Содержание
- 2. Just In Time Just in Time (JIT) – a Business Philosophy Production system: manufacturing & movement
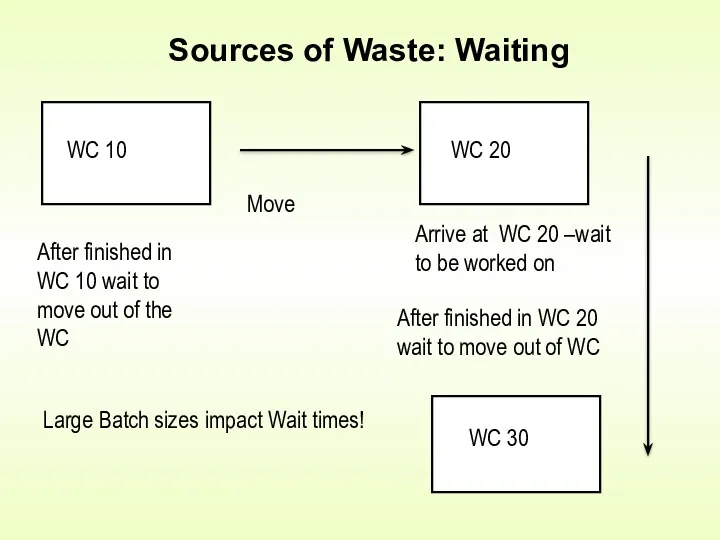
- 3. Sources of Waste: Waiting WC 10 WC 20 WC 30 After finished in WC 10 wait
- 4. JIT Wastes Overproduction – making more than we can sell now Waiting time – for the
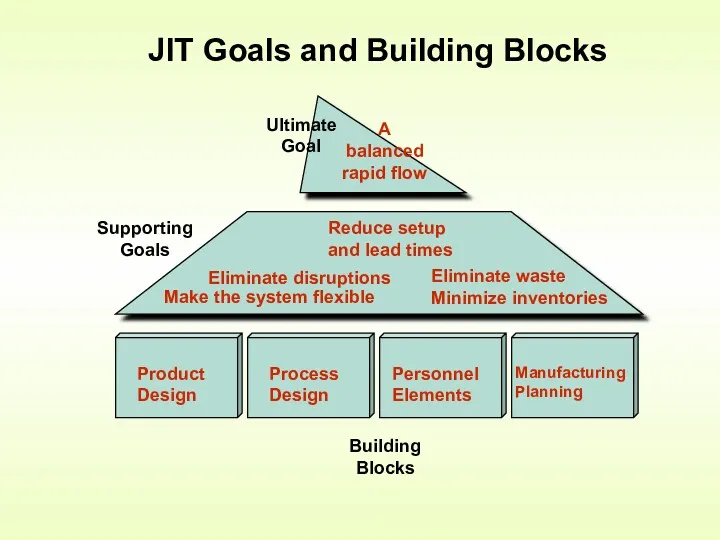
- 5. JIT Goals and Building Blocks
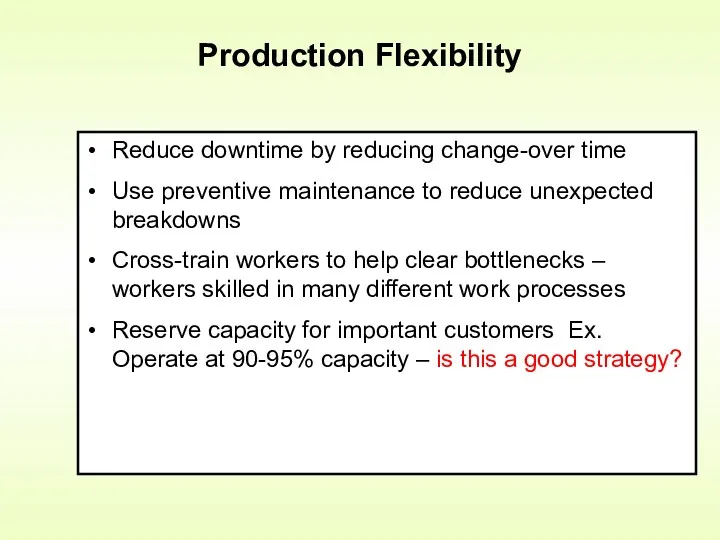
- 6. Production Flexibility Reduce downtime by reducing change-over time Use preventive maintenance to reduce unexpected breakdowns Cross-train
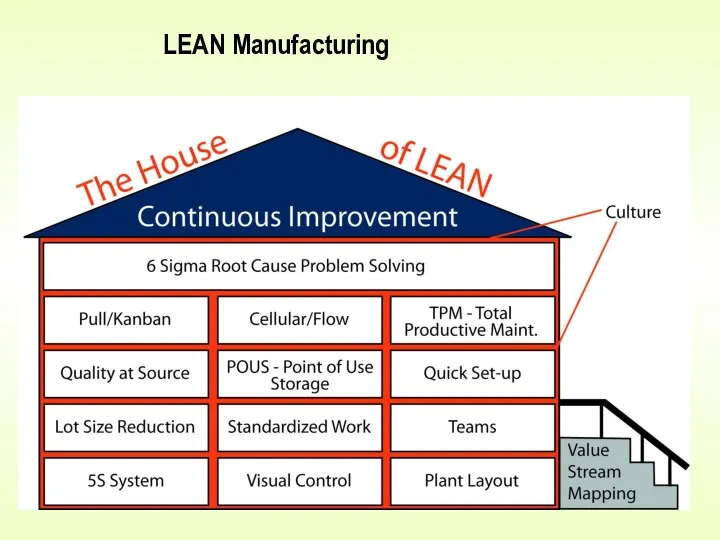
- 7. LEAN Manufacturing
- 8. Product Design Standardized parts Modular design Quality DFM (Design for Manufacturing) Mistake-proofing design
- 9. Process Design Smaller production lot sizes Setup time reduction Manufacturing cells Quality improvements –preventive actions Reduced
- 10. Work Cells Examples
- 11. Benefits of Small Lot Sizes
- 12. Small batch sizes and changing product mixes require frequent machine setups Workers are trained to do
- 13. Prevent Defects from occurring using: Six Sigma to reduce process variability Poka Yoke to mistake-proof Autonomation:
- 14. Personnel/Organizational Elements Workers as assets Cross-trained workers Train workers in problem-solving Form work cell teams
- 15. Manufacturing Planning and Control Level loading – keep consistent amount of production Example – always produce
- 16. Visual Controls
- 17. Pull/Push Systems and Kanban Pull system: System for moving work where a workstation pulls output from
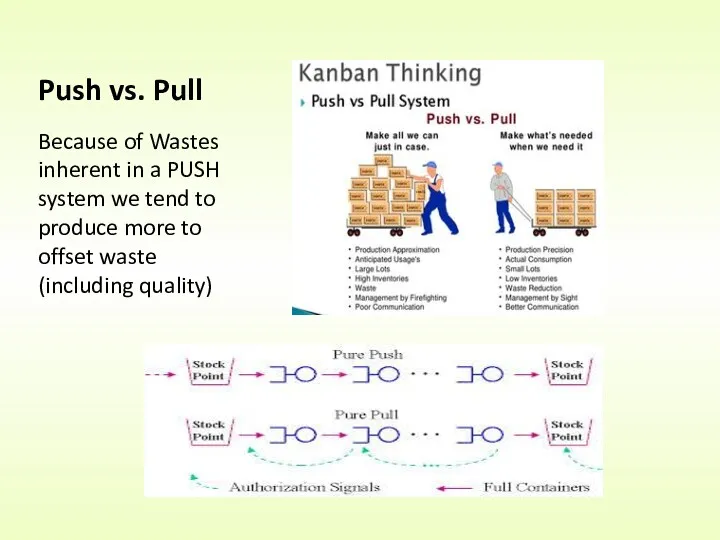
- 18. Push vs. Pull Because of Wastes inherent in a PUSH system we tend to produce more
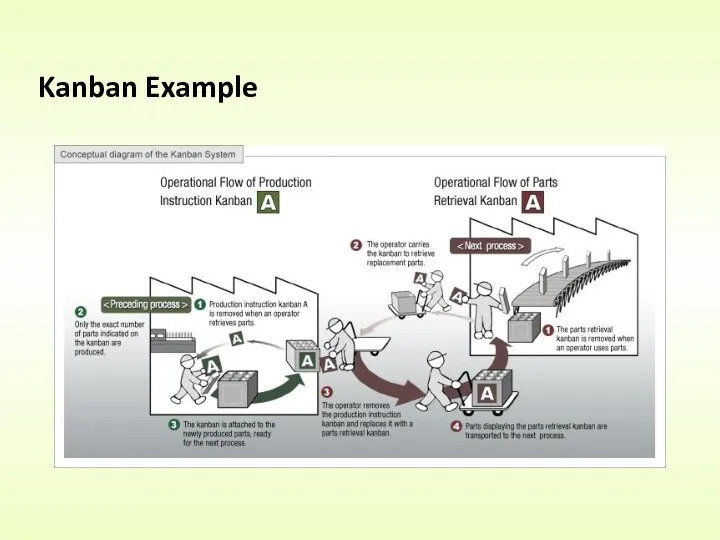
- 19. Kanban Example
- 20. Kanban Examples Two bin system – RED means empty – Stores to replenish Empty means –
- 21. Preventive Maintenance and Housekeeping Preventive maintenance Maintaining equipment in good operating condition and replacing parts that
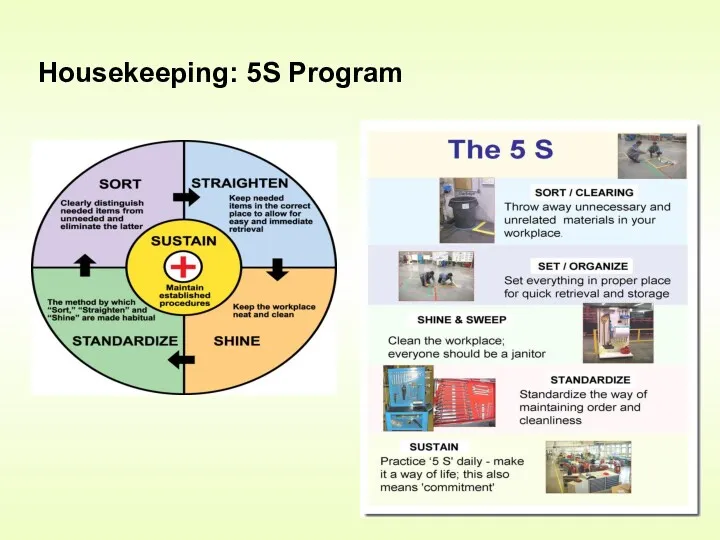
- 22. Housekeeping: 5S Program .
- 24. Скачать презентацию









 Зарубежный опыт управления собственностью
Зарубежный опыт управления собственностью Организационные коммуникации
Организационные коммуникации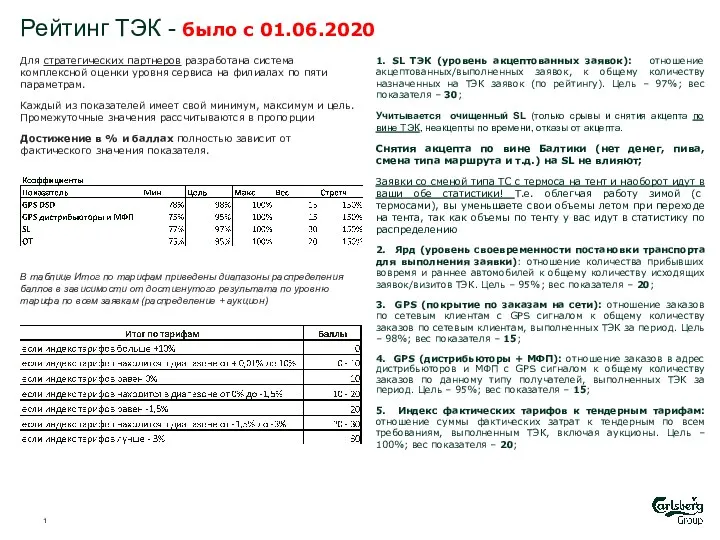 Рейтинг ТЭК
Рейтинг ТЭК Система государственного управления в Российской Федерации
Система государственного управления в Российской Федерации Совершенствование управления инфраструктурой предприятия АО Грузовой терминал Пулково
Совершенствование управления инфраструктурой предприятия АО Грузовой терминал Пулково Тренинг тренеров. Наставничество в продажах
Тренинг тренеров. Наставничество в продажах Поведенческие аспекты лидерства. (Тема 7)
Поведенческие аспекты лидерства. (Тема 7)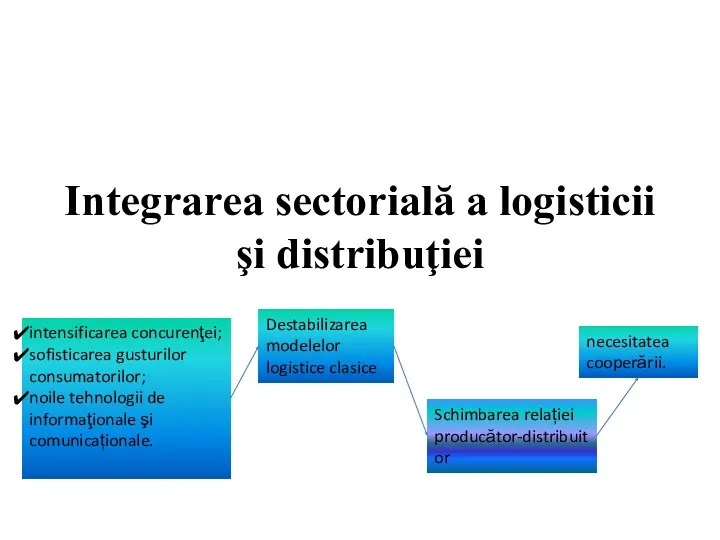 Integrarea sectorială a logisticii şi distribuţiei
Integrarea sectorială a logisticii şi distribuţiei Команды и капитаны
Команды и капитаны Системное управление и планирование здравоохранением
Системное управление и планирование здравоохранением Роль продукции в концепции распределительной логистики
Роль продукции в концепции распределительной логистики Групповая динамика
Групповая динамика Організаційна культура керівника
Організаційна культура керівника Научные подходы в менеджменте. (Лекция 3)
Научные подходы в менеджменте. (Лекция 3) Репутационный менеджент как особая разновидность ПР-деятельности. Лекция 2
Репутационный менеджент как особая разновидность ПР-деятельности. Лекция 2 Туризм, как сфера рыночных отношений
Туризм, как сфера рыночных отношений Управленческие решения
Управленческие решения Семинар - инструменты и методы системного анализа в решении управленческих задач
Семинар - инструменты и методы системного анализа в решении управленческих задач Основные понятия менеджмента
Основные понятия менеджмента New product development
New product development Инновационный менеджмент
Инновационный менеджмент Любое мероприятие своими руками от идеи до реализации
Любое мероприятие своими руками от идеи до реализации Сущность и базовые понятия процесса управления инновациями. (Тема 1-2)
Сущность и базовые понятия процесса управления инновациями. (Тема 1-2) Совершенствование системы управления персоналом на предприятии. Дипломная работа
Совершенствование системы управления персоналом на предприятии. Дипломная работа Разработка технологии и расширение ассортимента блюд и напитков в ресторане с национальной кухней на 280 посадочных мест
Разработка технологии и расширение ассортимента блюд и напитков в ресторане с национальной кухней на 280 посадочных мест Кадровая политика и кадровое планирование
Кадровая политика и кадровое планирование Еще больше возможностей
Еще больше возможностей Стратегическое планирование
Стратегическое планирование