Содержание
- 2. FORMAL LESSON PLAN By the end of this session you will be able to: Identify the
- 3. PLANNING PARADOX Prepare thoroughly, But teach the learners, not the plan… Jim Scrivener
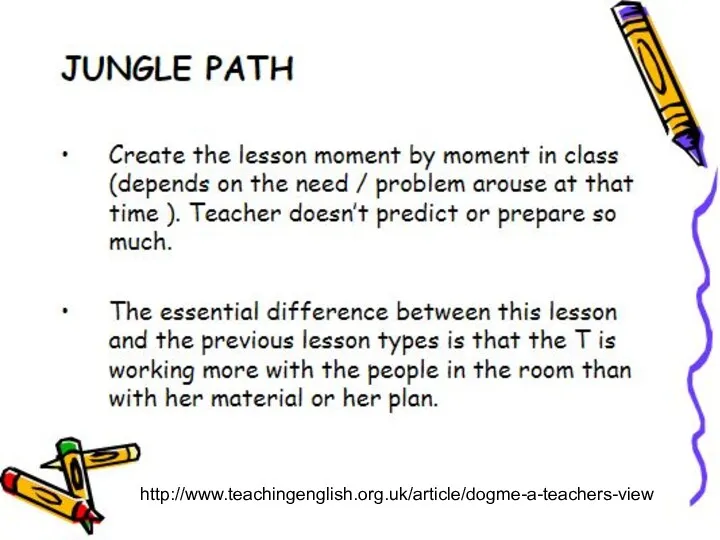
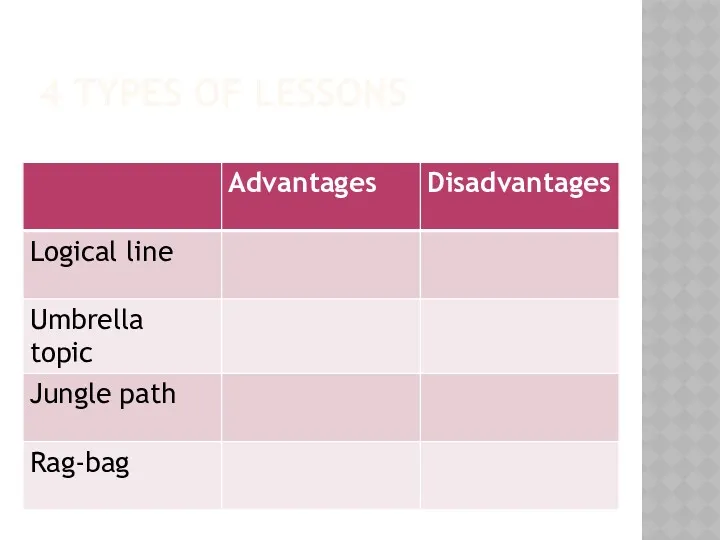
- 4. DIFFERENT LESSON FORMATS Logical line Topic umbrella Jungle path Rag-bag (J. Scrivener Learning teaching 2005)
- 7. http://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/article/dogme-a-teachers-view
- 9. 4 TYPES OF LESSONS
- 10. WHY PLAN AT ALL? The writing of lesson plans has a number of important functions for
- 11. FORMAL LESSON PLANNING Usually two pages background page procedure page sometimes, also includes language analysis of
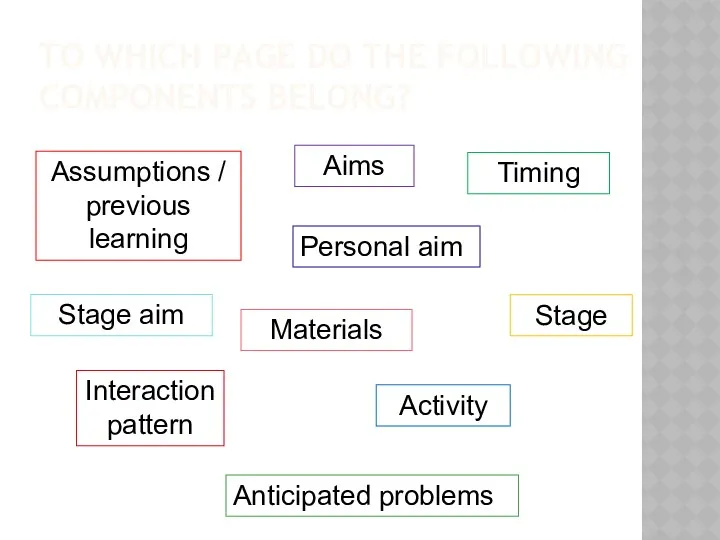
- 12. TO WHICH PAGE DO THE FOLLOWING COMPONENTS BELONG? Assumptions / previous learning Aims Timing Stage aim
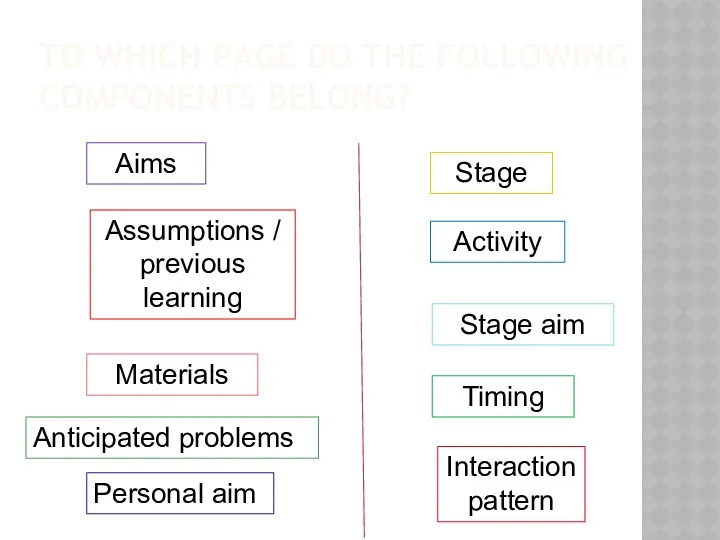
- 13. TO WHICH PAGE DO THE FOLLOWING COMPONENTS BELONG? Assumptions / previous learning Aims Timing Stage aim
- 14. BACKGROUND PAGE INCLUDES: Information about the class (age, level, background etc.) Information about the teacher and
- 15. TO WHAT PART OF THE PLAN DO THESE COMPONENTS BELONG? Reducing my TTT; get silent students
- 16. MAIN AIMS Describing aims What we are teaching or in terms of outcomes What the students
- 17. LESSON AIMS Describe what we want our students to be able to do after instruction What
- 18. LESSON AIMS ARE IMPORTANT BECAUSE ... teacher trainers (and directors of schools) require them they make
- 19. TYPICAL MISTAKE Trainee teachers typically use procedure aims instead of achievement aims Procedure aims – what
- 20. PROCEDURE OR ACHIEVEMENT? Students will be better able to ask and answer informal questions about a
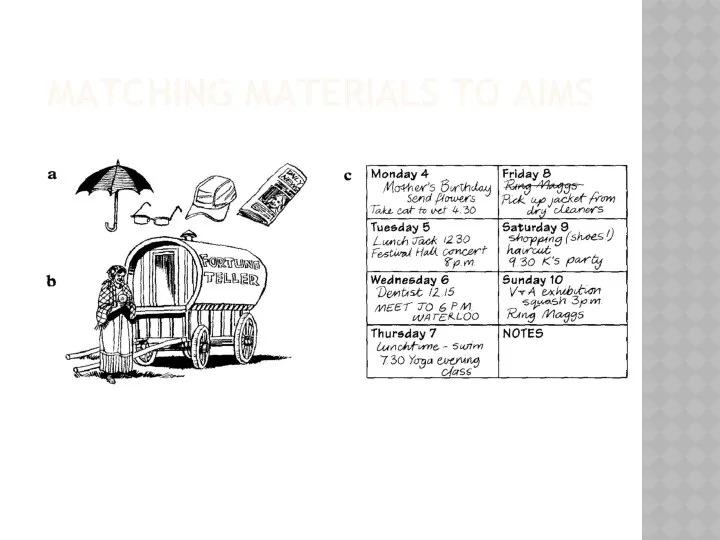
- 21. MATCHING MATERIALS TO AIMS
- 23. Скачать презентацию















 Анализ работы РМО учителей иностранного языка
Анализ работы РМО учителей иностранного языка Город мастеров. Виртуальная выставка
Город мастеров. Виртуальная выставка Система внеурочной деятельности Небоскрёб
Система внеурочной деятельности Небоскрёб Трудный диалог с учёбой или как помочь своему ребёнку учиться. Презентация к родительскому собранию
Трудный диалог с учёбой или как помочь своему ребёнку учиться. Презентация к родительскому собранию Адаптированная программа Семь вершин успеха
Адаптированная программа Семь вершин успеха Уральская Академии лидерства
Уральская Академии лидерства Творческий проект по технологии Топор-вешалка
Творческий проект по технологии Топор-вешалка Сценарий урока Знаний для 2 класса
Сценарий урока Знаний для 2 класса Профессия программист
Профессия программист Фрукты
Фрукты Практикум по организации культурно-просветительской и социально -педагогической деятельности
Практикум по организации культурно-просветительской и социально -педагогической деятельности Консультация - презентация Смена образовательной парадигмы. Реализация ФГТ в ДОУ
Консультация - презентация Смена образовательной парадигмы. Реализация ФГТ в ДОУ Пять простых правил, чтобы не иметь проблем с долгами.
Пять простых правил, чтобы не иметь проблем с долгами. Поделка Символ года
Поделка Символ года ЛОГИЧЕСКИЕ ЗАДАЧИ
ЛОГИЧЕСКИЕ ЗАДАЧИ Итоговое адаптационное занятие по теме Осень
Итоговое адаптационное занятие по теме Осень Нетрадиционные формы обучения. Вальдорфская педагогика
Нетрадиционные формы обучения. Вальдорфская педагогика праздник алфавита
праздник алфавита Внеклассное мероприятие За то, чтобы мы просто жили ( о героях настоящего времени) Диск
Внеклассное мероприятие За то, чтобы мы просто жили ( о героях настоящего времени) Диск Отчет по учебно-ознакомительной практике в газете Пермский университет
Отчет по учебно-ознакомительной практике в газете Пермский университет 21 октября - Международный день мира
21 октября - Международный день мира Духовно- нравственное воспитание
Духовно- нравственное воспитание Презентация к классному часу по профориентации
Презентация к классному часу по профориентации Диагностическая компетентность преподавателя
Диагностическая компетентность преподавателя День защиты детей в детском саду
День защиты детей в детском саду Цветы из фоамирана
Цветы из фоамирана Своя игра. Невский проспект
Своя игра. Невский проспект Методика проведения беседы в дошкольном образовательном учреждении
Методика проведения беседы в дошкольном образовательном учреждении