Содержание
- 2. 1 Definition of risk factors 2 Linear decomposition of financial instruments into risk factors 4 Sensitivity
- 3. Class #8 – Linear Risks 1 Definition of risk factors and risk exposures 2 Linear decomposition
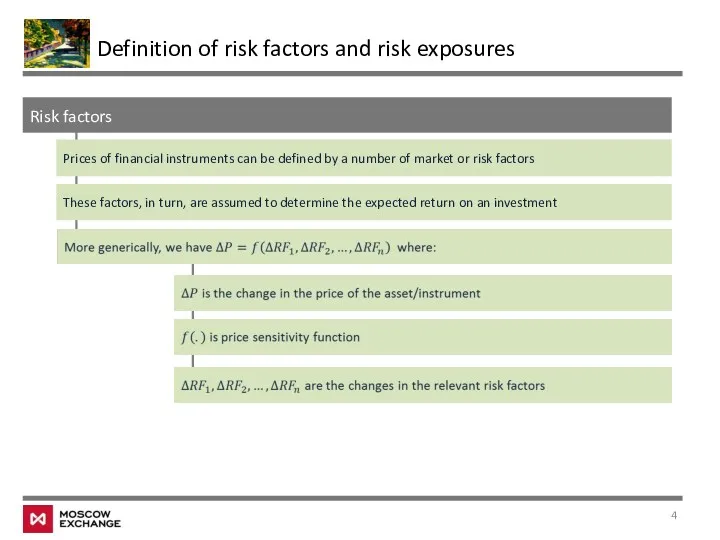
- 4. Risk factors Prices of financial instruments can be defined by a number of market or risk
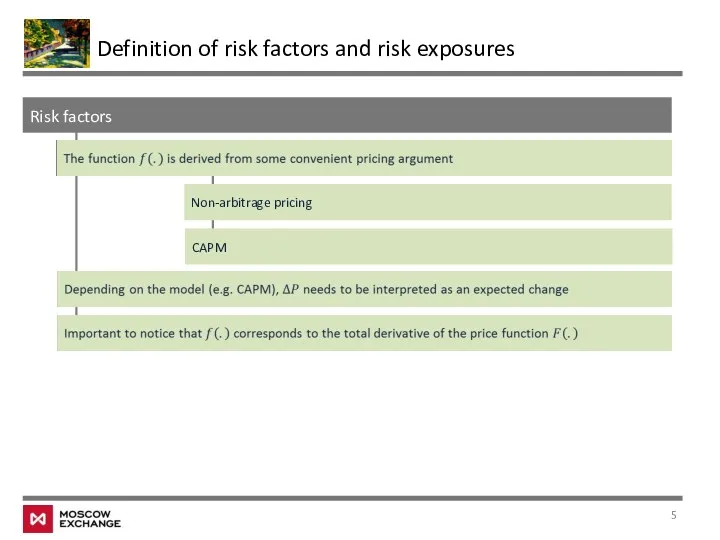
- 5. Risk factors Non-arbitrage pricing Definition of risk factors and risk exposures CAPM
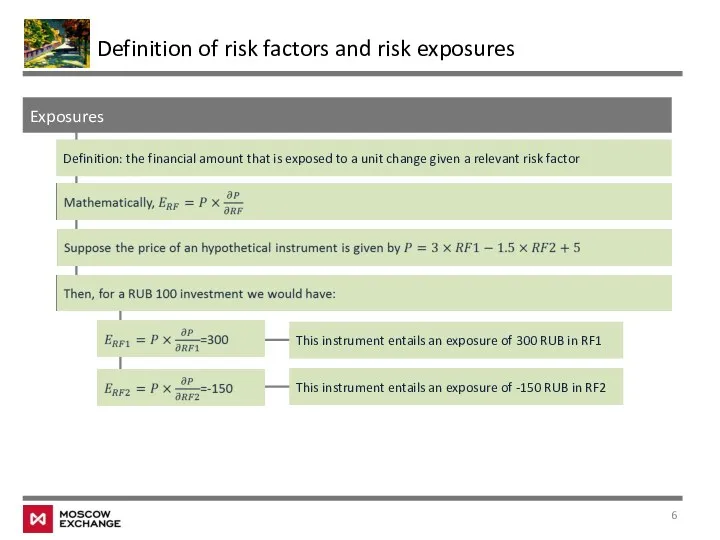
- 6. Exposures Definition: the financial amount that is exposed to a unit change given a relevant risk
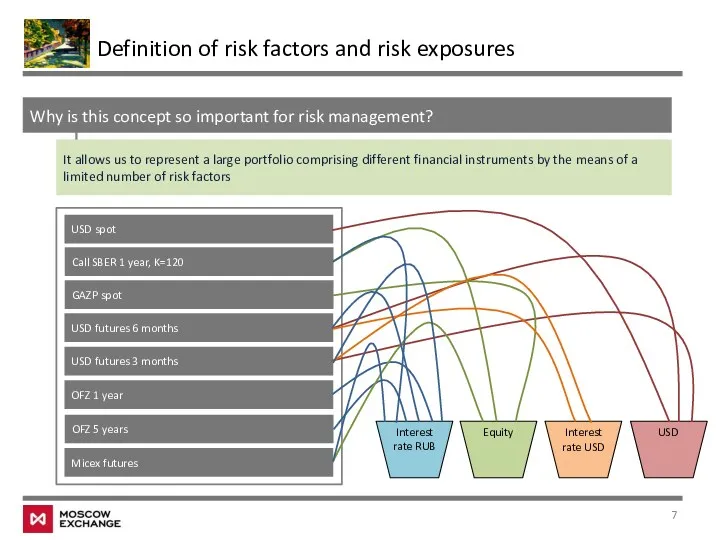
- 7. Why is this concept so important for risk management? It allows us to represent a large
- 8. Class #8 – Linear Risks 1 Definition of risk factors and risk exposures 2 Linear decomposition
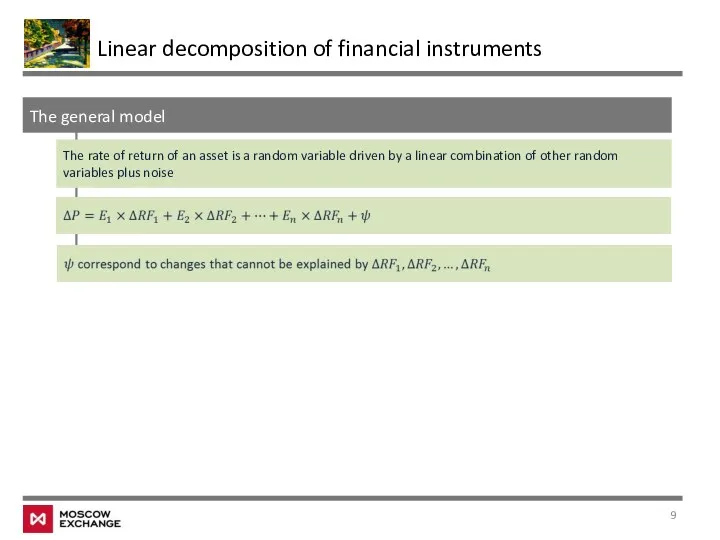
- 9. The general model The rate of return of an asset is a random variable driven by
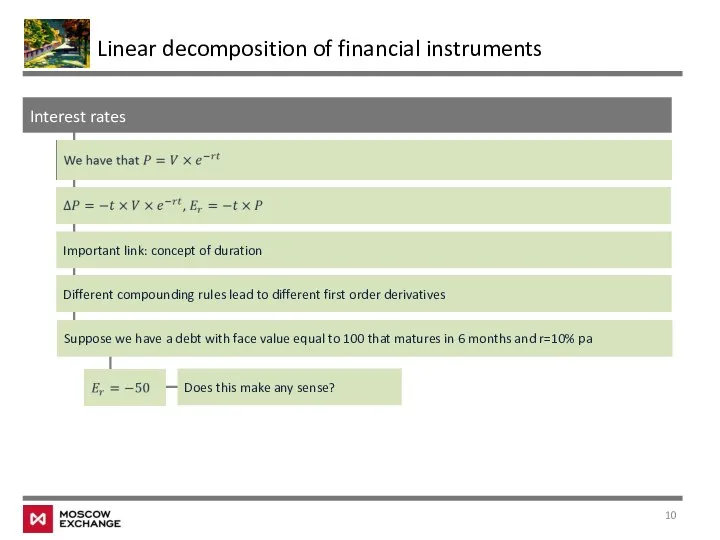
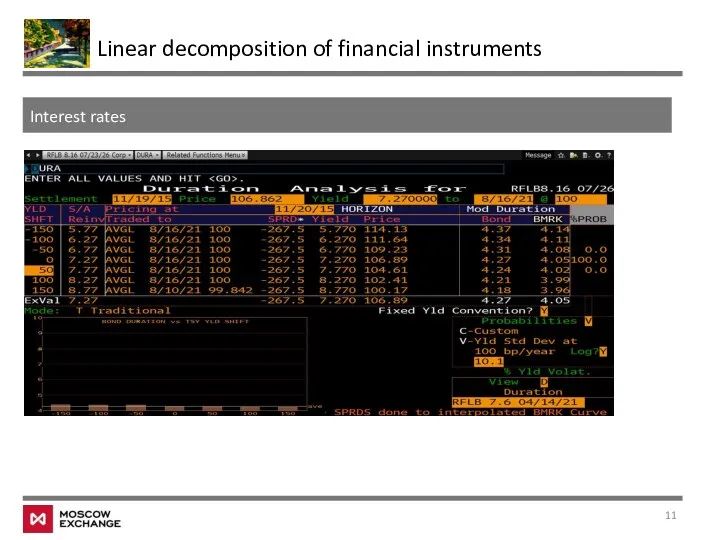
- 10. Interest rates Linear decomposition of financial instruments Suppose we have a debt with face value equal
- 11. Interest rates Linear decomposition of financial instruments
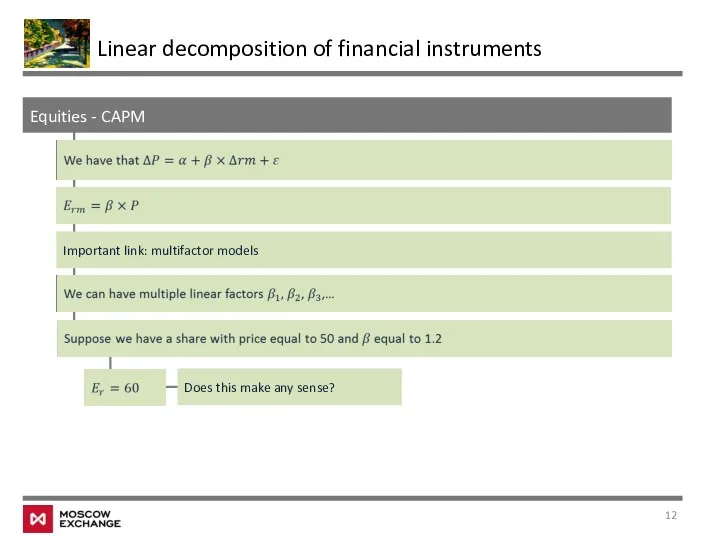
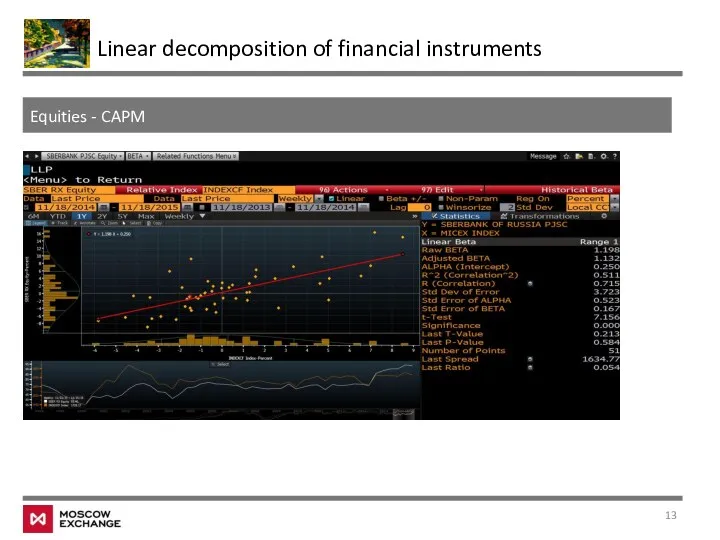
- 12. Equities - CAPM Linear decomposition of financial instruments Important link: multifactor models Does this make any
- 13. Equities - CAPM Linear decomposition of financial instruments
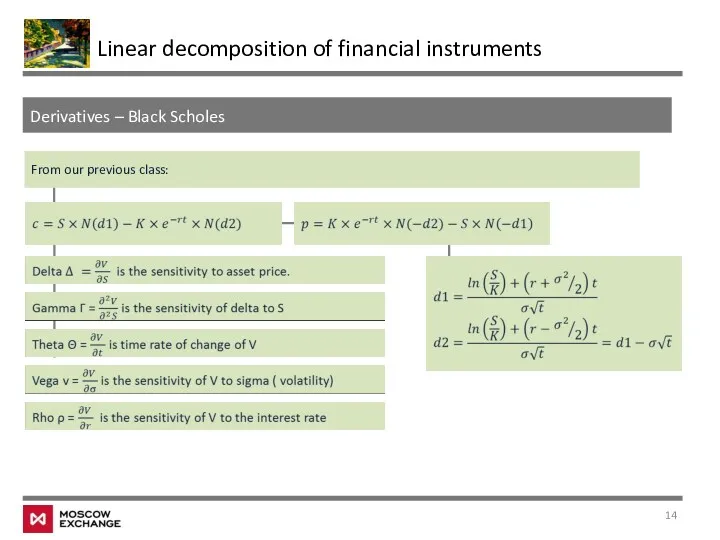
- 14. Derivatives – Black Scholes Linear decomposition of financial instruments From our previous class:
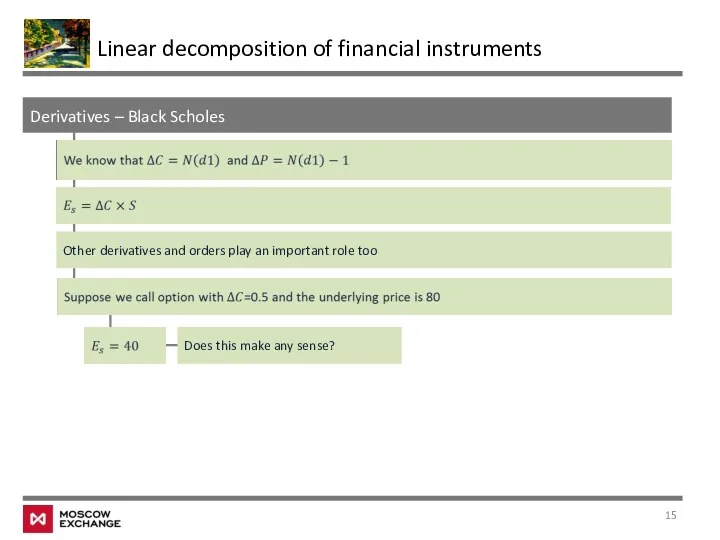
- 15. Derivatives – Black Scholes Linear decomposition of financial instruments Other derivatives and orders play an important
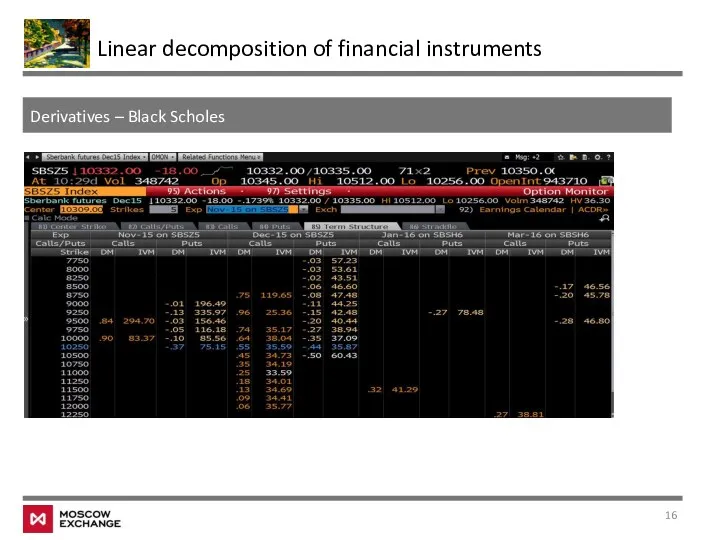
- 16. Derivatives – Black Scholes Linear decomposition of financial instruments
- 17. Class #8 – Linear Risks 1 Definition of risk factors and risk exposures 2 Linear decomposition
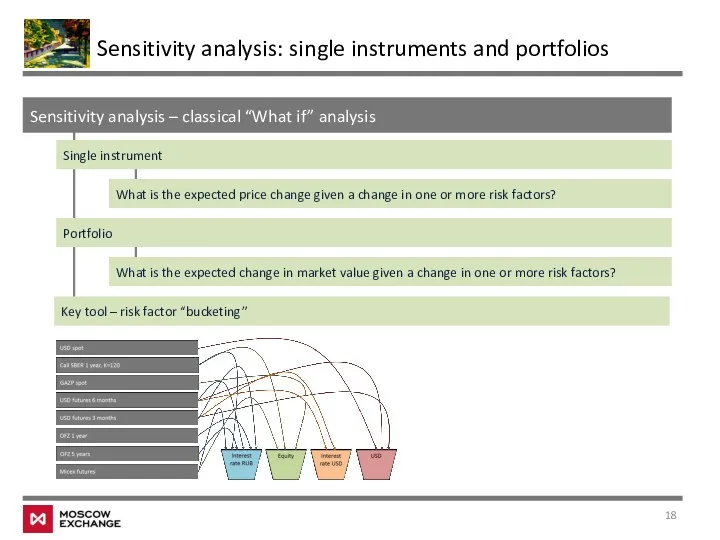
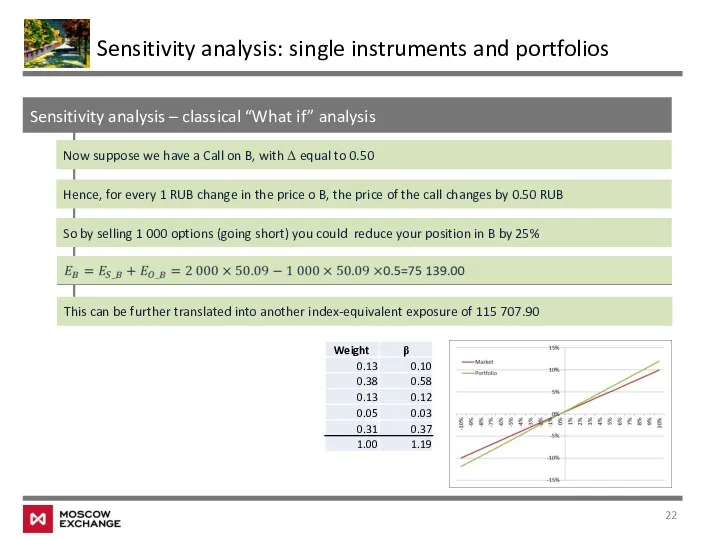
- 18. Sensitivity analysis – classical “What if” analysis Sensitivity analysis: single instruments and portfolios Single instrument What
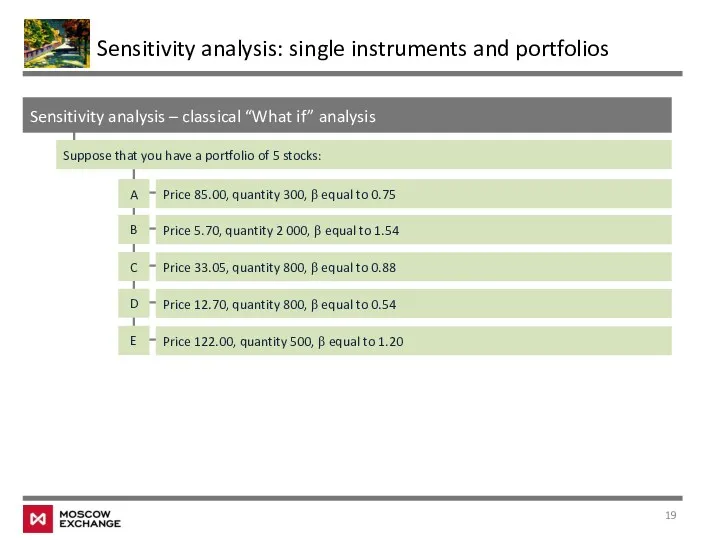
- 19. Sensitivity analysis – classical “What if” analysis Sensitivity analysis: single instruments and portfolios Suppose that you
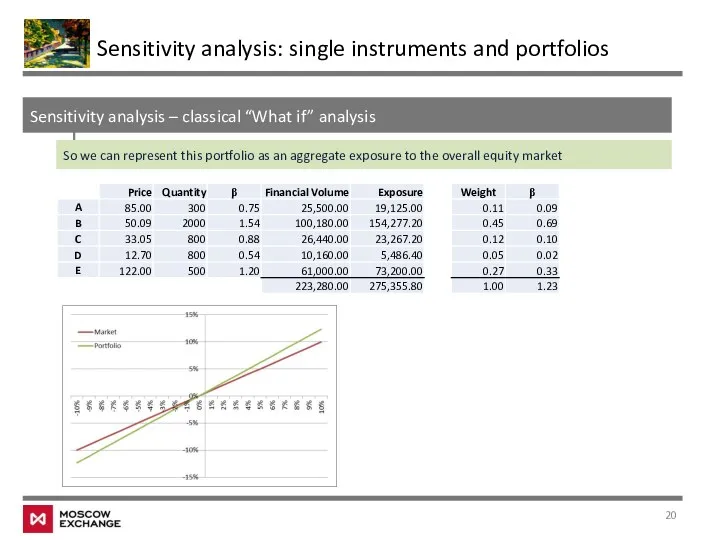
- 20. Sensitivity analysis – classical “What if” analysis Sensitivity analysis: single instruments and portfolios So we can
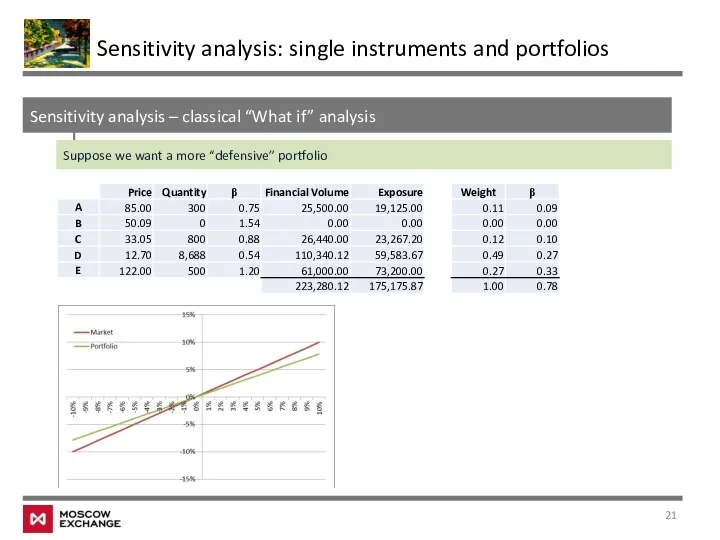
- 21. Sensitivity analysis – classical “What if” analysis Sensitivity analysis: single instruments and portfolios Suppose we want
- 22. Sensitivity analysis – classical “What if” analysis Sensitivity analysis: single instruments and portfolios Now suppose we
- 24. Скачать презентацию
 Проблемы формулирования при изложении научных исследований
Проблемы формулирования при изложении научных исследований Презентация Требования ФГОС к написанию программы отдельного учебного предмета на примере УМК Перспективная начальная школа
Презентация Требования ФГОС к написанию программы отдельного учебного предмета на примере УМК Перспективная начальная школа Вводный урок по обществознанию 9 класс
Вводный урок по обществознанию 9 класс Жоо-дағы студенттердің оқу үрдісіне әсер ететін факторлар
Жоо-дағы студенттердің оқу үрдісіне әсер ететін факторлар Мастер-класс Преемственность предпрофильной подготовки между начальным и средним звеном
Мастер-класс Преемственность предпрофильной подготовки между начальным и средним звеном Педагогический баттл-16
Педагогический баттл-16 Исследование опыта подготовки кадров парикмахеров в системе СПО
Исследование опыта подготовки кадров парикмахеров в системе СПО Как подготовить курсовую работу
Как подготовить курсовую работу Колледж экономики, управления и права ДГТУ. История. Цели и задачи курса
Колледж экономики, управления и права ДГТУ. История. Цели и задачи курса Новые поступления литературы в НБ УГГУ. Учебные пособия
Новые поступления литературы в НБ УГГУ. Учебные пособия Отчет по производственной практике
Отчет по производственной практике Конспект непосредственно образовательной деятельности с использованием электронных образовательных ресурсов (презентация) с детьми старшего дошкольного возраста.Русский народный костюм – хранитель истории
Конспект непосредственно образовательной деятельности с использованием электронных образовательных ресурсов (презентация) с детьми старшего дошкольного возраста.Русский народный костюм – хранитель истории Основная образовательная программа дошкольного образования Детского сада Мэри Поппинс
Основная образовательная программа дошкольного образования Детского сада Мэри Поппинс Планирование работы БОУ города Омска Казачья кадетская школа-интернат среднего общего образования на 2023/2024 гг
Планирование работы БОУ города Омска Казачья кадетская школа-интернат среднего общего образования на 2023/2024 гг Методология научных исследований
Методология научных исследований Роль организаторов при проведении устной части ОГЭ по иностранным языкам, русскому языку, физике, информатике и ИКТ, географии
Роль организаторов при проведении устной части ОГЭ по иностранным языкам, русскому языку, физике, информатике и ИКТ, географии Київський професійний будівельний ліцей. Професія - опоряджувальник будівельний
Київський професійний будівельний ліцей. Професія - опоряджувальник будівельний ФГОС: первый опыт, проблемы и перспективы
ФГОС: первый опыт, проблемы и перспективы VII региональный конкурс ученических инициатив Молодежь Севастополя – взгляд в будущее!
VII региональный конкурс ученических инициатив Молодежь Севастополя – взгляд в будущее! Мобильное электронное образование для детей с ОВЗ. Инклюзивное образование
Мобильное электронное образование для детей с ОВЗ. Инклюзивное образование Современный урок
Современный урок Технологические направления (образовательные программы)
Технологические направления (образовательные программы) Наша школа- наши учителя. Республика Коми, район Сосногорск, поселок городского типа Войвож
Наша школа- наши учителя. Республика Коми, район Сосногорск, поселок городского типа Войвож Інавацыйнае развіццё. Планшэт у адукацыі
Інавацыйнае развіццё. Планшэт у адукацыі Анализ предметной области. Понятие бизнес-процессов
Анализ предметной области. Понятие бизнес-процессов Всероссийский образовательный СТЕМ-проект Закрутим спираль
Всероссийский образовательный СТЕМ-проект Закрутим спираль Шаблон презентации проекта
Шаблон презентации проекта Красноярский государственный педагогический университет. Бизнес-психология. Институт психолого-педагогического образования
Красноярский государственный педагогический университет. Бизнес-психология. Институт психолого-педагогического образования