of scapula
A- scapular elevation; scapular
elevation
Слайд 91
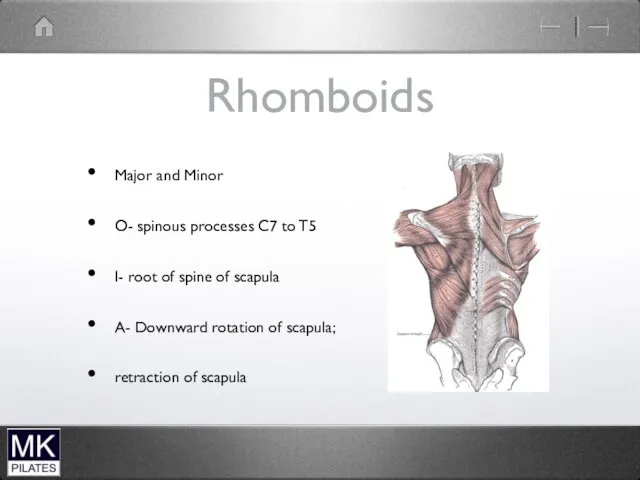
Rhomboids
Major and Minor
O- spinous processes C7 to T5
I- root of
spine of scapula
A- Downward rotation of scapula;
retraction of scapula
Слайд 92
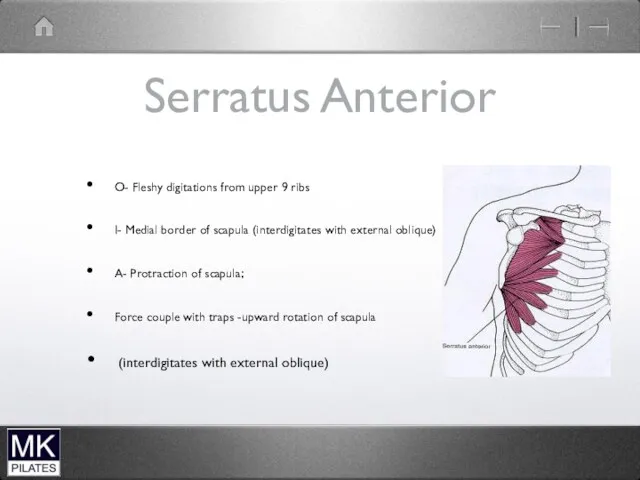
Serratus Anterior
O- Fleshy digitations from upper 9 ribs
I- Medial border of
scapula (interdigitates with external oblique)
A- Protraction of scapula;
Force couple with traps -upward rotation of scapula
(interdigitates with external oblique)
Слайд 93
Scapula to Humerus
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres Minor
Subscapularis
Deltoid
Coracobrachialis
Teres Major
Biceps (long head)
Triceps(long head)
Слайд 94

Teres Major
O- post surface of inferior angle of scapular
I- lesser tubercle
of humerus
A - GH extension (particularly from a raised position)
internal rotation
Слайд 95
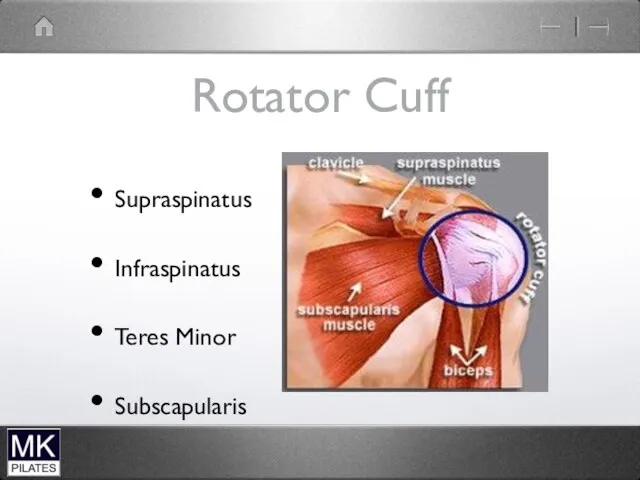
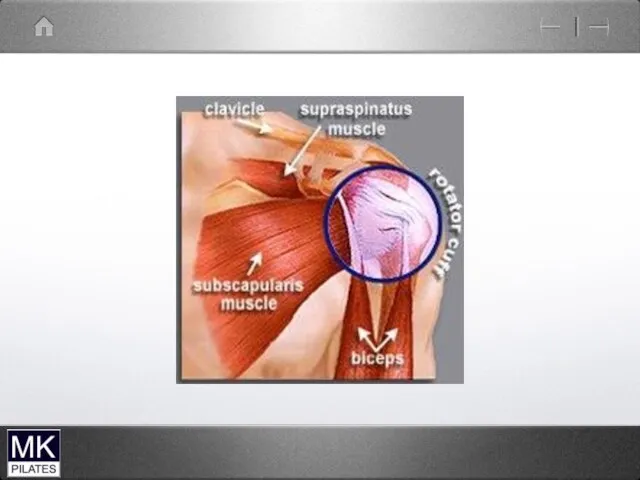
Rotator Cuff
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres Minor
Subscapularis
Слайд 96

Supraspinatus
O- supraspinous fossa of scapula
I- Greater tubercle of humerus
A- GH Abduction
prevents
superior movement of humeral head
Слайд 97
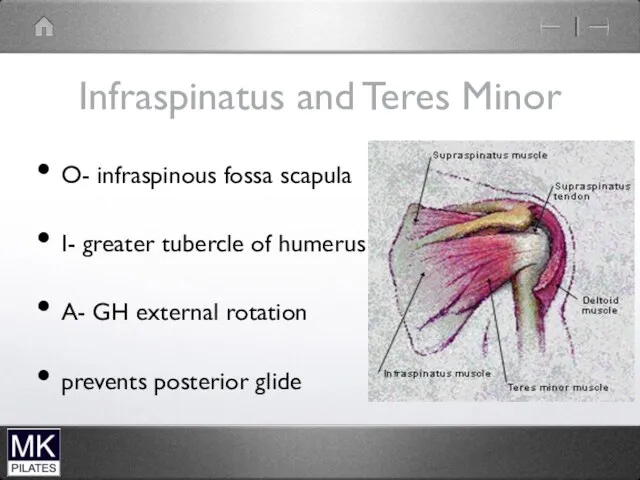
Infraspinatus and Teres Minor
O- infraspinous fossa scapula
I- greater tubercle of humerus
A-
GH external rotation
prevents posterior glide
Слайд 98
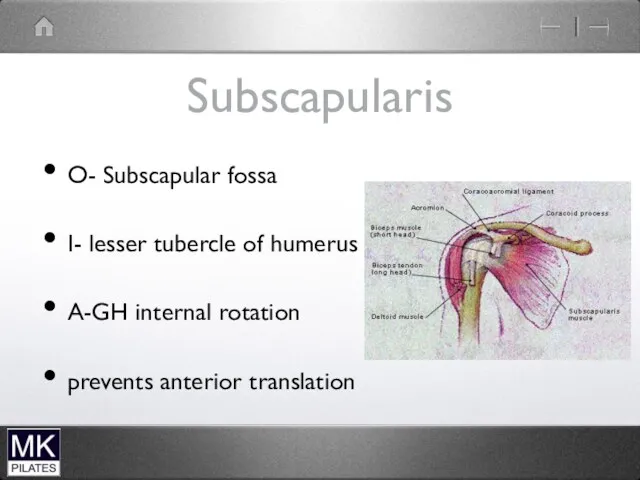
Subscapularis
O- Subscapular fossa
I- lesser tubercle of humerus
A-GH internal rotation
prevents anterior translation
Слайд 99

Слайд 100

Слайд 101
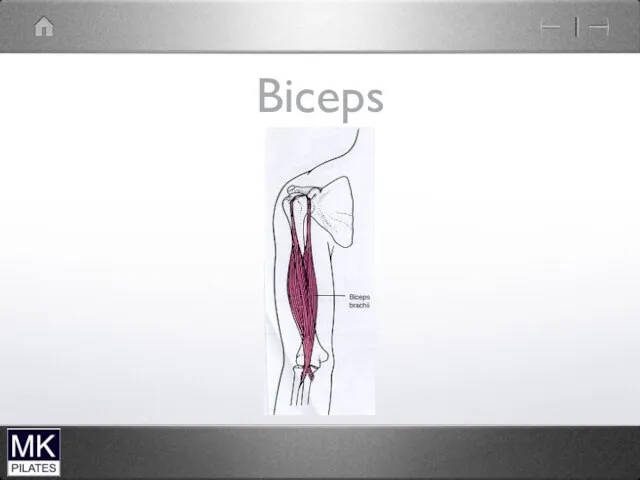
Слайд 102
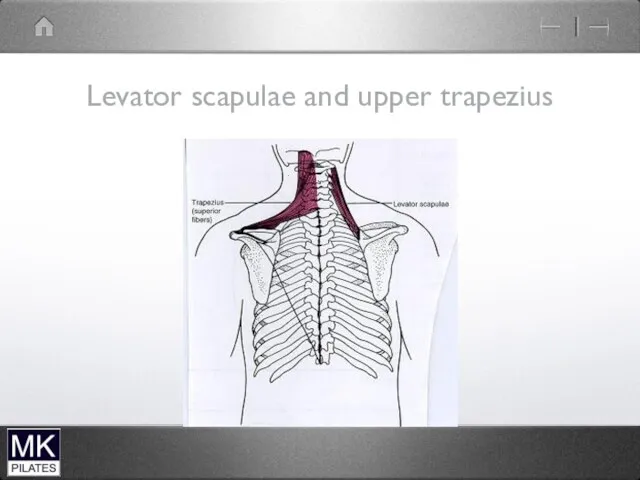
Levator scapulae and upper trapezius
Слайд 103

Scapular stabilisers
Serratus anterior
protracts the scapula
upward rotation of the glenoid
Trapezius
Upper and Middle
fibres retract and upwardly rotate
Lower fibres upward rotation of glenoid and counterbalance lateral pull of serratus anterior
Слайд 104

Scapula Mobility Muscles
Levator Scapulae -scapula elevation
-glenoid downward rotation
Pectoralis minor -glenoid downward
rotation
-pseudo winging
Rhomboids -scapula elevation and retraction
-glenoid downward rotation
Слайд 105

Glenohumeral Stability
Supraspinatus - abduction
- resists anterior translation
Infraspinatus and Teres Minor
- external
rotation
- resist posterior translation
Subscapularis -medial rotation -resists anterior translation
Слайд 106
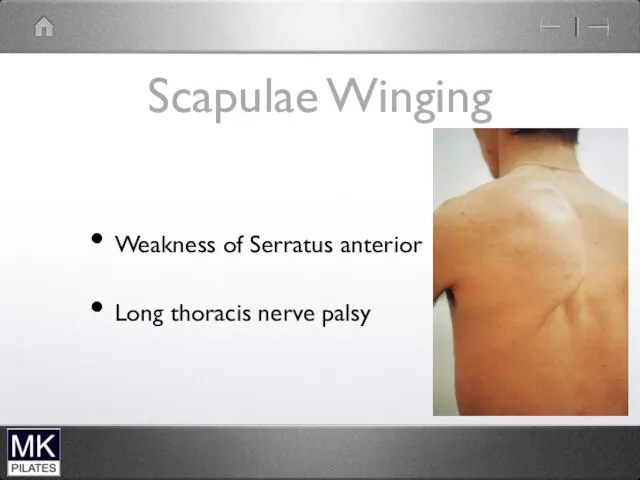
Scapulae Winging
Weakness of Serratus anterior
Long thoracis nerve palsy
Слайд 107
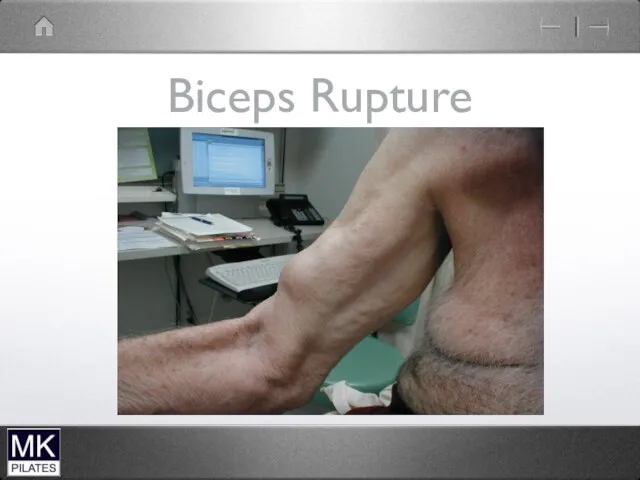
Слайд 108
Слайд 109

Слайд 110

Слайд 111

Слайд 112
Слайд 113

Слайд 114

Слайд 115

Слайд 116

The to do list gets longer



















































































































 Подходы в диагностике и лечении болезней перикарда
Подходы в диагностике и лечении болезней перикарда Умирание, смерть и трупные изменения
Умирание, смерть и трупные изменения Нейродегенеративные заболевания
Нейродегенеративные заболевания Жүйке жүйесі
Жүйке жүйесі Патофизиология обмена веществ
Патофизиология обмена веществ Жаңа туған нәрестенің физиологиясы және патологиясы
Жаңа туған нәрестенің физиологиясы және патологиясы Лечение в санаториях Белокурихи
Лечение в санаториях Белокурихи Диспансеризация и диспансерное наблюдение
Диспансеризация и диспансерное наблюдение Отходы медицинских учреждений
Отходы медицинских учреждений Вирусные инфекции кожи и слизистых оболочек
Вирусные инфекции кожи и слизистых оболочек Инфекционная безопасность пациентов ОРИТ
Инфекционная безопасность пациентов ОРИТ Биполярное расстройство I типа
Биполярное расстройство I типа Мировые стандарты оказания неотложной медицинской помощи
Мировые стандарты оказания неотложной медицинской помощи Асептика. Определение асептики
Асептика. Определение асептики Свойства рыбы. Рубрика Какая рыба полезнее?
Свойства рыбы. Рубрика Какая рыба полезнее? Олигофрения: классификация, профилактика, пути коррекции
Олигофрения: классификация, профилактика, пути коррекции Дәлелді медицина бойынша қоғам пікірі. Біздің елде және тмд елдеріндегі дәлелді медицина орталықтары
Дәлелді медицина бойынша қоғам пікірі. Біздің елде және тмд елдеріндегі дәлелді медицина орталықтары Дифференциальный диагноз нефротического синдрома
Дифференциальный диагноз нефротического синдрома Режимы аппаратной (механической) вентиляции лёгких
Режимы аппаратной (механической) вентиляции лёгких Генные заболевания
Генные заболевания ВИЧ-инфекция
ВИЧ-инфекция Гнозис и его расстройства
Гнозис и его расстройства Острые респираторные заболевания у детей
Острые респираторные заболевания у детей Методы исследования сердечно-сосудистой системы
Методы исследования сердечно-сосудистой системы Острая ревматическая лихорадка и тактика ведения больных с ревматическими пороками сердца
Острая ревматическая лихорадка и тактика ведения больных с ревматическими пороками сердца Эндодонтическая система K3 Endo (Kerr)
Эндодонтическая система K3 Endo (Kerr) Гнойно-воспалительные заболевания мягких тканей. Медиастинит
Гнойно-воспалительные заболевания мягких тканей. Медиастинит Қан қозғалысының гемодинамикалық заңдылықтары. Қанның реологиялық қасиеттері
Қан қозғалысының гемодинамикалық заңдылықтары. Қанның реологиялық қасиеттері