Содержание
- 2. Outline What are environmental rights? The interpretation of environmental rights in Chinese legal systems The protection
- 3. Environmental rights Environmental rights mean any proclamation of a human right to environmental conditions of a
- 4. Environmental rights Substantive rights Procedural rights
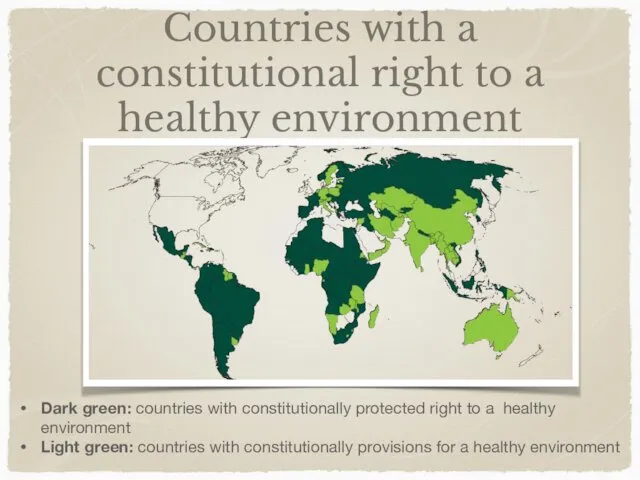
- 5. Countries with a constitutional right to a healthy environment Dark green: countries with constitutionally protected right
- 6. National constitutions Environmental rights have been enshrined in more than 150 national constitutions, expressed in a
- 7. International & regional treaties Human rights and the environment European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR) Article
- 8. How environmental rights are defined in China? Constitution of People’s Republic of China (2018) Article 26:
- 9. Different approaches to environment protection Regulatory-based approach Right-based approach Environment protection as a state duty Environmental
- 10. Ecological Civilization Constitution of People’s Republic of China (2018) Preamble: …promote the coordinated development of material,
- 11. Ecologization of Law China’s vision to prioritize ecological civilization and green development in a wide range
- 12. Substantive environmental rights in China Civil rights: the right to life ,the right to health, property
- 13. Substantive environmental rights in China Public rights: the right to challenge the substantive and procedural legality
- 14. Procedural environmental rights in China Public participation as one of the fundamental principles in China’s policy
- 15. Access to environment information Article 53, EPL 2015: citizens, legal persons and other organizations shall, according
- 16. Public participation in decision making Public participation in Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Article 56, EPL 2015:
- 17. Access to justice Private damage vs. Public nuisance Widespread nature of environmental damage No individual victim
- 18. The legislative development of PIL in China Civil Procedural Law 2014/2017 Environmental Protection Law 2015 Administrative
- 19. competent authorities Polluters NGOs Procurators Recommendations Public authorities Ecological damage compensation Public interest litigation
- 20. NGOs The standing conditions of NGOs: Article 58, EPL 2014 Legally registered under the civil affairs
- 21. Procurators Civil Public Interest Litigation Article 55, Civil Procedural Law 2017 Procuratorarte may file a lawsuit
- 22. Competent authorities Ecological damage compensation system (2017) The competent authorities could sue the polluters for the
- 23. Challenges for PIL in China The multiple approaches for the protection of environmental rights To encourage
- 24. Challenges for PIL in China The conflicts of interests between different actors The division between administrative
- 26. Скачать презентацию





















 Мозжилкина Д.А. ИБМ4 11-А (5)
Мозжилкина Д.А. ИБМ4 11-А (5) Нормативное обоснование предпродажная подготовка ТАА
Нормативное обоснование предпродажная подготовка ТАА Профилактика пожаров в повседневной жизни и организация защиты населения
Профилактика пожаров в повседневной жизни и организация защиты населения Трансформаторный метод контроля
Трансформаторный метод контроля Еволюція одноклiтинних і багатоклітинних організмів. Перiодизація еволюційних явищ
Еволюція одноклiтинних і багатоклітинних організмів. Перiодизація еволюційних явищ Cholesterol and Health
Cholesterol and Health План перспективного развития ТОР Находка
План перспективного развития ТОР Находка Дозаторы НПС
Дозаторы НПС Технология малярных работ
Технология малярных работ Презентация Золотая осень в средней группе.
Презентация Золотая осень в средней группе. Множественная миелома и другие парапротеинемии
Множественная миелома и другие парапротеинемии Масленица
Масленица Звуковая мозаика
Звуковая мозаика Сенсорное развитие предметно-манипулятивной деятельности детей раннего возраста
Сенсорное развитие предметно-манипулятивной деятельности детей раннего возраста Гражданское общество (Самарская область)
Гражданское общество (Самарская область) 20191116_sis_semeynaya_psmhoterapiya_v_tsdk
20191116_sis_semeynaya_psmhoterapiya_v_tsdk Анализ окружающей среды города Бобруйска
Анализ окружающей среды города Бобруйска География. Географическая викторина
География. Географическая викторина Средства и методы оценки качества непродовольственных товаров
Средства и методы оценки качества непродовольственных товаров Накорми собаку. Игра- тренажёр. 1 класс
Накорми собаку. Игра- тренажёр. 1 класс Опыты с песком (младший дошкольный возраст)
Опыты с песком (младший дошкольный возраст) Художественное объединение символистской направленности Голубая роза (1907-1910)
Художественное объединение символистской направленности Голубая роза (1907-1910) Мобильное приложение для москвичей и гостей столицы
Мобильное приложение для москвичей и гостей столицы Результат проектной деятельности. Тема -Музей
Результат проектной деятельности. Тема -Музей Витамины
Витамины Кожа, подкожножировая клетчатка и лимфатические узлы у детей
Кожа, подкожножировая клетчатка и лимфатические узлы у детей Развитие творческих способностей у детей младшего школьного возраста на занятии в мастерской Сувенир
Развитие творческих способностей у детей младшего школьного возраста на занятии в мастерской Сувенир ОРКСЭ для родителей
ОРКСЭ для родителей