Слайд 2
![Общая форма одномерного индексатора тип_элемента this[int индекс] { // Аксессор](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/73754/slide-1.jpg)
Общая форма одномерного индексатора
тип_элемента this[int индекс]
{
// Аксессор для получения
данных
get
{
// Возврат значения, которое определяет индекс.
}
// Аксессор для установки данных
set
{
// Установка значения, которое определяет индекс.
}
}
Слайд 3
![Пример применения индексатора public class AClass1 { int[] imyArray =](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/73754/slide-2.jpg)
Пример применения индексатора
public class AClass1
{
int[] imyArray = new
int[20];
public int this[int ind1]
{
get
{ return imyArray[ind1]; }
set
{ imyArray[ind1] = value; }
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
AClass1 Ac1 = new AClass1();
Random ran = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
Ac1[i] = ran.Next(1, 100);
Console.Write("{0}\t", Ac1[i]);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
Слайд 4
![Применение двумерных индексаторов public class AClass1 { int[] imyArray =](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/73754/slide-3.jpg)
Применение двумерных индексаторов
public class AClass1
{
int[] imyArray = new
int[20];
int[,] imyArray1 = new int[20,10];
public int this[int ind1]
{
get
{ return imyArray[ind1]; }
set
{ imyArray[ind1] = value; }
}
public int this[int ind1, int ind2]
{
get
{ return imyArray1[ind1, ind2]; }
set
{ imyArray1[ind1, ind2] = value; }
} }
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args)
{
AClass1 Ac1 = new AClass1();
Random ran = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
Ac1[i] = ran.Next(1, 100);
Console.Write("{0}\t", Ac1[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++)
{
Ac1[i, j] = ran.Next(1, 100);
Console.Write("{0}\t", Ac1[i, j]);
}
Console.Write("\n"); }
Console.ReadLine(); } }
Слайд 5
![Перегрузка индексаторов public class AClass1 { int[] imyArray = new](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/73754/slide-4.jpg)
Перегрузка индексаторов
public class AClass1 {
int[] imyArray = new int[5];
int[] imyArray1 = new int[10];
public int this[int ind1]
{ get { return imyArray[ind1]; }
set { imyArray[ind1] = value; }
}
public int this[double ind2]
{get {
int ind;
if ((ind2 - (int)ind2) < 0.5)
ind = (int)ind2;
else ind = (int)ind2 + 1;
return imyArray1[ind]; }
set {
int ind;
if ((ind2 - (int)ind2) < 0.5)
ind = (int)ind2;
else ind = (int)ind2 + 1;
imyArray1[ind] = value; }
} }
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
AClass1 Ac1 = new AClass1();
Random ran = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Ac1[i] = ran.Next(1, 100);
Console.Write("[{0}] = {1}\n", i, Ac1[i]);
}
Console.Write("\n");
for (double i = 0; i < 0.9; i=i+0.1)
{
Ac1[i] = ran.Next(1, 100);
Console.Write("[{0}] = {1}\n", i, Ac1[i]);
}
Console.ReadLine();
} }
Слайд 6
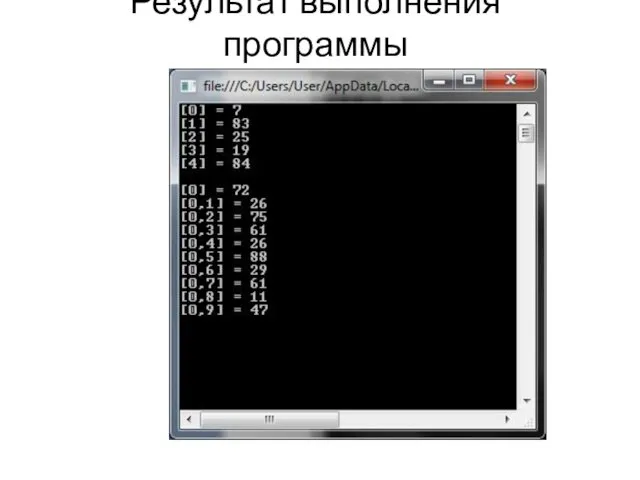
Результат выполнения программы
Слайд 7
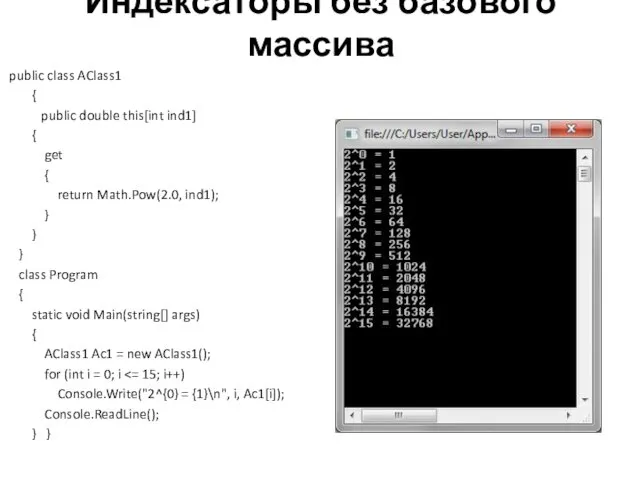
Индексаторы без базового массива
public class AClass1
{
public double
this[int ind1]
{
get
{
return Math.Pow(2.0, ind1);
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
AClass1 Ac1 = new AClass1();
for (int i = 0; i <= 15; i++)
Console.Write("2^{0} = {1}\n", i, Ac1[i]);
Console.ReadLine();
} }
Слайд 8

Применение модификаторов доступа в аксессорах
class PropAccess
{
int prop;
public
PropAccess() { prop = 0; }
public int MyProp
{
get
{ return prop; }
private set
{ prop = value; }
}
public void IncrProp()
{
MyProp++;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PropAccess ob = new PropAccess();
Console.WriteLine("Первоначальное значение ob.MyProp: " +
ob.MyProp);
// ob.MyProp = 100;
ob.IncrProp();
Console.WriteLine("Значение ob.MyProp после инкременирования:"
+ ob.MyProp);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
![Общая форма одномерного индексатора тип_элемента this[int индекс] { // Аксессор](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/73754/slide-1.jpg)
![Пример применения индексатора public class AClass1 { int[] imyArray =](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/73754/slide-2.jpg)
![Применение двумерных индексаторов public class AClass1 { int[] imyArray =](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/73754/slide-3.jpg)
![Перегрузка индексаторов public class AClass1 { int[] imyArray = new](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/73754/slide-4.jpg)



 Проблемы юридической техники в уголовном праве
Проблемы юридической техники в уголовном праве Автоматизация звука Р
Автоматизация звука Р Теоретические основы товароведения продовольственных товаров
Теоретические основы товароведения продовольственных товаров Технология изготовления и монтаж деревянных лестниц. Устройство деревянного перекрытия
Технология изготовления и монтаж деревянных лестниц. Устройство деревянного перекрытия Способы организации пространства в ландшафтной архитектуре
Способы организации пространства в ландшафтной архитектуре Основы общественного производства
Основы общественного производства Процедура выбора страховой компании для строительной организации ООО Паркинг-М
Процедура выбора страховой компании для строительной организации ООО Паркинг-М Разработка технологии внесения растворов жидких комплексных удобрений (жку) в посевы сельскохозяйственных культур
Разработка технологии внесения растворов жидких комплексных удобрений (жку) в посевы сельскохозяйственных культур Традиционные общества востока
Традиционные общества востока Кошки
Кошки Христианин в труде
Христианин в труде День космонавтики.
День космонавтики. Порядок проверки и замены компрессора Dvm plus III
Порядок проверки и замены компрессора Dvm plus III 20231021_lyubit_svoego_podrostka_2012
20231021_lyubit_svoego_podrostka_2012 Ислам мәдениеті
Ислам мәдениеті Виды химической связи
Виды химической связи Деловая игра Знатоки ФГОС ДО
Деловая игра Знатоки ФГОС ДО Рейди мэйд в искусстве XX века
Рейди мэйд в искусстве XX века Роль воспитателя в процессе музык. воспитания
Роль воспитателя в процессе музык. воспитания образование в жизни человека
образование в жизни человека Моделирование и конструирование
Моделирование и конструирование Ознакомление детей дошкольного возраста с изобразительным искусством
Ознакомление детей дошкольного возраста с изобразительным искусством Проецирование. Проекция
Проецирование. Проекция Döwletleriň syýasy kartada şekillendirilşi
Döwletleriň syýasy kartada şekillendirilşi Современные способы обеззараживания воды
Современные способы обеззараживания воды Экономическая сущность предпринимательской деятельности
Экономическая сущность предпринимательской деятельности Эксплуатация системы кондиционирования воздуха пассажирских вагонов в пути следования
Эксплуатация системы кондиционирования воздуха пассажирских вагонов в пути следования Театр Моды Силуэт, коллекция Цвета жизни
Театр Моды Силуэт, коллекция Цвета жизни