Слайд 2
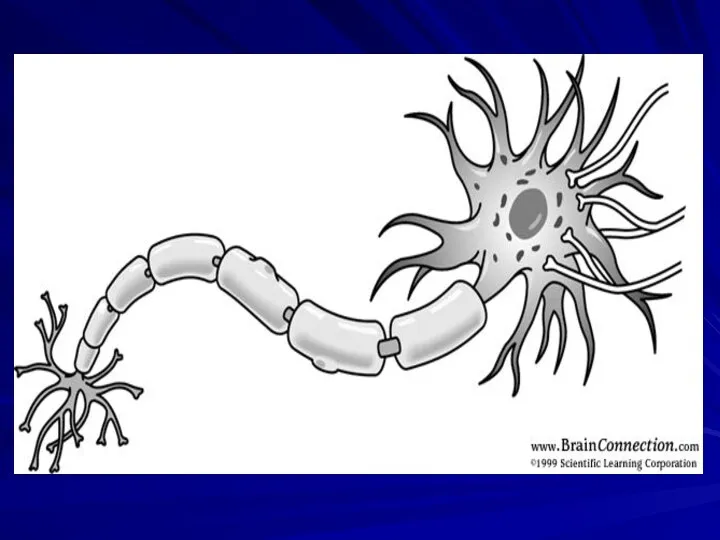
Слайд 3
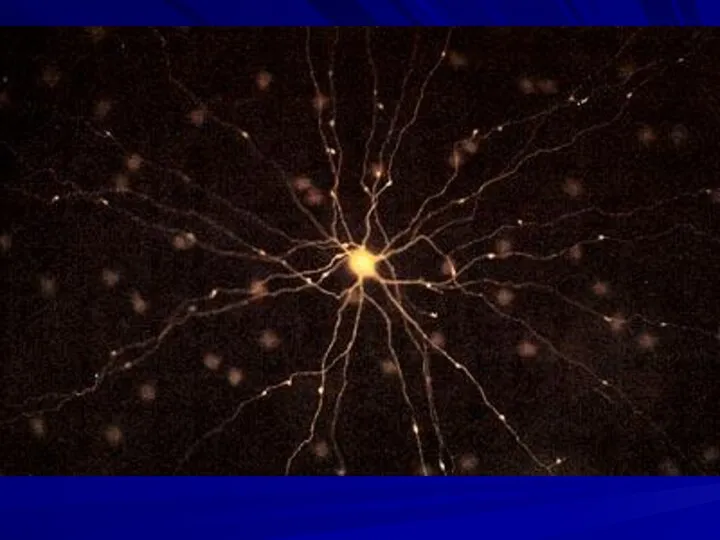
Слайд 4
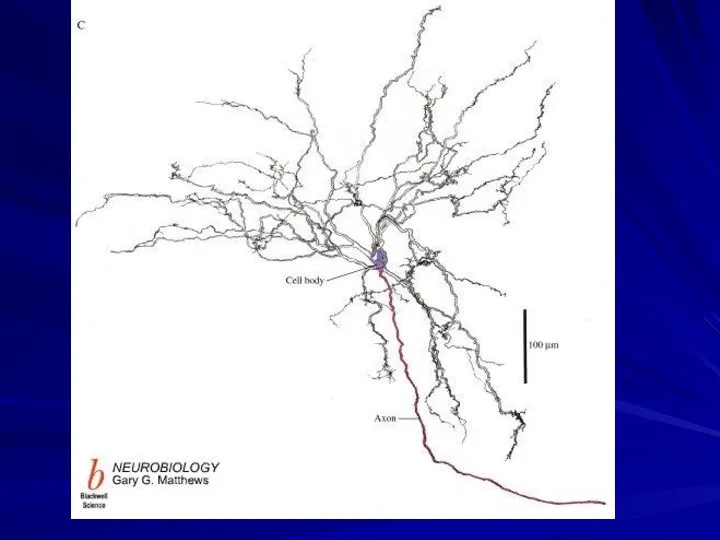
Слайд 5

Слайд 6
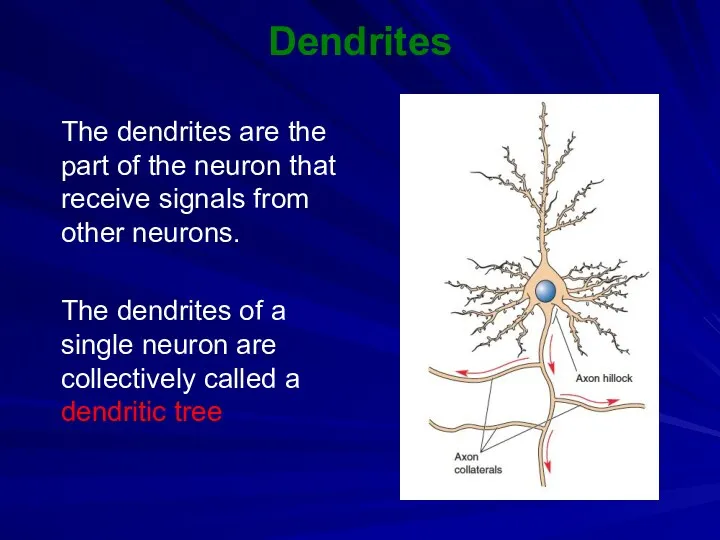
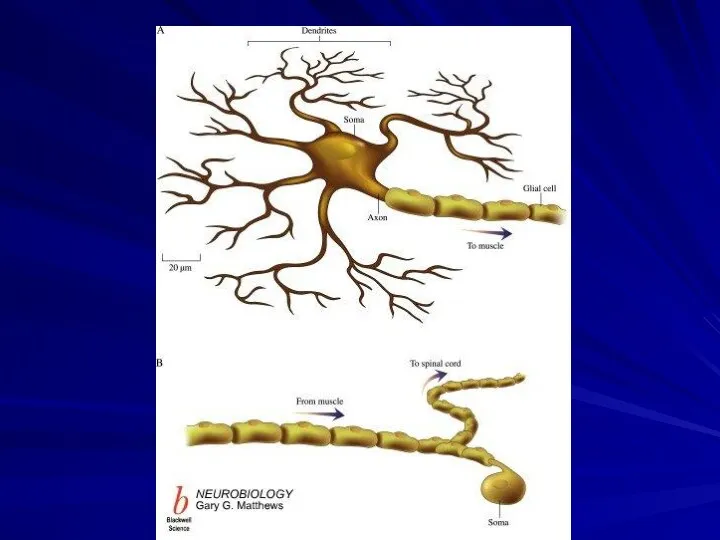
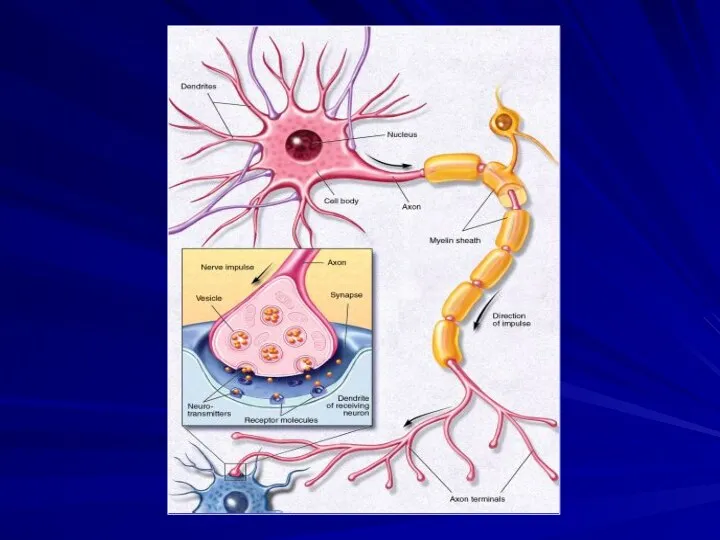
Dendrites
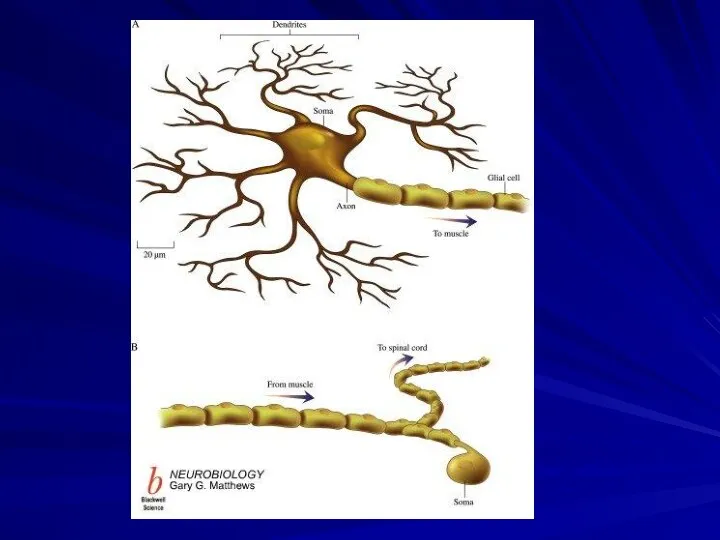
The dendrites are the part of the neuron that receive
signals from other neurons.
The dendrites of a single neuron are collectively called a dendritic tree
Слайд 7
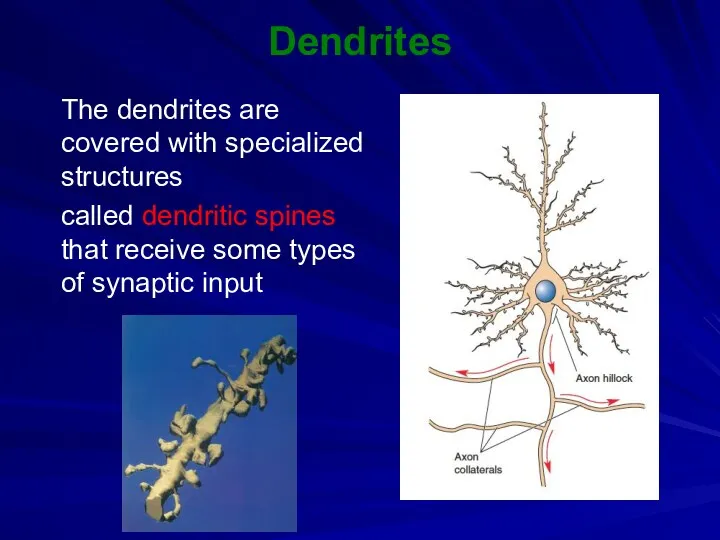
Dendrites
The dendrites are covered with specialized structures
called dendritic spines that
receive some types of synaptic input
Слайд 8
Слайд 9
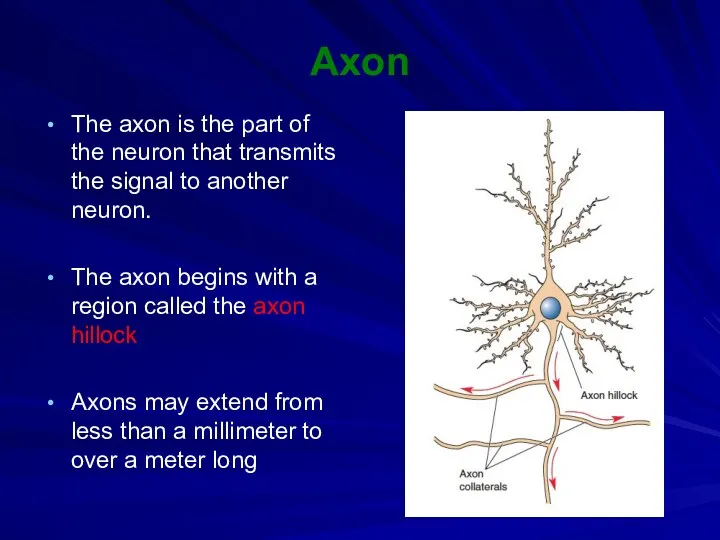
Axon
The axon is the part of the neuron that transmits
the signal to another neuron.
The axon begins with a region called the axon hillock
Axons may extend from less than a millimeter to over a meter long
Слайд 10

Axon
The end of axon is called the axon terminal
The terminal
is a site where the axon comes in contact with other neurons and passes information on to them.
Axon usually is covered by myelin sheath
Слайд 11
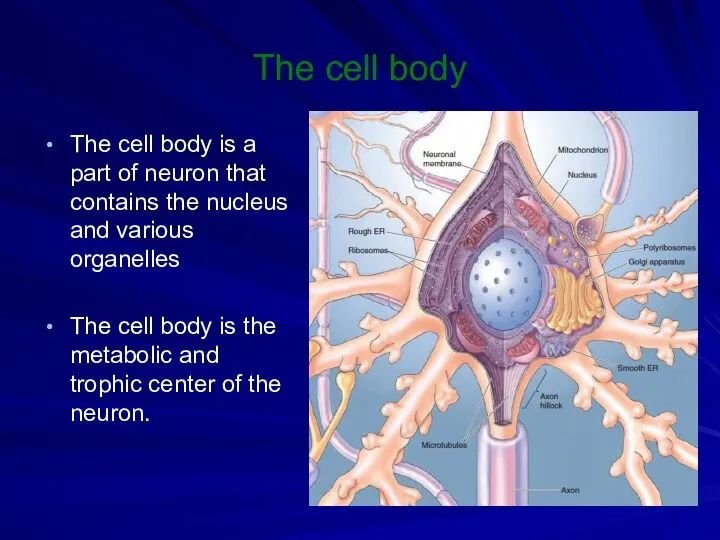
The cell body
The cell body is a part of neuron
that contains the nucleus and various organelles
The cell body is the metabolic and trophic center of the neuron.
Слайд 12
Слайд 13
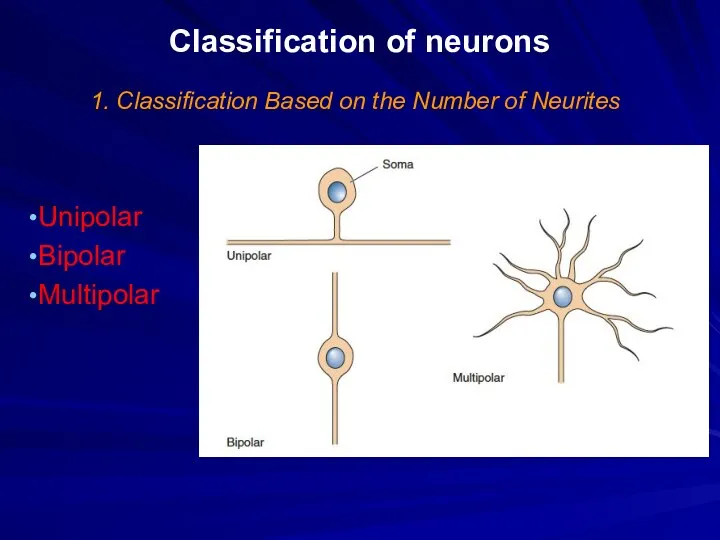
Classification of neurons
1. Classification Based on the Number of Neurites
Unipolar
Bipolar
Multipolar
Слайд 14
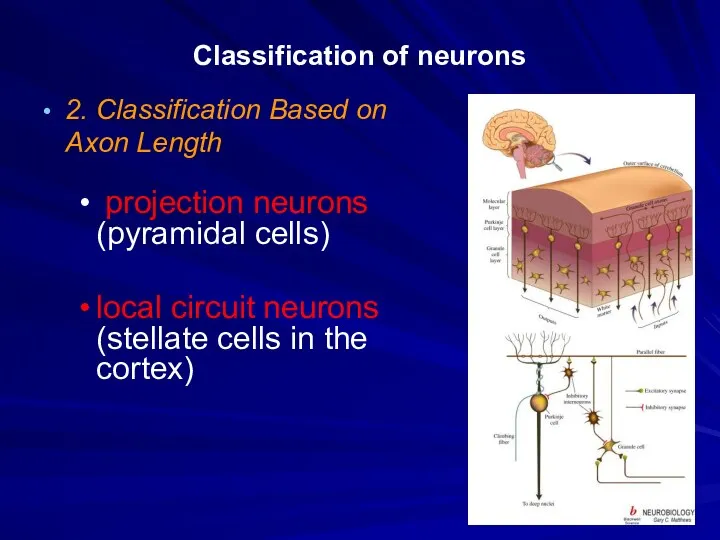
Classification of neurons
2. Classification Based on Axon Length
projection neurons (pyramidal
cells)
local circuit neurons (stellate cells in the cortex)
Слайд 15
Слайд 16
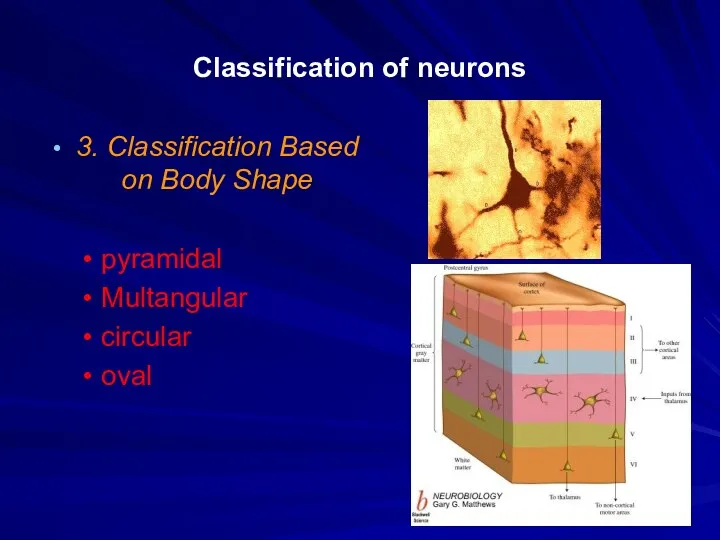
Classification of neurons
3. Classification Based on Body Shape
pyramidal
Multangular
circular
oval
Слайд 17
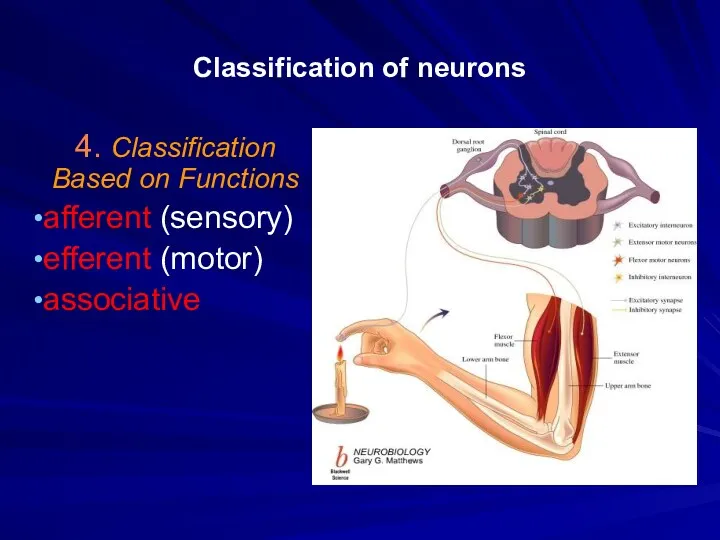
Classification of neurons
4. Classification Based on Functions
afferent (sensory)
efferent (motor)
associative
Слайд 18
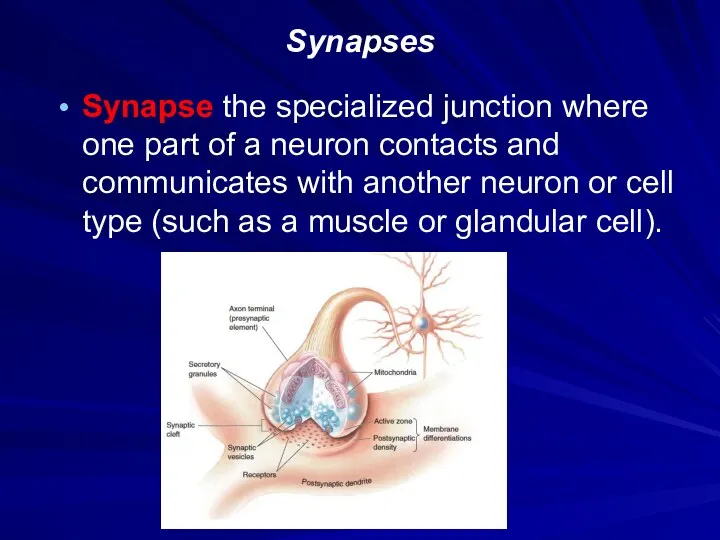
Synapses
Synapse the specialized junction where one part of a neuron contacts
and communicates with another neuron or cell type (such as a muscle or glandular cell).
Слайд 19
Слайд 20
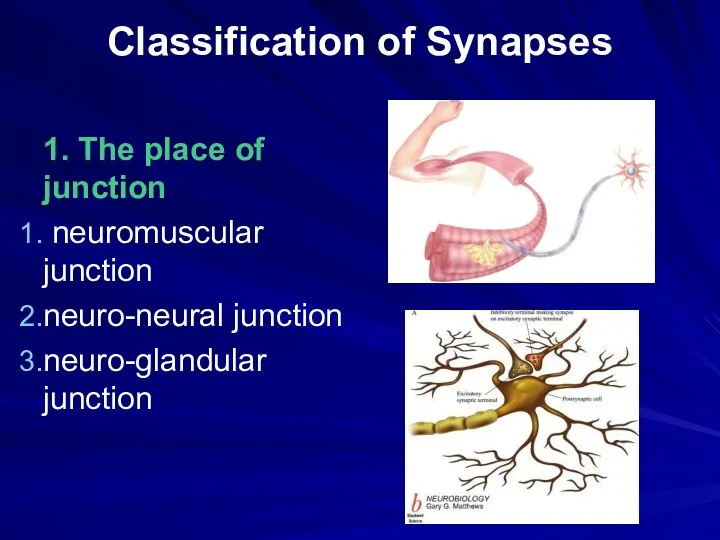
Classification of Synapses
1. The place of junction
neuromuscular junction
neuro-neural junction
neuro-glandular junction
Слайд 21
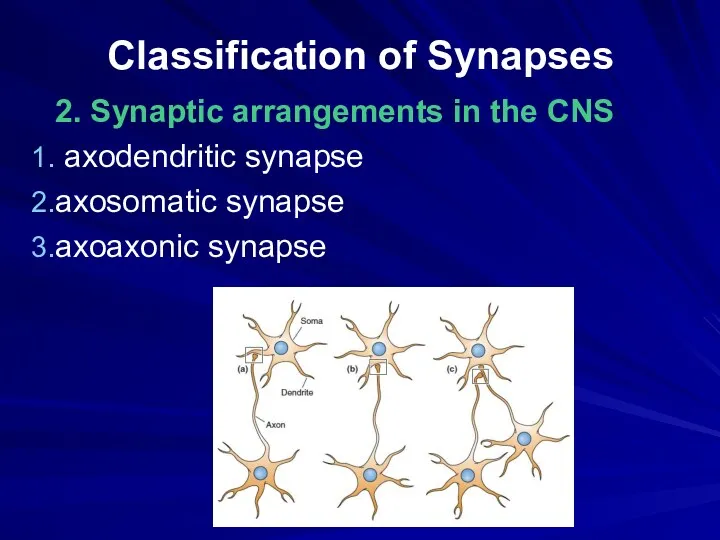
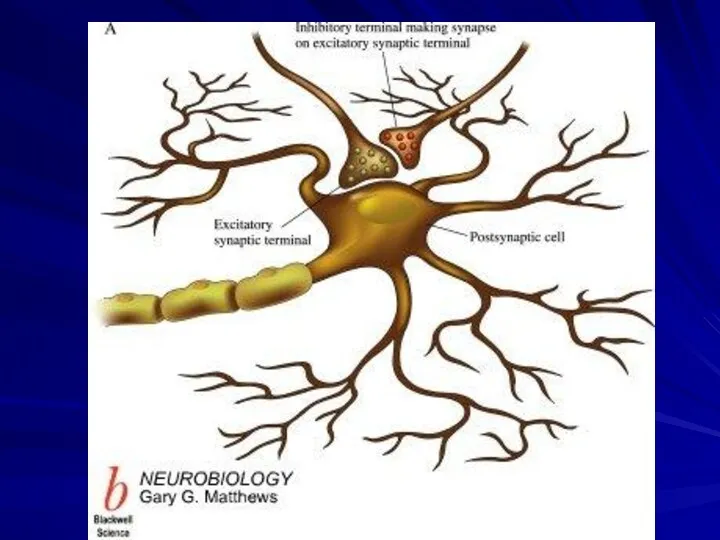
Classification of Synapses
2. Synaptic arrangements in the CNS
axodendritic synapse
axosomatic synapse
axoaxonic
synapse
Слайд 22
Слайд 23
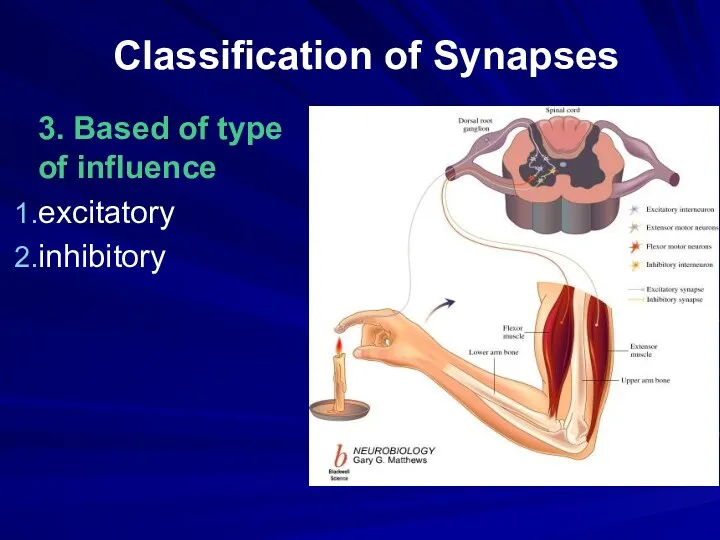
Classification of Synapses
3. Based of type of influence
excitatory
inhibitory
Слайд 24
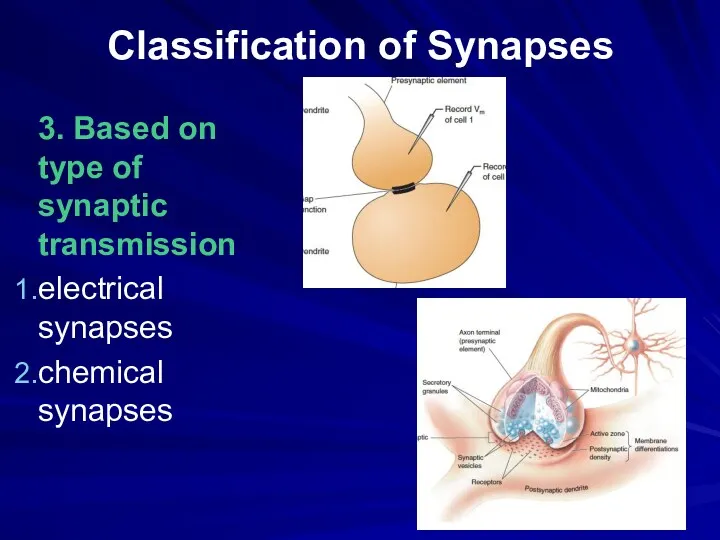
Classification of Synapses
3. Based on type of synaptic transmission
electrical synapses
chemical synapses
Слайд 25
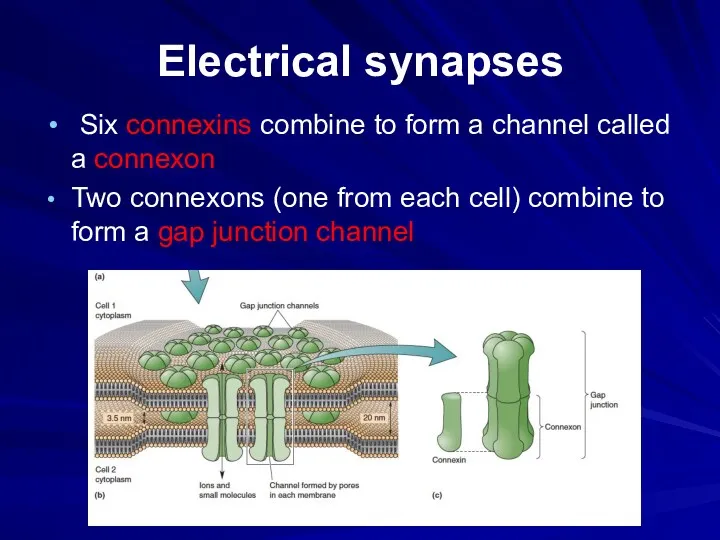
Electrical synapses
Six connexins combine to form a channel called a
connexon
Two connexons (one from each cell) combine to form a gap junction channel
Слайд 26
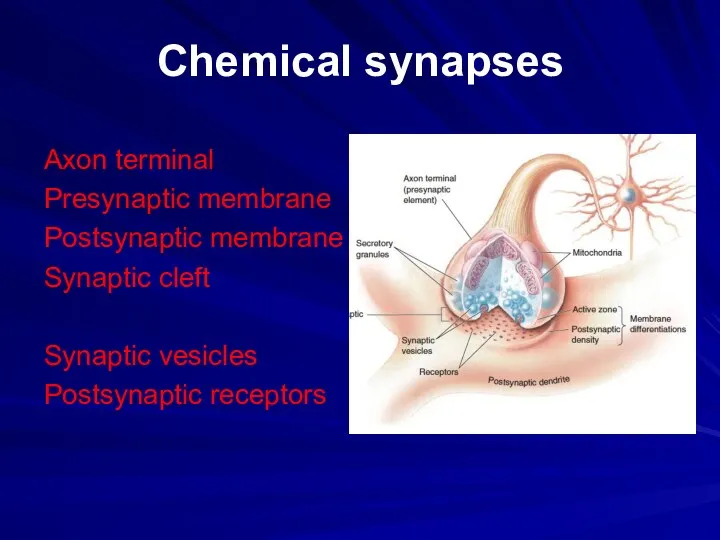
Chemical synapses
Axon terminal
Presynaptic membrane
Postsynaptic membrane
Synaptic cleft
Synaptic vesicles
Postsynaptic receptors
Слайд 27
Слайд 28
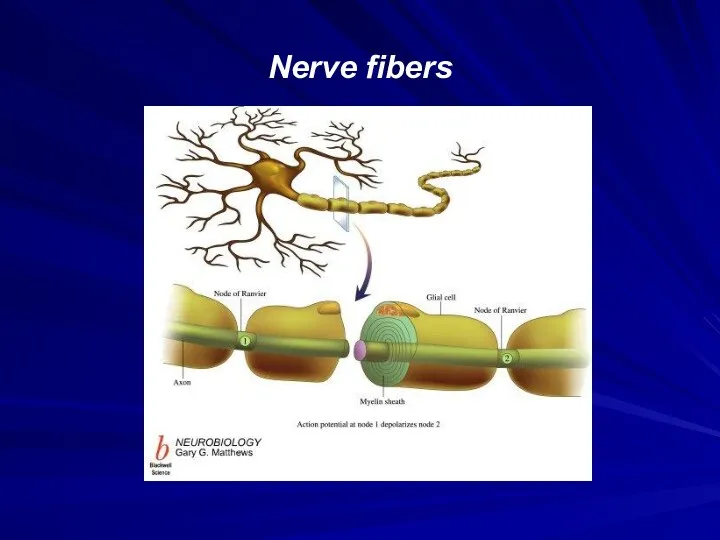
Слайд 29
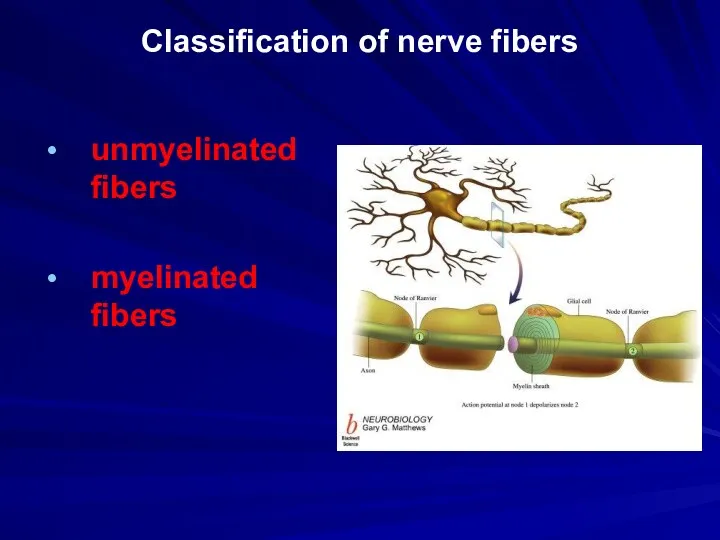
Classification of nerve fibers
unmyelinated fibers
myelinated fibers
Слайд 30
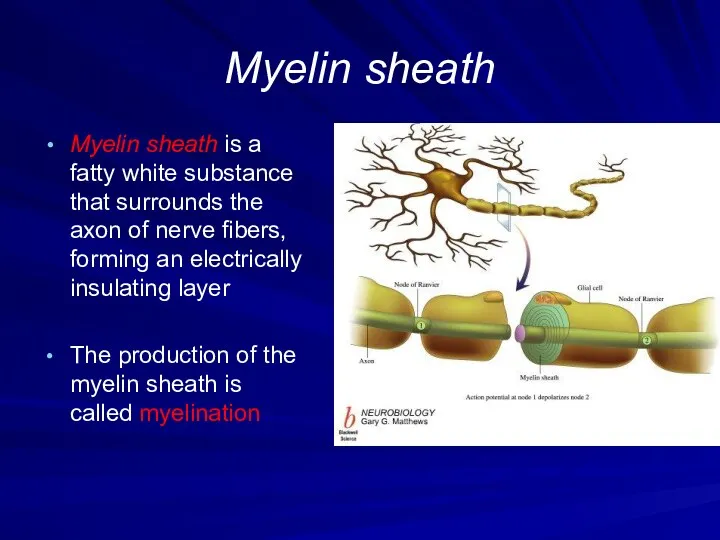
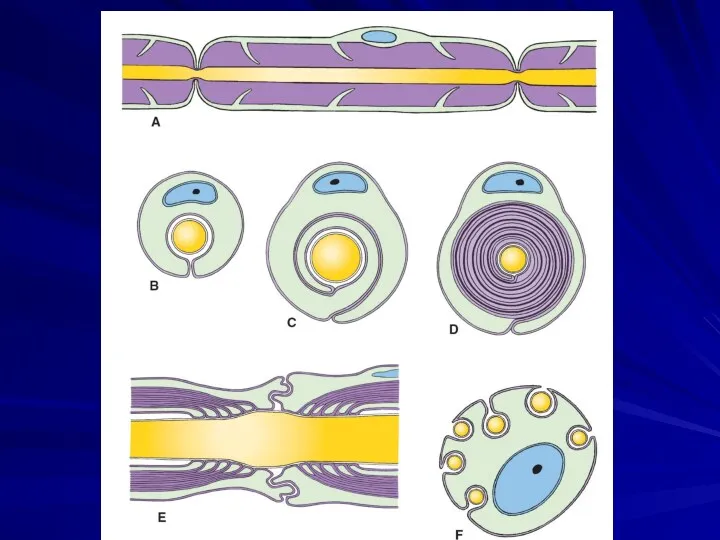
Myelin sheath
Myelin sheath is a fatty white substance that surrounds the
axon of nerve fibers, forming an electrically insulating layer
The production of the myelin sheath is called myelination
Слайд 31
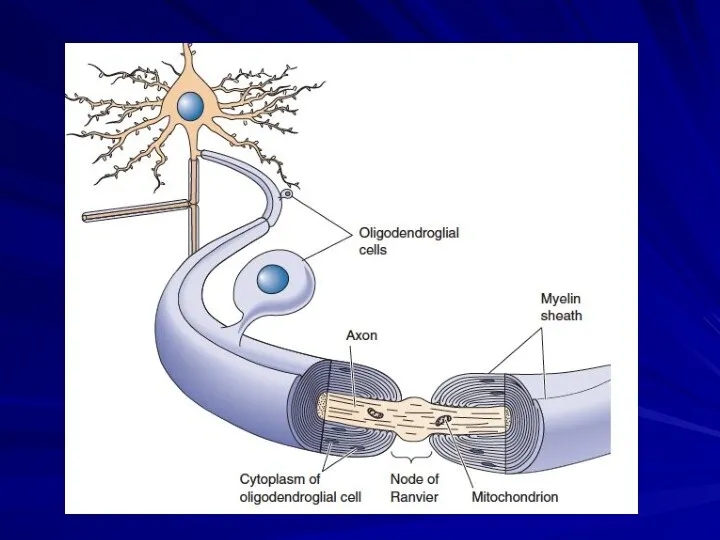
Слайд 32
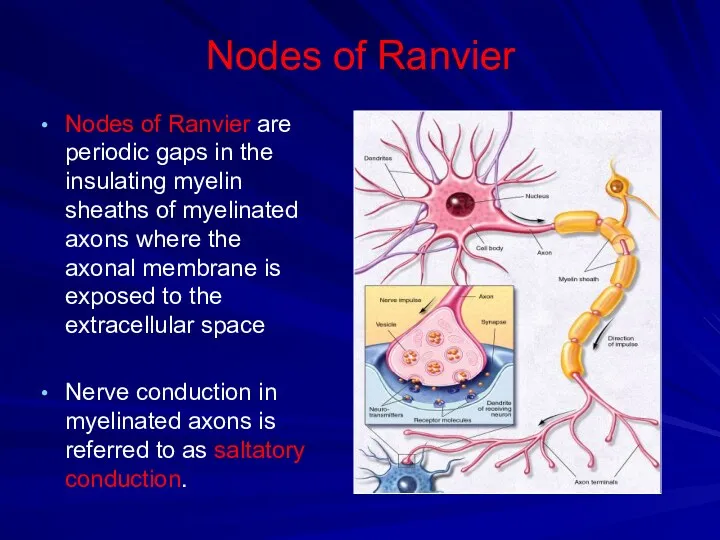
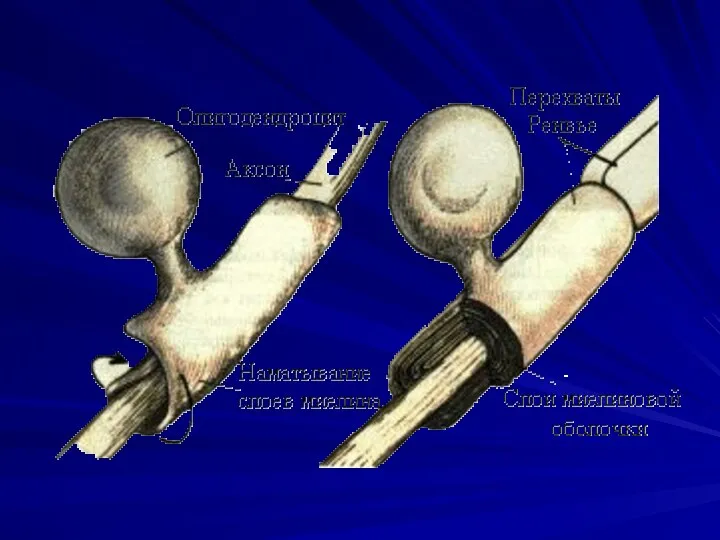
Nodes of Ranvier
Nodes of Ranvier are periodic gaps in the insulating
myelin sheaths of myelinated axons where the axonal membrane is exposed to the extracellular space
Nerve conduction in myelinated axons is referred to as saltatory conduction.
Слайд 33
Слайд 34
Слайд 35

Glial cells
Glial cells (neuroglia or glia) are non-neuronal cells that maintain
homeostasis, form myelin, and provide support and protection for neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems
Слайд 36
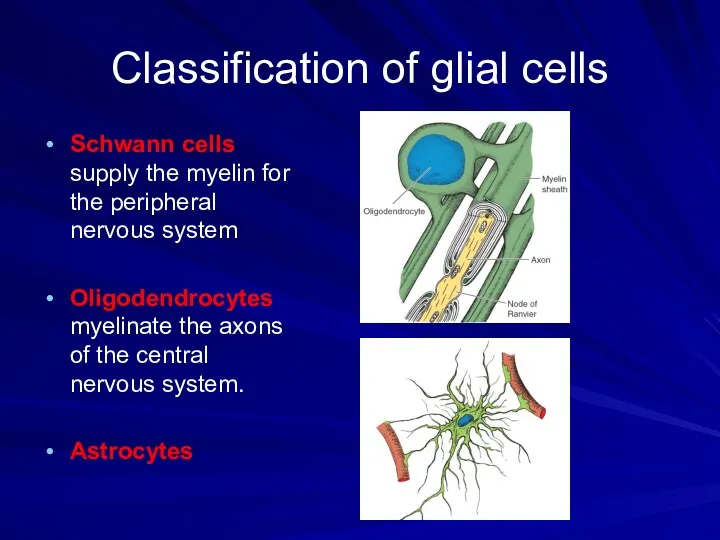
Classification of glial cells
Schwann cells supply the myelin for the peripheral
nervous system
Oligodendrocytes myelinate the axons of the central nervous system.
Astrocytes



































 Способы словообразования. Частотные отрезки, наиболее часто употребляемые в названиях медицинских терминов
Способы словообразования. Частотные отрезки, наиболее часто употребляемые в названиях медицинских терминов Общественное здоровье. (Лекция 1.1)
Общественное здоровье. (Лекция 1.1) Конъюнктивиты
Конъюнктивиты ВБИ
ВБИ Денсаулық сақтау ұйымында сапа менеджмент жүйесі
Денсаулық сақтау ұйымында сапа менеджмент жүйесі Тромботический синдром
Тромботический синдром Теория рационального питания. Гигиенические требования к рациональному питанию человека
Теория рационального питания. Гигиенические требования к рациональному питанию человека Нейропатическая боль. Определение
Нейропатическая боль. Определение Моральні та правові аспекти лікарської таємниці
Моральні та правові аспекти лікарської таємниці Тамақтанудың ауыр бұзылысы
Тамақтанудың ауыр бұзылысы Өзгергіштік
Өзгергіштік Мужское бесплодие
Мужское бесплодие Патофизиология внешнего дыхания
Патофизиология внешнего дыхания Принципы клинической эпидемиологии
Принципы клинической эпидемиологии Роль труда, спорта, социальных и биологических факторов на строение костей
Роль труда, спорта, социальных и биологических факторов на строение костей Синдром слабости синусового узла
Синдром слабости синусового узла Радиоактивті индикаторларды халық шаруашылығының әртүрлі салаларында қолданылуы
Радиоактивті индикаторларды халық шаруашылығының әртүрлі салаларында қолданылуы Формы клинического течения инсульта
Формы клинического течения инсульта Blood vessels pathology. (Subject 14)
Blood vessels pathology. (Subject 14) Бронхиты. Бронхиальная астма. Эмфизема
Бронхиты. Бронхиальная астма. Эмфизема Нарушения пигментации кожи (дисхромии)
Нарушения пигментации кожи (дисхромии) Использование эндоскопических методов исследования в акушерстве и гинекологии
Использование эндоскопических методов исследования в акушерстве и гинекологии Болезни дыхательной системы и их предупреждение
Болезни дыхательной системы и их предупреждение Острый панкреатит и его лечение
Острый панкреатит и его лечение Участие медицинской сестры в инструментальных методах исследования
Участие медицинской сестры в инструментальных методах исследования Бір бөлімді және көп бөлімді қарындардың қимылы.Асқорыту ерекшеліктерінің реттелуі
Бір бөлімді және көп бөлімді қарындардың қимылы.Асқорыту ерекшеліктерінің реттелуі Основы токсикологии. (Лекция 1)
Основы токсикологии. (Лекция 1) Окислительный стресс
Окислительный стресс