Содержание
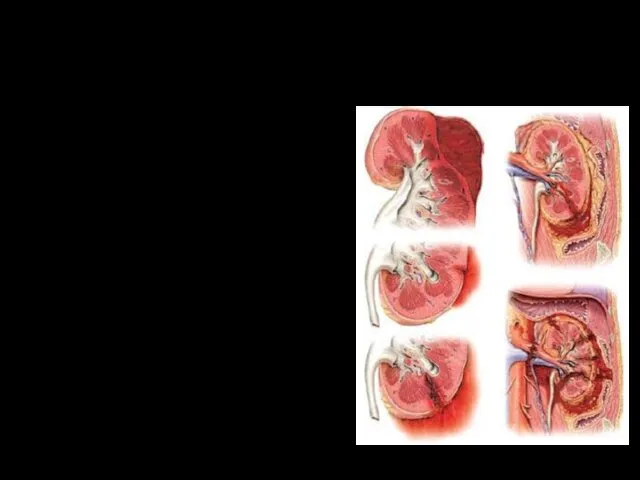
- 2. Closed kidney damage - Damage to the fat and fibrous capsules with the formation of a
- 3. Mechanism of closed kidney damage Causes: Blunt blunt objects Shaking Pressure The degree of damage depends
- 4. Open kidney damage By the type of the hurting projectile: firearms (bullet, shrapnel, explosive); non-fireable In
- 5. Iatrogenic exposure Retrograde pyelography Puncture Shockwave remote lithotripsy
- 6. Clinical manifestations Dysuria Symptoms of peritoneal irritation Nausea Vomiting Fever Gastrointestinal dysfunction Lumbar pain Hematuria Swelling
- 7. Three degrees of severity Mild kidney injury - the general condition of the victim is poorly
- 8. Diagnostics On examination: Hematoma, swelling in the lumbar region Local muscle tension Rib fractures Paleness of
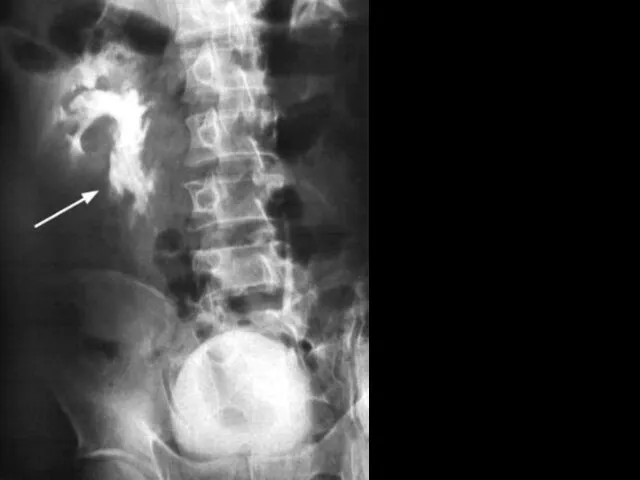
- 9. Contrast radiography
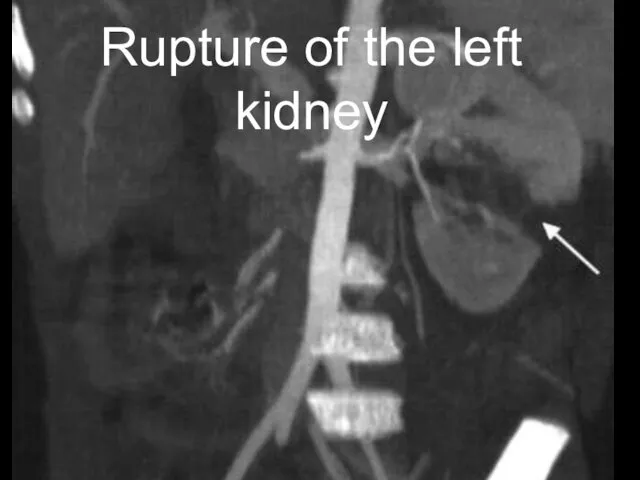
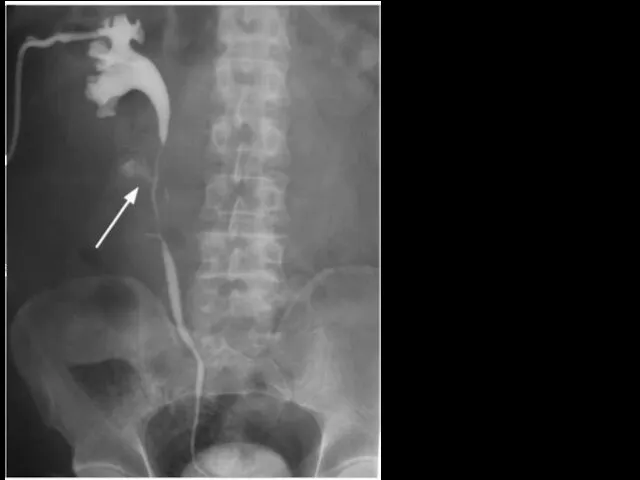
- 10. Rupture of the left kidney
- 11. Treatment Stopping bleeding Bed rest 10-15 days Control of hemodynamics and hematocrit Preventive parenteral administration of
- 12. Damage of the ureters Ureters are rarely damaged due to elasticity, displaceability and location. Iatrogenic damage
- 13. Classification By type: Closed ureteral injury (subcutaneous). Open ureteral injury (wound). By the nature: An isolated
- 14. Diagnostics Diagnosis is based on an analysis of the circumstances and mechanism of injury, clinical manifestations
- 15. Antegrade pyeloutraprogram
- 16. Differential diagnostics To distinguish between injuries of the ureter and bladder, use the method of filling
- 17. Bladder damage Causes: blunt or penetrating injury leading to rupture Mechanism Blunt blow to full bladder;
- 18. Closed (with integer integument): injury; incomplete rupture (external and internal); complete break; two-stage rupture of the
- 19. Clinical manifestations Intraperitoneal Pain over pubis Anuria Signs of peritonitis Bloating Symptom "Vanka-Vstanki" Extraperitoneal Pain over
- 20. Diagnostics Catheterization Zeldovich positive symptom (inconsistency between the injected and exiting fluid from the catheter) AS
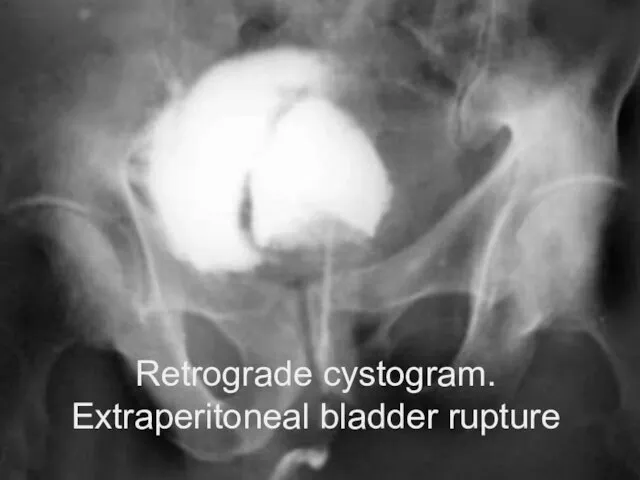
- 21. Retrograde cystogram. Extraperitoneal bladder rupture
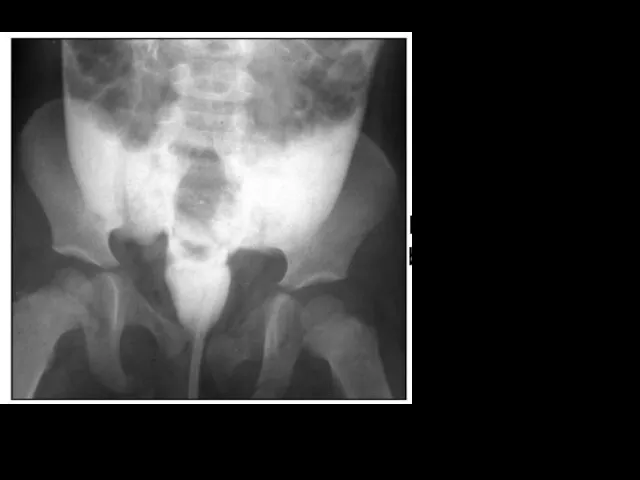
- 22. Intraperitoneal bladder rupture
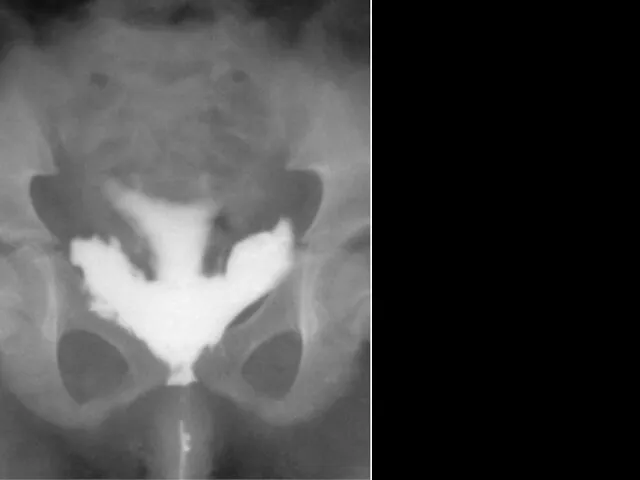
- 23. Flow of contrast fluid into paravesical space
- 24. Treatment Conservative Surgical Bed rest Uroseptics and antibiotics Hemostatic therapy NSAIDs Cold compresses on the stomach
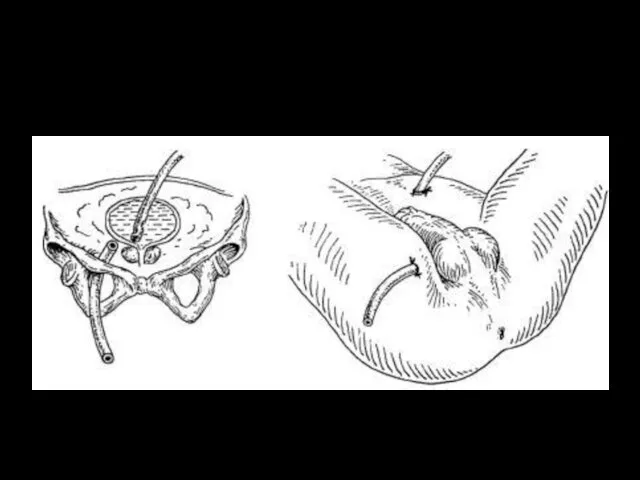
- 25. Drainage by Buyalsky-McWorthier
- 27. Скачать презентацию















 Микотоксины. Действие микотоксинов в истории
Микотоксины. Действие микотоксинов в истории Общие принципы лечения абсцессов и флегмон лица и шеи. Физиотерапия и реабилитация больных
Общие принципы лечения абсцессов и флегмон лица и шеи. Физиотерапия и реабилитация больных Диспансерное наблюдение за детьми с хроническими заболеваниями
Диспансерное наблюдение за детьми с хроническими заболеваниями Хронические расстройства питания у детей
Хронические расстройства питания у детей Наследственные заболевания человека
Наследственные заболевания человека Геморрагический шок
Геморрагический шок Гипогликемическая и гипергликемическая комы
Гипогликемическая и гипергликемическая комы Пути введения лекарственных средств
Пути введения лекарственных средств Обзор и принципы реанимации новорожденных
Обзор и принципы реанимации новорожденных Современные алгоритмы лечения сахарного диабета 2 типа
Современные алгоритмы лечения сахарного диабета 2 типа Нейропсихологическая диагностика
Нейропсихологическая диагностика Общая характеристика группы инфекционных болезней с воздушнокапельным механизмом передачи. Грипп
Общая характеристика группы инфекционных болезней с воздушнокапельным механизмом передачи. Грипп Вагинальные инфекции при беременности
Вагинальные инфекции при беременности Federal State Educational Institution of Higher Education
Federal State Educational Institution of Higher Education Синдром наличия жидкости и газа в плевральной полости. Плевриты
Синдром наличия жидкости и газа в плевральной полости. Плевриты Холера. Эпидемиология
Холера. Эпидемиология Хронический пылевой бронхит
Хронический пылевой бронхит Легочное сердце
Легочное сердце Инфекционный мононуклеоз у детей
Инфекционный мононуклеоз у детей Понятие гиподинамии, гипердинамии
Понятие гиподинамии, гипердинамии Действия ассистента, осуществляемые до прихода врача-стоматолога, после прихода врача-стоматолога и после окончания лечения
Действия ассистента, осуществляемые до прихода врача-стоматолога, после прихода врача-стоматолога и после окончания лечения Митральные пороки сердца
Митральные пороки сердца Критерии и качества стоматологических материалов. Система международных и национальных стандартов
Критерии и качества стоматологических материалов. Система международных и национальных стандартов Введение в венерологию. История развития венерологии. Инфекции, передающиеся половым путем
Введение в венерологию. История развития венерологии. Инфекции, передающиеся половым путем Доказательная профилактика. Скрининговые программы
Доказательная профилактика. Скрининговые программы Endocrine system
Endocrine system Современные подходы к лечению эндометриоидных кист яичников
Современные подходы к лечению эндометриоидных кист яичников Дисфункционалдық жатырдан қан кету
Дисфункционалдық жатырдан қан кету