Содержание
- 2. Line managers play a critical role in delivering HRM Line managers and employees have substantial discretion
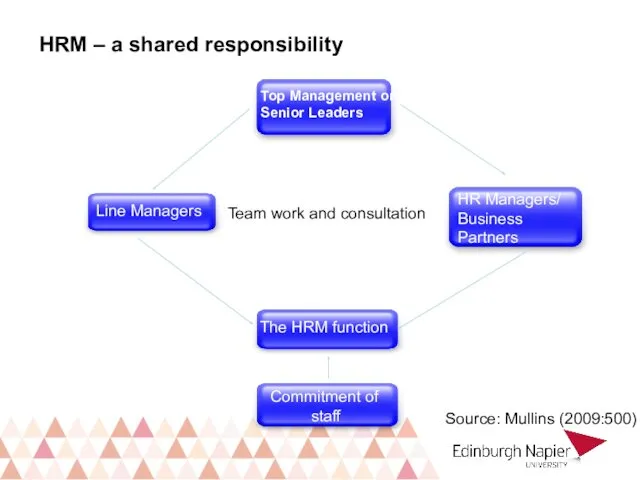
- 3. HRM – a shared responsibility Top Management or Senior Leaders Line Managers HR Managers/ Business Partners
- 4. Who are Line managers and why are they important? Managers of people – the non specialist
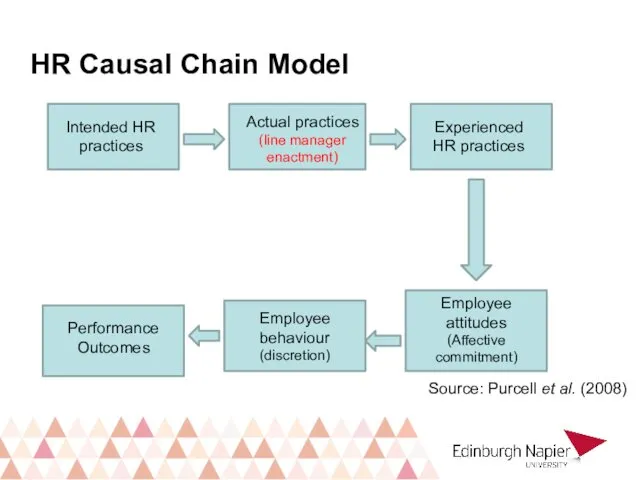
- 5. Intended HR practices Actual practices (line manager enactment) Experienced HR practices Employee attitudes (Affective commitment) Employee
- 6. Line managers views and responsibilities Operational Aspects Recruitment and selection Training Discipline Absence monitoring Leadership Roles
- 7. Devolution of responsibility to the line Varies in extent between countries – depends on the expectation
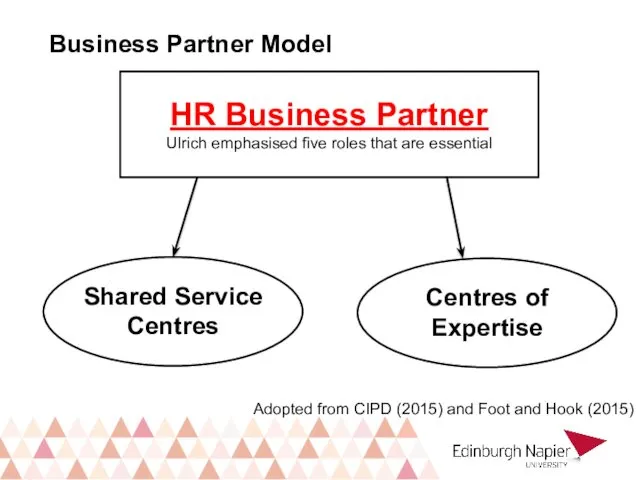
- 8. Business Partner Model HR Business Partner Ulrich emphasised five roles that are essential Shared Service Centres
- 9. Strategic partner Human capital developer Functional expert Employee advocates HRM leader Ulrich and Brockbank’s 5 Roles
- 10. Motivations for devolving responsibility Cost reduction and efficiency (avoiding duplication of effort) Provide a more comprehensive
- 11. Problems Lack of “ownership” Fear of constraint/bureaucracy in making decisions Lack of expertise or consistency between
- 12. Challenges Reconciling hard and soft HR Expectations of senior management? Expectations of subordinates? Selection and training
- 13. Supporting middle managers HR strategies should be broad themes, to be contextualised at operational level Middle
- 14. Do you agree with the research that interpersonal relationships are critical element of HR Systems? In
- 15. Questions to analyse the article: The Filling in the Sandwich: HRM and middle managers in the
- 16. Conclusions Devolution is viewed with mixed reaction, with some line managers enthusiastic about taking on HR
- 18. Скачать презентацию












 Философия управления персоналом
Философия управления персоналом Бизнес-план по дисциплине Стратегический менеджмент
Бизнес-план по дисциплине Стратегический менеджмент Source Code Manager
Source Code Manager Профессиональные компетенции менеджера организации
Профессиональные компетенции менеджера организации Преимущества и недостатки бюрократической школы управления
Преимущества и недостатки бюрократической школы управления Управление группой
Управление группой Закономерности, принципы и методы управления персоналом
Закономерности, принципы и методы управления персоналом Nəqliyyat qovşaqları (HUB)
Nəqliyyat qovşaqları (HUB) Бриф на промо-акцию Проведение дегустаций
Бриф на промо-акцию Проведение дегустаций Предпринимательские риски и угрозы безопасности. Тема № 2
Предпринимательские риски и угрозы безопасности. Тема № 2 Өнімді сертификаттау және оның негізгі бағыттары
Өнімді сертификаттау және оның негізгі бағыттары Коучинг - технология повышения эффективности персонала
Коучинг - технология повышения эффективности персонала Организация и планирование предприятия. Лекция 3. Принципы организации производственного процесса
Организация и планирование предприятия. Лекция 3. Принципы организации производственного процесса Менеджмент інформаційних систем. Лекція №1
Менеджмент інформаційних систем. Лекція №1 Управление человеческими ресурсами как интегральный компонент общего процесса управления
Управление человеческими ресурсами как интегральный компонент общего процесса управления Понятие и этапы планирования потребности в персонале
Понятие и этапы планирования потребности в персонале Современная нормативная база по делопроизводству
Современная нормативная база по делопроизводству Основные требования к проектированию
Основные требования к проектированию Жапонияда персоналдарды басқару
Жапонияда персоналдарды басқару Модель корпоративного управления в Казахстане
Модель корпоративного управления в Казахстане QSR Competitive Analysis
QSR Competitive Analysis 8 стандартов обслуживания покупателей. Работа с возражениями
8 стандартов обслуживания покупателей. Работа с возражениями Підготовка прийняття та організація управлінських рішень. Лекция 6
Підготовка прийняття та організація управлінських рішень. Лекция 6 Миссия компании
Миссия компании Психология эффективного управления
Психология эффективного управления Контроль и принятие управленческих решений в системе стратегического контроллинга
Контроль и принятие управленческих решений в системе стратегического контроллинга Менеджмент рекреационных объектов. Конкурентоспособность рекреационных услуг
Менеджмент рекреационных объектов. Конкурентоспособность рекреационных услуг Традиционная система управления таможенными органами
Традиционная система управления таможенными органами