Содержание
- 2. Issues... Why are we interested in research? What is research? Key concepts and issues Introduction to
- 3. Why must we understand research? help make informed decisions need to produce research in career evaluating
- 4. Why is research a valued source of knowledge? Common ways of knowing… personal experience/intuition experts/traditions/authority scientific
- 5. What is Science, the Scientific Method, and Research? Science… a body of established knowledge the observation,
- 6. What is Science, the Scientific Method, and Research? Theory… a set of inter-related constructs and propositions
- 7. What is Science, the Scientific Method, and Research? Scientific Method… involves the principles and processes regarded
- 8. What is Science, the Scientific Method, and Research? Research… the application of the scientific method a
- 9. Characteristics of Research objective precise verifiable parsimonious empirical logical probabilistic
- 10. Types of Research Trochim’s Classifications… descriptive e.g., percentage of regular exercisers relational e.g., link between age
- 11. Types of Research Other Common Classifications… basic vs. applied vs. evaluation experimental vs. non-experimental analytical vs.
- 12. Key Concepts and Issues time in research variables types of relationships hypotheses types of data fallacies
- 13. Time in Research cross-sectional vs. longitudinal
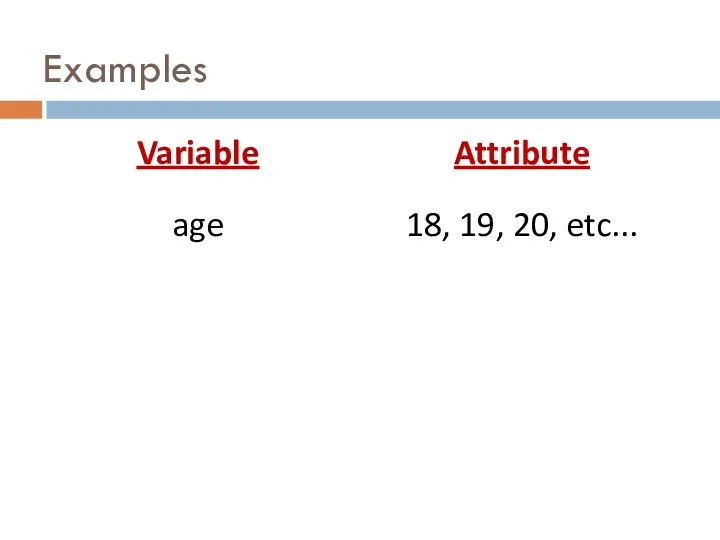
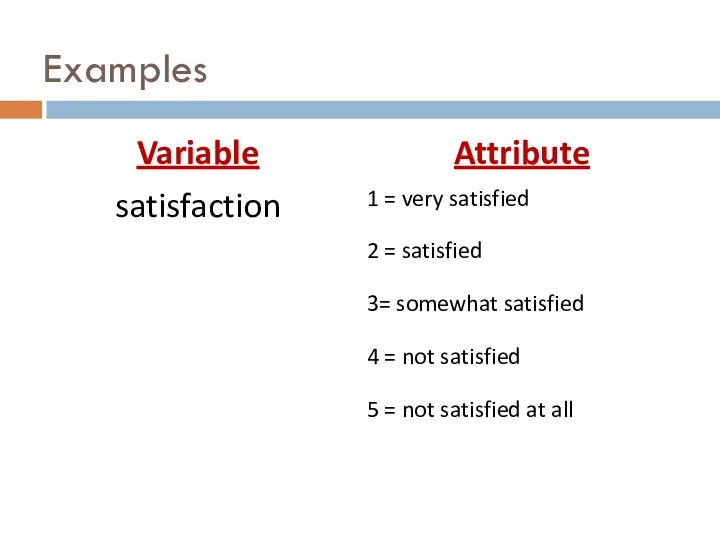
- 14. Variables variable… any observation that can take on different values attribute… a specific value on a
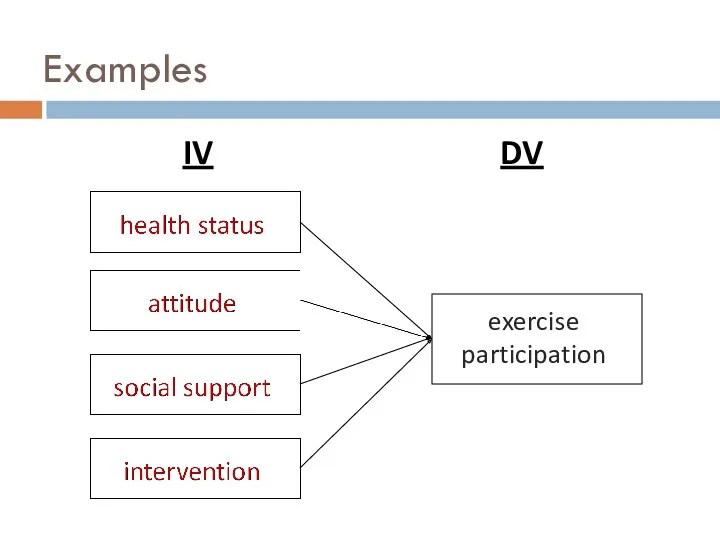
- 15. Examples
- 16. Examples
- 17. Examples
- 18. Examples
- 19. Examples
- 20. Examples
- 21. Types of Variables independent variable (IV)… what you (or nature) manipulates in some way dependent variable
- 22. Examples exercise participation
- 23. The purpose of the study was to… test whether the “Fair Play for Sport” curriculum is
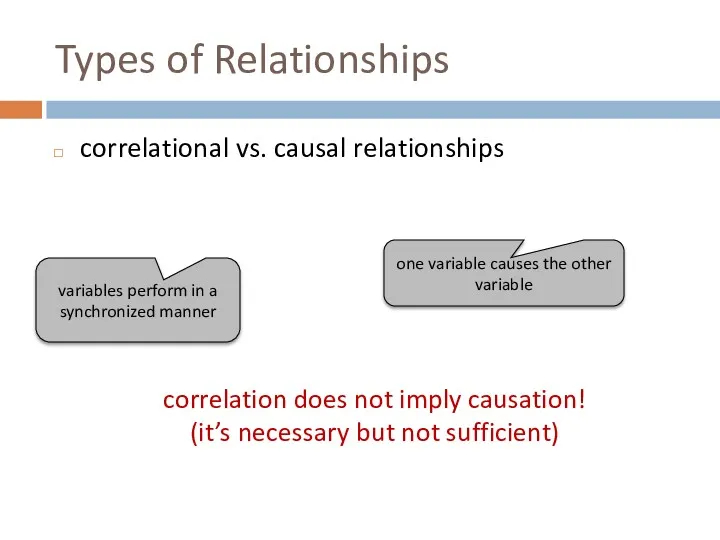
- 24. Types of Relationships correlational vs. causal relationships correlation does not imply causation! (it’s necessary but not
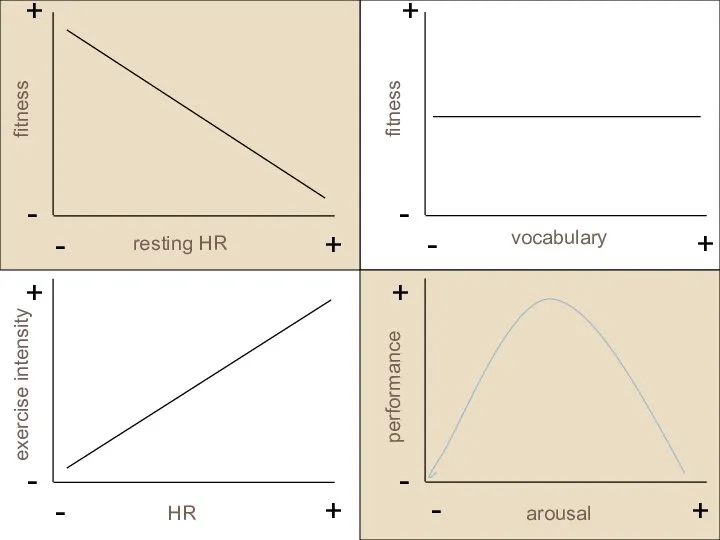
- 25. Types of Relationships patterns of relationships… no relationship positive relationship negative relationship curvilinear relationship
- 26. - + - + resting HR fitness - + - + vocabulary fitness - + -
- 27. Hypotheses hypothesis… a specific statement of prediction types of hypotheses alternative vs. null one-tailed vs. two-tailed
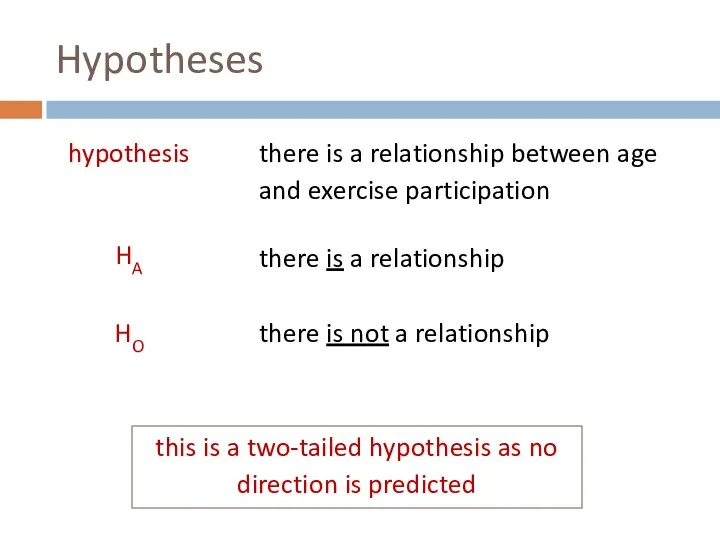
- 28. Hypotheses alternative hypothesis (HA)… An effect (that you predict) null hypothesis (HO) … Null effect
- 29. Hypotheses hypothesis there is a relationship between age and exercise participation HA there is a relationship
- 30. Hypotheses hypothesis an incentive program will increase exercise participation HA participation will increase HO participation will
- 31. Types of Data quantitative vs. qualitative
- 32. Research Fallacies fallacy… an error in reasoning (logic or premise) types of fallacies described by Trochim
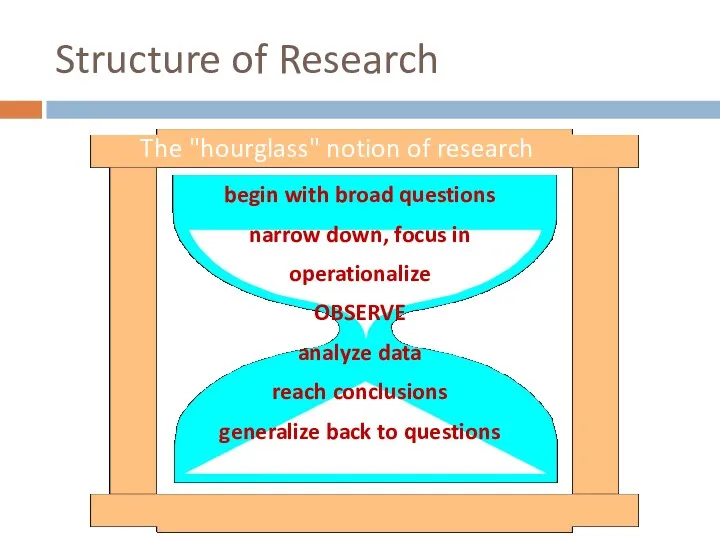
- 33. Structure of Research begin with broad questions narrow down, focus in operationalize OBSERVE analyze data reach
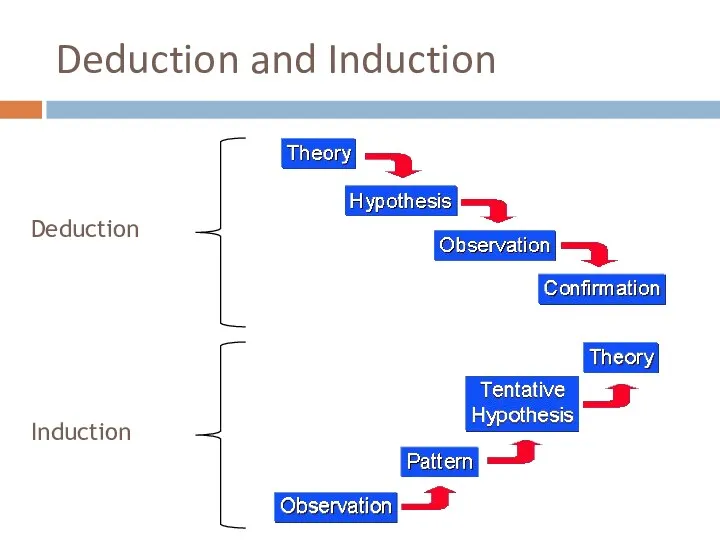
- 34. Deduction and Induction
- 35. Ethics in Research balance between protecting participants vs. quest for knowledge IRB provides one mechanism informed
- 36. Practice Questions Is the study descriptive, relational, or causal? Is the study cross-sectional or longitudinal? What
- 37. Practice Questions A. The purpose of the study was to examine the link between age and
- 38. Practice Questions B. The purpose of the study was to determine whether track athletes trained to
- 39. Practice Questions C. The study examined the effects of an acute bout of resistance training on
- 40. Practice Questions D. Participants at the 2009 Chicago Marathon were polled to determine their satisfaction with
- 41. Practice Questions E. A researcher was interested in the role of caffeine in sports performance. In
- 42. Introduction to Validity validity… the best available approximation to the truth of a given proposition, inference,
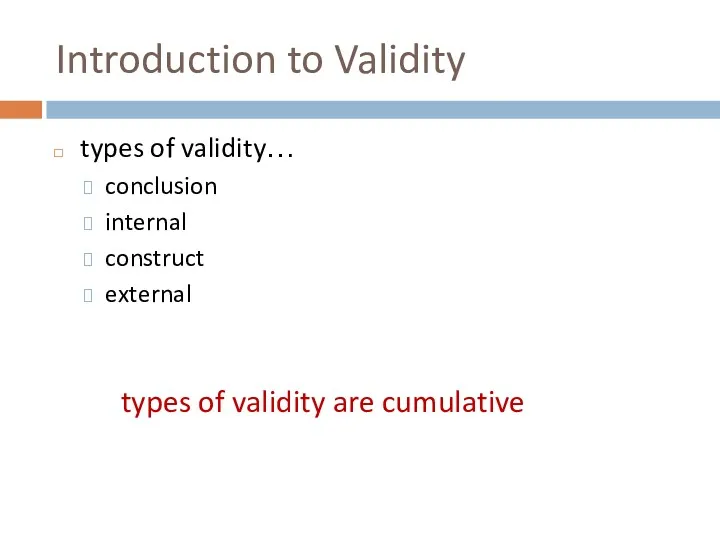
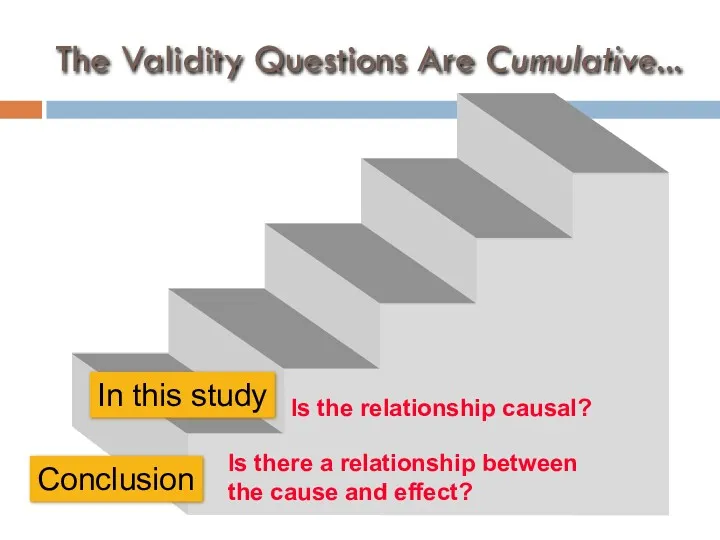
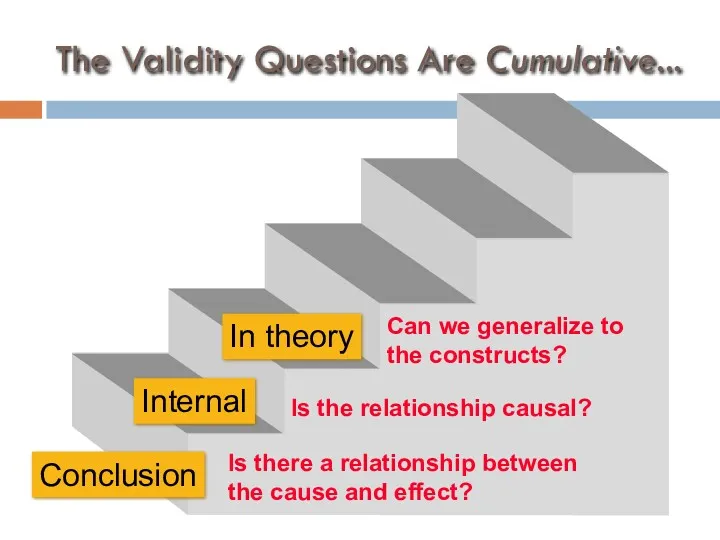
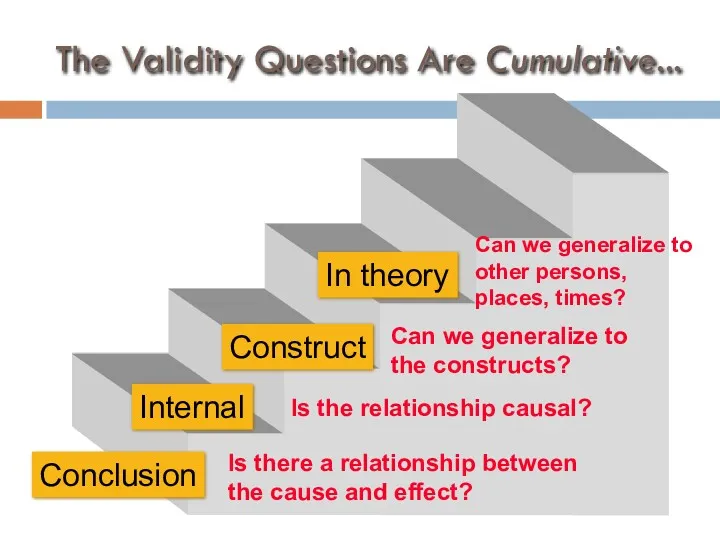
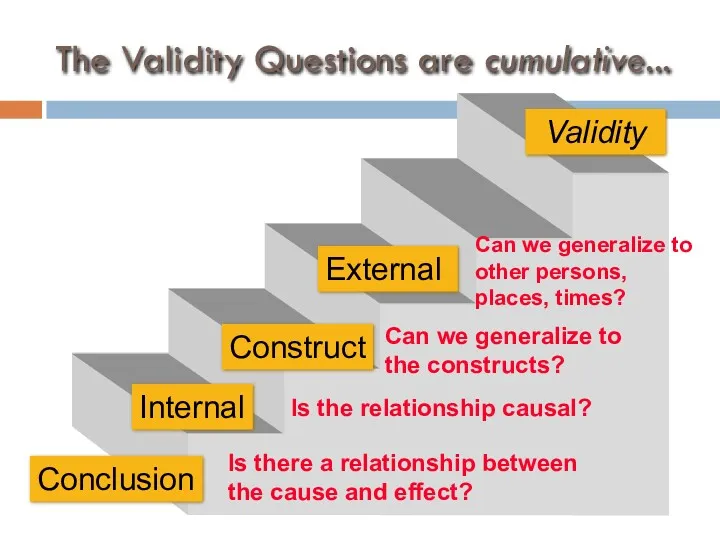
- 43. Introduction to Validity types of validity… conclusion internal construct external types of validity are cumulative
- 44. Introduction to Validity for each type of validity there are typical threats, and ways to reduce
- 45. Additional Information Describing Refereed Articles Sharing Research Findings with Clients
- 47. The Validity Questions Are Cumulative...
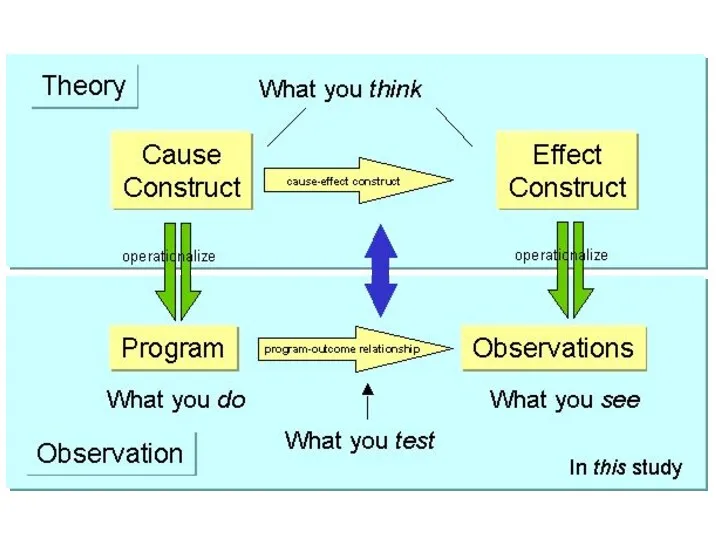
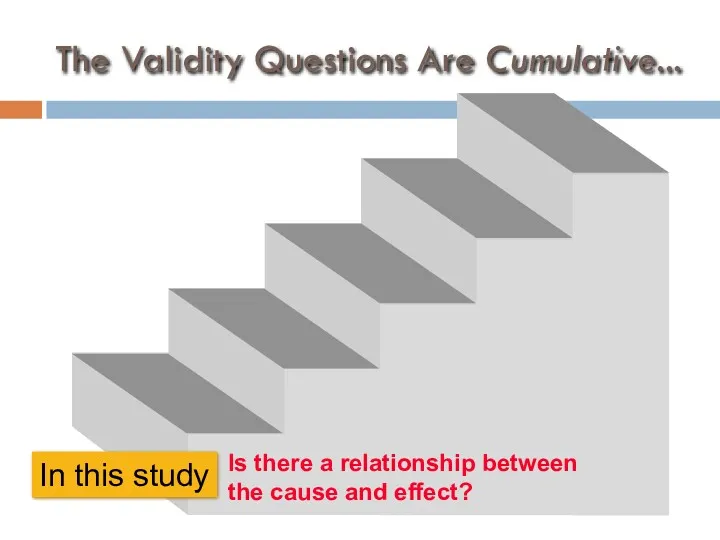
- 48. The Validity Questions Are Cumulative... In this study Is there a relationship between the cause and
- 49. The Validity Questions Are Cumulative... Conclusion Is there a relationship between the cause and effect? Is
- 50. The Validity Questions Are Cumulative... In theory Is there a relationship between the cause and effect?
- 51. The Validity Questions Are Cumulative... Construct Is there a relationship between the cause and effect? Is
- 52. The Validity Questions are cumulative... Is there a relationship between the cause and effect? Is the
- 54. Скачать презентацию































 Обновление содержания школьного образования
Обновление содержания школьного образования Дифференциация и индивидуализация в свете новых стандартов.
Дифференциация и индивидуализация в свете новых стандартов. Презентация по теме Формирование коммуникативных УУД средствами ИКТ
Презентация по теме Формирование коммуникативных УУД средствами ИКТ Об особенностях обновленных ФГОС
Об особенностях обновленных ФГОС Основы исследовательской работы в школе. Предпроектная работа в 8 классе. Проектная работа в 9 классе
Основы исследовательской работы в школе. Предпроектная работа в 8 классе. Проектная работа в 9 классе Оқушылар білімдерін, іскерліктері мен дағдыларын бақылау, бағалау және есепке алу
Оқушылар білімдерін, іскерліктері мен дағдыларын бақылау, бағалау және есепке алу Дополнительное образование детей в современной системе образования Российской Федерации
Дополнительное образование детей в современной системе образования Российской Федерации Итоговое сочинение (2018-2019 учебный год)
Итоговое сочинение (2018-2019 учебный год) Институт иностранных языков. Кафедра англистики и межкультурной коммуникации
Институт иностранных языков. Кафедра англистики и межкультурной коммуникации Содержание школьного экономического образования
Содержание школьного экономического образования ЕГЭ-2020. Приказ Минобрнауки России от 07.11.2018 N190/1512
ЕГЭ-2020. Приказ Минобрнауки России от 07.11.2018 N190/1512 Нормативные правовые акты и основные понятия ГИА
Нормативные правовые акты и основные понятия ГИА Магистерская программа Социология личности
Магистерская программа Социология личности Мастер-класс Моделирование - как один из способов формирования универсальных учебных действий
Мастер-класс Моделирование - как один из способов формирования универсальных учебных действий Презентация: Оценка и её роль в формировании рефлексии учащегося
Презентация: Оценка и её роль в формировании рефлексии учащегося ТРИЗ - педагогика в дошкольном образовании
ТРИЗ - педагогика в дошкольном образовании Добро пожаловать в Компьютерную Академию ШАГ
Добро пожаловать в Компьютерную Академию ШАГ презентация для детей Птицы Владимирского края
презентация для детей Птицы Владимирского края Технология сотрудничества как наиболее эффективная технология дифференцированного обучения
Технология сотрудничества как наиболее эффективная технология дифференцированного обучения Формирование читательской компетентности как базовой основы ключевых компетенций учащихся
Формирование читательской компетентности как базовой основы ключевых компетенций учащихся Организационное собрание студентов 1 курса педиатрического факультета
Организационное собрание студентов 1 курса педиатрического факультета Программы академической мобильности. Стипендия президента РФ для обучения за рубежом
Программы академической мобильности. Стипендия президента РФ для обучения за рубежом Основные рекомендации первокурсникам. Сочинский государственный университет
Основные рекомендации первокурсникам. Сочинский государственный университет Факультет информационных технологий и робототехники
Факультет информационных технологий и робототехники Калифорния университеті
Калифорния университеті Иностранные языки в НИУ ВШЭ
Иностранные языки в НИУ ВШЭ Система дошкольного образования в Республике Беларусь
Система дошкольного образования в Республике Беларусь О введении федеральных основных общеобразовательных программ и стандартов общего образования
О введении федеральных основных общеобразовательных программ и стандартов общего образования