Содержание
- 2. Class #1 – Risk Management 1 Course Objectives, Program and Dynamics 2 Risk, Uncertainty and Complexity
- 3. Class #1 – Risk Management 1 Course Objectives, Program and Dynamics 2 Risk, Uncertainty and Complexity
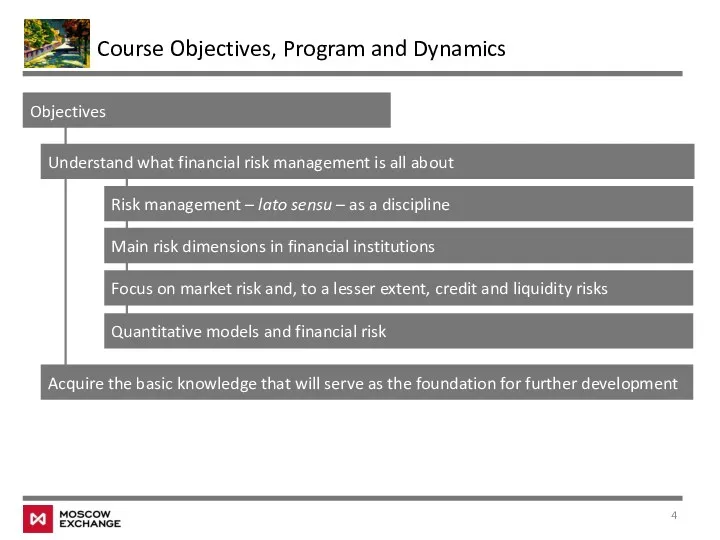
- 4. Course Objectives, Program and Dynamics Objectives Understand what financial risk management is all about Risk management
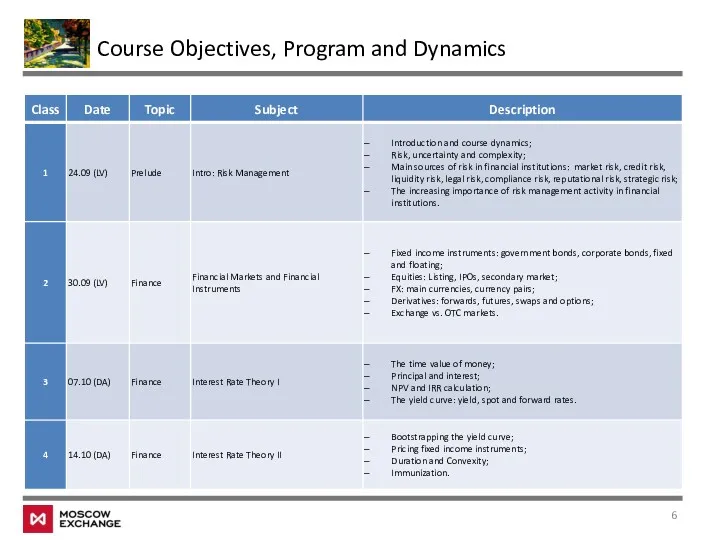
- 5. Course Objectives, Program and Dynamics Format 14 classes during 3 ½ months Handouts, bibliography, exercises Individual
- 6. Course Objectives, Program and Dynamics
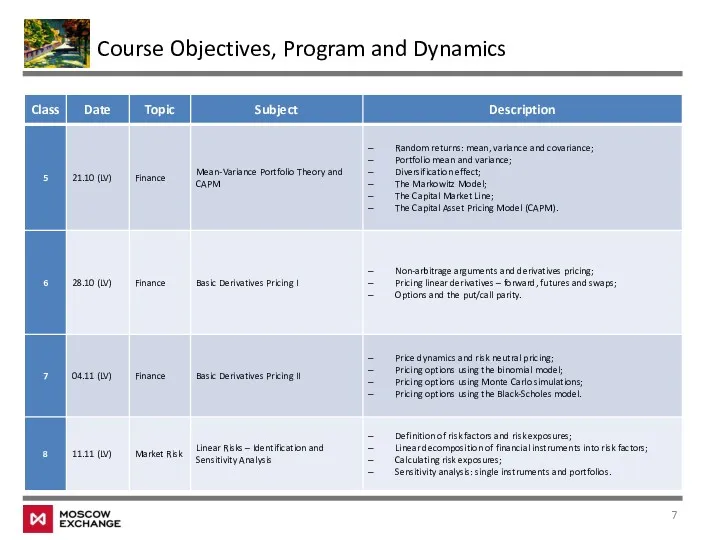
- 7. Course Objectives, Program and Dynamics
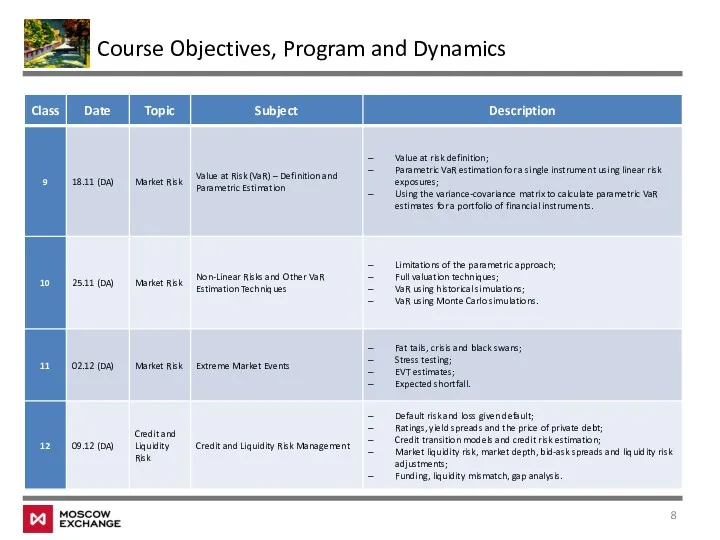
- 8. Course Objectives, Program and Dynamics
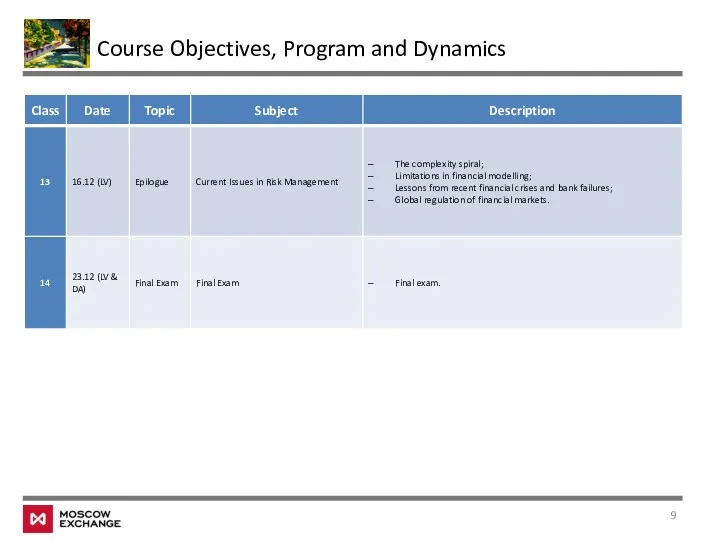
- 9. Course Objectives, Program and Dynamics
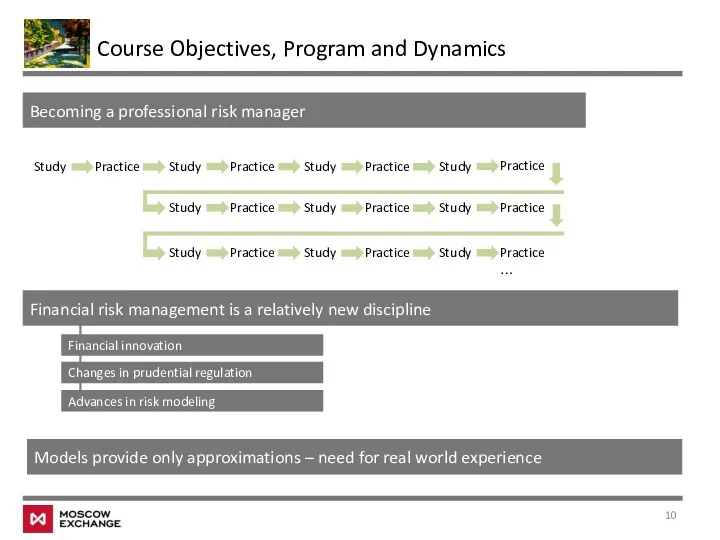
- 10. Course Objectives, Program and Dynamics Becoming a professional risk manager Study Practice Study Practice Study Practice
- 11. Class #1 – Risk Management 1 Course Objectives, Program and Dynamics 2 Risk, Uncertainty and Complexity
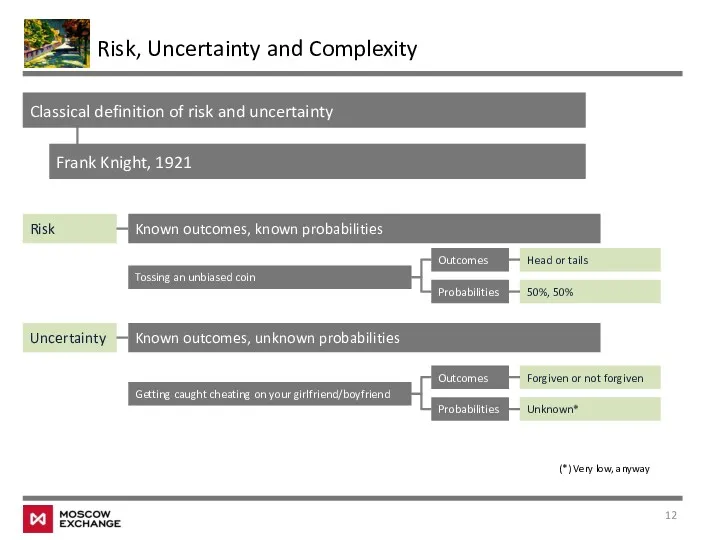
- 12. Risk, Uncertainty and Complexity Classical definition of risk and uncertainty Risk Uncertainty Known outcomes, known probabilities
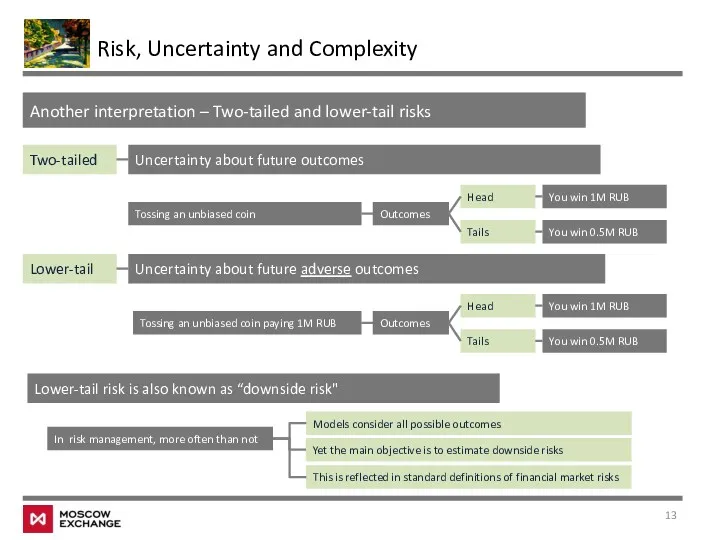
- 13. Risk, Uncertainty and Complexity Another interpretation – Two-tailed and lower-tail risks Two-tailed Uncertainty about future outcomes
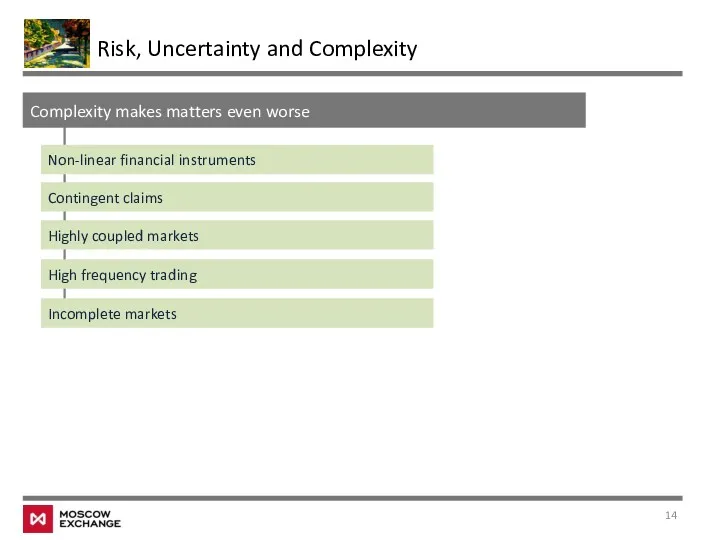
- 14. Risk, Uncertainty and Complexity Complexity makes matters even worse Non-linear financial instruments Contingent claims Highly coupled
- 15. Class #1 – Risk Management 1 Course Objectives, Program and Dynamics 2 Risk, Uncertainty and Complexity
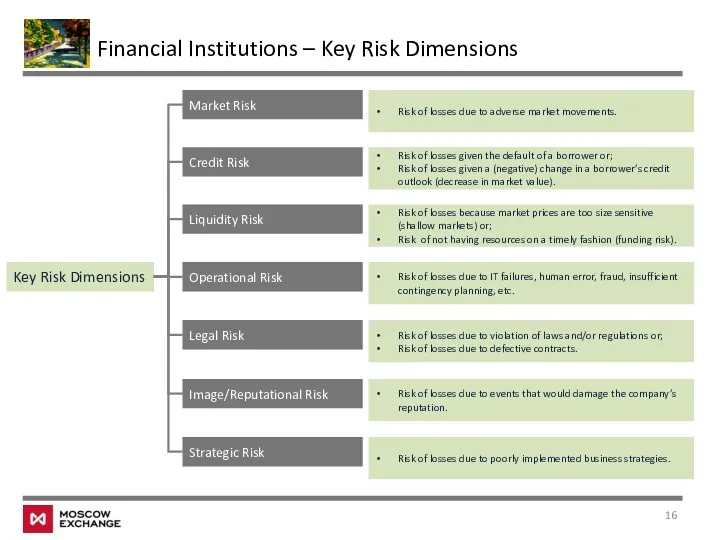
- 16. Financial Institutions – Key Risk Dimensions Key Risk Dimensions Market Risk Credit Risk Liquidity Risk Operational
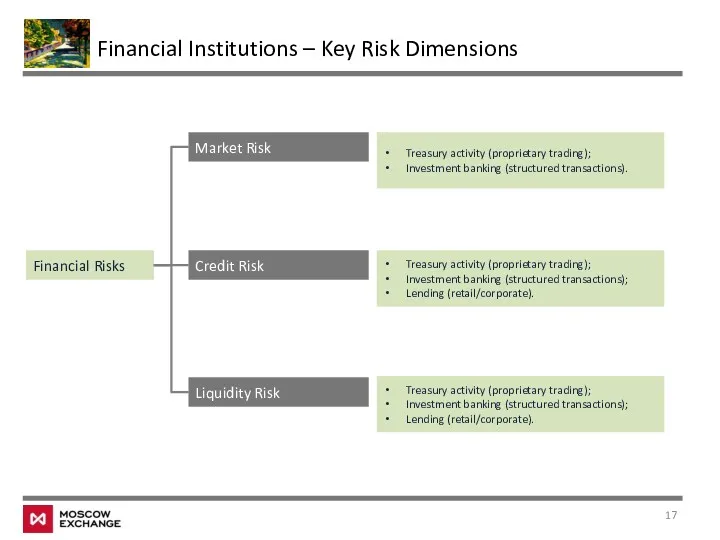
- 17. Financial Institutions – Key Risk Dimensions Financial Risks Market Risk Credit Risk Liquidity Risk Treasury activity
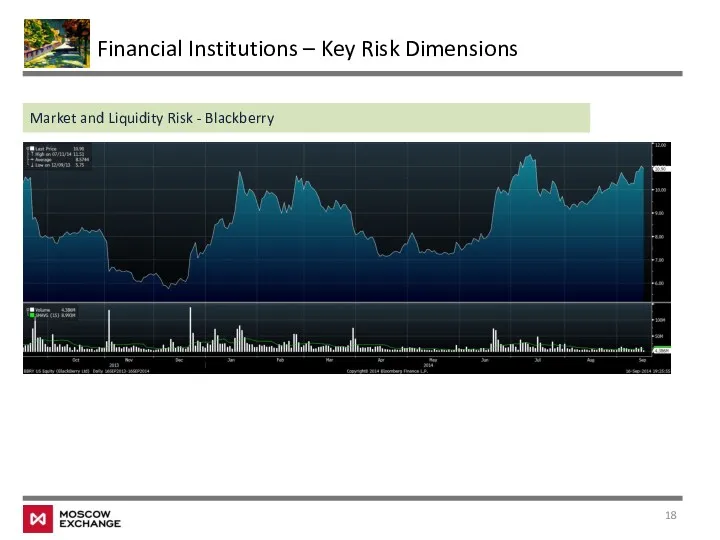
- 18. Financial Institutions – Key Risk Dimensions Market and Liquidity Risk - Blackberry
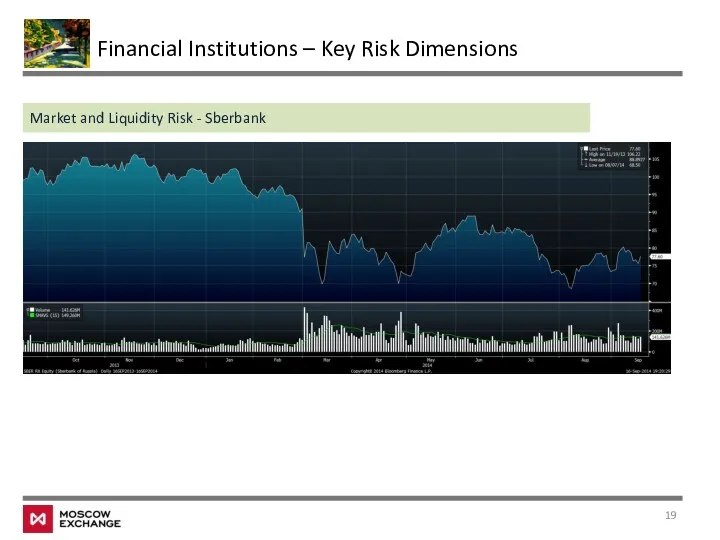
- 19. Financial Institutions – Key Risk Dimensions Market and Liquidity Risk - Sberbank
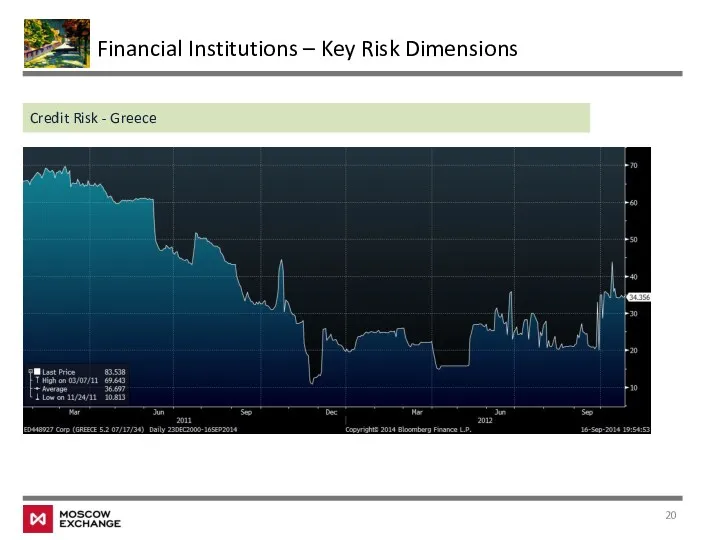
- 20. Financial Institutions – Key Risk Dimensions Credit Risk - Greece
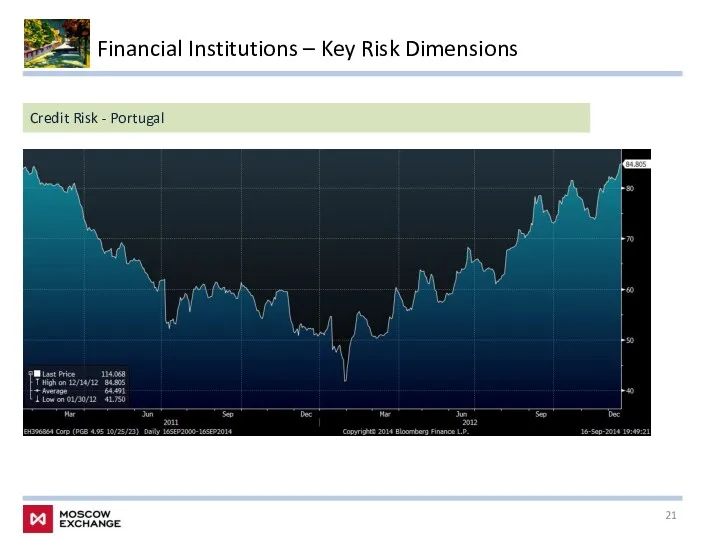
- 21. Financial Institutions – Key Risk Dimensions Credit Risk - Portugal
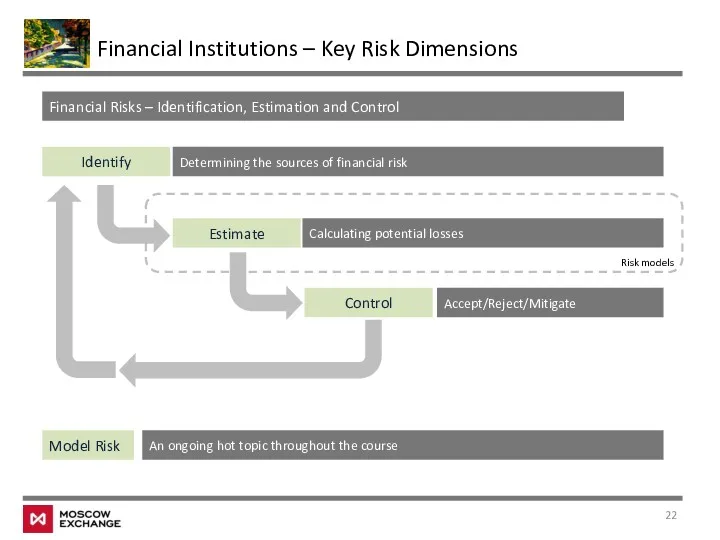
- 22. Financial Institutions – Key Risk Dimensions Identify Estimate Control Financial Risks – Identification, Estimation and Control
- 23. Class #1 – Risk Management 1 Course Objectives, Program and Dynamics 2 Risk, Uncertainty and Complexity
- 24. The Increasing Importance of Financial Risk Management From the financial sector perspective Financial innovation creates new
- 25. The Increasing Importance of Financial Risk Management Financial Innovation Is there a real social benefit in
- 26. Class #1 – Risk Management 1 Course Objectives, Program and Dynamics 2 Risk, Uncertainty and Complexity
- 27. Annex Useful References Risk Management and Financial Institutions, John Hull, (2012); Value at Risk: The New
- 29. Скачать презентацию




 Как составить бизнес-план
Как составить бизнес-план Як змінити систему роботи навчальних закладів, щоб зробити їх незалежними майже від всіх коштів, які витрачає держава на їх
Як змінити систему роботи навчальних закладів, щоб зробити їх незалежними майже від всіх коштів, які витрачає держава на їх Моё портфолио
Моё портфолио Организация внеурочной деятельности в начальной школе
Организация внеурочной деятельности в начальной школе Подготовка и проведение государственной итоговой аттестации в 2022 году
Подготовка и проведение государственной итоговой аттестации в 2022 году Мектеп – құқықтық кеңістік
Мектеп – құқықтық кеңістік Реализация ФГОС начального общего образования средствами УМК ШКОЛА РОССИИ
Реализация ФГОС начального общего образования средствами УМК ШКОЛА РОССИИ Система військової освіти в Україні
Система військової освіти в Україні Кафедра радиоэлектроники и защиты информации. Информационная безопасность автоматизированных систем
Кафедра радиоэлектроники и защиты информации. Информационная безопасность автоматизированных систем Электронная библиотека Издательского дома Гребенников: стратегия работы с авторами и образовательными учебными заведениями
Электронная библиотека Издательского дома Гребенников: стратегия работы с авторами и образовательными учебными заведениями Оқытудың жаңа инновациялық технологиялары
Оқытудың жаңа инновациялық технологиялары Познакомьтесь: Наша школа!
Познакомьтесь: Наша школа! Как разработать ООП по новым ФГОС НОО и ООО
Как разработать ООП по новым ФГОС НОО и ООО Психолого-педагогическое сопровождение детей с ОВЗ
Психолого-педагогическое сопровождение детей с ОВЗ Организация и проведение урока – исследования в начальной школе
Организация и проведение урока – исследования в начальной школе Нобелевская премия
Нобелевская премия Russia Theme4
Russia Theme4 Аттестации педагогических работников на 2016 год
Аттестации педагогических работников на 2016 год Montpellier business school
Montpellier business school Классификация здоровьесберегающих технологий: общая характеристика
Классификация здоровьесберегающих технологий: общая характеристика Учебно-методическая поддержка учителей при подготовке обучающихся к написанию итогового сочинения по литературе
Учебно-методическая поддержка учителей при подготовке обучающихся к написанию итогового сочинения по литературе Przedszkole mini Harvard
Przedszkole mini Harvard Отчет по производственной практике
Отчет по производственной практике Информационные технологии в образовании
Информационные технологии в образовании Механизм организации производственной практики студентов
Механизм организации производственной практики студентов Нормативно-правовая база, регламентирующая работу с детьми с ОВЗ и детьми-инвалидами в образовательных организациях
Нормативно-правовая база, регламентирующая работу с детьми с ОВЗ и детьми-инвалидами в образовательных организациях Морские кадетские классы
Морские кадетские классы Портфолио ученика, как интегративная оценка результатов деятельности в рамках реализации ФГОС
Портфолио ученика, как интегративная оценка результатов деятельности в рамках реализации ФГОС