Содержание
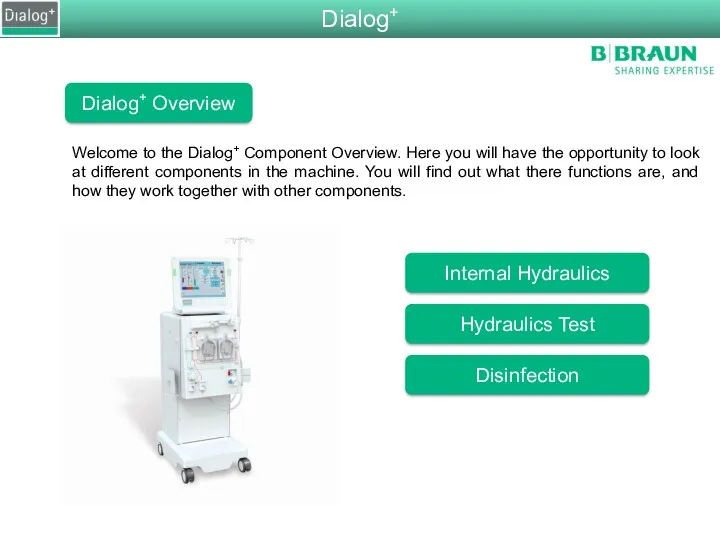
- 2. Welcome to the Dialog+ Component Overview. Here you will have the opportunity to look at different
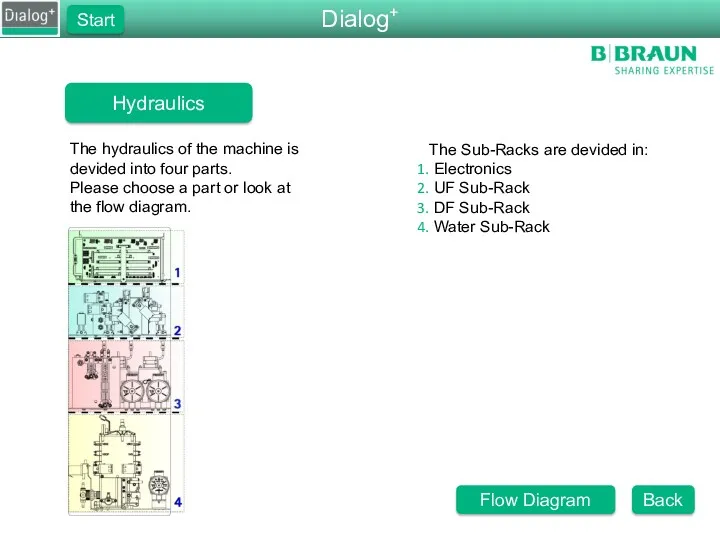
- 3. The Sub-Racks are devided in: Electronics UF Sub-Rack DF Sub-Rack Water Sub-Rack The hydraulics of the
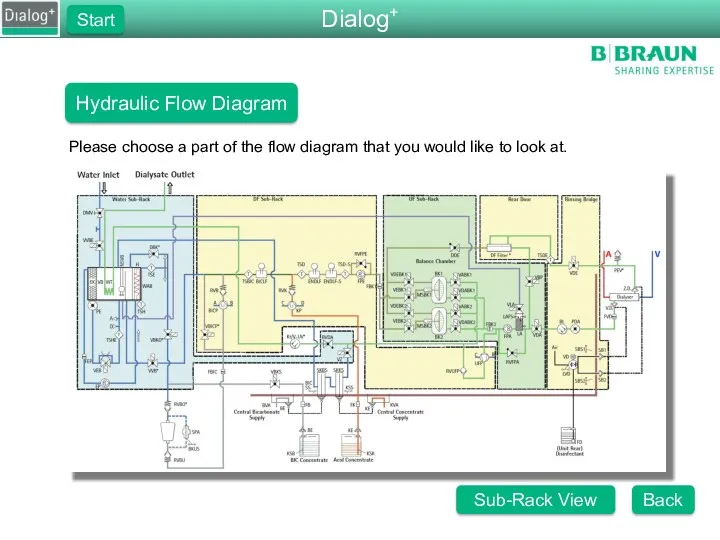
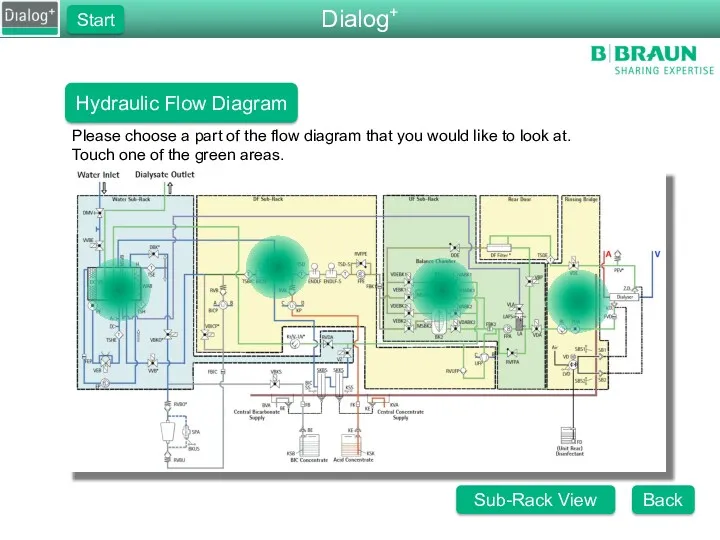
- 4. Dialog+ Start Hydraulic Flow Diagram Please choose a part of the flow diagram that you would
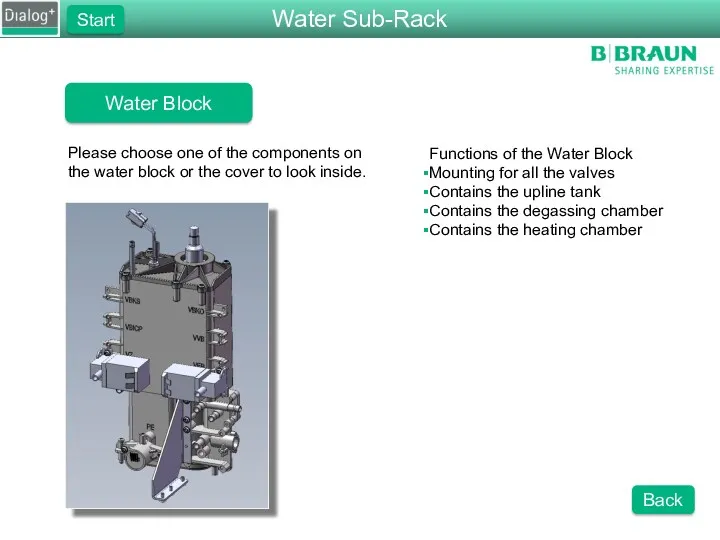
- 5. Water Sub-Rack Please choose one of the component groups of the water sub-rack. Functions of the
- 6. Pressure Reduction Valve Functions of the Pressure Reduction Valve Reduces ring-line pressure to 0.9 bar Functions
- 7. Water Block Please choose one of the components on the water block or the cover to
- 8. Upline Tank Please choose one of the components in the upline tank. Components in the Upline
- 9. Degassing Valve VEB Functions of the Degassing Valve Creates a restriction in the water flow The
- 10. Heater Rod Functions of the Heater Rod Heats up incoming water Properties of the Heater Rod
- 11. Float Switch Functions of the Float Switch Regulates the water level in the upline tank Turns
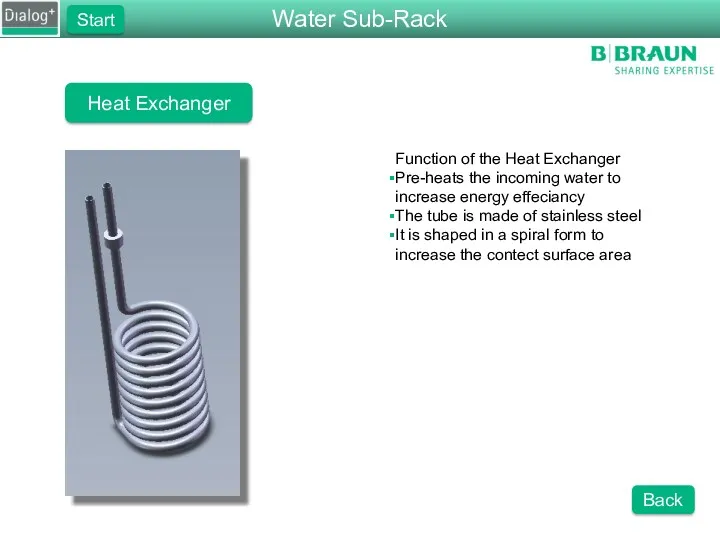
- 12. Heat Exchanger Function of the Heat Exchanger Pre-heats the incoming water to increase energy effeciancy The
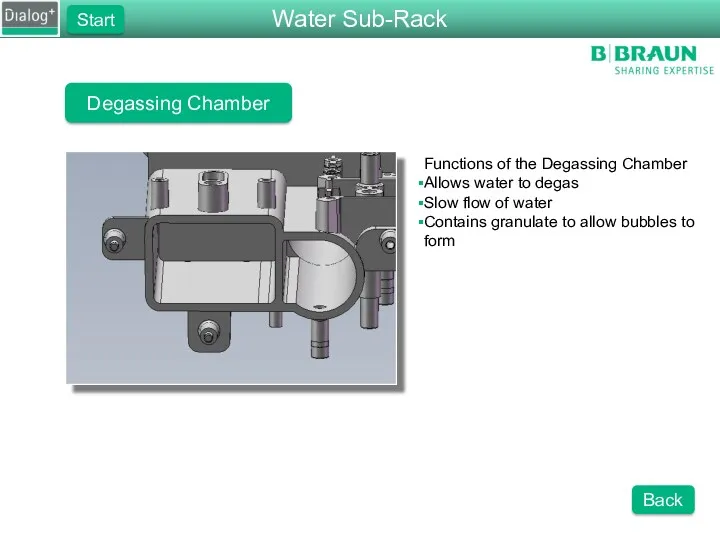
- 13. Degassing Chamber Functions of the Degassing Chamber Allows water to degas Slow flow of water Contains
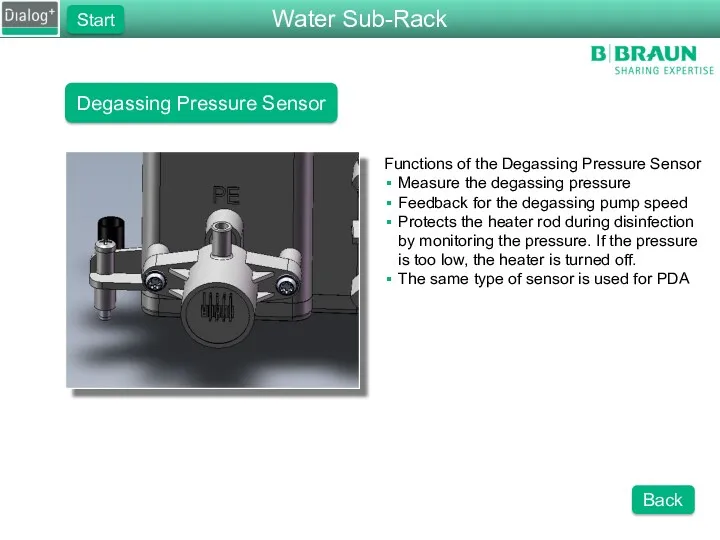
- 14. Degassing Pressure Sensor Functions of the Degassing Pressure Sensor Measure the degassing pressure Feedback for the
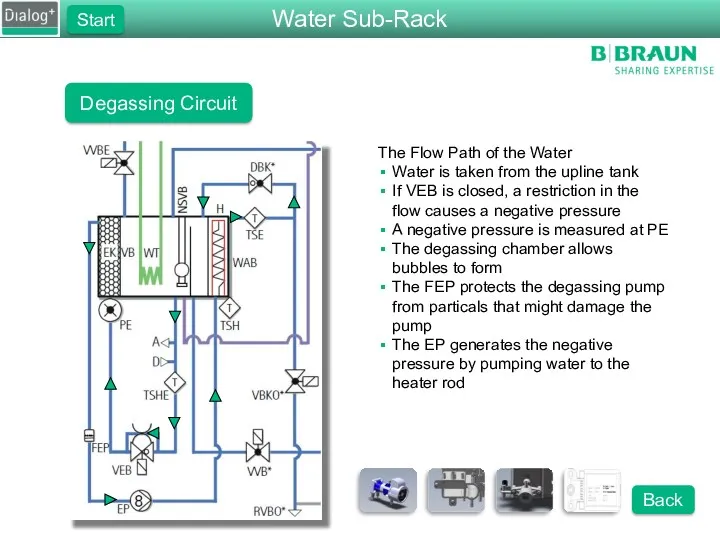
- 15. Degassing Circuit The Flow Path of the Water Water is taken from the upline tank If
- 16. Degassing Pump, Micropump Vers. 2 Please choose a part of the degassing pump that you would
- 17. Degassing Pump Functions of the Degassing Pump Creates a negative degassing pressure Pumps fluid with two
- 18. Degassing Motor Functions of the Degassing Motor Drives the degassing pump Onboard driving circuits Is regulated
- 19. Degassing Motor Cover Functions of the Degassing Motor Cover Protects the moving parts of the motor
- 20. Degassing Adaptor Block Function of the Adaptor Block Mounting of the degassing pump O-rings to seal
- 21. Degassing Pump Foot Piece Functions of the Foot Piece Holds the degassing pump module Absorbs vibrations
- 22. RVDA Functions of the RVDA Ensures a minimum pressure of 400 mmHg on the balance chamber
- 23. RVDA Rear view of the RVDA Pay attention to the assembly direction Water Sub-Rack Start Back
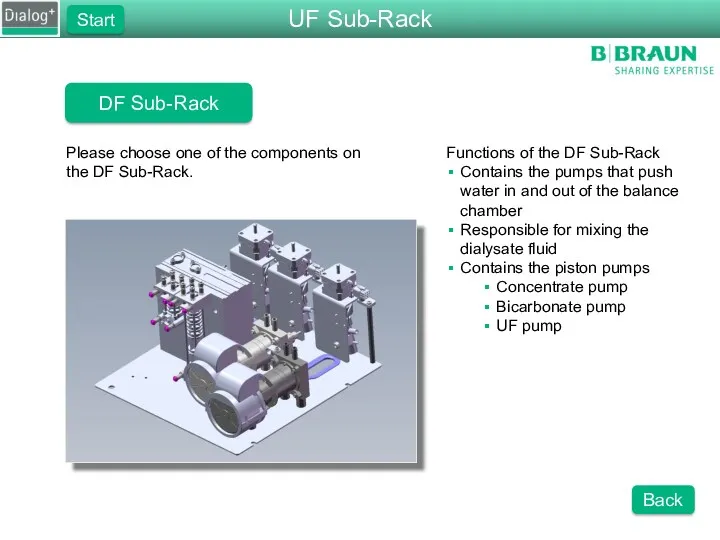
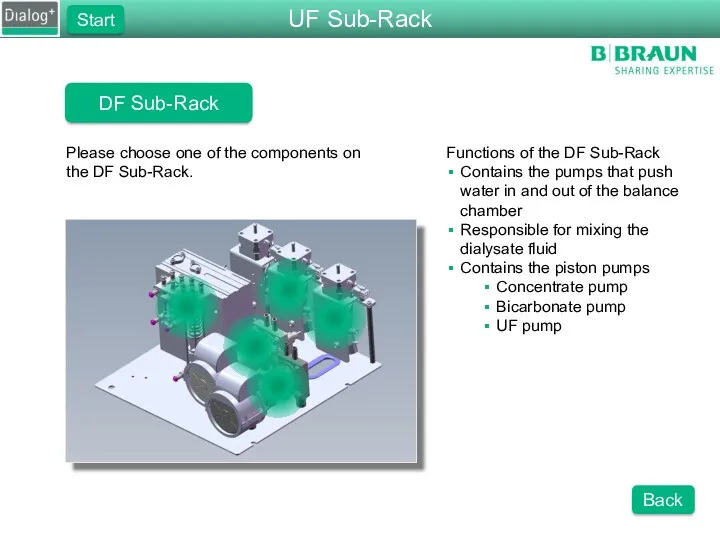
- 24. DF Sub-Rack Please choose one of the components on the DF Sub-Rack. Functions of the DF
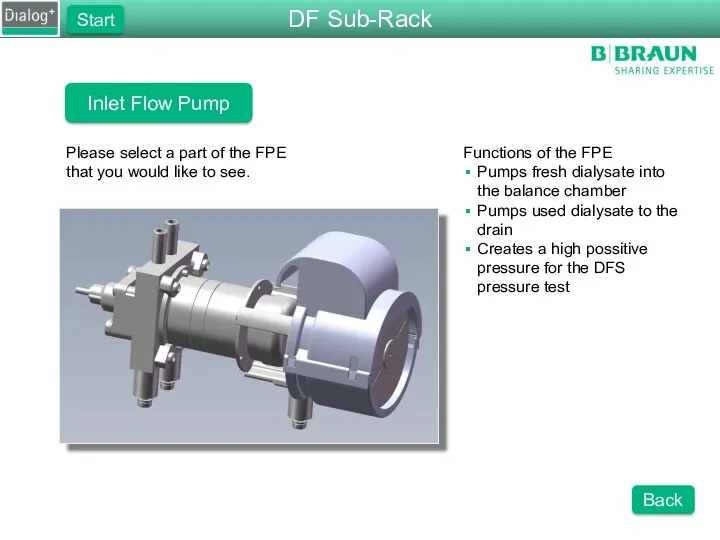
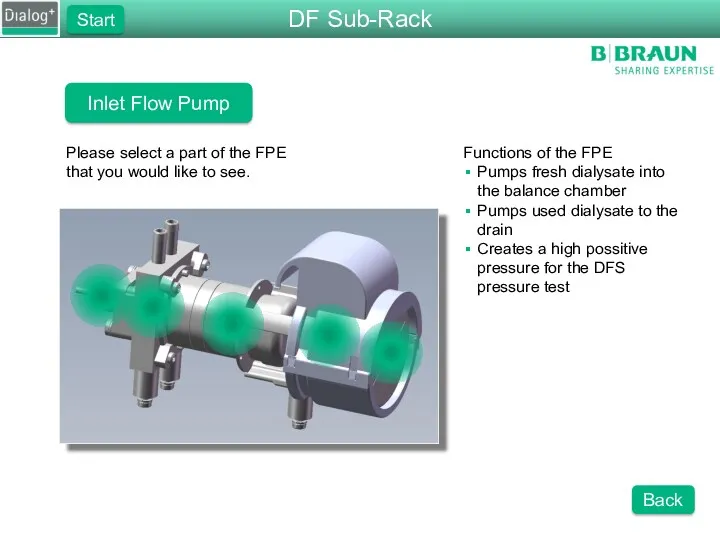
- 25. Inlet Flow Pump Please select a part of the FPE that you would like to see.
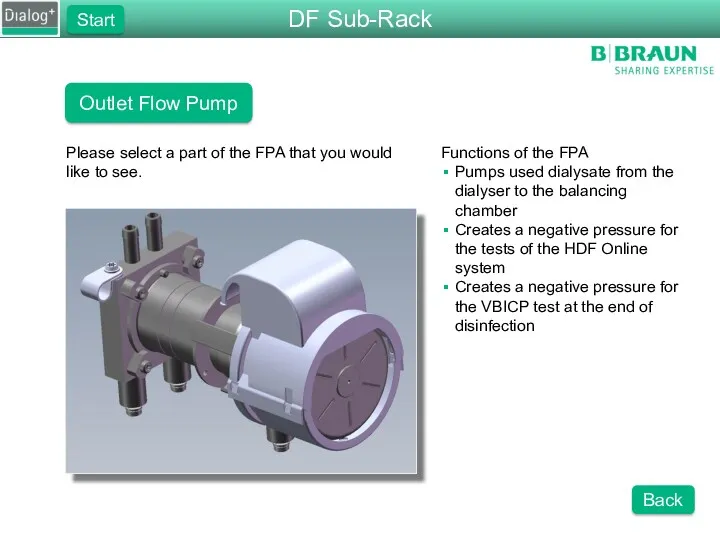
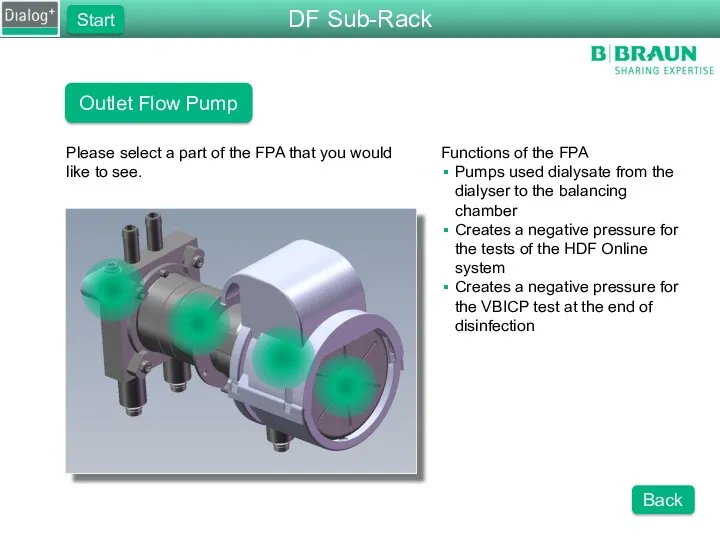
- 26. Outlet Flow Pump Please select a part of the FPA that you would like to see.
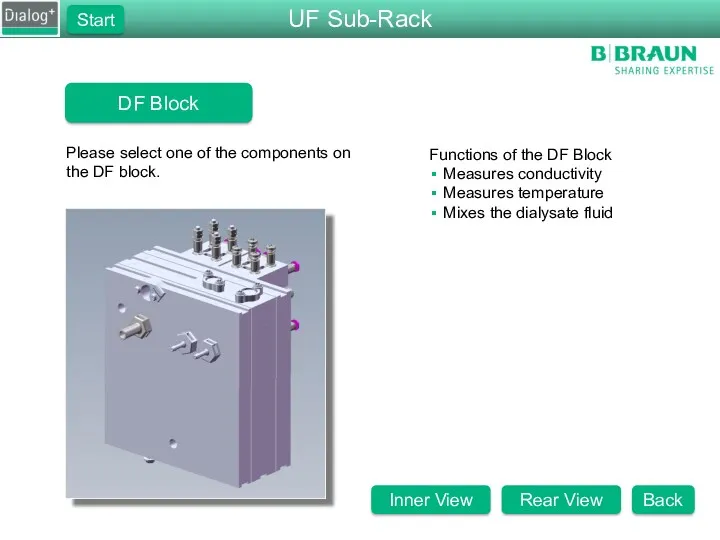
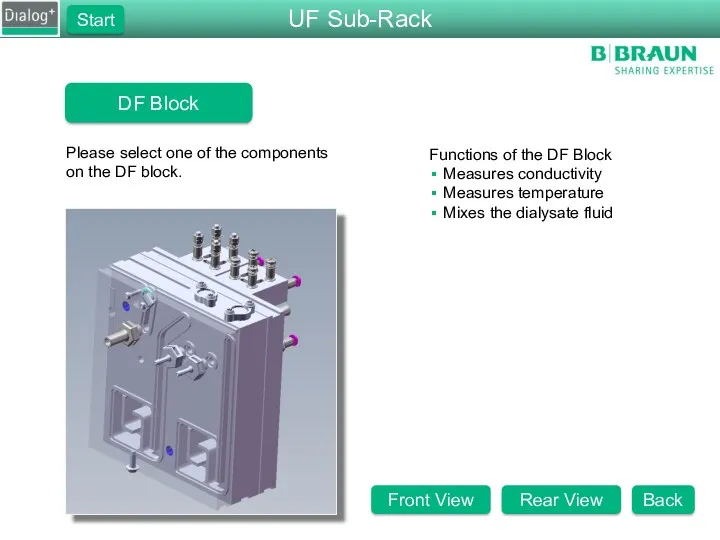
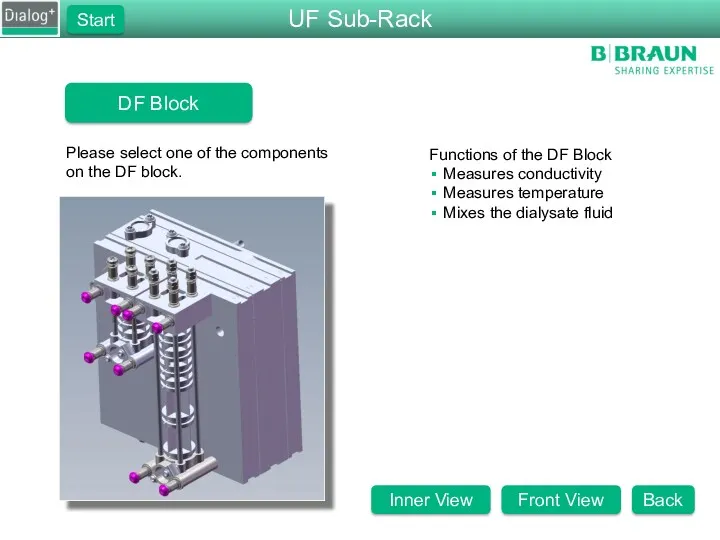
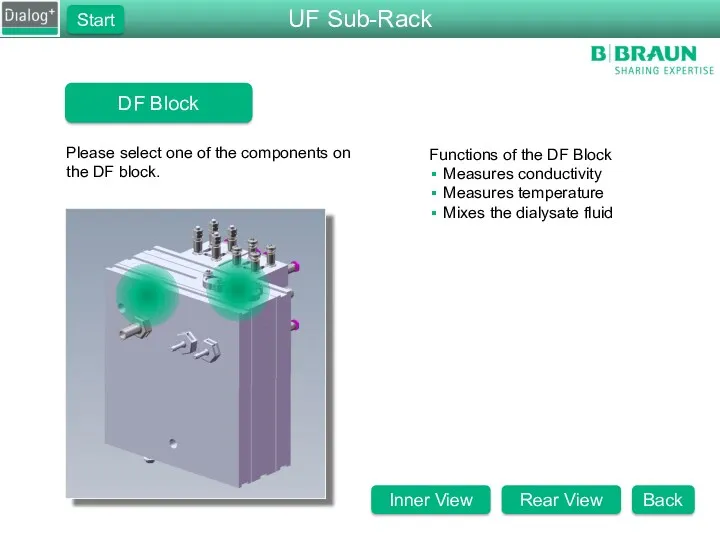
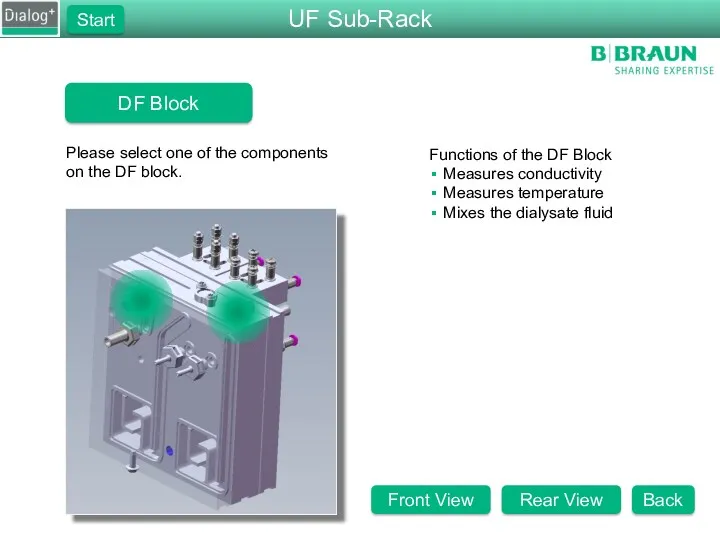
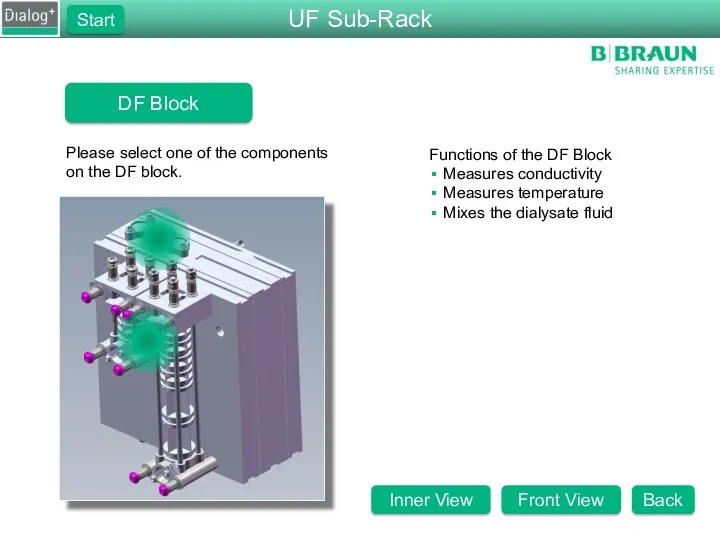
- 27. DF Block Please select one of the components on the DF block. Functions of the DF
- 28. DF Block Please select one of the components on the DF block. Functions of the DF
- 29. DF Block Please select one of the components on the DF block. Functions of the DF
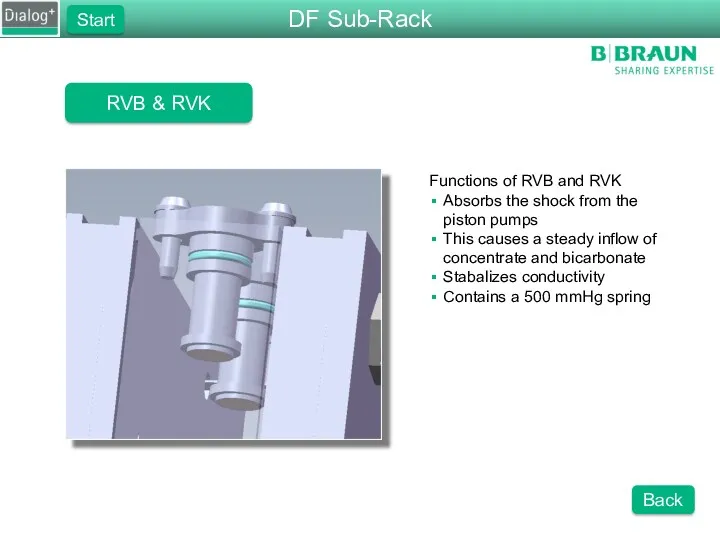
- 30. RVB & RVK Functions of RVB and RVK Absorbs the shock from the piston pumps This
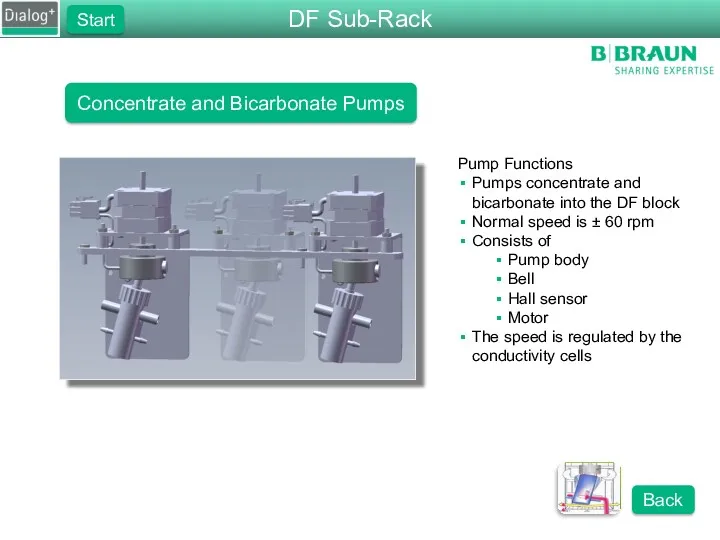
- 31. Concentrate and Bicarbonate Pumps Pump Functions Pumps concentrate and bicarbonate into the DF block Normal speed
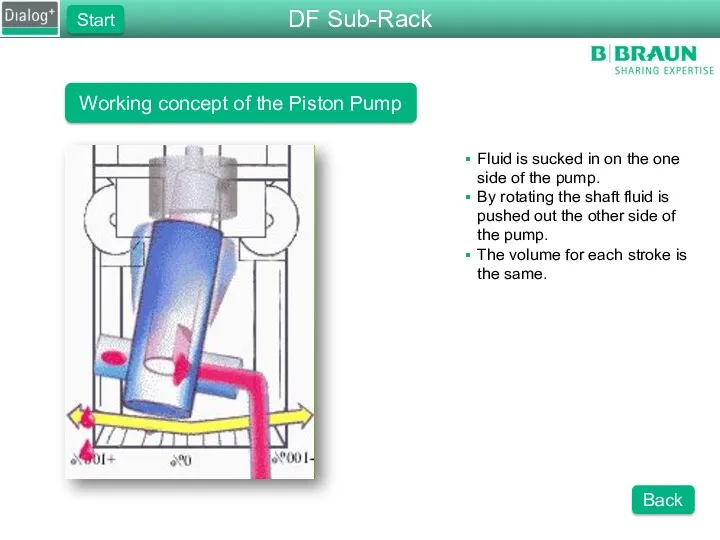
- 32. Working concept of the Piston Pump Fluid is sucked in on the one side of the
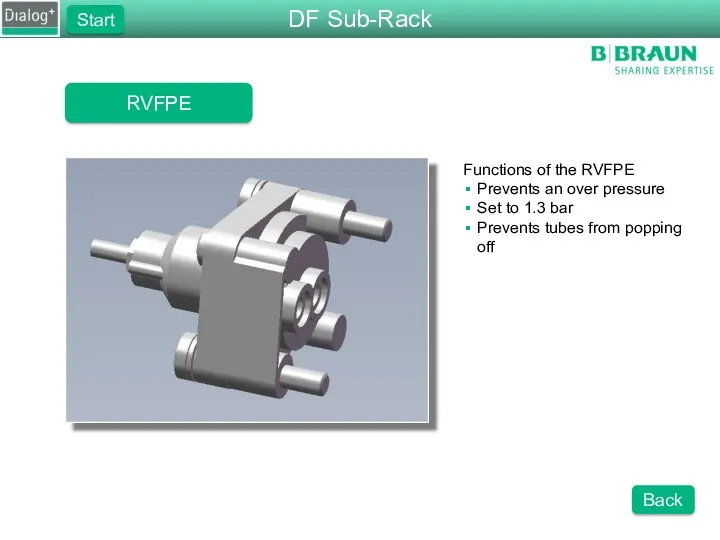
- 33. RVFPE Functions of the RVFPE Prevents an over pressure Set to 1.3 bar Prevents tubes from
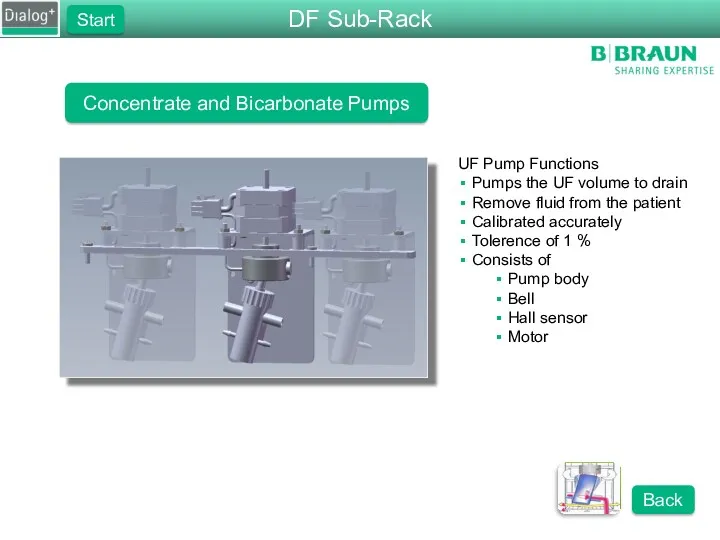
- 34. Concentrate and Bicarbonate Pumps UF Pump Functions Pumps the UF volume to drain Remove fluid from
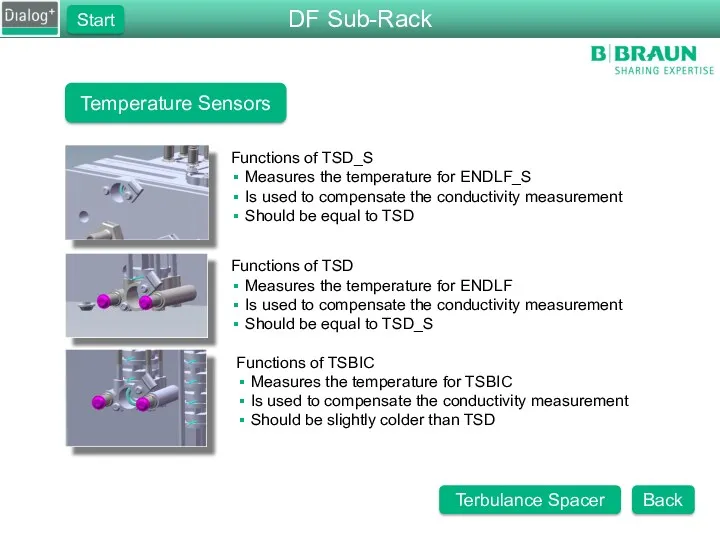
- 35. Temperature Sensors Functions of TSD_S Measures the temperature for ENDLF_S Is used to compensate the conductivity
- 36. Terbulance Spacer Functions of the Terbulance Spacer Creates terbulance on the temperature sensor Removes dead spaces
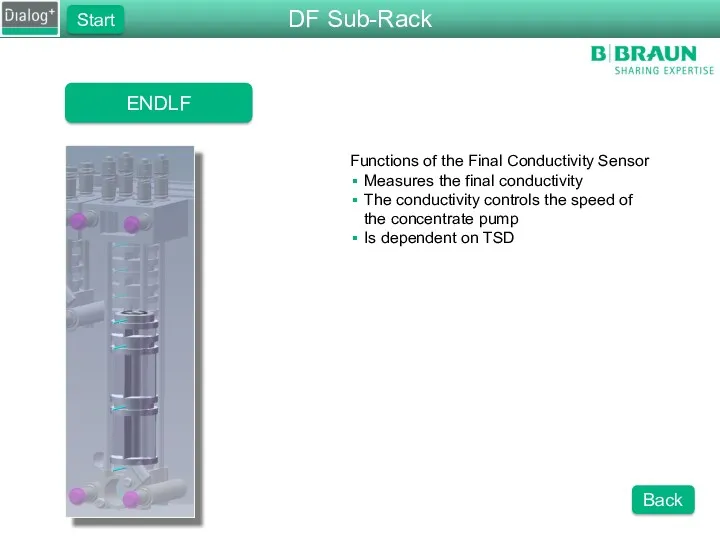
- 37. ENDLF Functions of the Final Conductivity Sensor Measures the final conductivity The conductivity controls the speed
- 38. ENDLF_S Functions of the Final Conductivity Sensor for the Supervisor Measures the final conductivity Is dependent
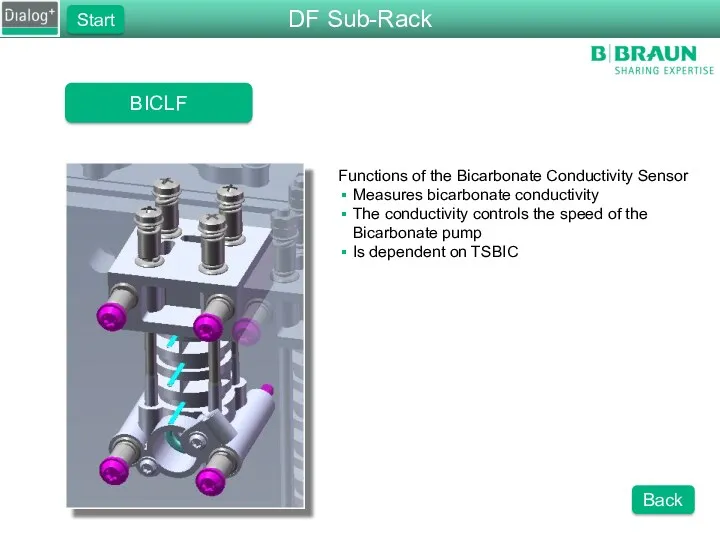
- 39. BICLF Functions of the Bicarbonate Conductivity Sensor Measures bicarbonate conductivity The conductivity controls the speed of
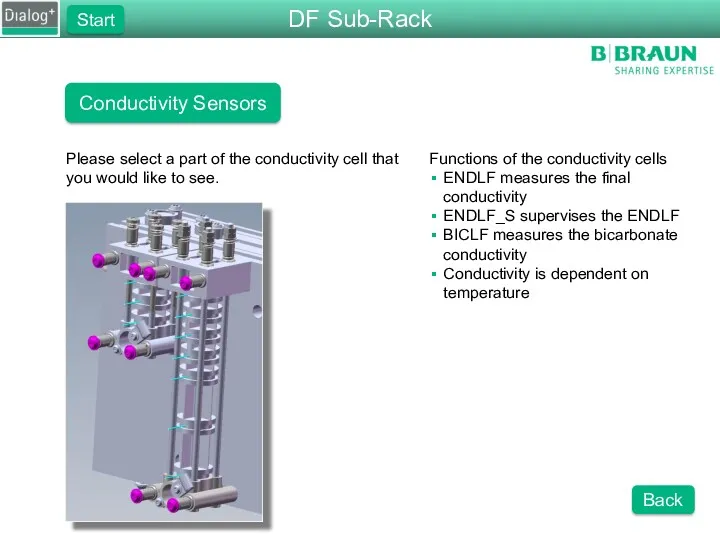
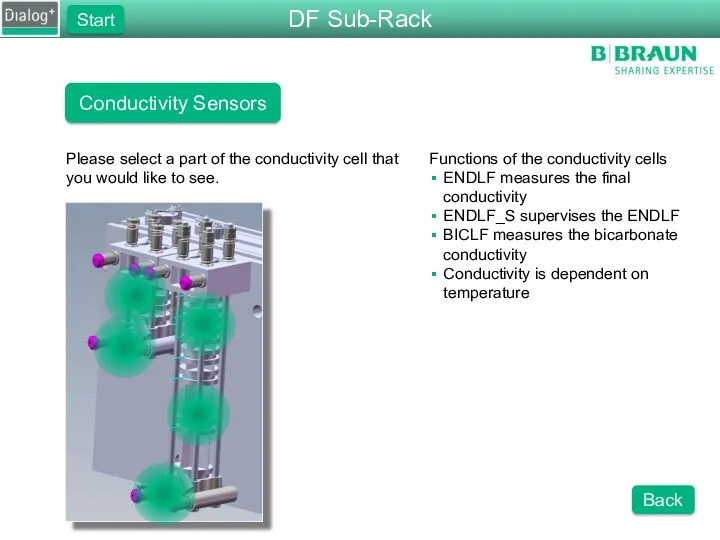
- 40. Conductivity Sensors Functions of the conductivity cells ENDLF measures the final conductivity ENDLF_S supervises the ENDLF
- 41. O-Rings of the Disinfection Valve Function of the O-Rings Lower O-ring: seals of the disinfection port
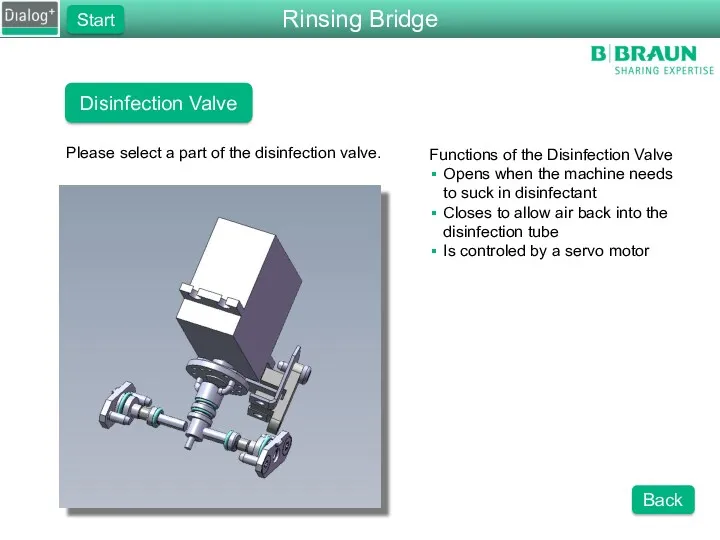
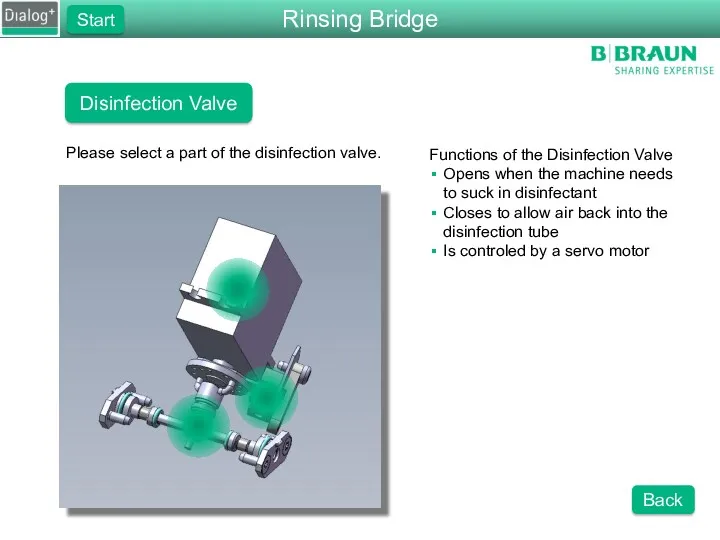
- 42. Disinfection Valve Please select a part of the disinfection valve. Functions of the Disinfection Valve Opens
- 43. Sub-Rack Start FPA Adaptor Block Back Functions of the FPA Adaptor Block Mounts the FPA Absorbs
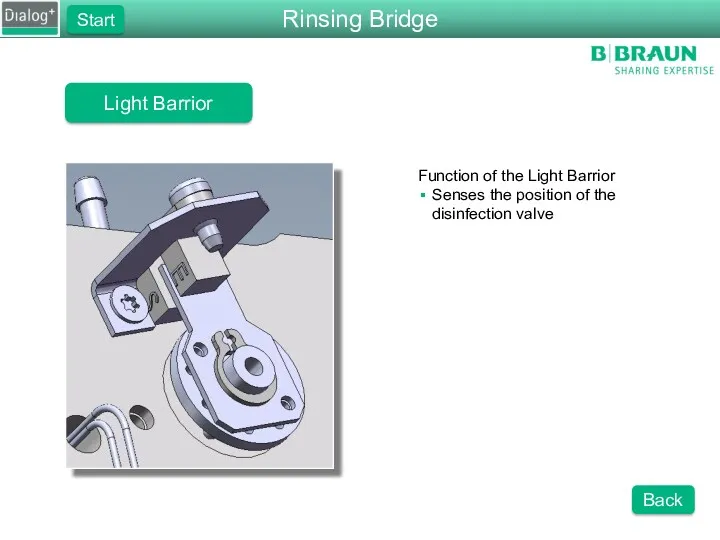
- 44. Rinsing Bridge Start Light Barrior Back Function of the Light Barrior Senses the position of the
- 45. Pressure Sensor Dialysate Functions of PDA Measure the dialysate pressure This is used to calculate TMP
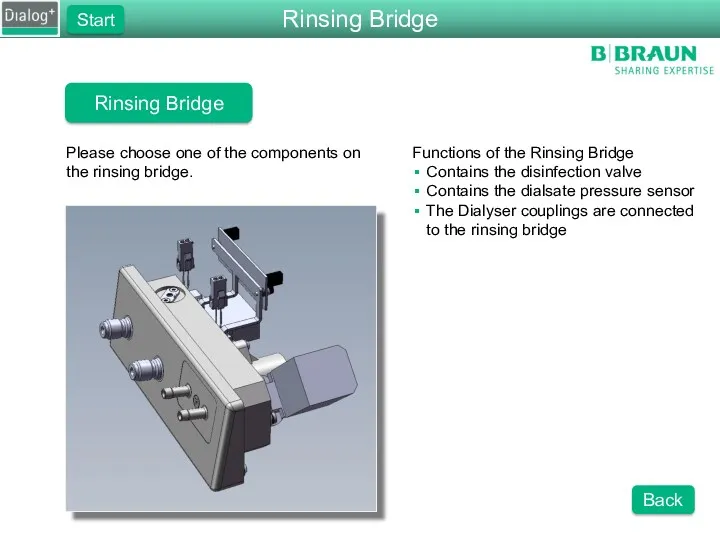
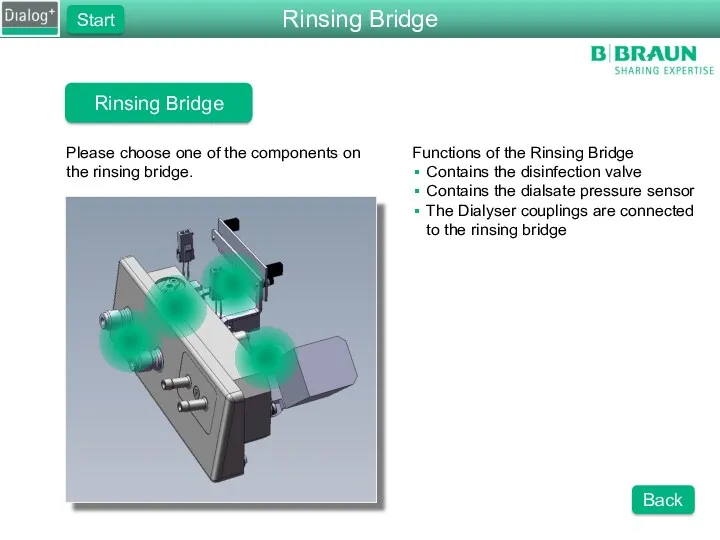
- 46. Rinsing Bridge Please choose one of the components on the rinsing bridge. Functions of the Rinsing
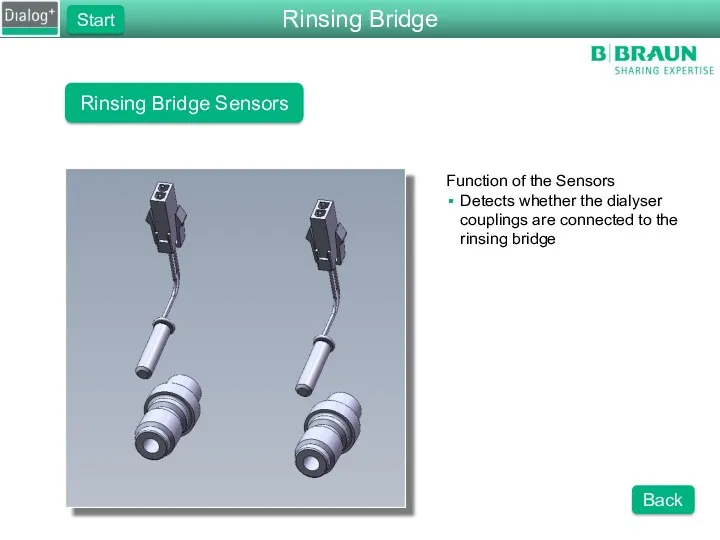
- 47. Rinsing Bridge Sensors Function of the Sensors Detects whether the dialyser couplings are connected to the
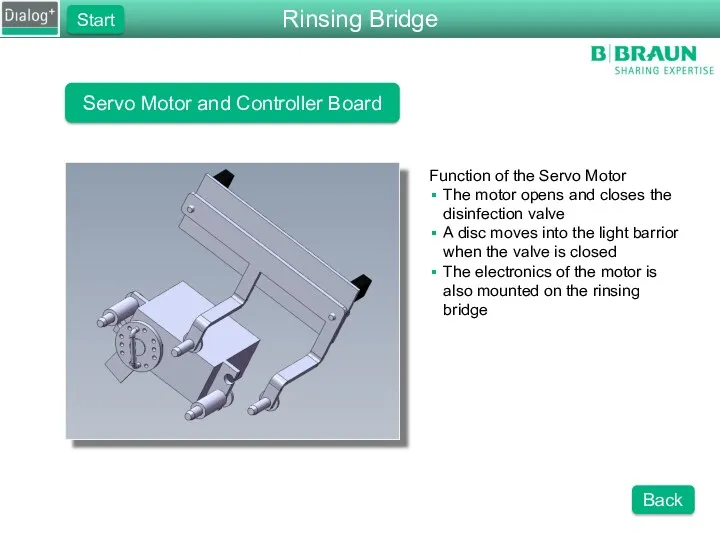
- 48. Servo Motor and Controller Board Function of the Servo Motor The motor opens and closes the
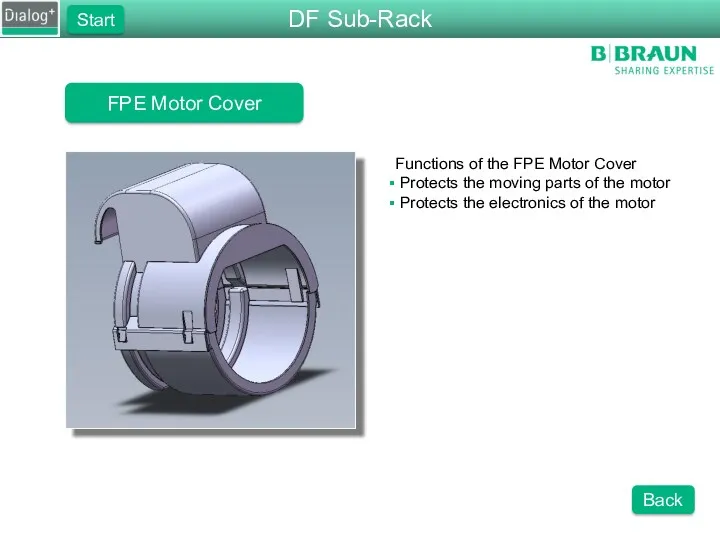
- 49. FPE Motor Cover Functions of the FPE Motor Cover Protects the moving parts of the motor
- 50. FPE Motor Functions of the FPE Motor Drives the degassing pump Onboard driving circuits Is regulated
- 51. FPA Motor Functions of the FPA Motor Drives the degassing pump Onboard driving circuits Is regulated
- 52. FPA Motor Cover Functions of the FPA Motor Cover Protects the moving parts of the motor
- 53. Hydraulic Flow Diagram Please choose a part of the flow diagram that you would like to
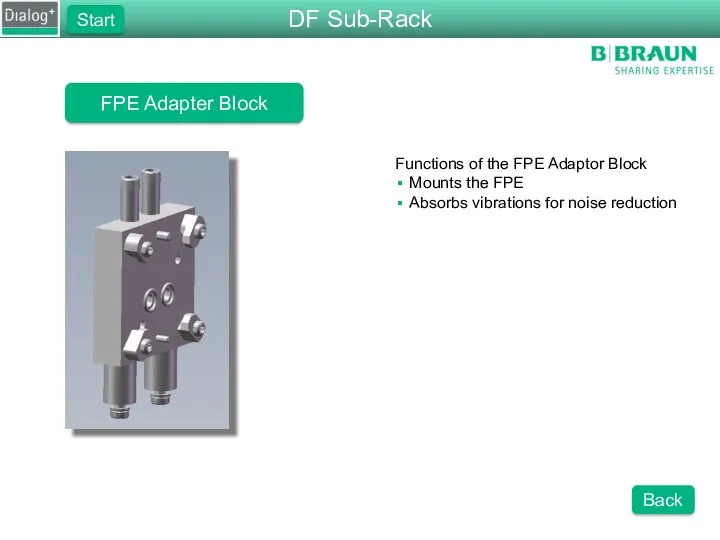
- 54. FPE Adapter Block Functions of the FPE Adaptor Block Mounts the FPE Absorbs vibrations for noise
- 55. FPE, Micropump Vers. 2 Functions of the FPE Pump Creates a positive pressure to refil the
- 56. FPA, Micrpump Vers. 1 Functions of the FPA Pump Creates a positive pressure to fill the
- 57. UF Sub-Rack Please choose one of the components on the UF Sub-Rack. Functions of the UF
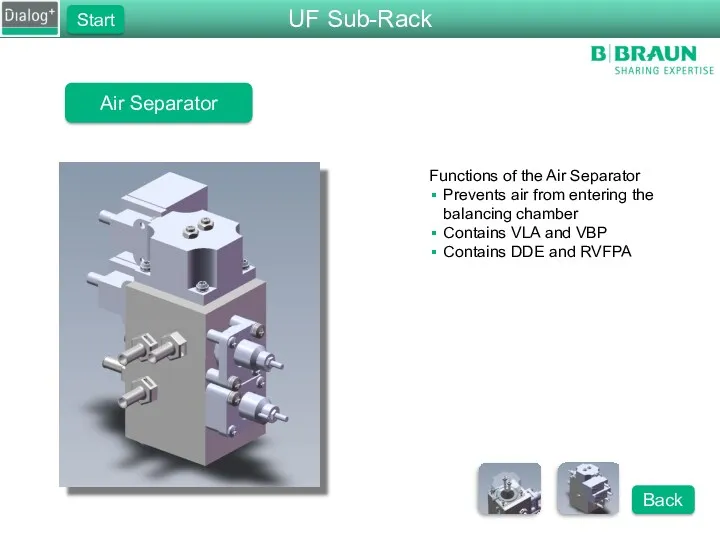
- 58. Air Separator Functions of the Air Separator Prevents air from entering the balancing chamber Contains VLA
- 59. Air Separator Functions of the Air Separator Prevents air from entering the balancing chamber Contains VLA
- 60. Air Separator Functions of the Air Separator There are 2 pins that sense the level of
- 61. Balance Chamber Functions of the Balance Chamber Consists of 2 chambers, with 8 valves Induction coils
- 62. Balance Chamber Membrane Functions of the Balance Chamber Membrane Separates fresh and used dialysate Controles incoming
- 63. Membrane Position Sensor Functions of the membrane position sensor Measures the position of the membrane Uses
- 64. Water Sub-Rack Please choose one of the component groups of the water sub-rack. Functions of the
- 65. Water Block Please choose one of the components on the water block or the cover to
- 66. Upline Tank Please choose one of the components in the upline tank. Components in the Upline
- 67. Degassing Pump, Micropump Vers. 2 Please choose a part of the degassing pump that you would
- 68. DF Sub-Rack Please choose one of the components on the DF Sub-Rack. Functions of the DF
- 69. Inlet Flow Pump Please select a part of the FPE that you would like to see.
- 70. Outlet Flow Pump Please select a part of the FPA that you would like to see.
- 71. DF Block Please select one of the components on the DF block. Functions of the DF
- 72. DF Block Please select one of the components on the DF block. Functions of the DF
- 73. DF Block Please select one of the components on the DF block. Functions of the DF
- 74. Conductivity Sensors Functions of the conductivity cells ENDLF measures the final conductivity ENDLF_S supervises the ENDLF
- 75. Disinfection Valve Please select a part of the disinfection valve. Functions of the Disinfection Valve Opens
- 76. Rinsing Bridge Please choose one of the components on the rinsing bridge. Functions of the Rinsing
- 77. UF Sub-Rack Please choose one of the components on the UF Sub-Rack. Functions of the UF
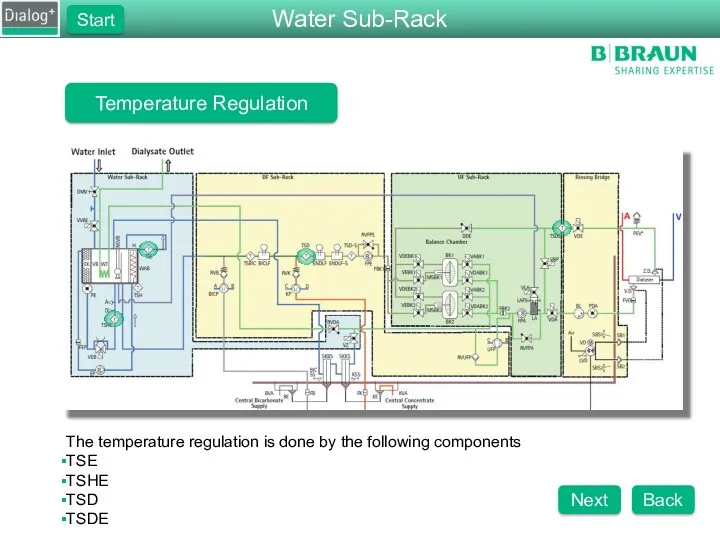
- 78. Temperature Regulation The temperature regulation is done by the following components TSE TSHE TSD TSDE Water
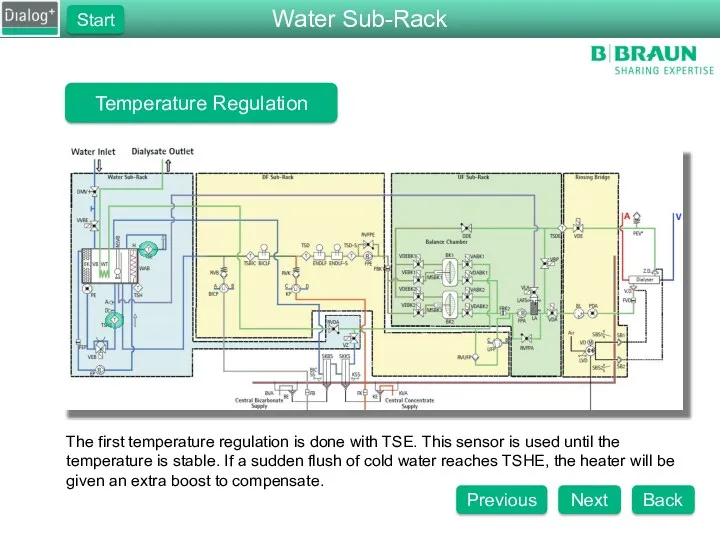
- 79. Temperature Regulation The first temperature regulation is done with TSE. This sensor is used until the
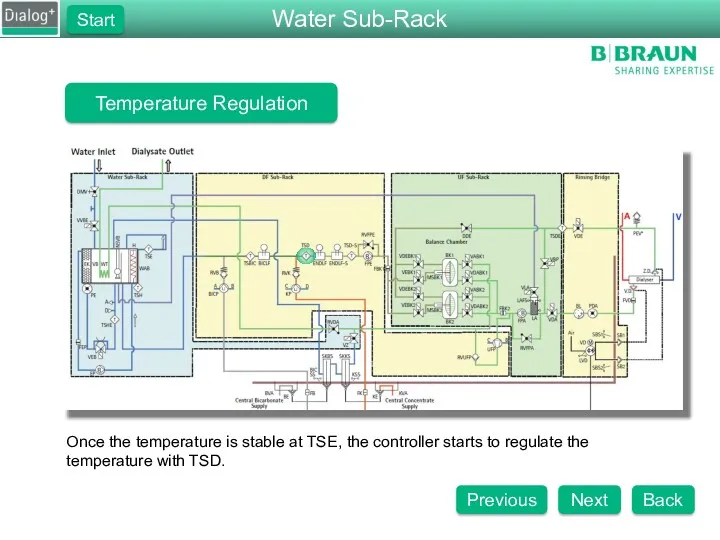
- 80. Temperature Regulation Once the temperature is stable at TSE, the controller starts to regulate the temperature
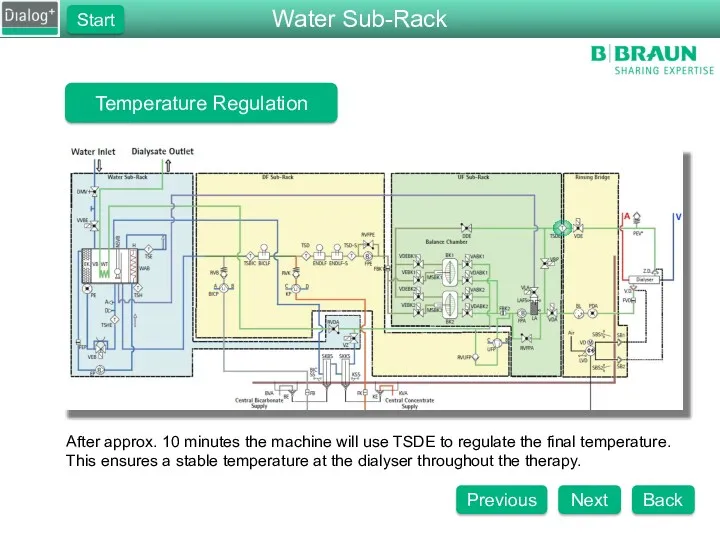
- 81. Temperature Regulation After approx. 10 minutes the machine will use TSDE to regulate the final temperature.
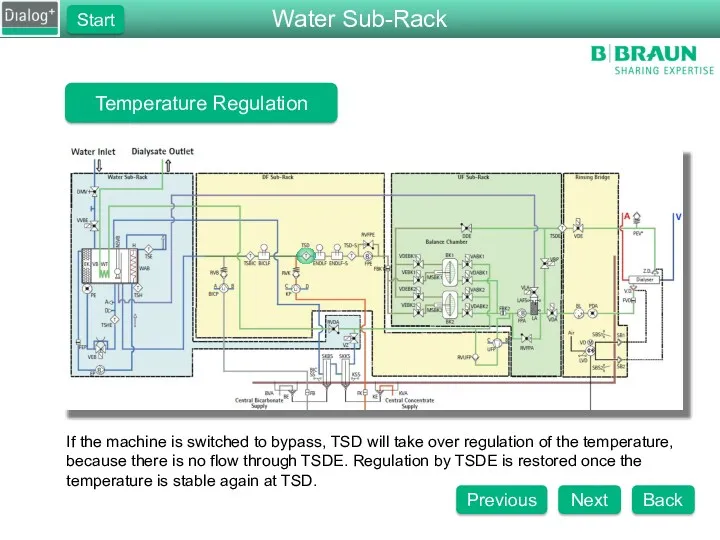
- 82. Temperature Regulation If the machine is switched to bypass, TSD will take over regulation of the
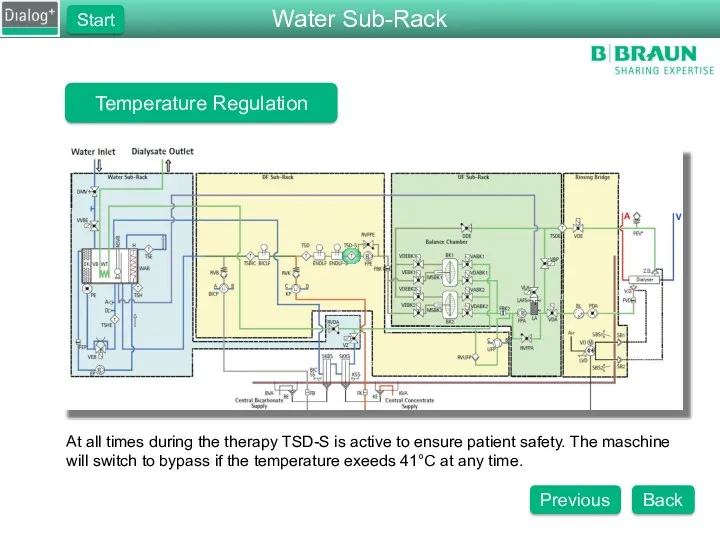
- 83. Temperature Regulation At all times during the therapy TSD-S is active to ensure patient safety. The
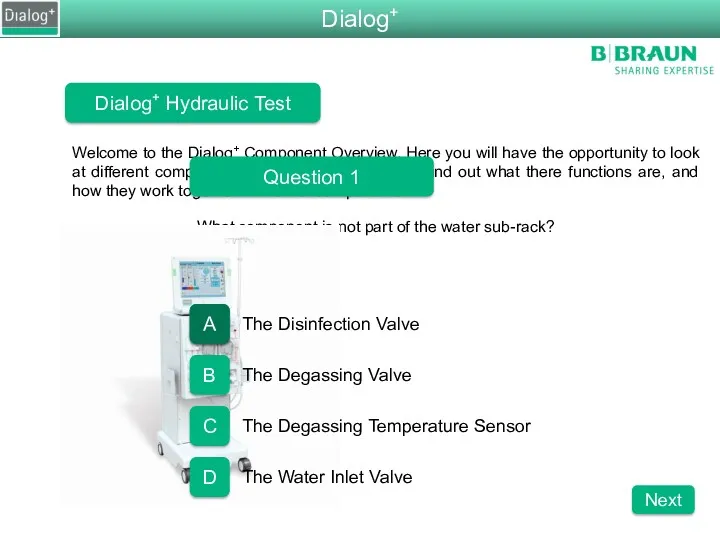
- 84. What compenent is not part of the water sub-rack? Welcome to the Dialog+ Component Overview. Here
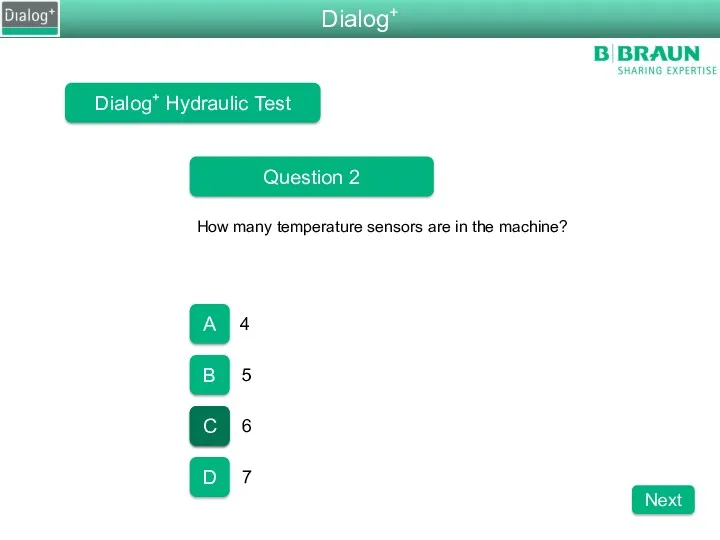
- 85. Dialog+ Hydraulic Test Question 2 How many temperature sensors are in the machine? 4 5 6
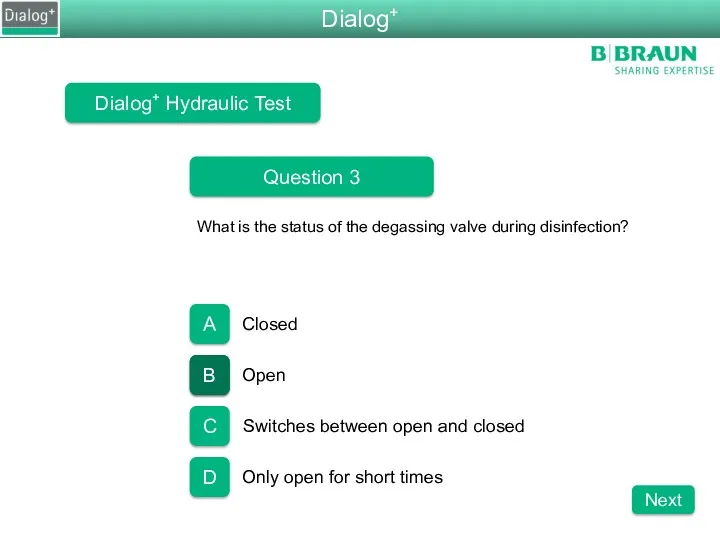
- 86. Dialog+ Hydraulic Test Question 3 What is the status of the degassing valve during disinfection? Closed
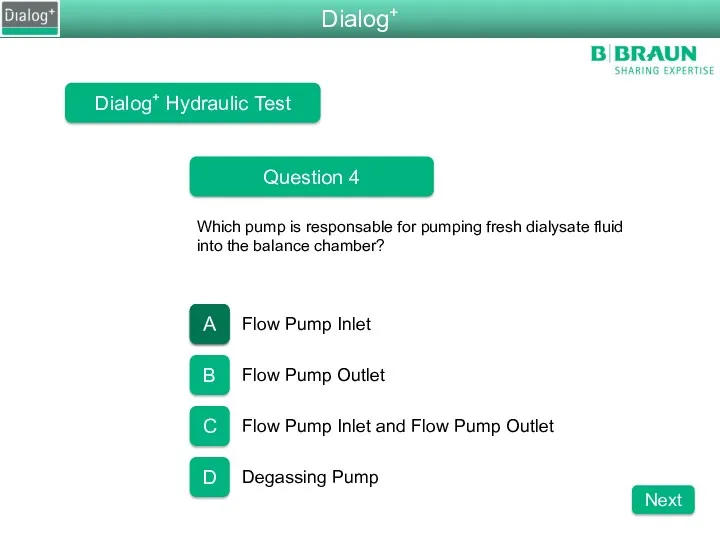
- 87. Dialog+ Hydraulic Test Question 4 Which pump is responsable for pumping fresh dialysate fluid into the
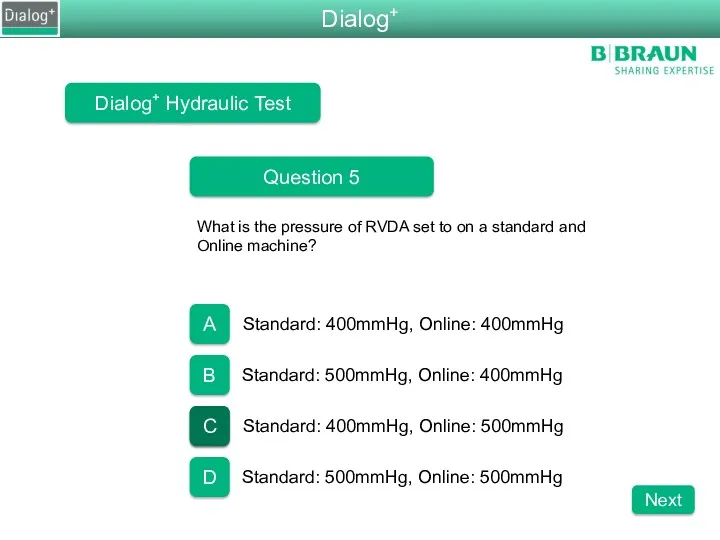
- 88. Dialog+ Hydraulic Test Question 5 What is the pressure of RVDA set to on a standard
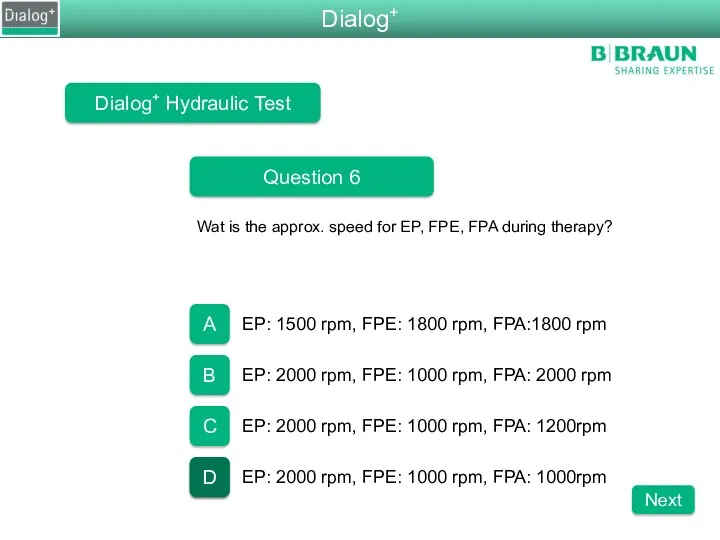
- 89. Dialog+ Hydraulic Test Question 6 Wat is the approx. speed for EP, FPE, FPA during therapy?
- 90. Dialog+ Hydraulic Test Test Completed Press the Show Results button to find out how many questions
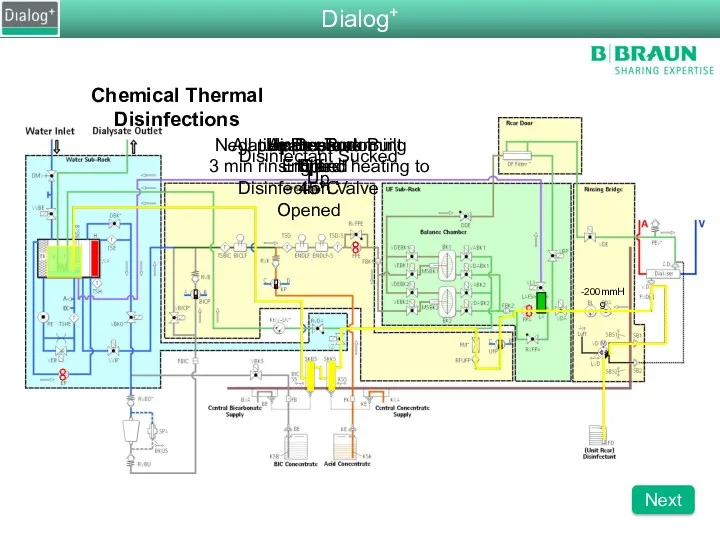
- 91. Chemical Thermal Disinfections All pumps are running 3 min rinsing and heating to 45°C Air Separator
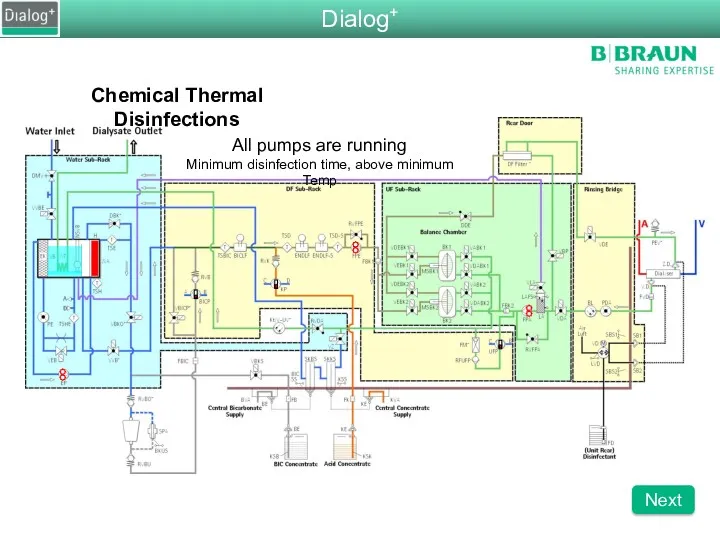
- 92. Chemical Thermal Disinfections All pumps are running Minimum disinfection time, above minimum Temp Dialog+ Next
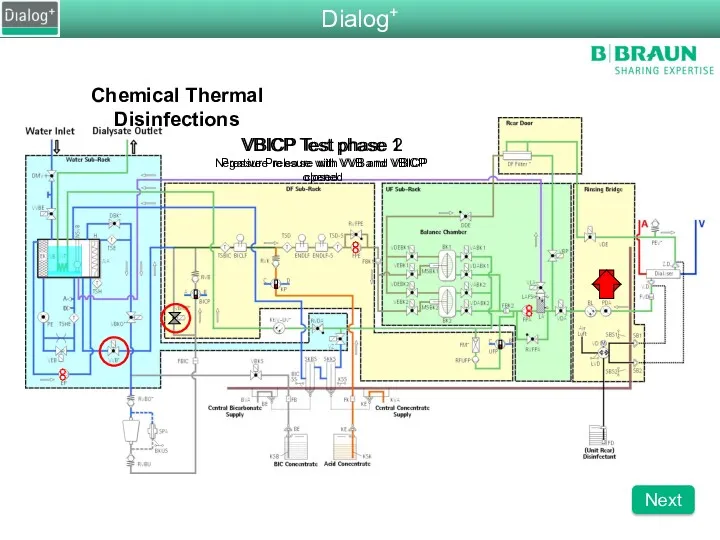
- 93. Chemical Thermal Disinfections VBICP Test phase 1 Negative Pressure with VVB and VBICP closed VBICP Test
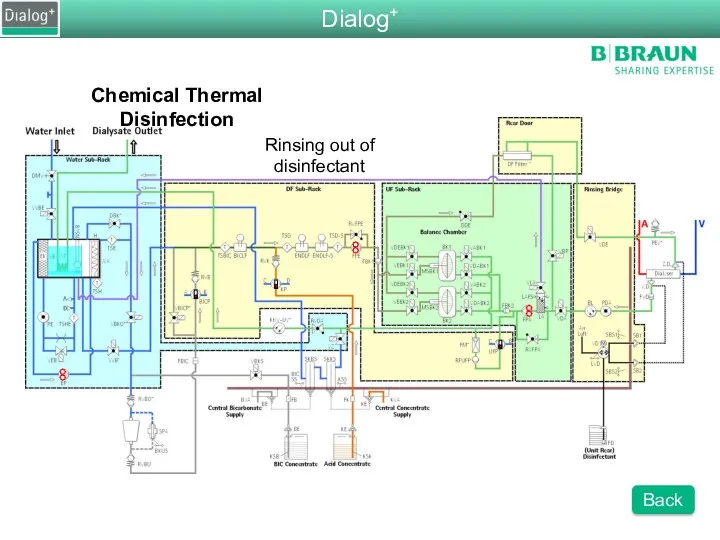
- 94. Chemical Thermal Disinfection Rinsing out of disinfectant Dialog+ Back
- 96. Скачать презентацию



































 С Новым Годом
С Новым Годом Презентация Microsoft PowerPoint
Презентация Microsoft PowerPoint Арктика. Природная зона арктических пустынь
Арктика. Природная зона арктических пустынь Анализ рынка рабочей силы. Оценка перспектив пополнения предприятия кадрами
Анализ рынка рабочей силы. Оценка перспектив пополнения предприятия кадрами Матрешка
Матрешка Александр Николаевич Островский
Александр Николаевич Островский Базовые методы и понятия программирования
Базовые методы и понятия программирования Горные ландшафты и туризм
Горные ландшафты и туризм Депонирование и мобилизация жиров
Депонирование и мобилизация жиров Личные местоимения
Личные местоимения Михаил Петрович Лазарев и его географические открытия
Михаил Петрович Лазарев и его географические открытия презентация на семинар
презентация на семинар Планируемые результаты обучения обществознанию в основной школе в соответствии с требованиями ФГОС
Планируемые результаты обучения обществознанию в основной школе в соответствии с требованиями ФГОС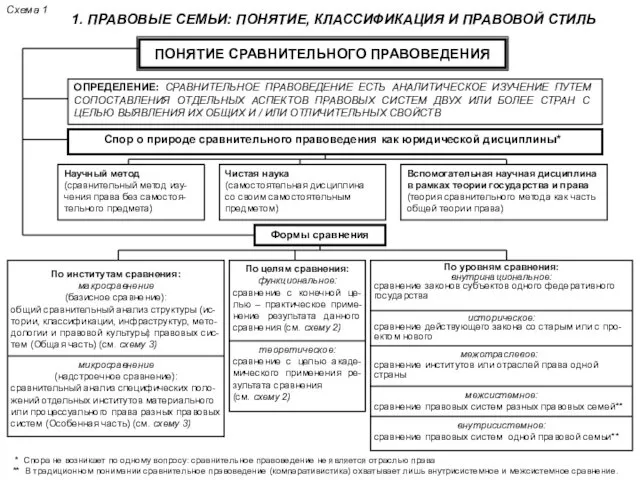 Правовые семьи: понятие, классификация и правовой стиль
Правовые семьи: понятие, классификация и правовой стиль презентация к уроку
презентация к уроку Швейная отрасль УИС
Швейная отрасль УИС Книжный магазин
Книжный магазин Самара вчера, сегодня, завтра
Самара вчера, сегодня, завтра Умная теплица
Умная теплица Фрэнсис Бэкон как основоположник эмпиризма
Фрэнсис Бэкон как основоположник эмпиризма Формы расселения населения
Формы расселения населения Квантавыя ўласцівасці выпраменьвання
Квантавыя ўласцівасці выпраменьвання Синтаксичні особливості українського ділового мовлення
Синтаксичні особливості українського ділового мовлення 20231001_seminar_08.12.2022
20231001_seminar_08.12.2022 Принципы и методы обучения ИЯ
Принципы и методы обучения ИЯ Спортивный бальный танец
Спортивный бальный танец Урок-презентация Петроград-колыбель Октября
Урок-презентация Петроград-колыбель Октября Дидактическая игра Народные промыслы
Дидактическая игра Народные промыслы