Содержание
- 2. Understand the importance of project schedules and good project time management Define activities as the basis
- 3. Managers often cite delivering projects on time as one of their biggest challenges Time has the
- 4. One dimension of the Meyers-Briggs Type Indicator focuses on peoples’ attitudes toward structure and deadlines Some
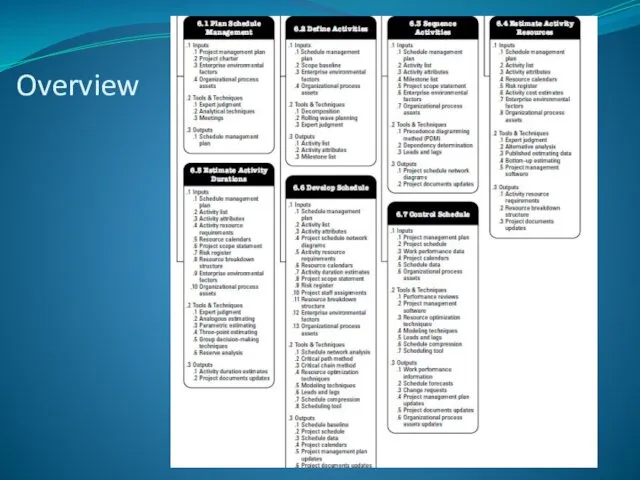
- 5. Overview
- 6. Plan Schedule Management: process of establishing the policies, procedures, and documentation for planning, developing, managing, executing,
- 7. Plan Schedule Management is the process of establishing the policies, procedures, and documentation for planning, developing,
- 8. An activity or task is an element of work normally found on the work breakdown structure
- 9. An activity list is a tabulation of activities to be included on a project schedule that
- 10. A milestone is a significant event that normally has no duration It often takes several activities
- 11. Involves reviewing activities and determining dependencies Key benefit – defines the logical sequence of work to
- 12. Network diagrams are the preferred technique for showing activity sequencing A network diagram is a schematic
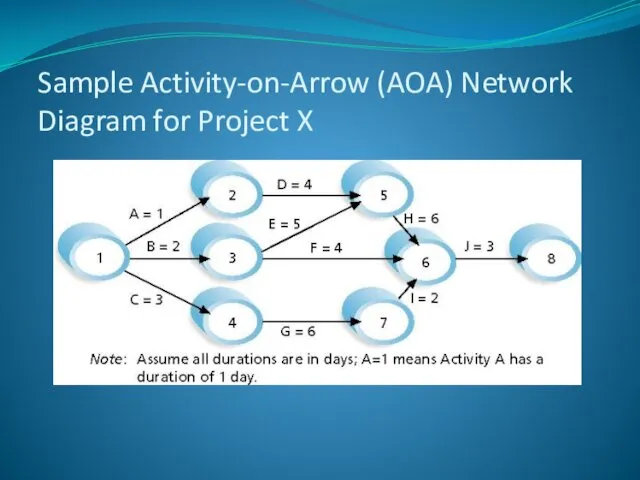
- 13. Also called activity-on-arrow (AOA) network diagrams Activities are represented by arrows Nodes or circles are the
- 14. Sample Activity-on-Arrow (AOA) Network Diagram for Project X
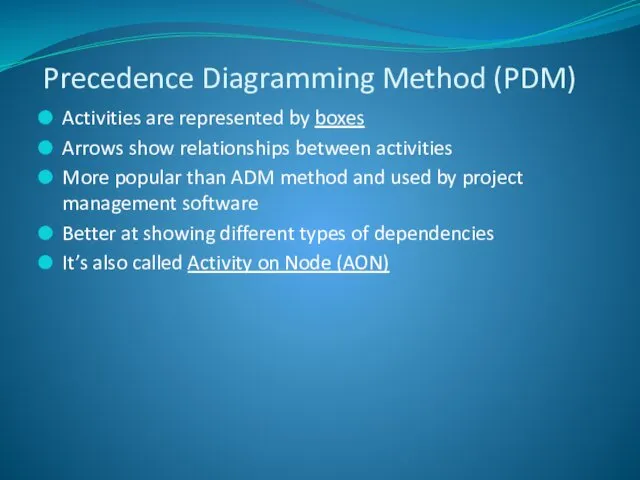
- 15. Activities are represented by boxes Arrows show relationships between activities More popular than ADM method and
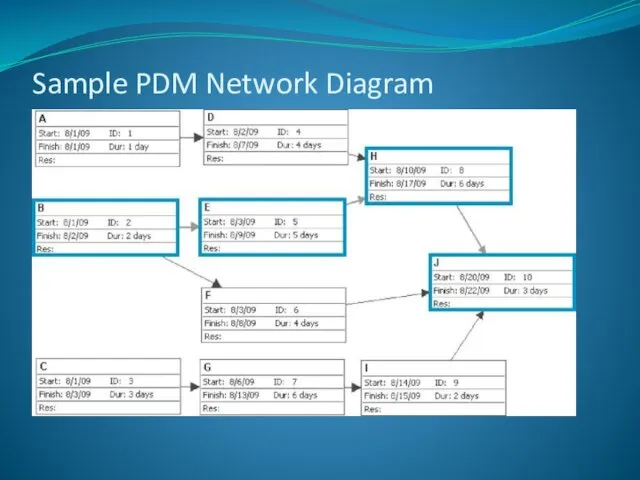
- 16. Sample PDM Network Diagram
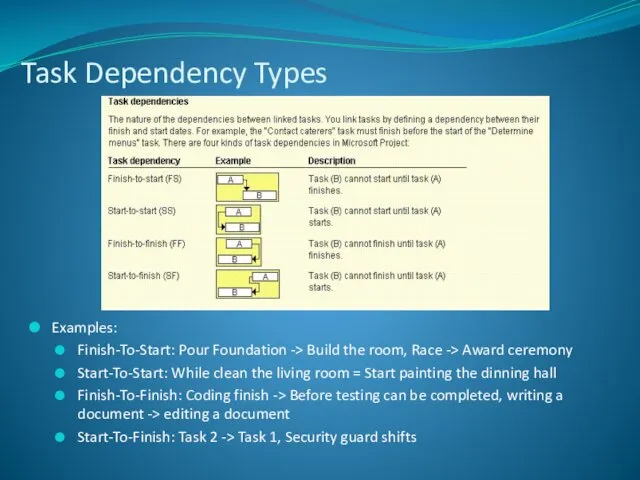
- 17. Task Dependency Types Examples: Finish-To-Start: Pour Foundation -> Build the room, Race -> Award ceremony Start-To-Start:
- 18. Before estimating activity durations, you must have a good idea of the quantity and type of
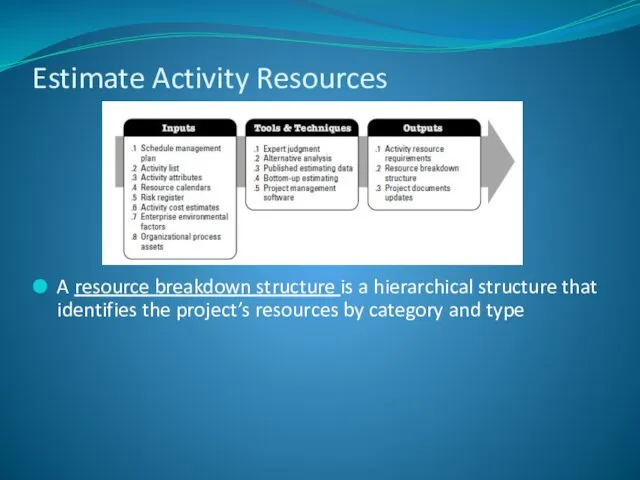
- 19. Estimate Activity Resources A resource breakdown structure is a hierarchical structure that identifies the project’s resources
- 20. Process of estimating the number of work periods needed to complete individual activities with estimated resources
- 21. Analogous estimating: Is a technique for estimating the duration or cost of an activity or a
- 22. Uses results of the other time management processes to determine the start and end date of
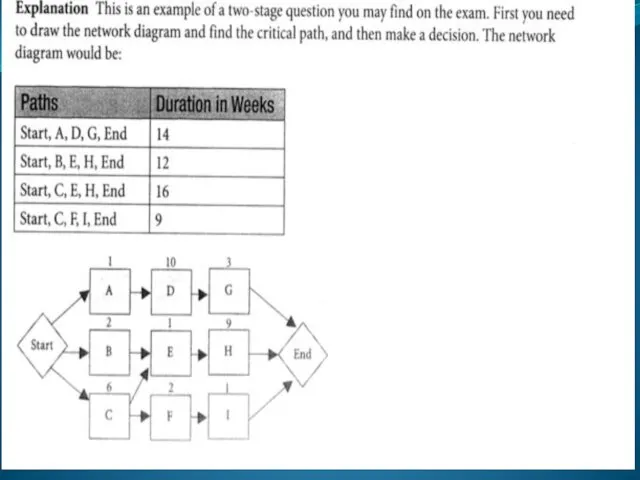
- 23. CPM is a network diagramming technique used to predict total project duration A critical path for
- 24. First develop a good network diagram Add the duration estimates for all activities on each path
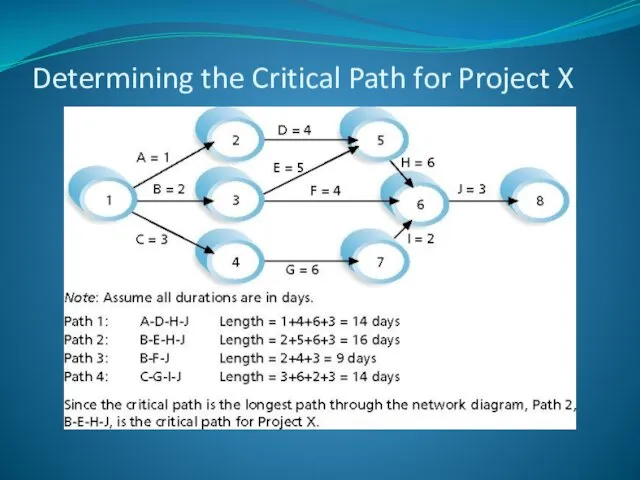
- 25. Determining the Critical Path for Project X
- 28. Three main techniques for shortening schedules Shortening durations of critical activities/tasks by adding more resources or
- 29. It is important to update project schedule information to meet time goals for a project The
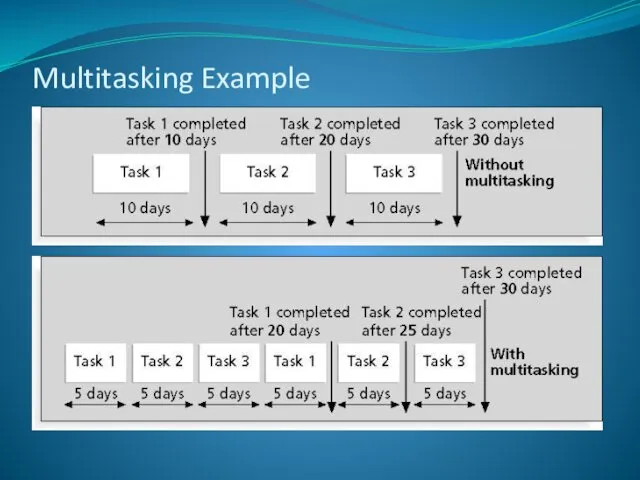
- 30. Multitasking Example
- 31. PERT is a network analysis technique used to estimate project duration when there is a high
- 32. PERT weighted average = optimistic time + 4X most likely time + pessimistic time 6 Example:
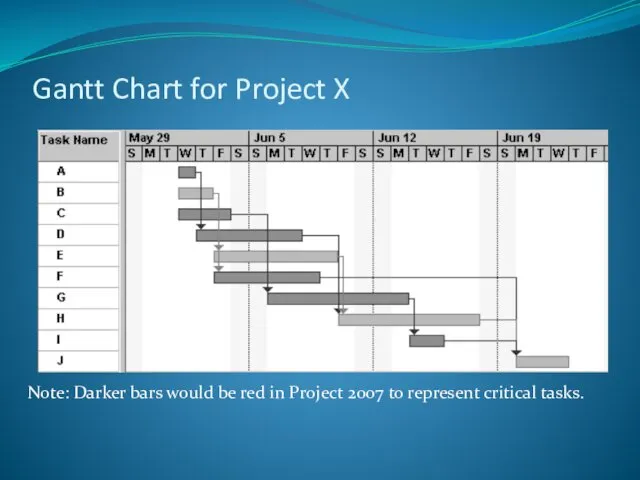
- 33. Gantt charts provide a standard format for displaying project schedule information by listing project activities and
- 34. Gantt Chart for Project X Note: Darker bars would be red in Project 2007 to represent
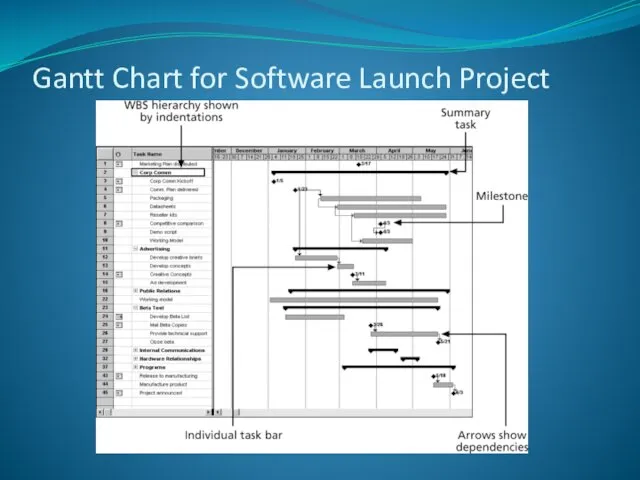
- 35. Gantt Chart for Software Launch Project
- 36. Goals are to know the status of the schedule, influence factors that cause schedule changes, determine
- 37. Perform reality checks on schedules Allow for contingencies Don’t plan for everyone to work at 100%
- 38. First review the draft schedule or estimated completion date in the project charter Prepare a more
- 39. Strong leadership helps projects succeed more than good PERT charts Project managers should use: Empowerment Incentives
- 41. Скачать презентацию


























 Функции планирования и контроля
Функции планирования и контроля Виды корпоративных культур в сравнительном менеджменте
Виды корпоративных культур в сравнительном менеджменте Конкурентоспособность предприятия. (Лекция 2)
Конкурентоспособность предприятия. (Лекция 2) Управление энергетическими ресурсами. Энергетический менеджмент
Управление энергетическими ресурсами. Энергетический менеджмент Организация ремонтного хозяйства
Организация ремонтного хозяйства Логистика складирования. Место склада в логистической системе
Логистика складирования. Место склада в логистической системе Теория мотивации. Урок № 10
Теория мотивации. Урок № 10 Корпоративное управление в образовании
Корпоративное управление в образовании Корпоративный кодекс ГК Вектор
Корпоративный кодекс ГК Вектор Типология управленческих решений
Типология управленческих решений Управление процессом создания и освоения новых столярных изделий на примере ООО ЗЗСИ КРОНА
Управление процессом создания и освоения новых столярных изделий на примере ООО ЗЗСИ КРОНА Бармен: функции, внешний вид
Бармен: функции, внешний вид Система безопасности в гостиничном бизнесе
Система безопасности в гостиничном бизнесе ООО МАЯК ТК. Организация автомобильных грузоперевозок по России, Иркутской области и городу Иркутску
ООО МАЯК ТК. Организация автомобильных грузоперевозок по России, Иркутской области и городу Иркутску How to overcome barriers?
How to overcome barriers? Кейс-метод при отборе персонала
Кейс-метод при отборе персонала SWOT-талдау
SWOT-талдау Национальные модели менеджмента. Лекция 4
Национальные модели менеджмента. Лекция 4 Набор и отбор персонала
Набор и отбор персонала Управление реализацией проекта
Управление реализацией проекта Эволюция управленческой мысли. Тема 2
Эволюция управленческой мысли. Тема 2 Основы организации пассажирских перевозок. Оценка качества пассажирских перевозок
Основы организации пассажирских перевозок. Оценка качества пассажирских перевозок Общая характеристика логистики
Общая характеристика логистики Введение в менеджмент
Введение в менеджмент Проектный семинар: компания и потребитель
Проектный семинар: компания и потребитель Дизайн-мышление
Дизайн-мышление Философия управления персоналом
Философия управления персоналом Тайм-менджмент
Тайм-менджмент