- Главная
- Английский язык
- Ethnic conflict

Содержание
- 2. Done by the student of the Faculty of International Relations group 305 Nurgisaeva Aizhan Aims of
- 4. Ethnic conflict is a form of conflict in which the objectives of at least one party
- 5. Ethnic identity is created by social interactions between individuals and groups and remains therefore beyond a
- 7. Causes and main factors I n several scholarly articles, Michael Edward Brown provided a useful approach
- 8. Once ethnic conflict breaks out, it is difficult to stop. Massive human-rights violations and physical attacks
- 9. Ethnic conflict is one of the major threats to international peace and security. Conflicts in the
- 10. Cultural differences and ethnic conflicts are important issues shaping international politics. Because cultural affiliations and ethnic
- 13. Скачать презентацию
Done
by the student of the Faculty of International Relations group
Done by the student of the Faculty of International Relations group
Aims of the project: To investigate such phenomenon as a part of social processes
To clarify causes , consequences of ethnic conflicts
To give examples of ethnic conflicts
Ethnic conflict is a form of conflict in which the objectives
Ethnic conflict is a form of conflict in which the objectives
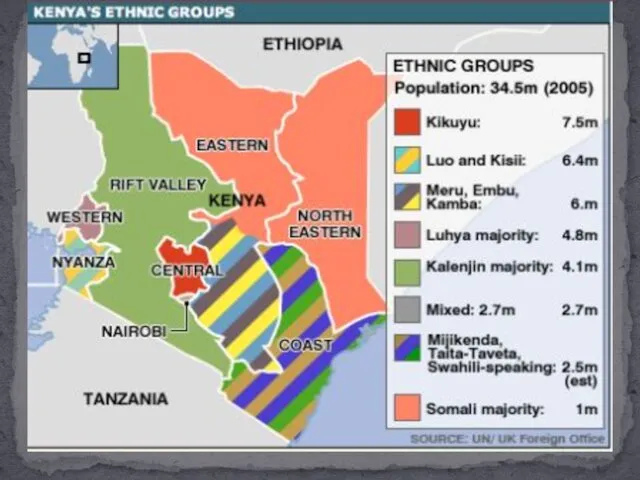
T he terms ethnic and ethnicity have their roots in the Greek word ethnos, which describes a community of common descent. In ethnic conflict research, the terms ethnic group, communal group, ethnic community, people, and minority are mostly used interchangeably. Two elements provide the basis to identify ethnic groups: first, the accentuation of cultural traits and, second, the sense that those traits distinguish the group from the members of the society who do not share the differentiating characteristics.
Ethnic identity is formed by both tangible and intangible characteristics. Tangible characteristics, such as shared culture or common visible physical traits, are important because they contribute to the group’s feeling of identity, solidarity, and uniqueness.
Definition and origin if the term
Ethnic identity is created by social interactions between individuals and groups
Ethnic identity is created by social interactions between individuals and groups
Causes
Causes and main factors
I n several scholarly articles, Michael Edward Brown
Causes and main factors
I n several scholarly articles, Michael Edward Brown
Once ethnic conflict breaks out, it is difficult to stop. Massive
Once ethnic conflict breaks out, it is difficult to stop. Massive
Even if fought at a low level of intensity, protracted ethnic conflicts have a great impact on the affected society. The lack of functional or legitimate political institutions, weak economic performance, a nonexistent or polarized structure of civil society, and antagonized elites lead to polarization and separation, leaving societies deeply divided and prone to further ethnic strife. In addition, ethnic conflicts have very direct effects far beyond their epicentres
Dynamics of ethnic conflict
Ethnic conflict is one of the major threats to international peace
Ethnic conflict is one of the major threats to international peace
Examples
Cultural differences and ethnic conflicts are important issues shaping international politics.
Cultural differences and ethnic conflicts are important issues shaping international politics.
Conclusion









 Welcome to Canada
Welcome to Canada Irregular Verbs
Irregular Verbs Give the number
Give the number Past Simple (Прошедшее простое время)
Past Simple (Прошедшее простое время) Things i like
Things i like Cheburashka. Past Simple
Cheburashka. Past Simple The best of times. 3 класс
The best of times. 3 класс Учимся читать
Учимся читать Describing graphs
Describing graphs Milk and milk products
Milk and milk products basic English grammar. Present+Simple
basic English grammar. Present+Simple London – the сapital of UK
London – the сapital of UK Who want to be a millioner
Who want to be a millioner Visiting animals
Visiting animals The United States of America
The United States of America The best Christmas movies are
The best Christmas movies are What are you look like
What are you look like George Washington
George Washington Как интересно провести завершающий урок в учебном году
Как интересно провести завершающий урок в учебном году Английский язык в современном мире
Английский язык в современном мире Seasons and the weather
Seasons and the weather Sport in our life
Sport in our life Urbanization. Urban and rural population of the world
Urbanization. Urban and rural population of the world Spotlight 4. Module 7. Units 13-14. Days to remember
Spotlight 4. Module 7. Units 13-14. Days to remember Мои первые уроки чтения (гласные)
Мои первые уроки чтения (гласные) Lukoil company
Lukoil company House and home
House and home A landslide
A landslide