Содержание
- 2. Topics Post World War II Economics German Economy vs. American Economy Solidarity Eurozone Economics
- 3. Post World War II Economics World War II destroyed 20% of housing Scorched earth policy Food
- 4. Post World War II Economics How would West Germany recover? Elimination of price controls Price controls
- 5. Post World War II Economics What about the Marshall Plan? Aid programs only totaled $2 billion
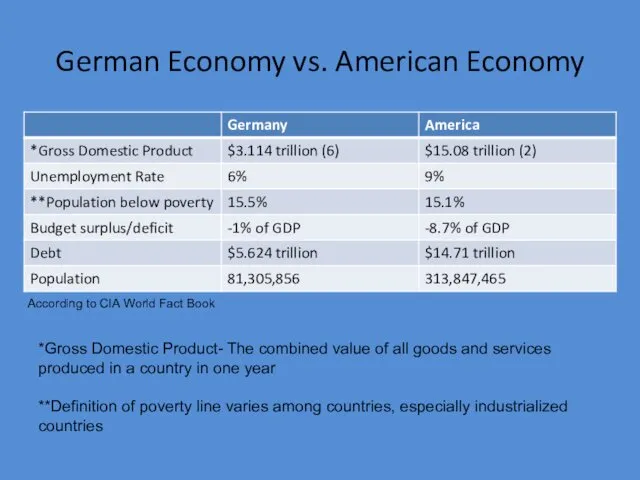
- 6. German Economy vs. American Economy *Gross Domestic Product- The combined value of all goods and services
- 7. Solidarity in Oberhausen $11,000 debt per capita Higher than anywhere else in Germany Borrows $500,000 a
- 8. Eurozone Economics German Chancellor Angela Merkel and French President François Hollande dine at “Das Austerity Euro-Café”
- 9. Summary Post World War II Economics Price controls eliminated, marginal tax reduced German Economy vs. American
- 11. Скачать презентацию







 Государственная поддержка развития предпринимательства в Ленинградской области
Государственная поддержка развития предпринимательства в Ленинградской области Классическая политическая экономия
Классическая политическая экономия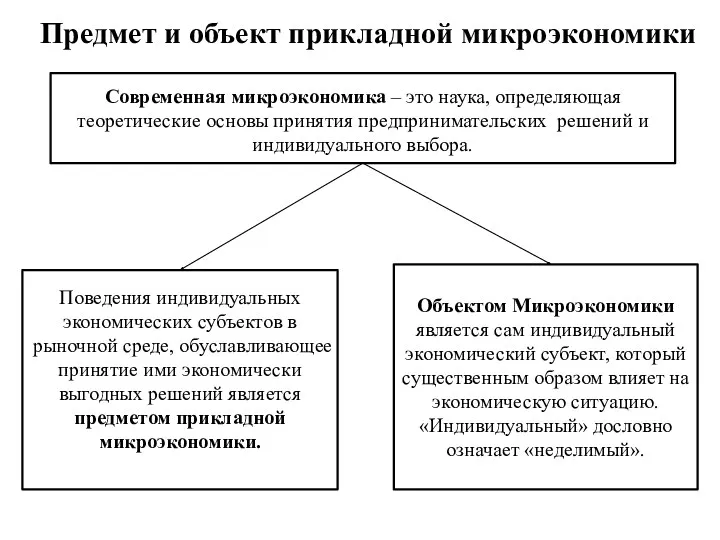 Предмет и объект прикладной микроэкономики
Предмет и объект прикладной микроэкономики Повышение финансовой грамотности в области семейного бюджета
Повышение финансовой грамотности в области семейного бюджета Қазақстандағы жергілікті басқаруды ұйымдастыру
Қазақстандағы жергілікті басқаруды ұйымдастыру International Economic. Analysis 1.1
International Economic. Analysis 1.1 Формы статистического наблюдения
Формы статистического наблюдения Банковская система Российской Федерации и проблемы её развития
Банковская система Российской Федерации и проблемы её развития Микроэкономика и макроэкономика
Микроэкономика и макроэкономика Инвестиционный проект: Увеличение мощности хранения газа в ПХГ Бозой
Инвестиционный проект: Увеличение мощности хранения газа в ПХГ Бозой Деньги и их функции в экономике
Деньги и их функции в экономике Проверочная работа по разделу Хозяйство России
Проверочная работа по разделу Хозяйство России Предпринимательство и его роль в экономике
Предпринимательство и его роль в экономике Макроэкономика - продвинутый уровень
Макроэкономика - продвинутый уровень Инфляция. Антиинфляционная политика. (Тема 8)
Инфляция. Антиинфляционная политика. (Тема 8) Міжнародна економічна інтеграція
Міжнародна економічна інтеграція Экономикалық талдаудың аспектілері
Экономикалық талдаудың аспектілері Өндіріс факторларының нарығы
Өндіріс факторларының нарығы Главные вопросы экономики. Тема 19
Главные вопросы экономики. Тема 19 Economics and management of network. Industries
Economics and management of network. Industries Административно-правовые основы управления отдельными отраслями экономики в Республике Беларусь
Административно-правовые основы управления отдельными отраслями экономики в Республике Беларусь Экспертно-аналитические технологии и инструментальные средства подготовки и принятия управленческих решений
Экспертно-аналитические технологии и инструментальные средства подготовки и принятия управленческих решений Қазақстандағы жел энергиясының даму жолдары
Қазақстандағы жел энергиясының даму жолдары Итоги социально-экономического развития Липецкого муниципального района за 6 месяцев 2019 года
Итоги социально-экономического развития Липецкого муниципального района за 6 месяцев 2019 года Ресурсы предприятия
Ресурсы предприятия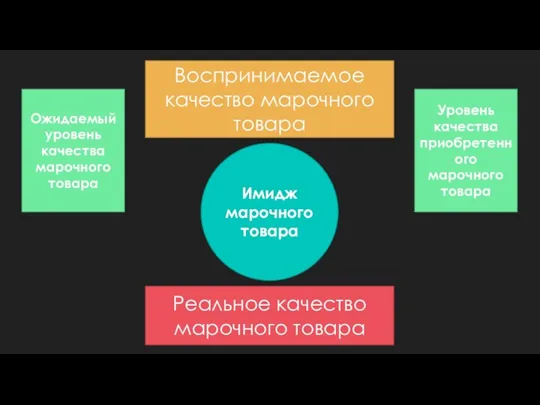 Ожидаемый уровень качества марочного товара
Ожидаемый уровень качества марочного товара От бюджета стагнации к устойчивому росту экономики
От бюджета стагнации к устойчивому росту экономики Методическая разработка урока Деятельность человека
Методическая разработка урока Деятельность человека