Содержание
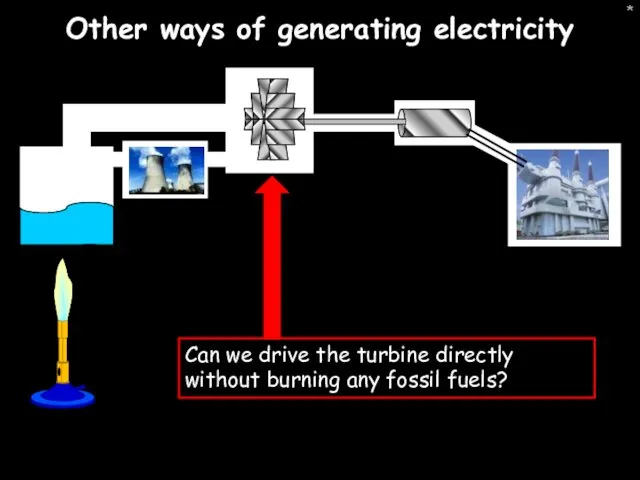
- 2. * Other ways of generating electricity
- 3. * Wind Power
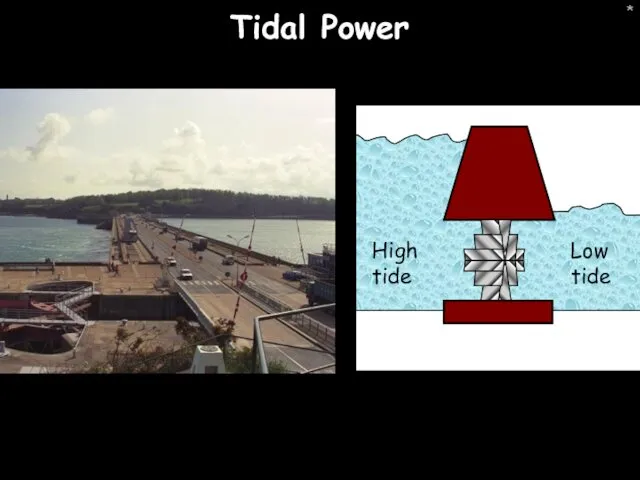
- 4. * Tidal Power
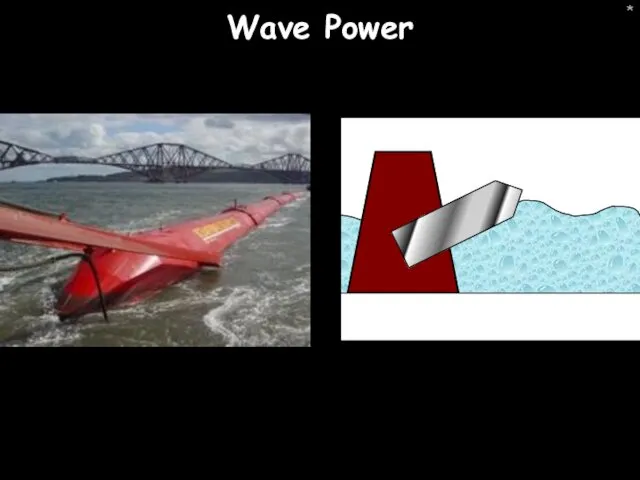
- 5. * Wave Power
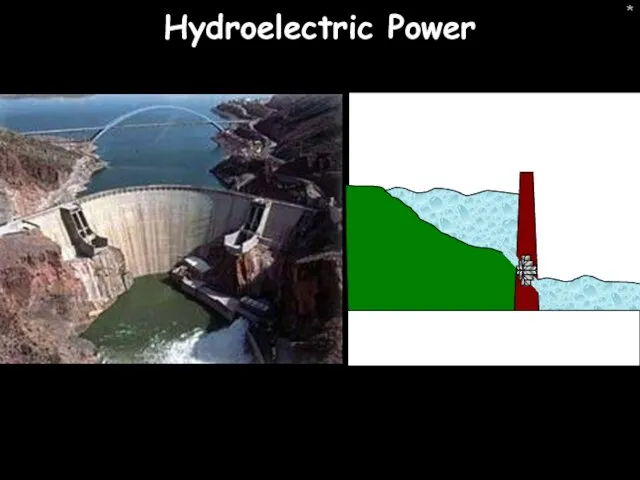
- 6. * Hydroelectric Power
- 7. * Biomass
- 8. * Biofuels Biomass can be used as a fuel in a number of ways: Fast-growing trees
- 9. * Solar Energy Heating for homes – these pipes carry water that absorbs heat energy and
- 10. * Geothermal Energy
- 11. * Geothermal Energy
- 12. * Solar Panels and Thermal Towers
- 13. * Using Solar Energy in remote places
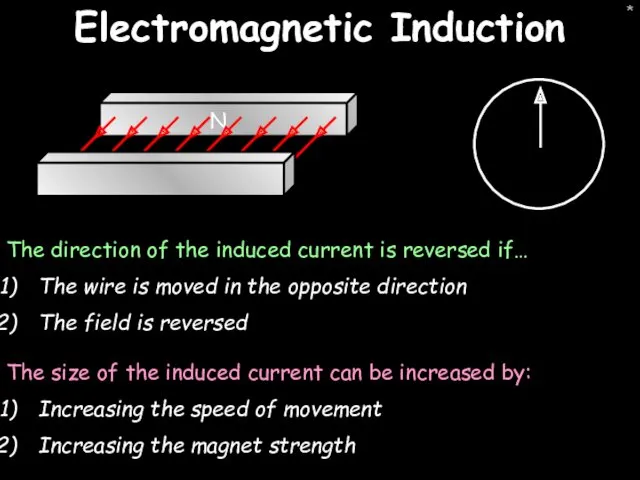
- 14. * Electromagnetic Induction N The direction of the induced current is reversed if… The wire is
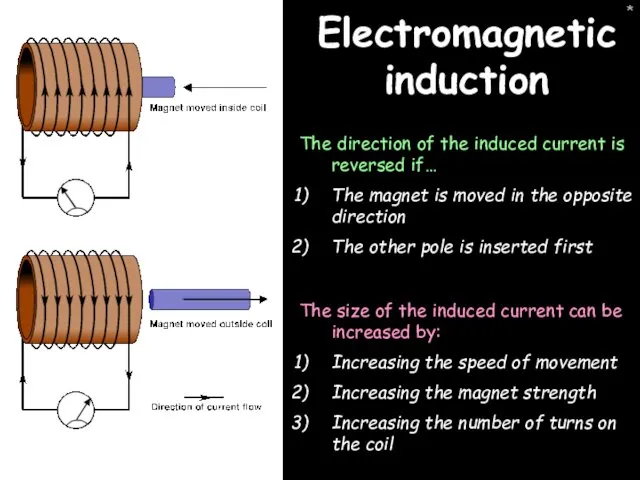
- 15. * Electromagnetic induction The direction of the induced current is reversed if… The magnet is moved
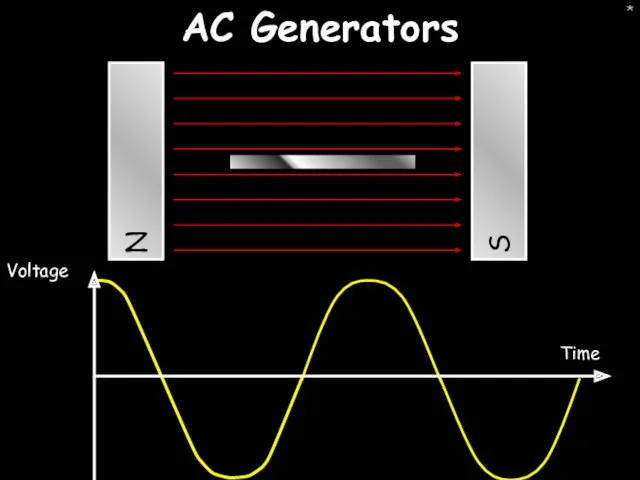
- 16. * AC Generators
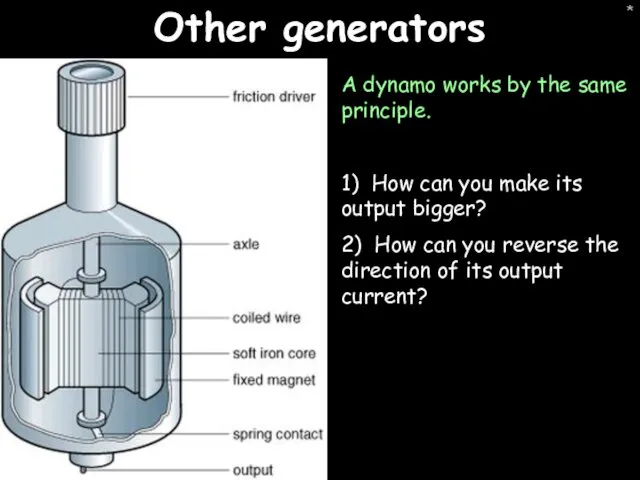
- 17. * Other generators A dynamo works by the same principle. 1) How can you make its
- 18. Large-scale production of Electricity *
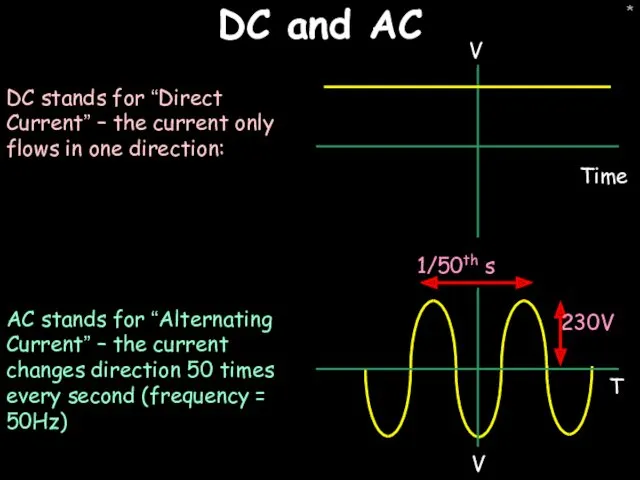
- 19. * DC and AC DC stands for “Direct Current” – the current only flows in one
- 20. * The National Grid Electricity reaches our homes from power stations through the National Grid: If
- 21. * Power Lines Here’s my new shed. I want to connect it to the electricity I
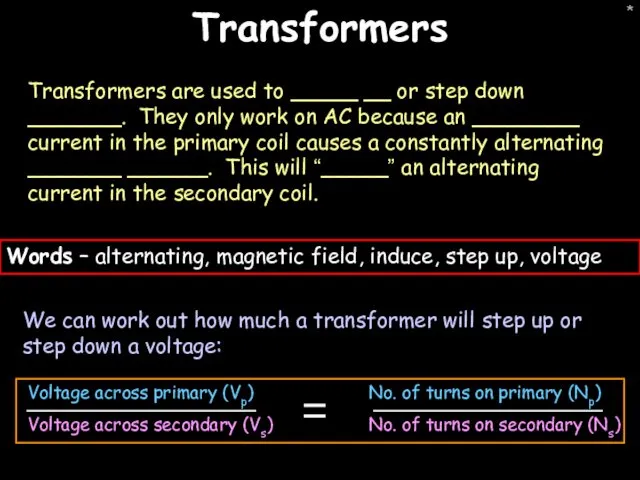
- 22. * Transformers Transformers are used to _____ __ or step down _______. They only work on
- 23. * Some transformer questions
- 24. * Some example questions A transformer increases voltage from 10V to 30V. What is the ratio
- 25. * The Cost of Electricity Electricity is measured in units called “kilowatt hours” (kWh). For example…
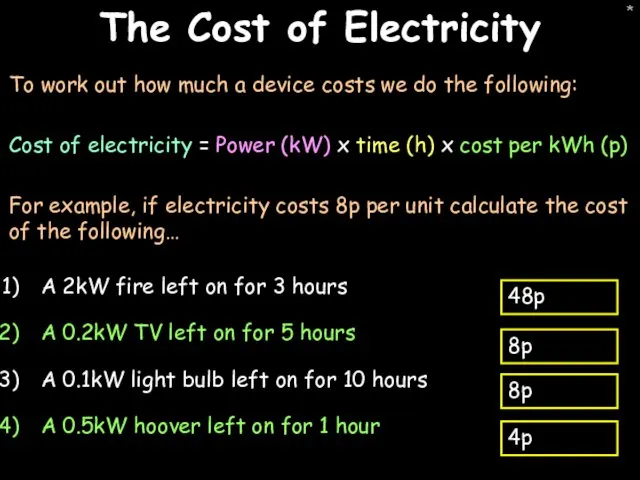
- 26. * The Cost of Electricity To work out how much a device costs we do the
- 27. * Reducing Energy Consumption Which one is more cost-effective? Jane wants to replace all the bulbs
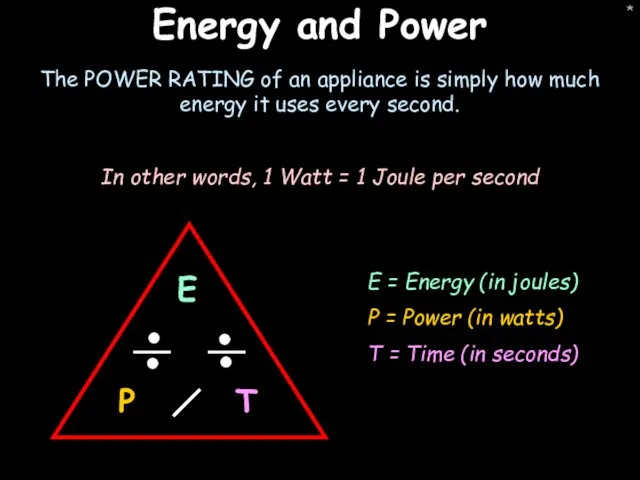
- 28. * Energy and Power The POWER RATING of an appliance is simply how much energy it
- 29. * Some example questions What is the power rating of a light bulb that transfers 120
- 30. Topic 6 – Energy and the Future *
- 31. * The 9 types of energy
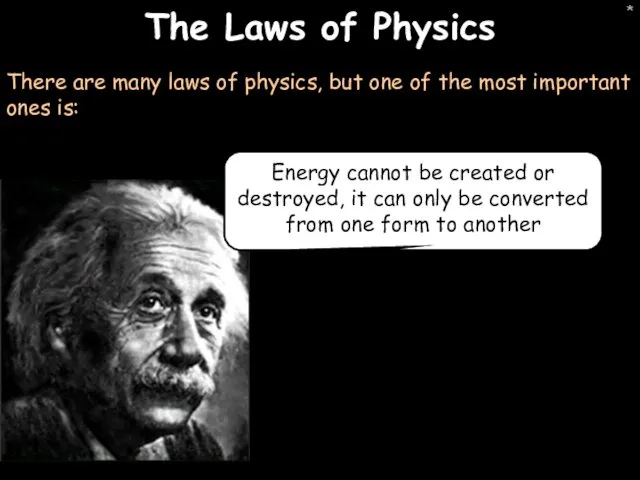
- 32. * The Laws of Physics There are many laws of physics, but one of the most
- 33. * Energy changes To describe an energy change for a light bulb we need to do
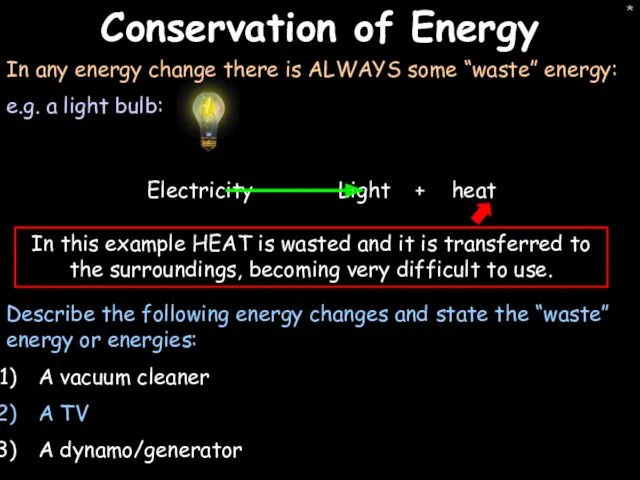
- 34. * Conservation of Energy In any energy change there is ALWAYS some “waste” energy: e.g. a
- 35. * Efficiency Efficiency is a measure of how much USEFUL energy you get out of an
- 36. * Some examples of efficiency… 5000J of electrical energy are put into a motor. The motor
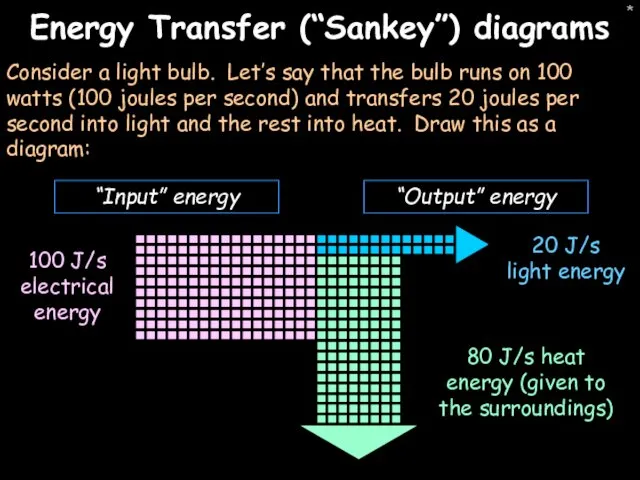
- 37. * Energy Transfer (“Sankey”) diagrams Consider a light bulb. Let’s say that the bulb runs on
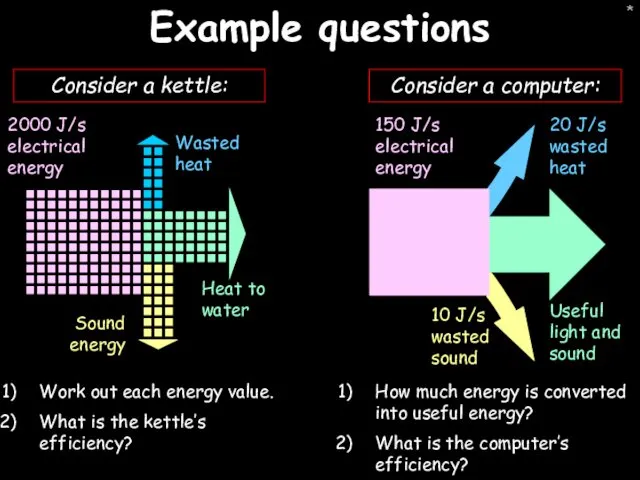
- 38. * Example questions
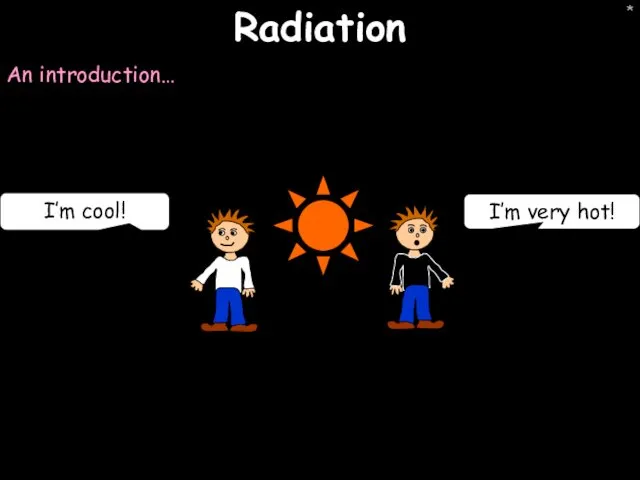
- 39. * Radiation An introduction… I’m very hot! I’m cool!
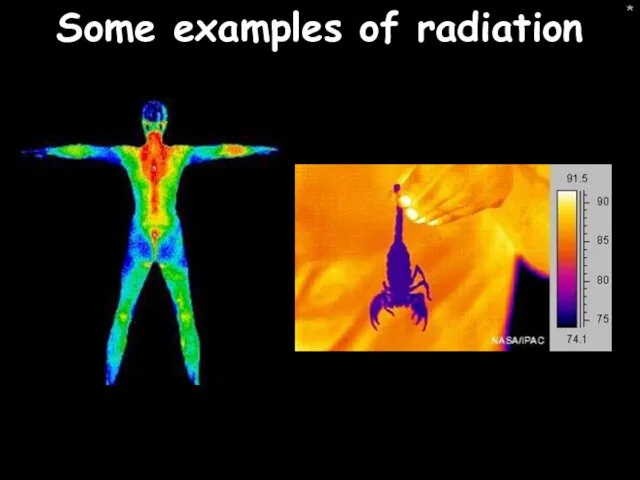
- 40. * Some examples of radiation
- 41. * Some examples of radiation
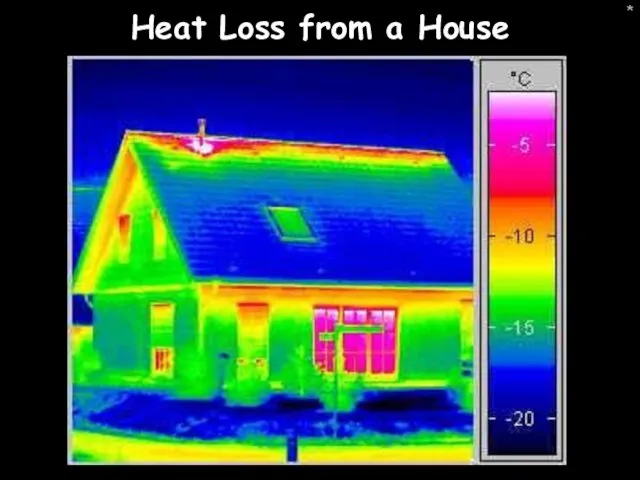
- 42. * Heat Loss from a House
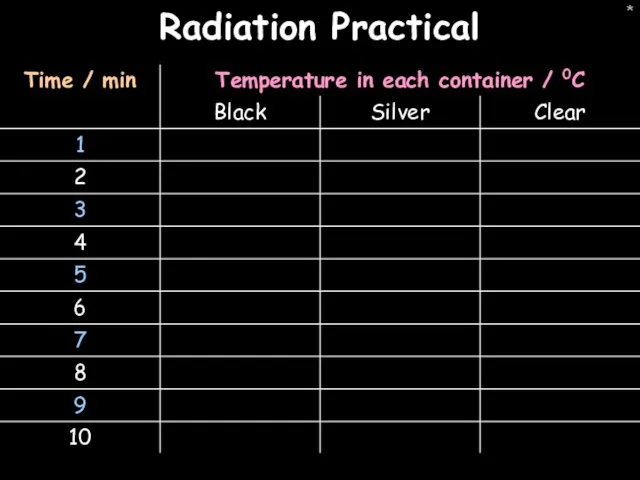
- 43. * Radiation Practical
- 45. Скачать презентацию






















 Первые фотоаппараты
Первые фотоаппараты Малые архитектурные формы МАФ. Стили и концепция
Малые архитектурные формы МАФ. Стили и концепция Мотивация и лидерство на предприятиях бережливого производства
Мотивация и лидерство на предприятиях бережливого производства Проблемы трудоустройства молодых специалистов в России
Проблемы трудоустройства молодых специалистов в России Project: Global Social Media PlanTopic:Traffic Light Beetle Subline: An interactive game showing the range of colourful Beetle
Project: Global Social Media PlanTopic:Traffic Light Beetle Subline: An interactive game showing the range of colourful Beetle Реалізація програмного комплексу ip-телефонії на основі PBX Asterisk
Реалізація програмного комплексу ip-телефонії на основі PBX Asterisk Короткие и длинные волны на воде
Короткие и длинные волны на воде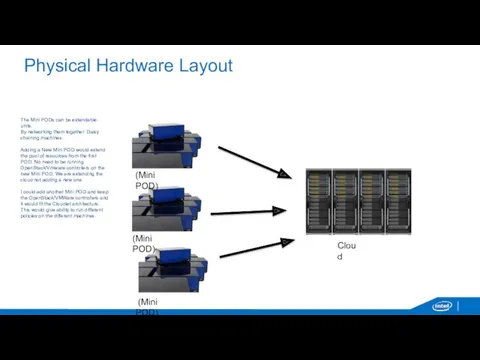 Physical Hardware Layout
Physical Hardware Layout Проекты систем диспетчеризации жилых домов
Проекты систем диспетчеризации жилых домов Десять основных положений нового закона Об образовании в РФ
Десять основных положений нового закона Об образовании в РФ Цитомегалоловирустар, хламидиялық герпестік инфекция және жүктілік
Цитомегалоловирустар, хламидиялық герпестік инфекция және жүктілік Интерфейс передачи сообщений MPI
Интерфейс передачи сообщений MPI Сфинксы. 10 класс
Сфинксы. 10 класс Характеристики камеры
Характеристики камеры Презентация Органические вещества
Презентация Органические вещества Игра Собери портфель
Игра Собери портфель Флора и фауна озера Байкал
Флора и фауна озера Байкал Тайны магических квадратов
Тайны магических квадратов Основные понятия информационных технологий
Основные понятия информационных технологий Фразеологизмы. Что это? Как их понять?
Фразеологизмы. Что это? Как их понять? Настройка репликации на Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Standard
Настройка репликации на Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Standard Фронтальное занятие с детьми старшей логопедической группы по лексической теме Продукты питания
Фронтальное занятие с детьми старшей логопедической группы по лексической теме Продукты питания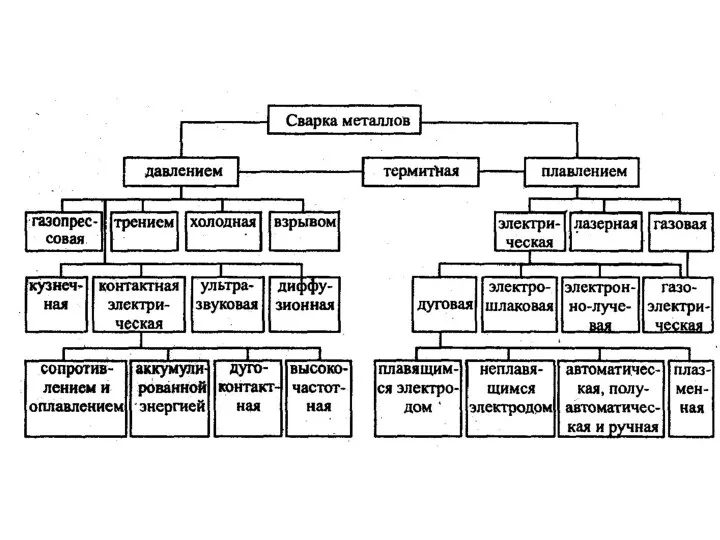 Сварка металлов
Сварка металлов Темперамент. Тема 6
Темперамент. Тема 6 Методы активизации поиска решений нестандартных задач. Формализованные методы генерации идей
Методы активизации поиска решений нестандартных задач. Формализованные методы генерации идей Повесть о житии и о храбрости благоверного и великого князя Александра Невского
Повесть о житии и о храбрости благоверного и великого князя Александра Невского Флористика. Коллаж из природного материала
Флористика. Коллаж из природного материала Презентация ко Дню Героев России
Презентация ко Дню Героев России