Содержание
- 2. Introduction to Course What is an Audit? What is the purpose of an audit? Why study
- 3. Examples of ‘Audits’ Financial Statement Audit Environmental Audit Medical Audit Forensic Audit Technology audits Teaching audits
- 4. What is an Audit? An audit is: an investigation or a search for evidence to enable
- 5. ISA (UK and Ireland) 200 The purpose of an audit is to increase the confidence of
- 6. ISA 200 para 7 The ISAs require that the auditor exercise professional judgment and maintain professional
- 7. Justifications for Audit Agency Theory Information Hypothesis Insurance Hypothesis
- 8. Agency theory basic ideas Both the owners (principals) of organisation and the managers (agents) employed to
- 9. Information & Insurance Hypotheses An insurance policy over the accuracy of the accounts
- 10. Reasonable Assurance The auditor does not guarantee that the accounts are 100% correct. The auditor provides
- 11. Truth & Fairness Stated in the auditor’s opinion that the financial statements are ‘true and fair’.
- 12. Audit Process Preliminary Stages (Client acceptance & Planning) Systems work and transaction testing Preparation for final
- 13. Why Study Auditing?
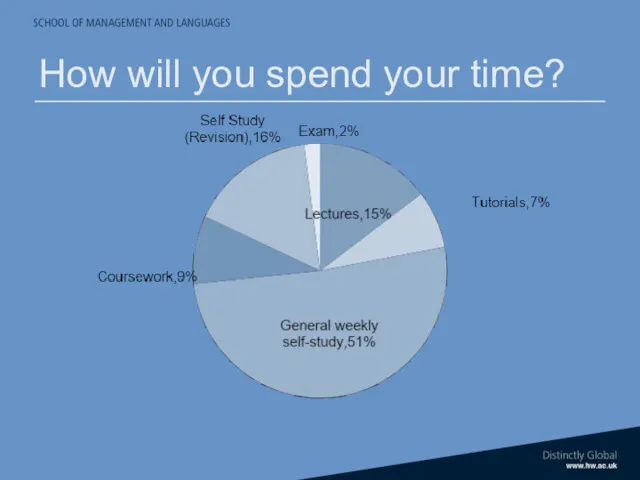
- 16. How will you spend your time?
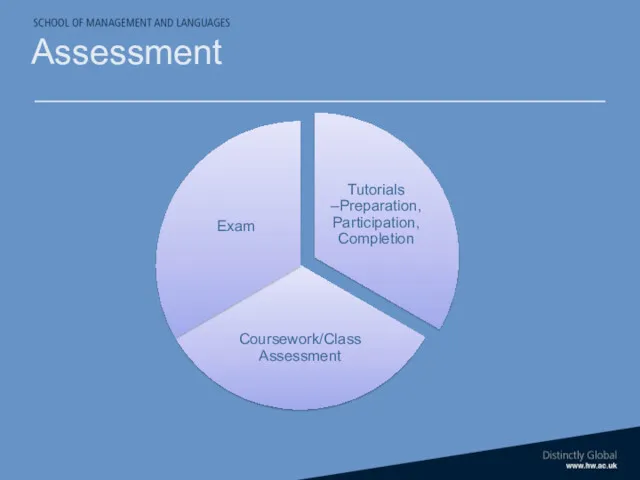
- 17. Assessment
- 18. My Role
- 19. Practical Issues Sign up for tutorial groups Start thinking about Coursework
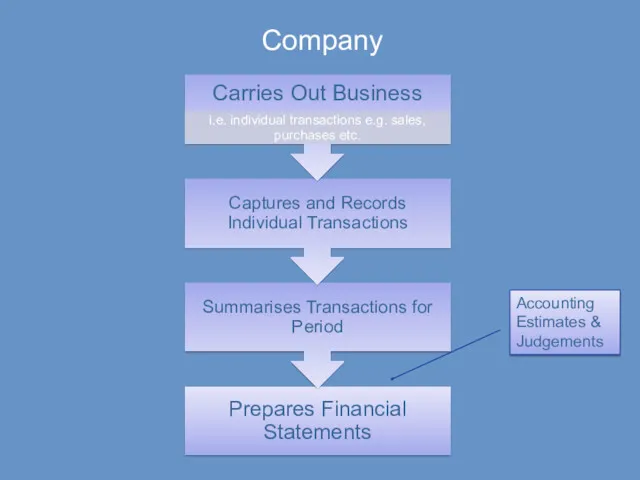
- 20. Company Accounting Estimates & Judgements
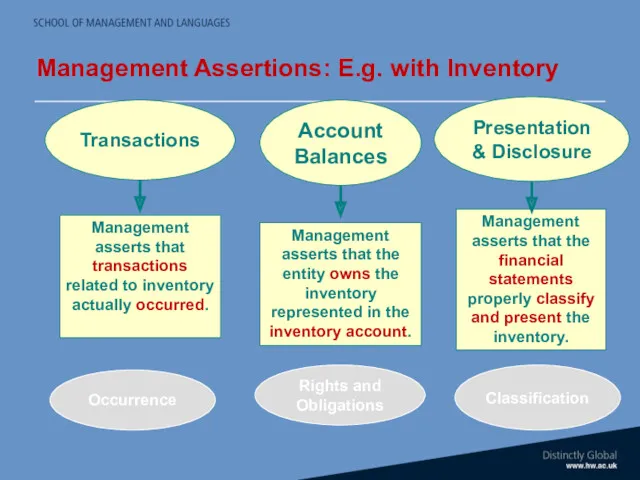
- 21. Assertions in Financial Statements Financial Statements issued by management contain explicit and implicit assertions e.g. Inventory
- 22. Management Assertions: E.g. with Inventory Occurrence Rights and Obligations Classification
- 23. Assertions are about: Classes of transactions and events Account balances Presentation & disclosure Key assertions are:
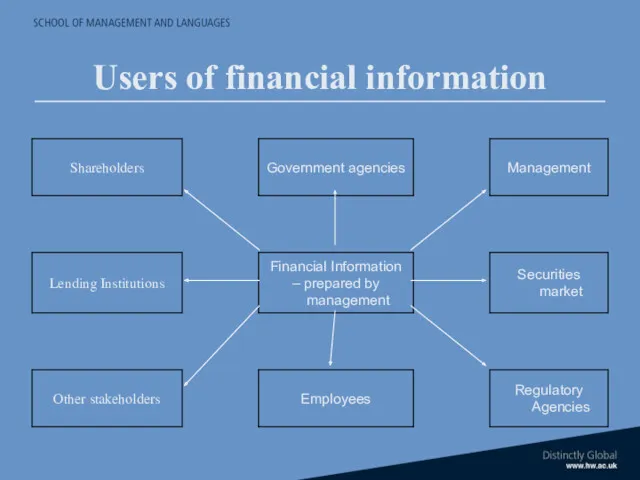
- 24. Users of financial information
- 25. Why need audit? Conflict of Interest Remoteness Complexity Public Interest Public Trust
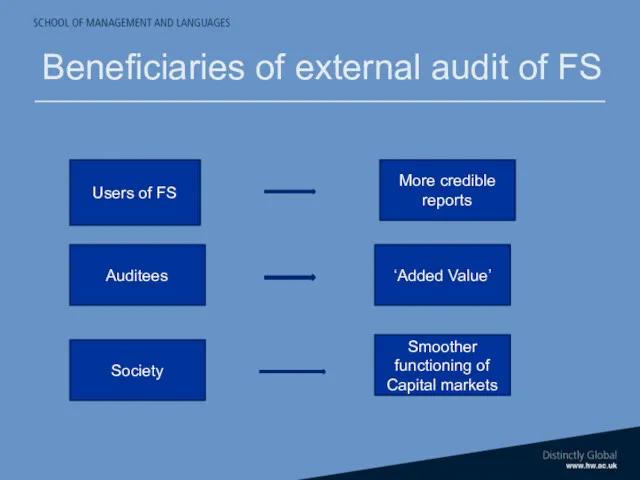
- 26. Beneficiaries of external audit of FS Users of FS More credible reports ‘Added Value’ Auditees Smoother
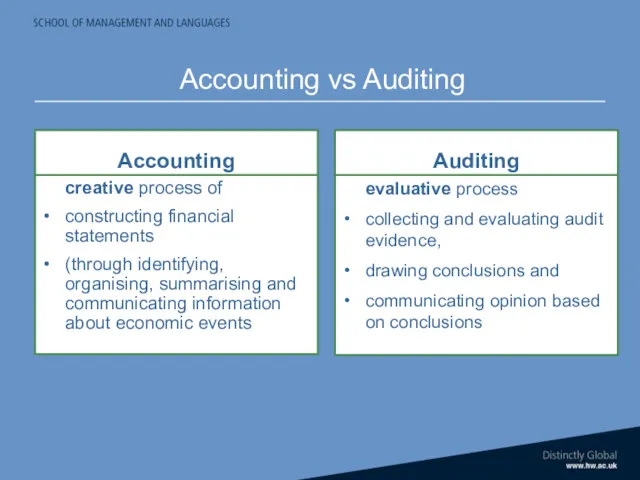
- 27. Accounting creative process of constructing financial statements (through identifying, organising, summarising and communicating information about economic
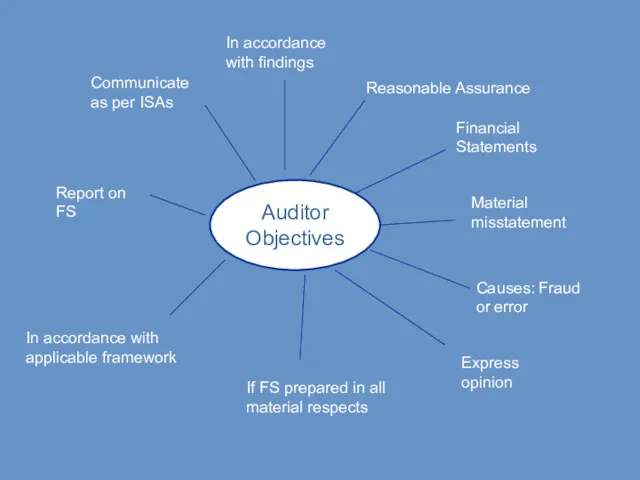
- 28. Auditor Objectives Reasonable Assurance Financial Statements Material misstatement Causes: Fraud or error Express opinion If FS
- 29. Overall Objectives of the Auditor To obtain Reasonable Assurance About whether the FS as a whole
- 30. Key Audit Terms Fill in the Blanks Ask for explanations of any words you don’t understand
- 31. Postulates of Auditing FS and Financial data are verifiable; Existence of a satisfactory system of internal
- 33. Скачать презентацию




















 Тайм-менеджмент
Тайм-менеджмент Logistika letecké dopravy
Logistika letecké dopravy Управление людьми. Управление человеческим капиталом. (Раздел 1.2)
Управление людьми. Управление человеческим капиталом. (Раздел 1.2) SWOT-анализ
SWOT-анализ Теории управления персоналом
Теории управления персоналом Восемь принципов менеджмента качества
Восемь принципов менеджмента качества Поиск работы
Поиск работы Объекты и субъекты сферы услуг
Объекты и субъекты сферы услуг Корпоративный имидж и репутация фирмы
Корпоративный имидж и репутация фирмы Закупочная логистика. Планирование закупок
Закупочная логистика. Планирование закупок Кадровое делопроизводство. (Лекция 1)
Кадровое делопроизводство. (Лекция 1) Стратегия управления репутацией компании
Стратегия управления репутацией компании Операционный сервис-менеджмент во фронт-офисах государственной корпорации Правительство для граждан
Операционный сервис-менеджмент во фронт-офисах государственной корпорации Правительство для граждан Мотивация розницы. Торговая сеть Перекресток
Мотивация розницы. Торговая сеть Перекресток Организация как функция управления
Организация как функция управления Ұйымның сыртқы ортасын бағалау және талдау. Ұйым қызымет атқаратын саладағы бәсекелестік күштер және олардың ұйымға әсері
Ұйымның сыртқы ортасын бағалау және талдау. Ұйым қызымет атқаратын саладағы бәсекелестік күштер және олардың ұйымға әсері Көшбасшылық
Көшбасшылық Инструменты и методы бережливого производства
Инструменты и методы бережливого производства Принципы управления
Принципы управления Понятие и сущность логистики. (Раздел 1.1)
Понятие и сущность логистики. (Раздел 1.1) Основные принципы современных систем менеджмента
Основные принципы современных систем менеджмента Управління інноваційною діяльністю
Управління інноваційною діяльністю Сутність планування та особливості його здійснення на підприємстві
Сутність планування та особливості його здійснення на підприємстві Функциональное моделирование систем. Методики: SADT - IDEF0, DFD, IDEF3
Функциональное моделирование систем. Методики: SADT - IDEF0, DFD, IDEF3 DHL – международная логистическая компания
DHL – международная логистическая компания HSJ Chapter 5. Business-Level Strategy
HSJ Chapter 5. Business-Level Strategy Начала менеджмента. Менеджмент и менеджеры
Начала менеджмента. Менеджмент и менеджеры Функции менеджмента
Функции менеджмента