Содержание
- 2. Introduction Scheduling Establishing the timing of the use of equipment, facilities & labor in an organization
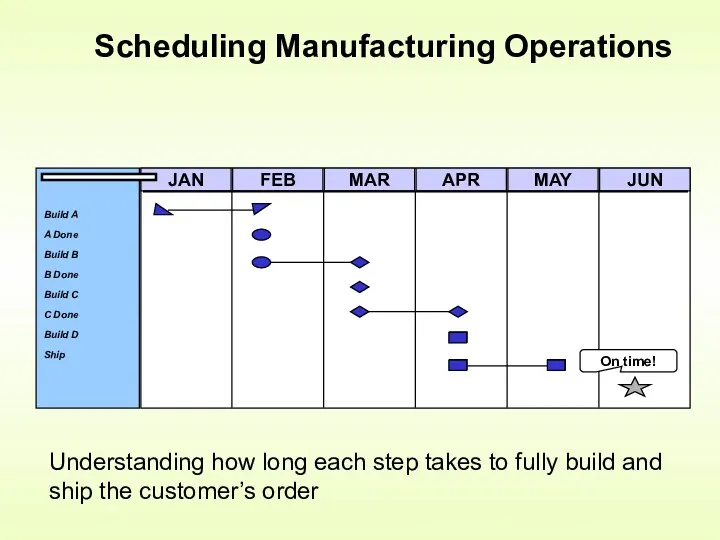
- 3. Scheduling Manufacturing Operations Understanding how long each step takes to fully build and ship the customer’s
- 4. Scheduling in high volume systems (continuous flow and assembly lines) –refinery, beer, automobiles Goal is to
- 5. High-Volume Success Factors Relatively simple process and product design Preventive maintenance is a top priority Rapid
- 6. Scheduling in Batch volume systems Items are processed intermittently – some of A, then some of
- 7. Scheduling Low-Volume Systems (Job Shops) Job Shop scheduling Scheduling for low volume systems with many variations
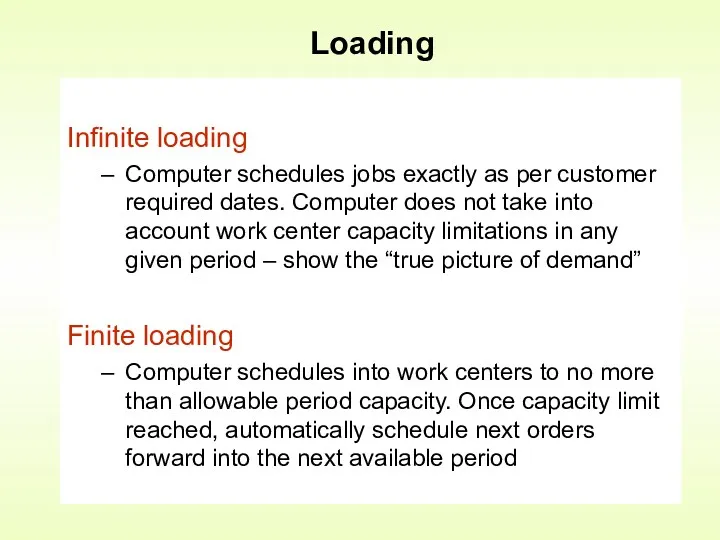
- 8. Infinite loading Computer schedules jobs exactly as per customer required dates. Computer does not take into
- 9. Forward scheduling Scheduling ahead, starting from the start date of a job or when the work
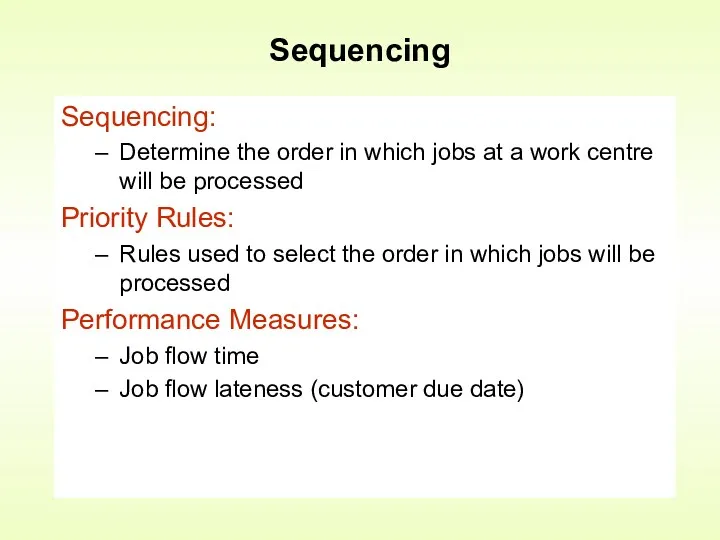
- 10. Sequencing Sequencing: Determine the order in which jobs at a work centre will be processed Priority
- 11. Priority Rules FCFS - first come, first served SPT - shortest processing time SRPT - shortest
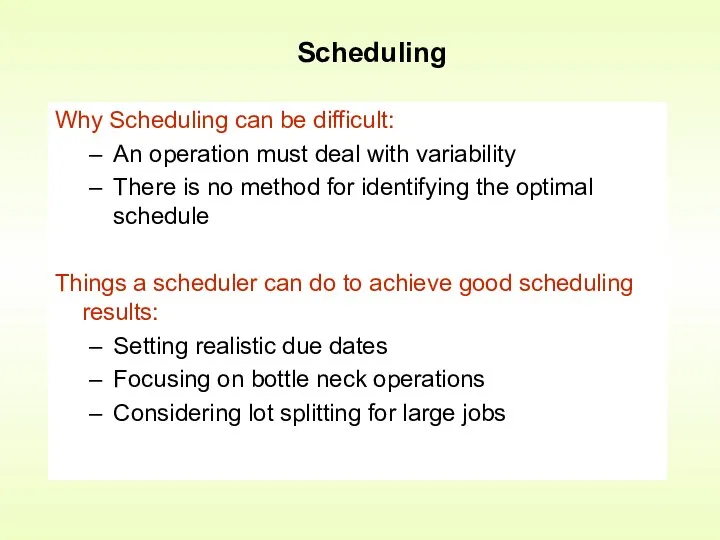
- 12. Scheduling Why Scheduling can be difficult: An operation must deal with variability There is no method
- 13. Scheduling Services Appointment systems Controls customer arrivals for service Scheduling the workforce Manages capacity for service
- 14. Service Operation Problems Cannot store or inventory services ahead of time Customer service requests can be
- 15. Extra Slides Not covered during class lecture
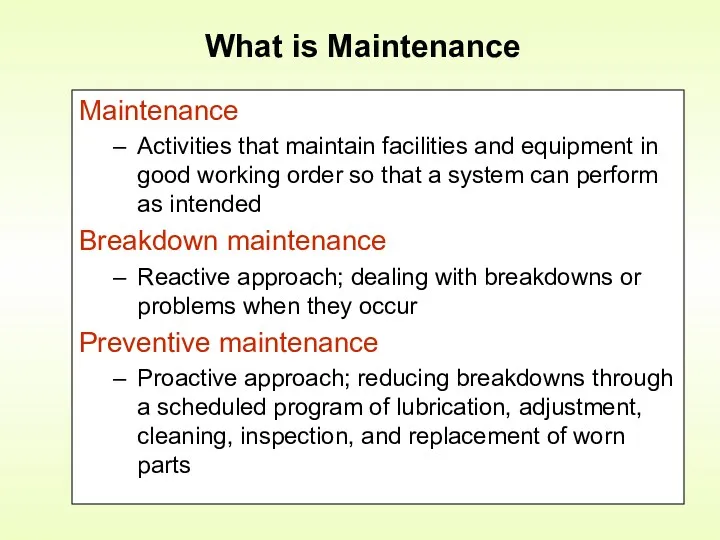
- 16. Maintenance Activities that maintain facilities and equipment in good working order so that a system can
- 17. Reasons for keeping equipment running: Avoid production disruptions – “Factory down” Maintain high quality Avoid missed
- 18. Production capacity is reduced Orders are delayed No production Overhead continues Cost per unit increases Quality
- 19. Preventive maintenance: goal is to reduce the incidence of breakdowns or failures in the plant or
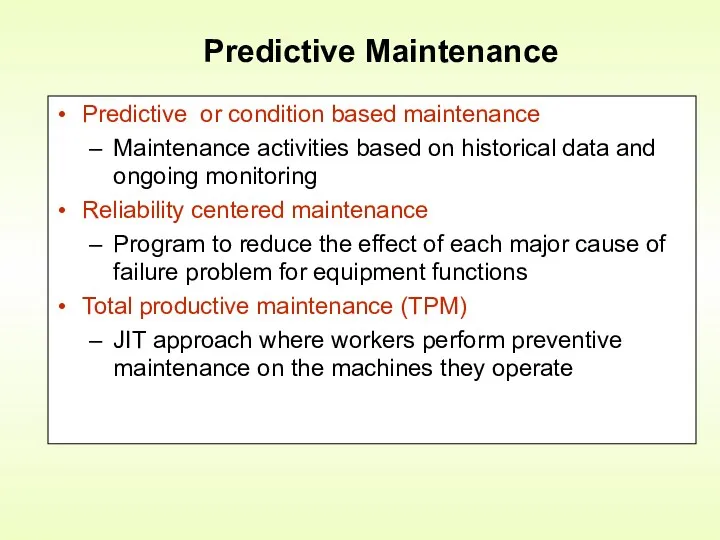
- 20. Predictive Maintenance Predictive or condition based maintenance Maintenance activities based on historical data and ongoing monitoring
- 21. Breakdown Maintenance How to deal with breakdowns? Standby or backup equipment that can be quickly put
- 23. Скачать презентацию












 Организация трудового процесса
Организация трудового процесса Раскрытие функции менеджмента на примере АЗС ЛенОил
Раскрытие функции менеджмента на примере АЗС ЛенОил Документальная регламентация деятельности управленцев. Тема 14
Документальная регламентация деятельности управленцев. Тема 14 How managers can make a decision in risk – and uncertainty environment? (continuation)
How managers can make a decision in risk – and uncertainty environment? (continuation) Теоретико-методологические и практические основы организационного поведения
Теоретико-методологические и практические основы организационного поведения Роль логистики распределения в логистической системе
Роль логистики распределения в логистической системе Эффективные коммуникации. Приемы и навыки
Эффективные коммуникации. Приемы и навыки Управление функциями проекта
Управление функциями проекта Формирование индивидуального плана развития
Формирование индивидуального плана развития Инструкция по работе в программе ЗИНГАЯ
Инструкция по работе в программе ЗИНГАЯ Рабочая программа курса закупочная логистика по специальности 1-26 02 05 логистика
Рабочая программа курса закупочная логистика по специальности 1-26 02 05 логистика Методы обучения персонала
Методы обучения персонала Organizational culture
Organizational culture Основы управления персоналом
Основы управления персоналом Кадровая политика и её планирование на предприятии
Кадровая политика и её планирование на предприятии Развитие управленческой деятельности руководителя
Развитие управленческой деятельности руководителя Создание логистического центра. Проект Питер
Создание логистического центра. Проект Питер The Evolution of Management Theory
The Evolution of Management Theory Понятие и причины текучести кадров. Расчёт коэффициента текучести
Понятие и причины текучести кадров. Расчёт коэффициента текучести Определения и понятия транспортной логистики
Определения и понятия транспортной логистики Ұйымдағы билік және коммуникация
Ұйымдағы билік және коммуникация Управление материальным потоком. Практическое занятие 3
Управление материальным потоком. Практическое занятие 3 Специфические методы исследования
Специфические методы исследования Типы клиентов работа с ними
Типы клиентов работа с ними Технологическая стандартизация и унификация
Технологическая стандартизация и унификация Понятие абсентеизма. Способы снижения абсентеизма на предприятии
Понятие абсентеизма. Способы снижения абсентеизма на предприятии Активные методы обучения
Активные методы обучения Подбор сотрудников. Собеседование на рядовые позиции
Подбор сотрудников. Собеседование на рядовые позиции