Содержание
- 2. Description of Operation Liquid nitrogen from a supply reservoir is fed through an inlet tube into
- 3. Description of Operation The Liquid detection/evaporator (diagnostic signal #9) assembly includes a liquid detector capable of
- 4. Description of Operation When liquid has been detected, in the liquid detect/evaporator assembly, droplets passing over
- 5. Description of Operation In this design, the evaporator can not only evaporates droplets of cooling agent
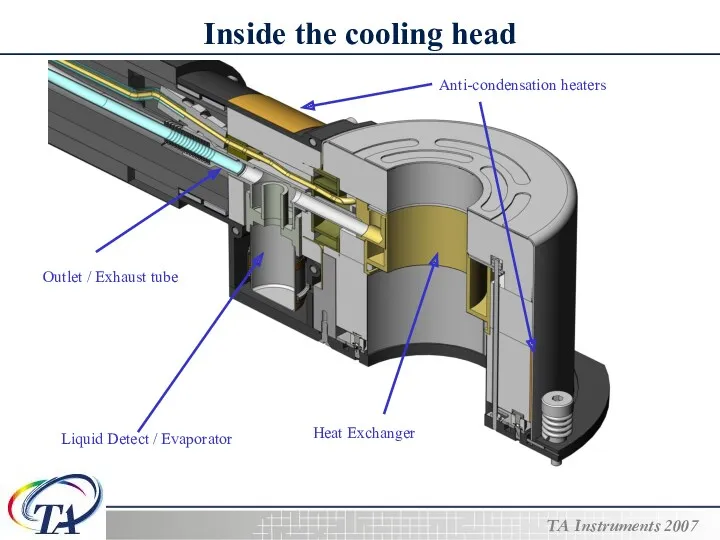
- 6. Inside the cooling head Liquid Detect / Evaporator Outlet / Exhaust tube Anti-condensation heaters Heat Exchanger
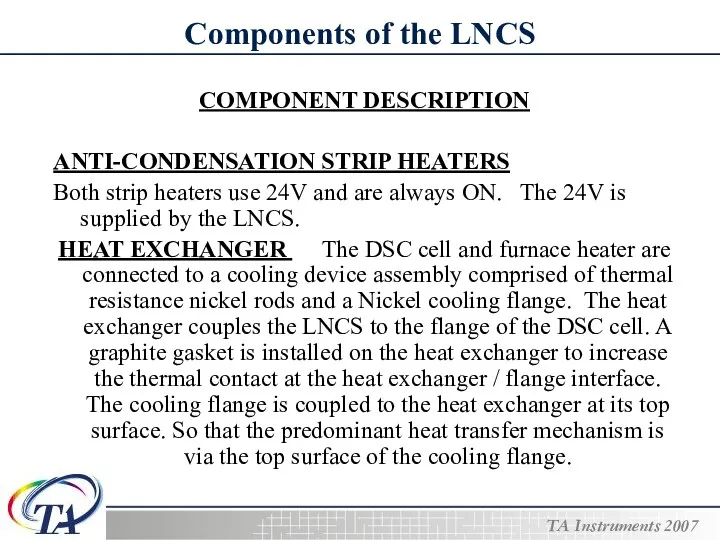
- 7. Components of the LNCS COMPONENT DESCRIPTION ANTI-CONDENSATION STRIP HEATERS Both strip heaters use 24V and are
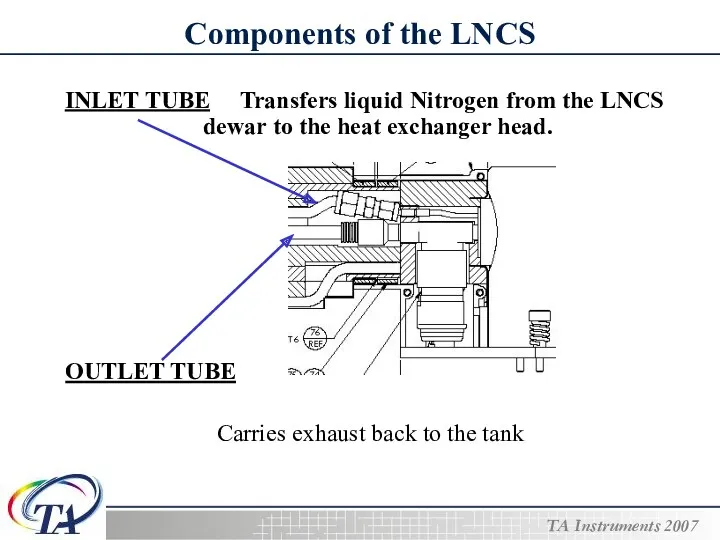
- 8. Components of the LNCS INLET TUBE Transfers liquid Nitrogen from the LNCS dewar to the heat
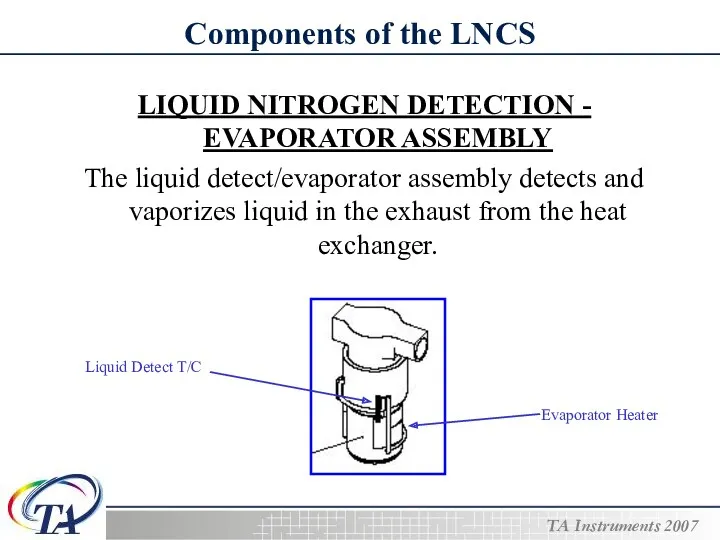
- 9. Components of the LNCS LIQUID NITROGEN DETECTION - EVAPORATOR ASSEMBLY The liquid detect/evaporator assembly detects and
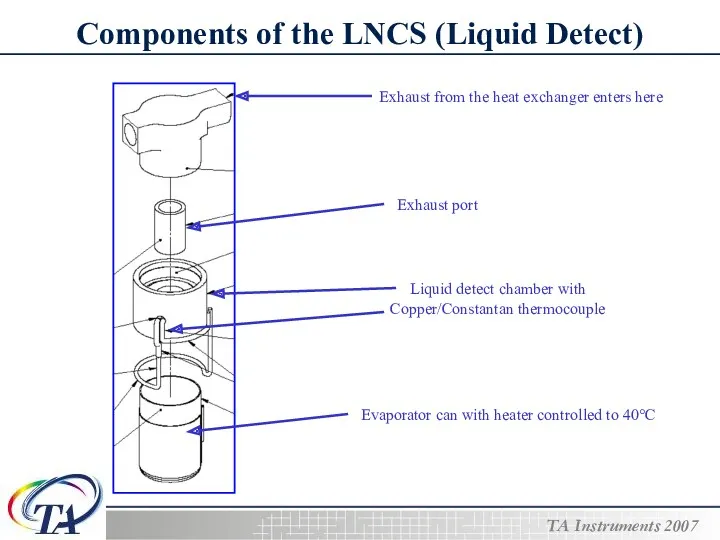
- 10. Components of the LNCS (Liquid Detect) Exhaust from the heat exchanger enters here Exhaust port Liquid
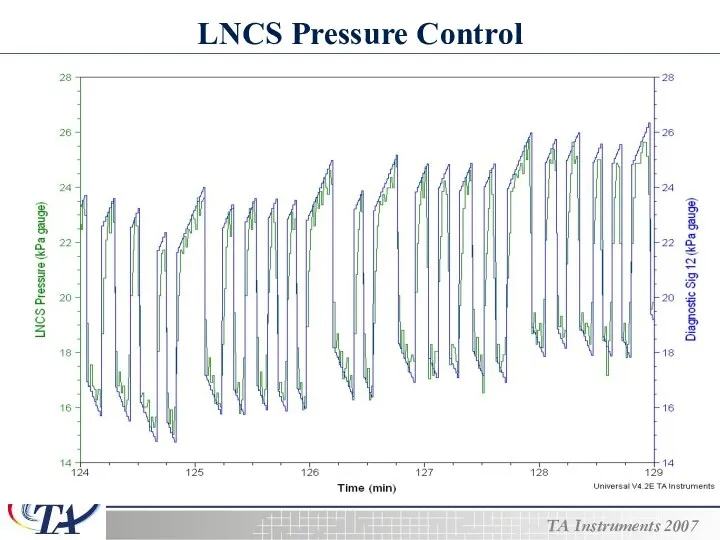
- 11. LNCS Pressure Control
- 12. LNCS Pressure range Coolant pressure requirements will vary with the heat load on the heat exchanger,
- 13. Dewar pressure control The dewar pressure is controlled by a pressure control valve assembly, which regulates
- 14. Calibrating the LNCS
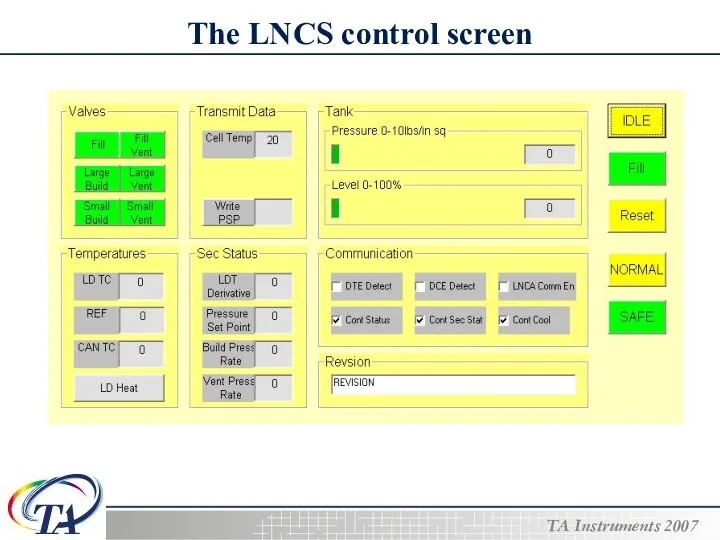
- 15. The LNCS control screen
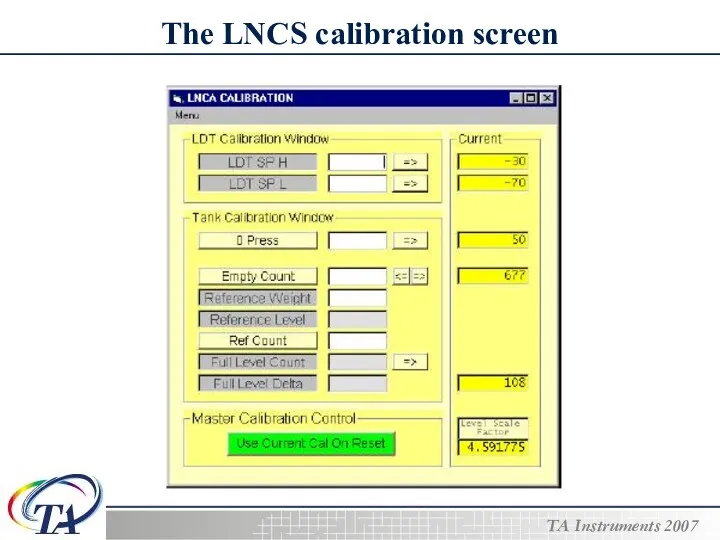
- 16. The LNCS calibration screen
- 17. Calibrating the LNCS To calibrate the LNCS before using it, follow these steps: 1. Select Menu/Control
- 18. Calibrating the LNCS 5. Click on the Commands pull down menu. Select Fill to the Neck.
- 19. Calibrating the LNCS 10. Ensure that the Master Calibration Control is set to “Use Current Cal
- 20. How to troubleshoot a LNCS Troubleshooting a LNCS system adds another layer of complexity to an
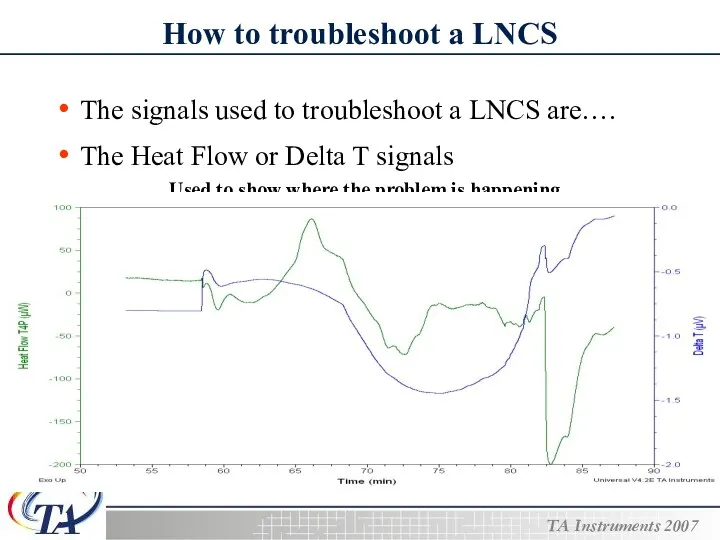
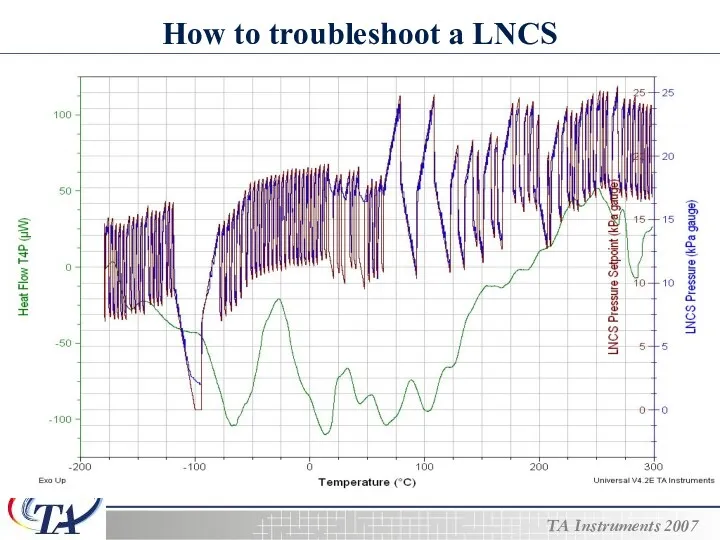
- 21. How to troubleshoot a LNCS The signals used to troubleshoot a LNCS are…. The Heat Flow
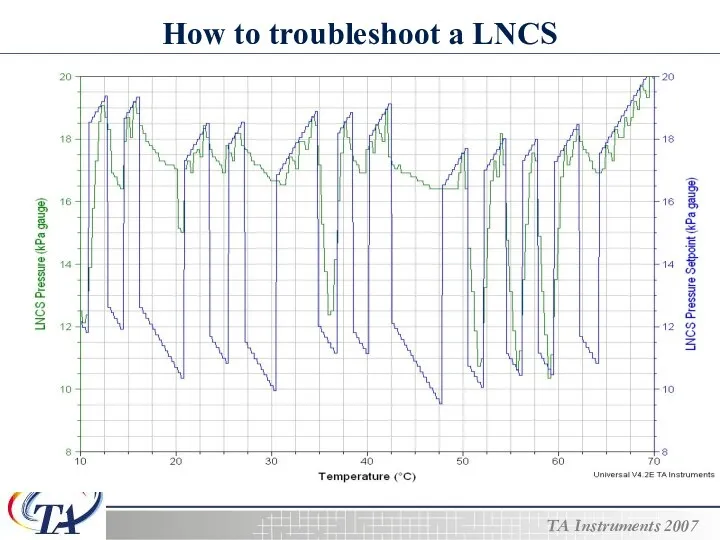
- 22. How to troubleshoot a LNCS
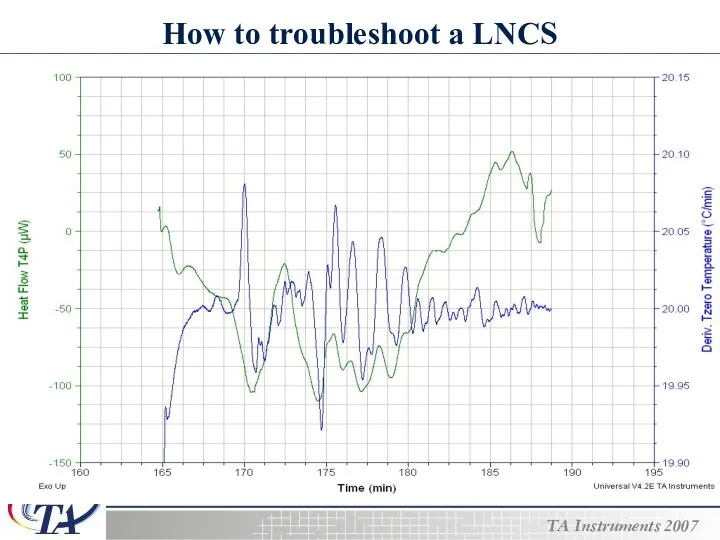
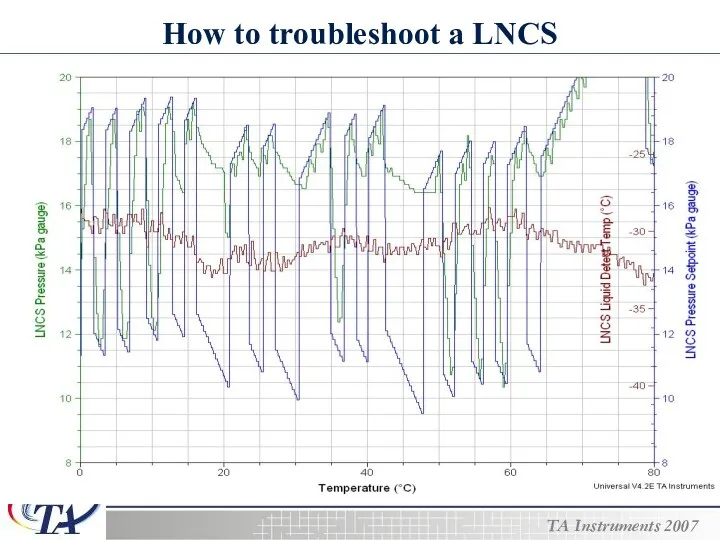
- 23. How to troubleshoot a LNCS
- 24. How to troubleshoot a LNCS
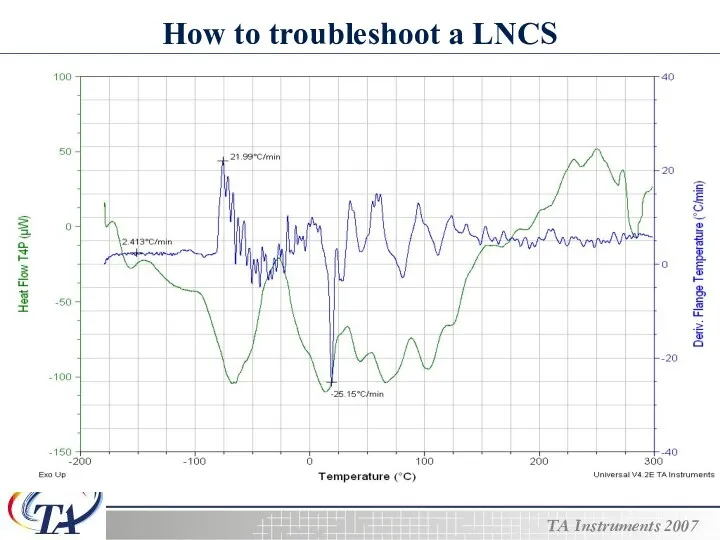
- 25. How to troubleshoot a LNCS
- 26. How to troubleshoot a LNCS
- 28. Скачать презентацию










 Презентация Әлифба бәйрәме
Презентация Әлифба бәйрәме Тренажёр - презентация Состав слова
Тренажёр - презентация Состав слова Металлургия және машина жасау өнеркәсібі
Металлургия және машина жасау өнеркәсібі Почему дует ветер
Почему дует ветер Презентация. Растительный мир России, 8 класс.
Презентация. Растительный мир России, 8 класс. The Cry of a Wounded Heart
The Cry of a Wounded Heart Основные принципы переливания крови
Основные принципы переливания крови Управление качеством эксплуатации объектов теплоэнергетики
Управление качеством эксплуатации объектов теплоэнергетики Классификация информационных систем
Классификация информационных систем Сестринский уход при гломерулонефритах
Сестринский уход при гломерулонефритах Рамка и основная надпись чертежа, для школ 8 вида
Рамка и основная надпись чертежа, для школ 8 вида Сестринский процесс при уходе за недоношенным ребенком. Лекция 2
Сестринский процесс при уходе за недоношенным ребенком. Лекция 2 Построение выреза детали ¼
Построение выреза детали ¼ Познавательное развитие в соответствии с ФГОС .
Познавательное развитие в соответствии с ФГОС . Три состояния воды
Три состояния воды Как развивать внимание ? (часть 4)
Как развивать внимание ? (часть 4) Первая помощь при повреждении грудной клетки и живота
Первая помощь при повреждении грудной клетки и живота Контроль сварных соединений
Контроль сварных соединений Минеральное питание растений
Минеральное питание растений Михаил Юрьевич Лермонтов
Михаил Юрьевич Лермонтов Повышение энергоэффективности работы сортировочного комплекса Нечётной системы станции Гомель
Повышение энергоэффективности работы сортировочного комплекса Нечётной системы станции Гомель Метод моделирования на уроках географии
Метод моделирования на уроках географии Основные понятия Управления проектами
Основные понятия Управления проектами Методы исследования механической активности сердца
Методы исследования механической активности сердца Презентация аналитического отчёта
Презентация аналитического отчёта Строение Земли. Горные породы
Строение Земли. Горные породы Автоматизация звука [Р]
Автоматизация звука [Р] ЗДОРОВЬСБЕРЕГАЮЩИЕ ТЕХНОЛОГИИ НА УРОКАХ ГЕОГРАФИИ
ЗДОРОВЬСБЕРЕГАЮЩИЕ ТЕХНОЛОГИИ НА УРОКАХ ГЕОГРАФИИ