Содержание
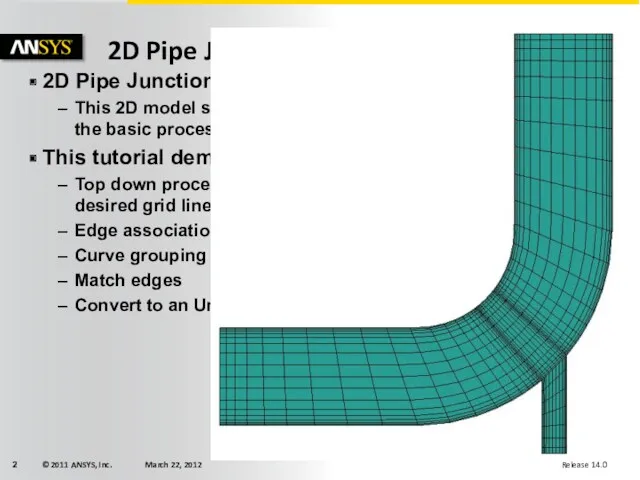
- 2. 2D Pipe Junction This 2D model starts you out simple, but shows the basic process and
- 3. Create a Project The pull down next to the file name can be used to quickly
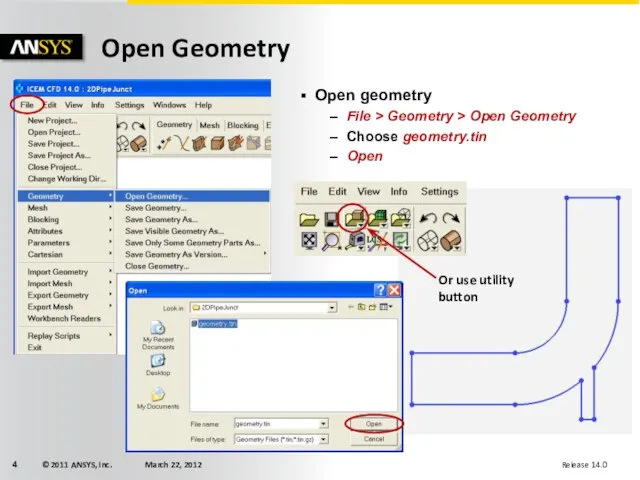
- 4. Open Geometry Open geometry File > Geometry > Open Geometry Choose geometry.tin Open Or use utility
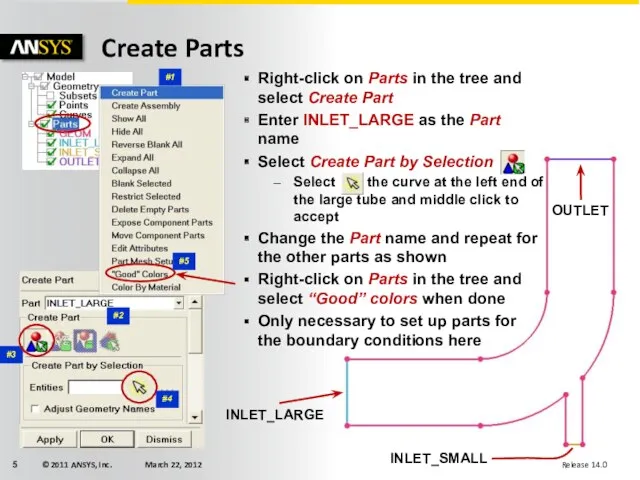
- 5. Create Parts INLET_LARGE INLET_SMALL OUTLET Right-click on Parts in the tree and select Create Part Enter
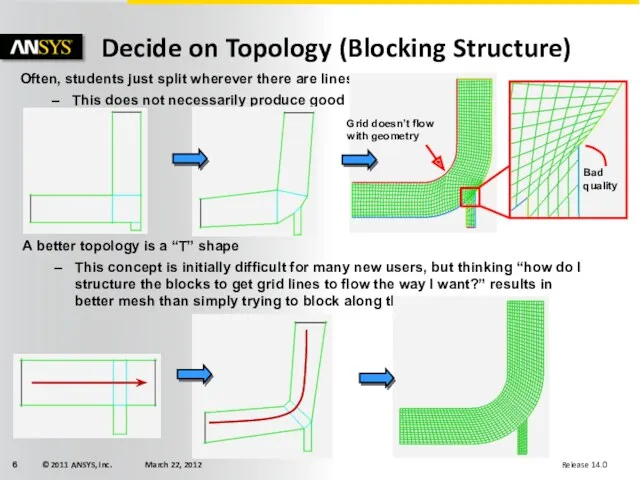
- 6. Often, students just split wherever there are lines or features This does not necessarily produce good
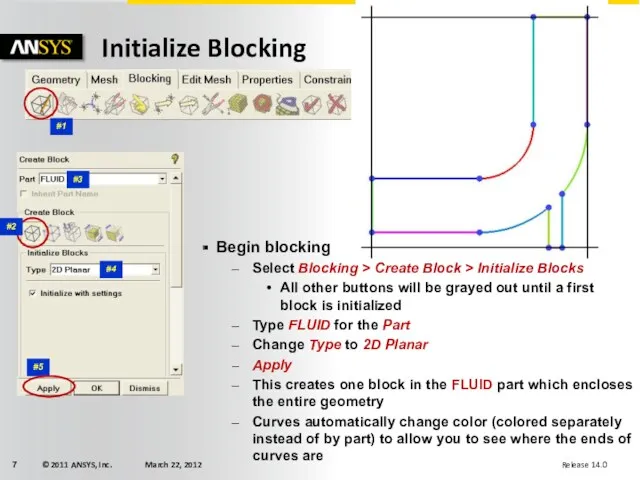
- 7. Initialize Blocking #4 #1 #5 #3 Begin blocking Select Blocking > Create Block > Initialize Blocks
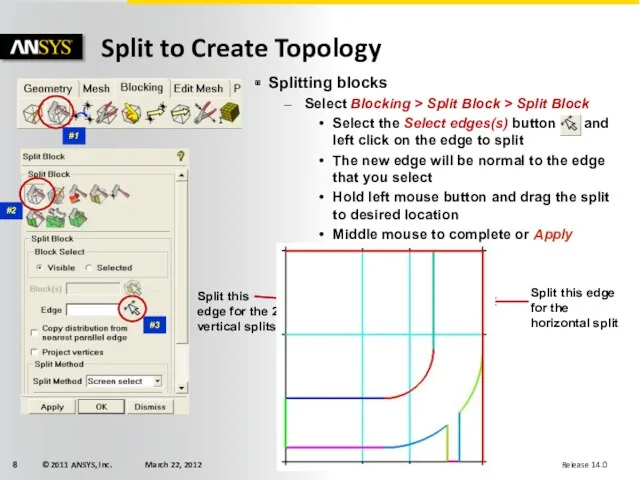
- 8. Splitting blocks Select Blocking > Split Block > Split Block Select the Select edges(s) button and
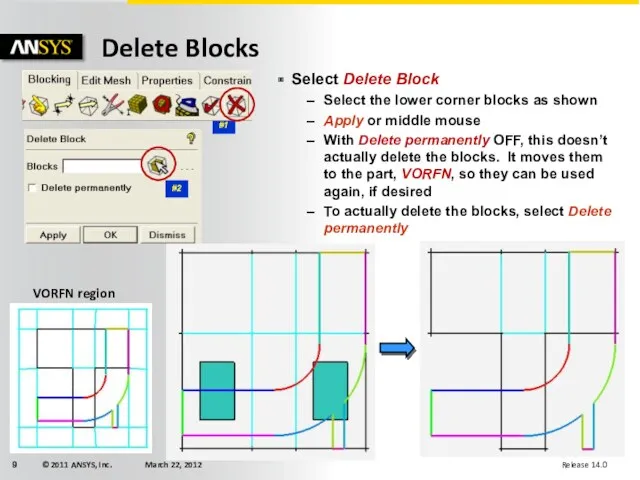
- 9. Delete Blocks #1 #2 Select Delete Block Select the lower corner blocks as shown Apply or
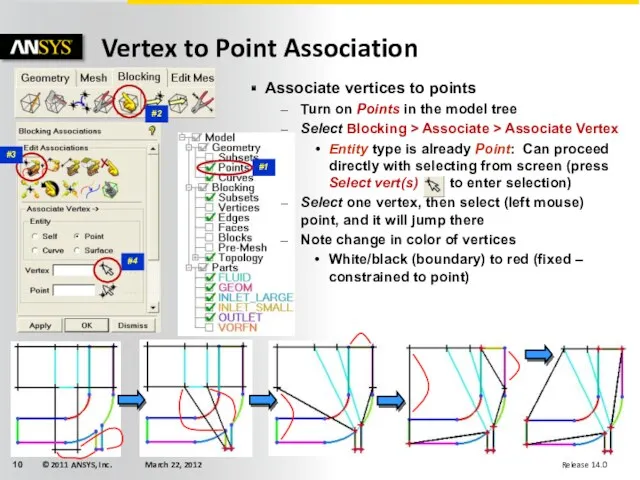
- 10. Associate vertices to points Turn on Points in the model tree Select Blocking > Associate >
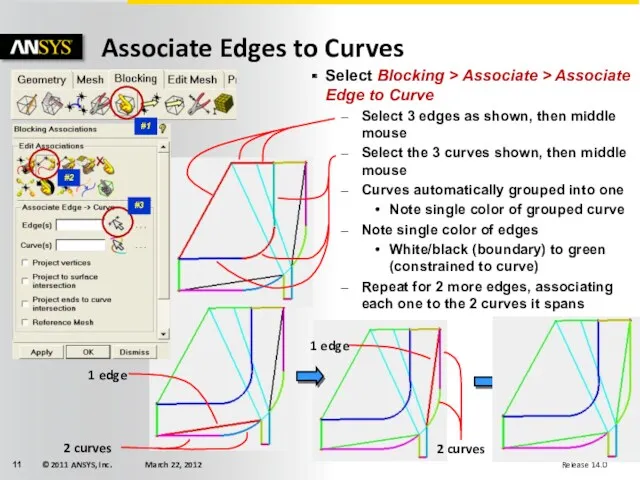
- 11. 1 edge 2 curves 1 edge 2 curves Select Blocking > Associate > Associate Edge to
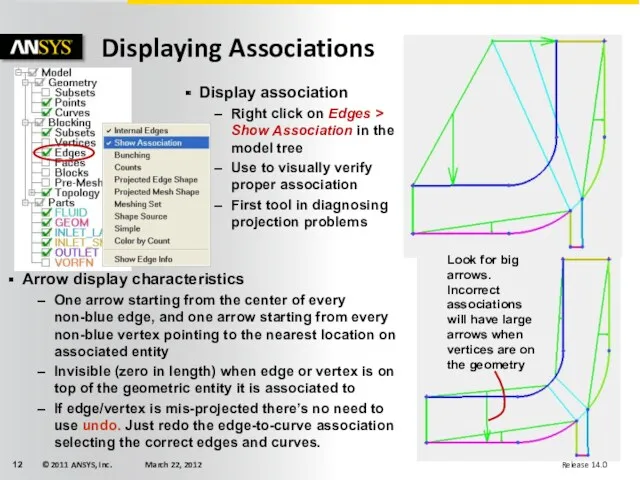
- 12. Displaying Associations Look for big arrows. Incorrect associations will have large arrows when vertices are on
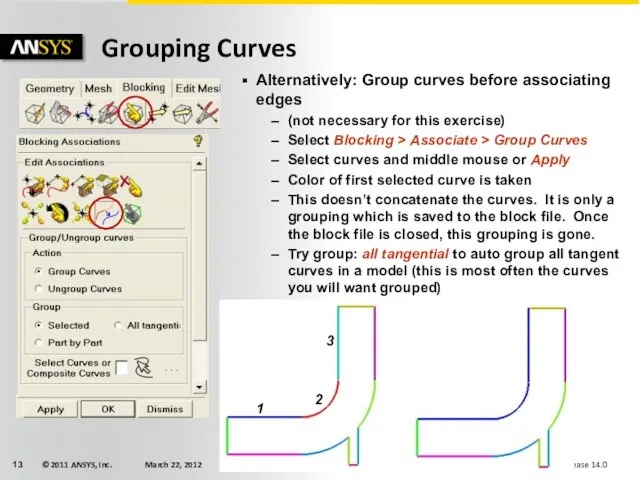
- 13. Grouping Curves 1 2 3 Alternatively: Group curves before associating edges (not necessary for this exercise)
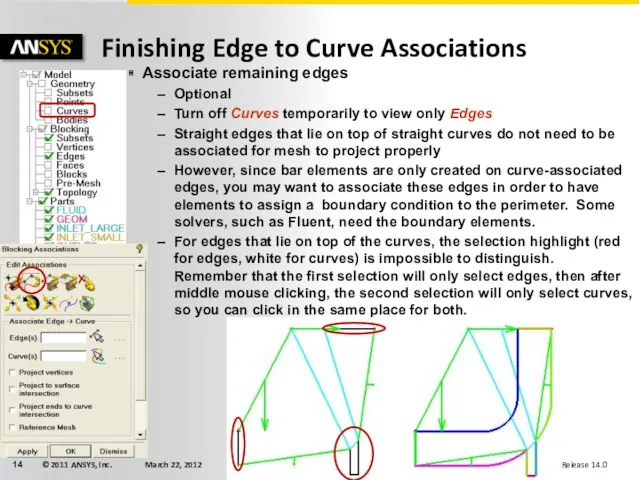
- 14. Associate remaining edges Optional Turn off Curves temporarily to view only Edges Straight edges that lie
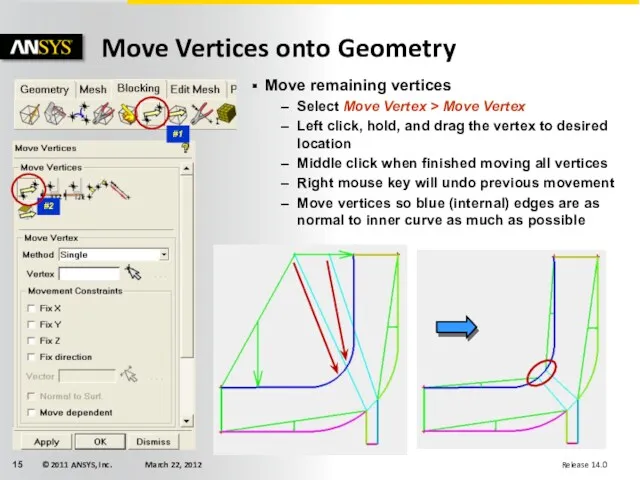
- 15. Move Vertices onto Geometry #1 #2 Move remaining vertices Select Move Vertex > Move Vertex Left
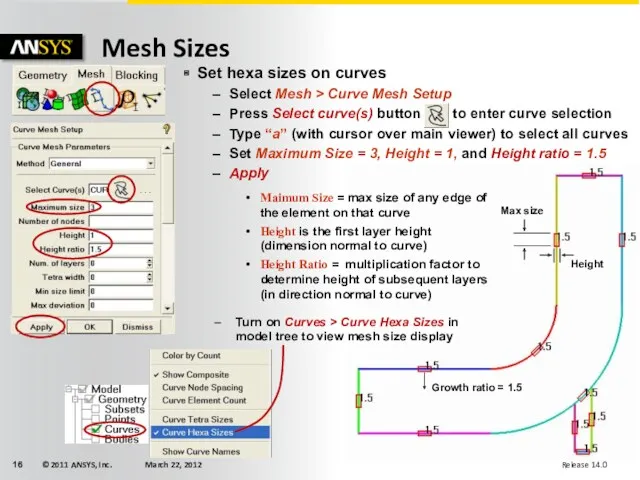
- 16. Set hexa sizes on curves Select Mesh > Curve Mesh Setup Press Select curve(s) button to
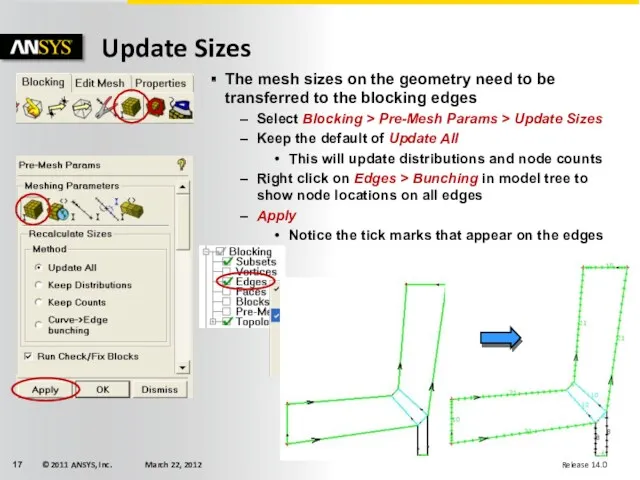
- 17. Update Sizes The mesh sizes on the geometry need to be transferred to the blocking edges
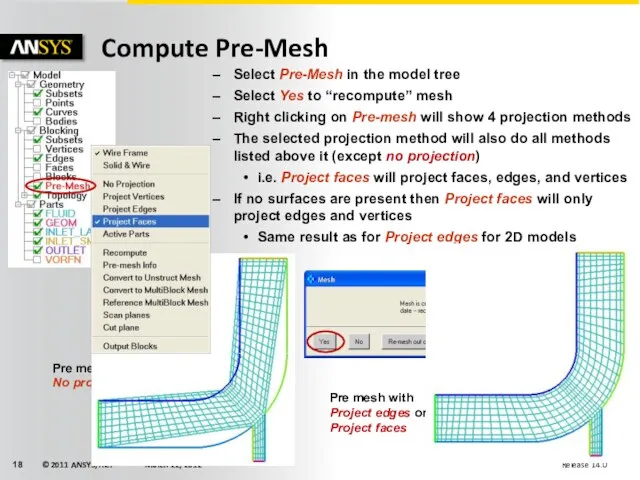
- 18. Compute Pre-Mesh Pre mesh with No projection Select Pre-Mesh in the model tree Select Yes to
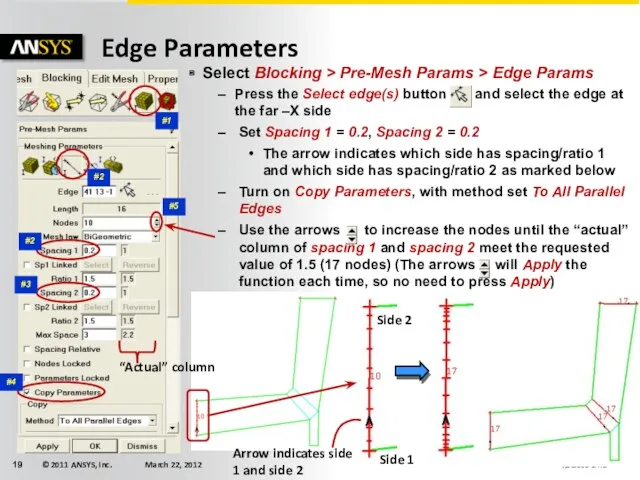
- 19. Edge Parameters Select Blocking > Pre-Mesh Params > Edge Params Press the Select edge(s) button and
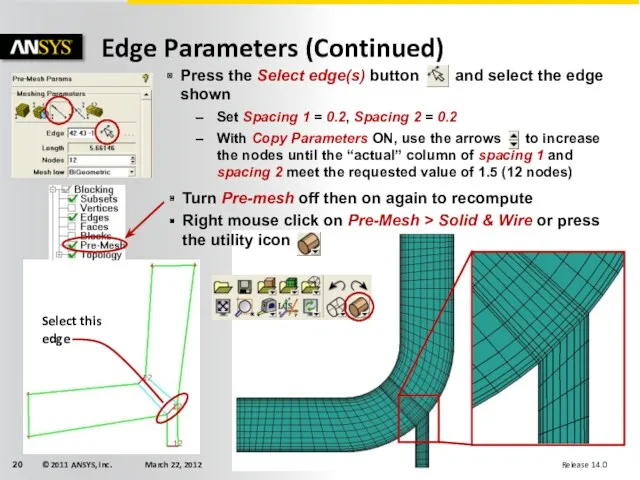
- 20. Edge Parameters (Continued) Press the Select edge(s) button and select the edge shown Set Spacing 1
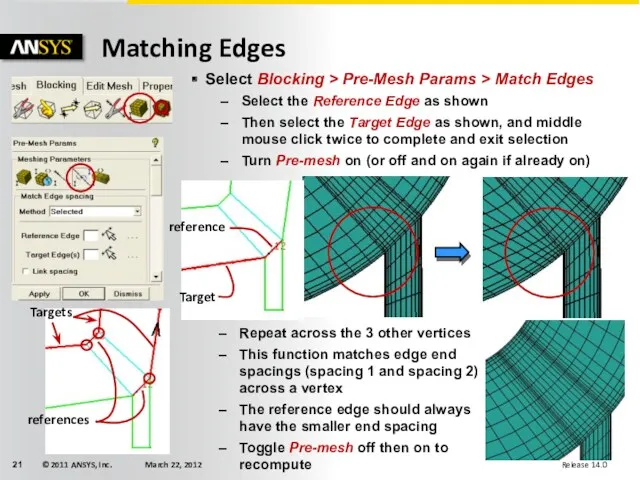
- 21. Matching Edges Select Blocking > Pre-Mesh Params > Match Edges Select the Reference Edge as shown
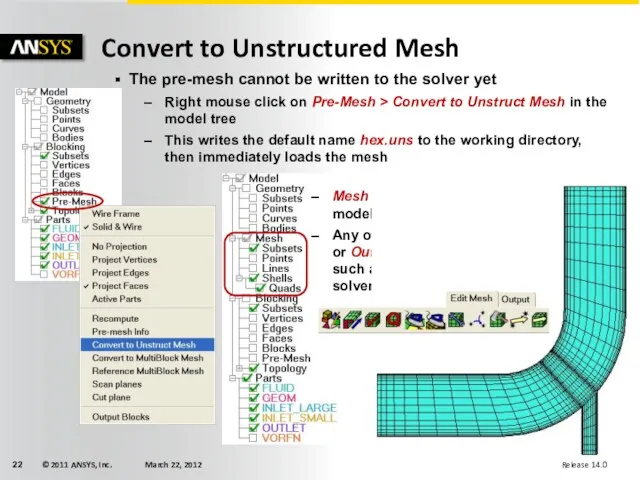
- 22. Convert to Unstructured Mesh The pre-mesh cannot be written to the solver yet Right mouse click
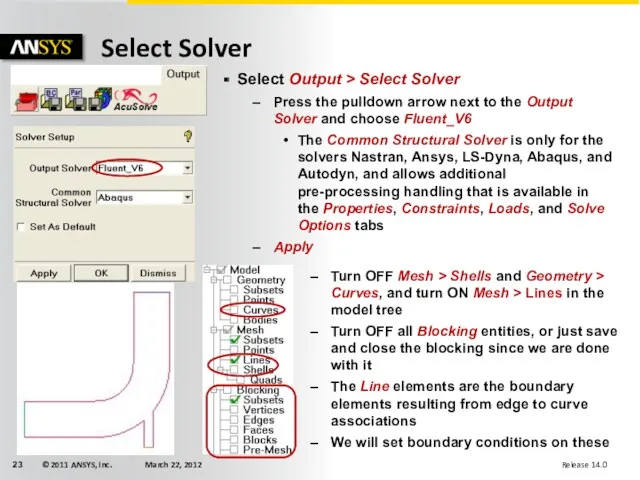
- 23. Select Solver Select Output > Select Solver Press the pulldown arrow next to the Output Solver
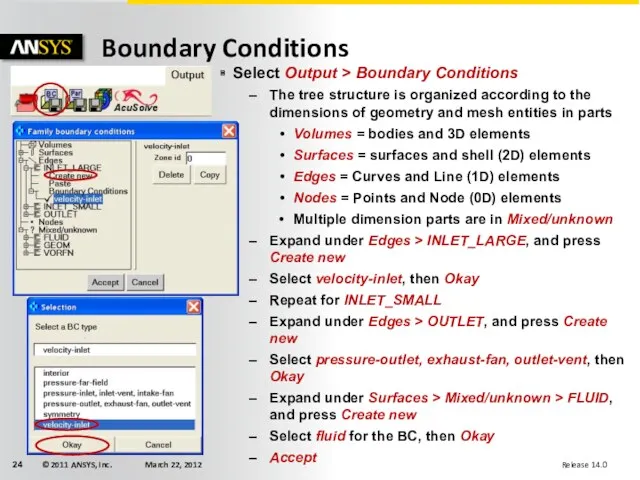
- 24. Boundary Conditions Select Output > Boundary Conditions The tree structure is organized according to the dimensions
- 26. Скачать презентацию
 Подзапросы в SQL
Подзапросы в SQL Многоуровневые списки
Многоуровневые списки Оператор цикла с параметром
Оператор цикла с параметром Database. Lection 3
Database. Lection 3 Таблицы
Таблицы Ajax. Генератор кода для вставки на сайт
Ajax. Генератор кода для вставки на сайт Функции в С++
Функции в С++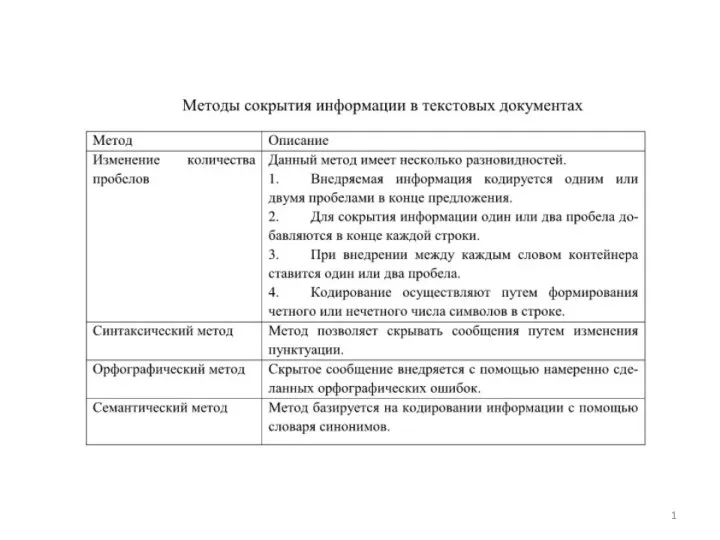 Стегосистемы для других покрывающих сообщений. Лекция 4
Стегосистемы для других покрывающих сообщений. Лекция 4 Введение в операционные системы
Введение в операционные системы Роль СМИ в политической жизни общества
Роль СМИ в политической жизни общества Моделирование ВС. Модели массового обслуживания. (Тема 3.2)
Моделирование ВС. Модели массового обслуживания. (Тема 3.2) Пять игр развивающих интеллект, для взрослых
Пять игр развивающих интеллект, для взрослых Компьютерные презентации
Компьютерные презентации Обзор онлайн аудитории Беларуси
Обзор онлайн аудитории Беларуси Spring Boot. Spring Data. ORM
Spring Boot. Spring Data. ORM Методическая разработка внеклассного мероприятия Турнир знатоков Информатики Внеклассное мероприятие по информатике для учащихся 6-го класса Внеклассное мероприятие по информатике для учащихся 6-го класса Турнир знатоков ИНФОРМАТ
Методическая разработка внеклассного мероприятия Турнир знатоков Информатики Внеклассное мероприятие по информатике для учащихся 6-го класса Внеклассное мероприятие по информатике для учащихся 6-го класса Турнир знатоков ИНФОРМАТ Языки программирования C++
Языки программирования C++ Рекурсивті тәртіптерді анықтау және GNU. Prolog қолдану
Рекурсивті тәртіптерді анықтау және GNU. Prolog қолдану Здоровье-сберегающие технологии на уроках информатики
Здоровье-сберегающие технологии на уроках информатики SAP HANA – платформа для бизнеса в реальном времени
SAP HANA – платформа для бизнеса в реальном времени Форматы_графических_файлов
Форматы_графических_файлов Поиск информации в Интернете
Поиск информации в Интернете Мобильді құрылғыларға арналған операциялық жүйелер
Мобильді құрылғыларға арналған операциялық жүйелер Обработка информации и алгоритмы
Обработка информации и алгоритмы Микропроцессор
Микропроцессор Навчальні проекти
Навчальні проекти Lecture 11. Even more normalization
Lecture 11. Even more normalization WEB-Index: Аудитория интернет-проектов. Desktop, Октябрь 2017, Москва
WEB-Index: Аудитория интернет-проектов. Desktop, Октябрь 2017, Москва