Содержание
- 2. Agenda ASP.NET Architecture ASP.NET MVC 3, 4, 5 Controllers Views
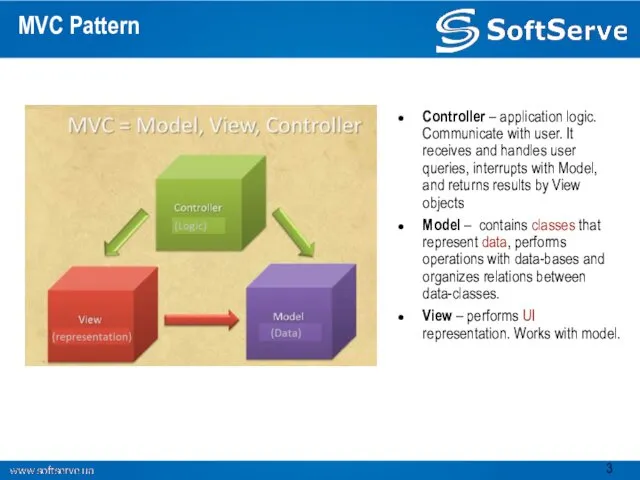
- 3. MVC Pattern Controller – application logic. Communicate with user. It receives and handles user queries, interrupts
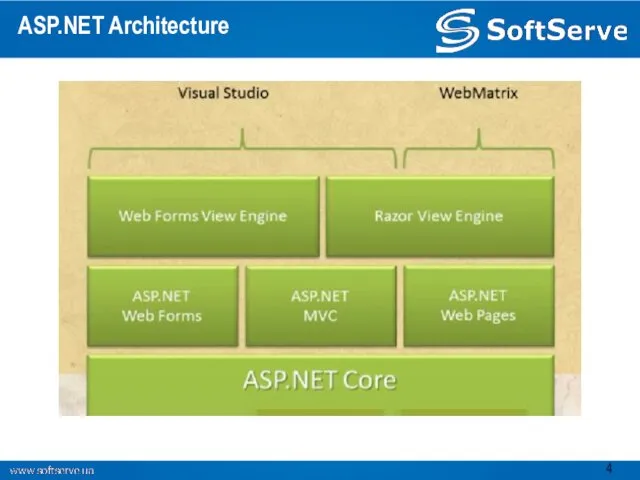
- 4. ASP.NET Architecture
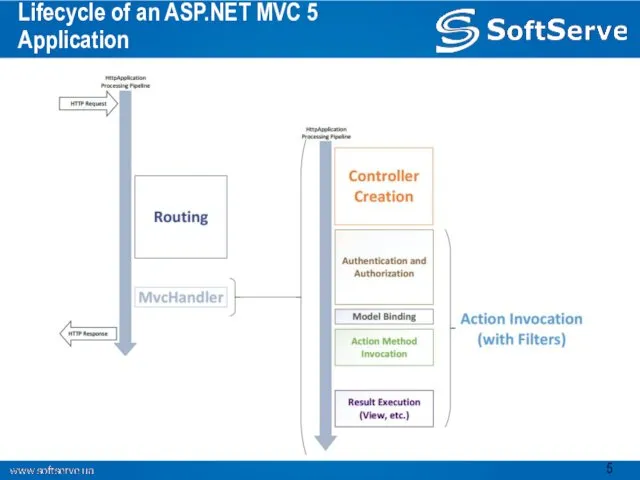
- 5. Lifecycle of an ASP.NET MVC 5 Application
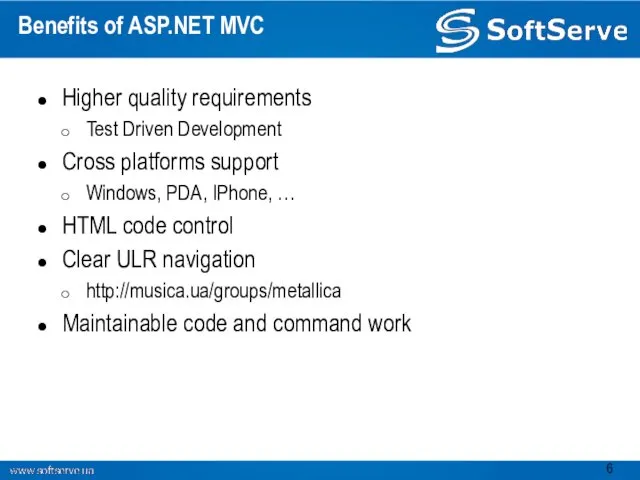
- 6. Benefits of ASP.NET MVC Higher quality requirements Test Driven Development Cross platforms support Windows, PDA, IPhone,
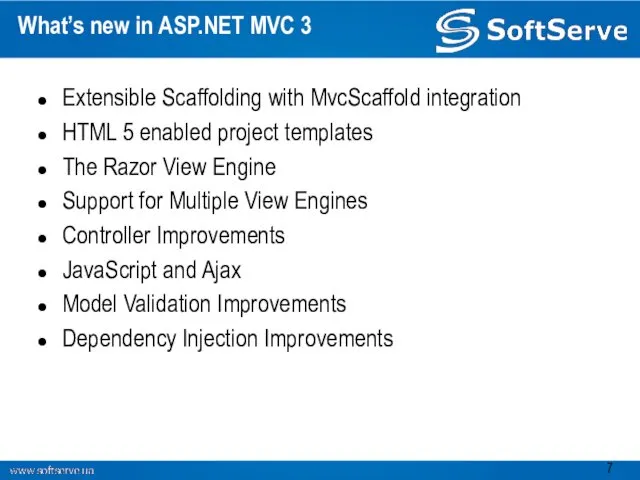
- 7. What’s new in ASP.NET MVC 3 Extensible Scaffolding with MvcScaffold integration HTML 5 enabled project templates
- 8. What’s new in ASP.NET MVC 4 ASP.NET Web API Enhancements to Default Project Templates Mobile Project
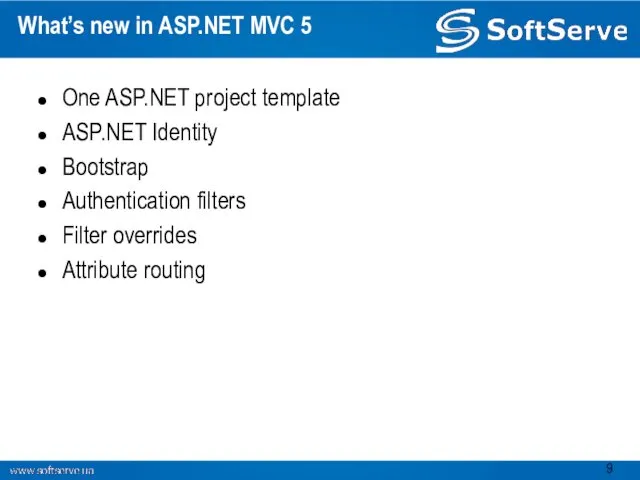
- 9. What’s new in ASP.NET MVC 5 One ASP.NET project template ASP.NET Identity Bootstrap Authentication filters Filter
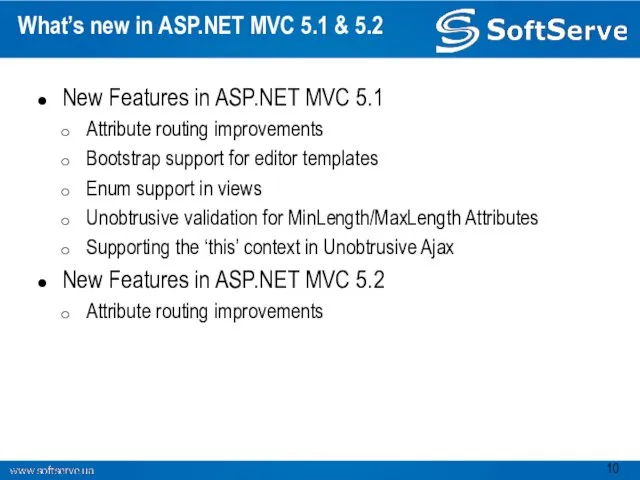
- 10. What’s new in ASP.NET MVC 5.1 & 5.2 New Features in ASP.NET MVC 5.1 Attribute routing
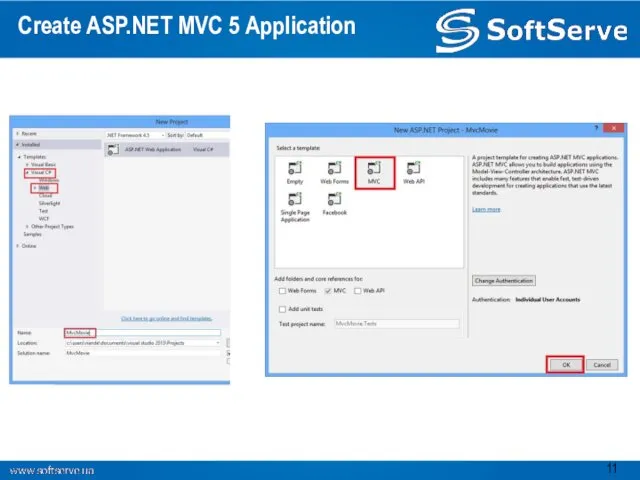
- 11. Create ASP.NET MVC 5 Application
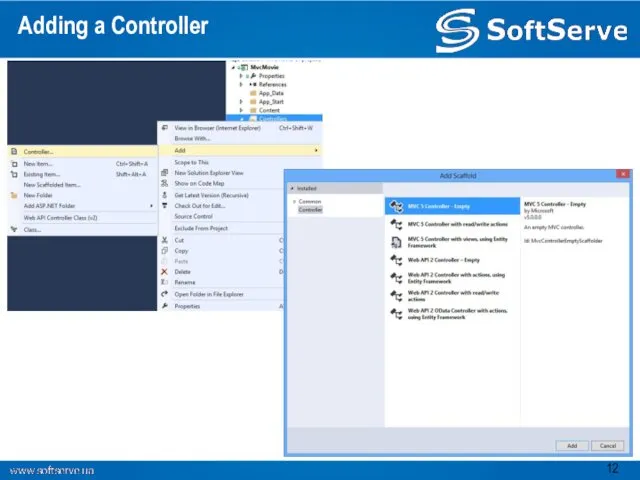
- 12. Adding a Controller
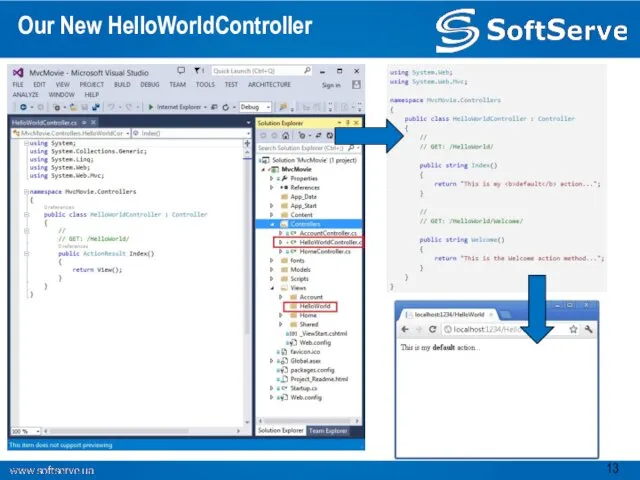
- 13. Our New HelloWorldController
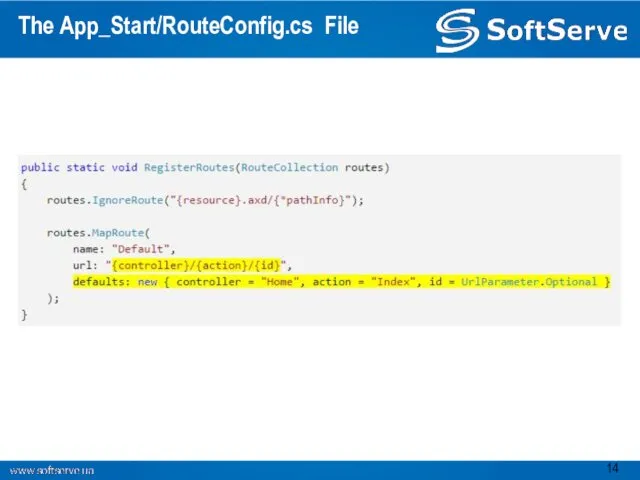
- 14. The App_Start/RouteConfig.cs File
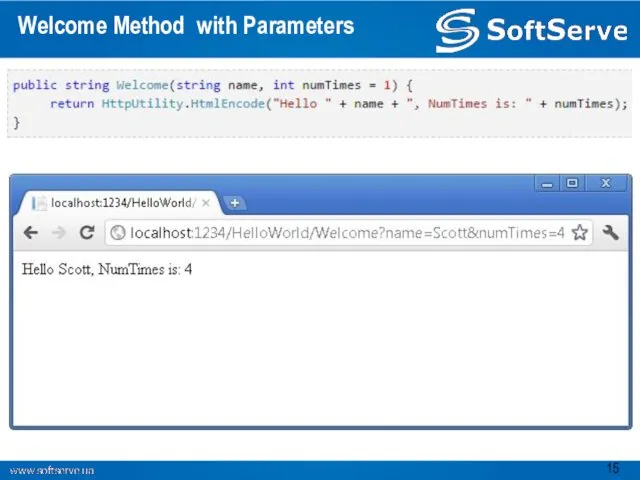
- 15. Welcome Method with Parameters
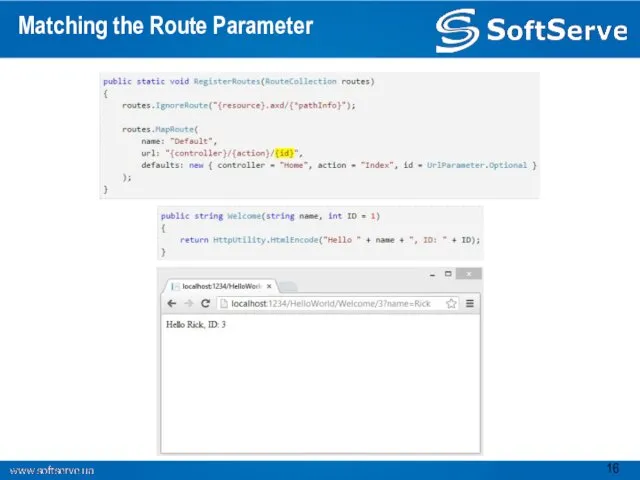
- 16. Matching the Route Parameter
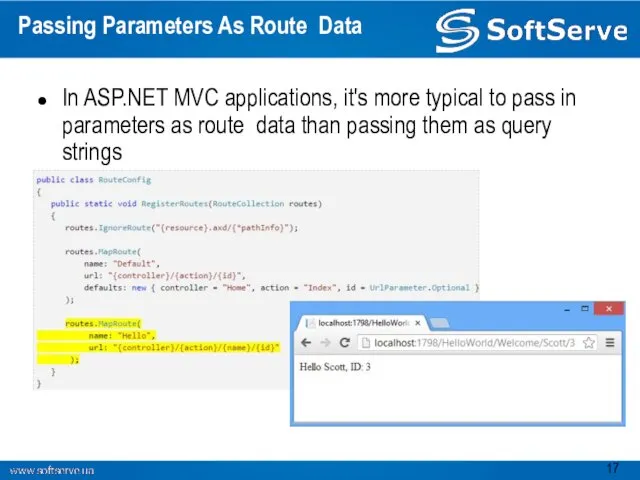
- 17. Passing Parameters As Route Data In ASP.NET MVC applications, it's more typical to pass in parameters
- 18. URL Route Mapping Features You can include "-", ".", ";" or any other characters you want
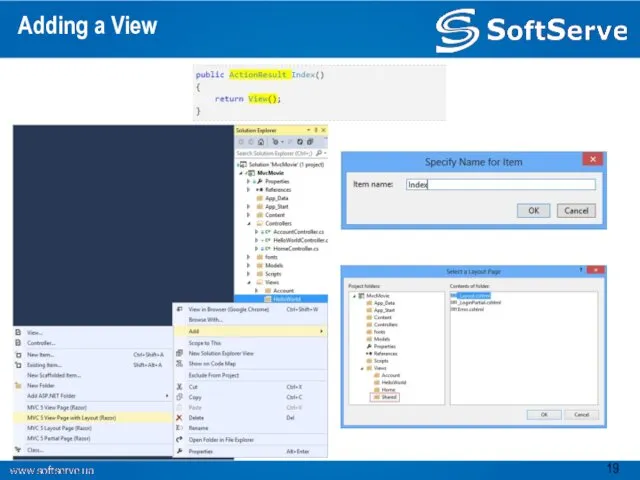
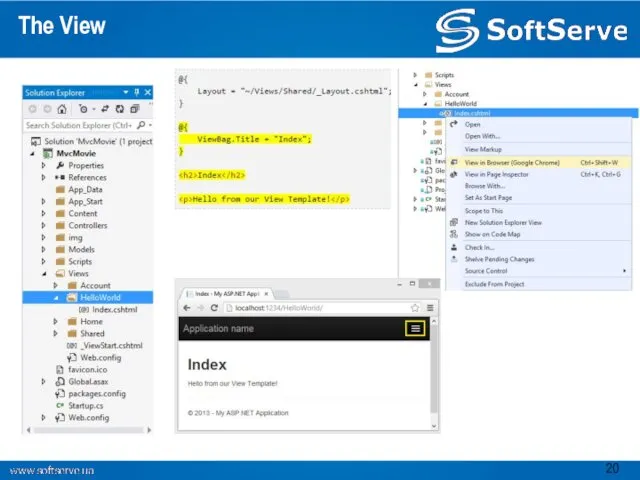
- 19. Adding a View
- 20. The View
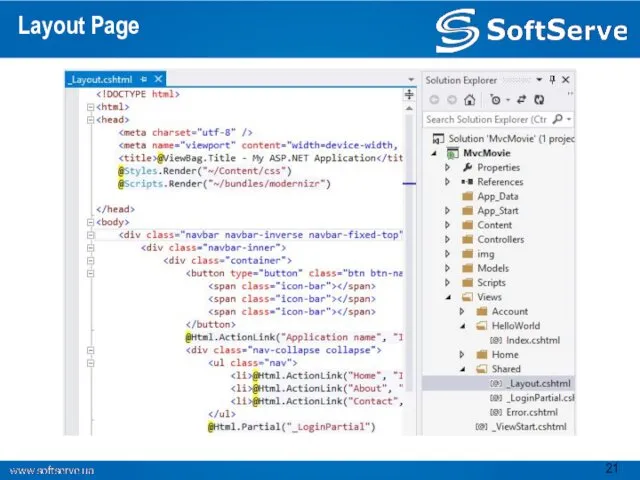
- 21. Layout Page
- 22. Layout Page The layout has access to the same properties the Razor view has, including: AjaxHelper
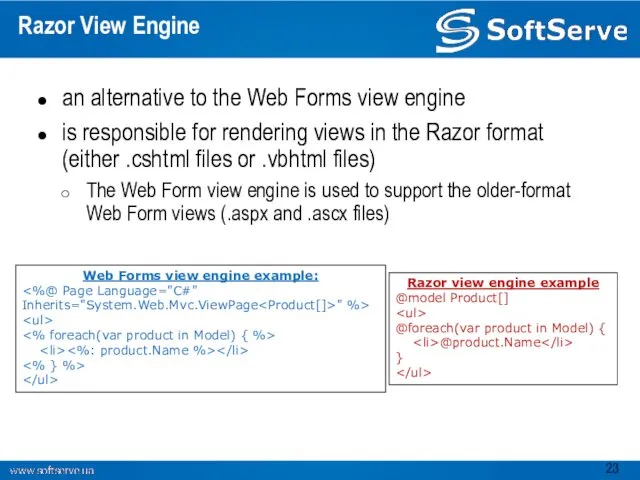
- 23. Razor View Engine an alternative to the Web Forms view engine is responsible for rendering views
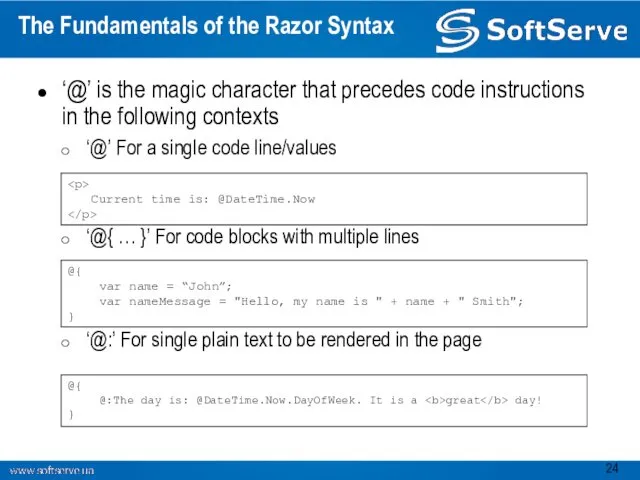
- 24. The Fundamentals of the Razor Syntax ‘@’ is the magic character that precedes code instructions in
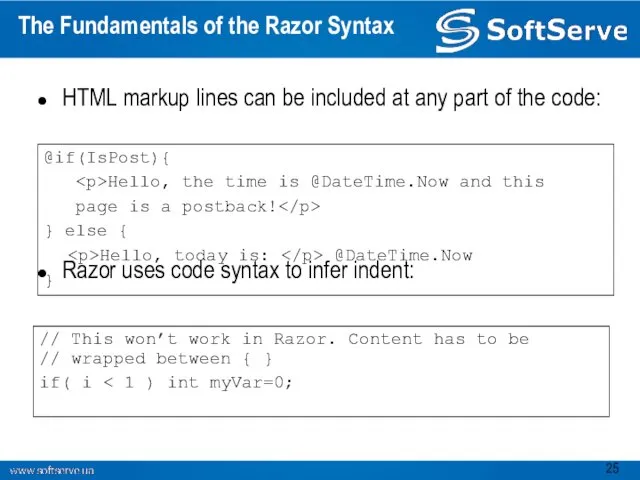
- 25. The Fundamentals of the Razor Syntax HTML markup lines can be included at any part of
- 26. Passing Data to the View There are three different ways to pass data to a view:
- 27. ViewDataDictionary It isn’t recommended to use ViewDataDictionary You have to perform type casts whenever you want
- 28. ViewBag It isn’t recommended to use ViewBag The ViewBag provides a way to pass data from
- 29. Strongly Typed Views Views can inherit from two types by default: System.Web.Mvc.WebViewPage or System.Web.Mvc.WebViewPage Class WebViewPage
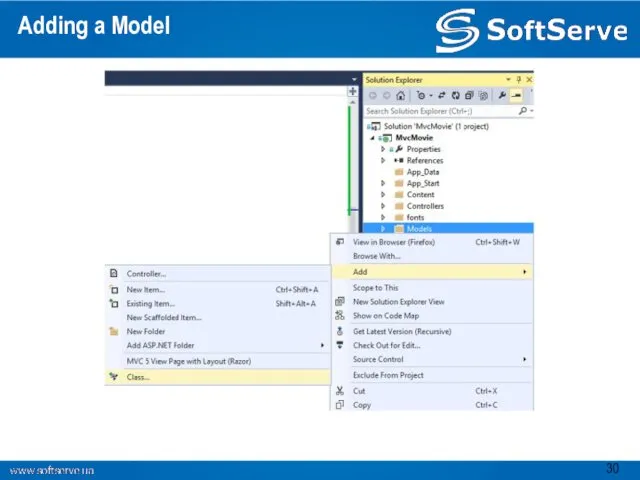
- 30. Adding a Model
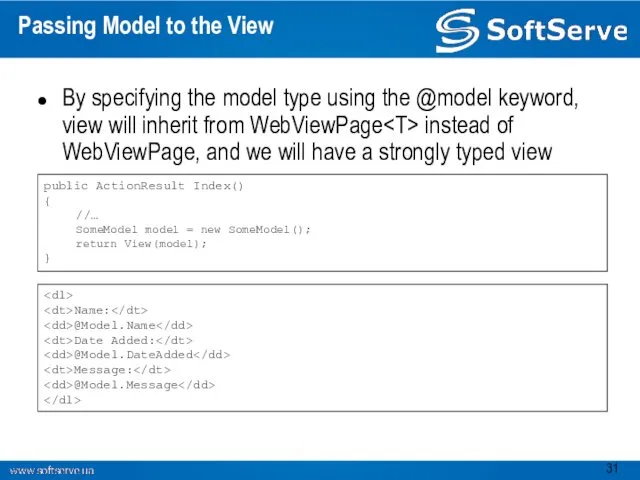
- 31. Passing Model to the View By specifying the model type using the @model keyword, view will
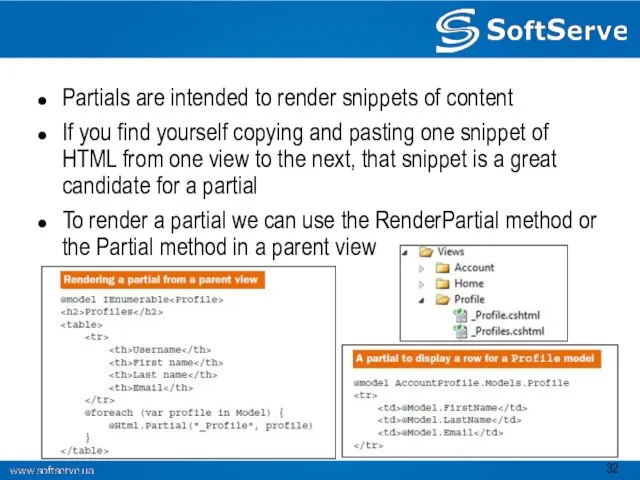
- 32. Partials are intended to render snippets of content If you find yourself copying and pasting one
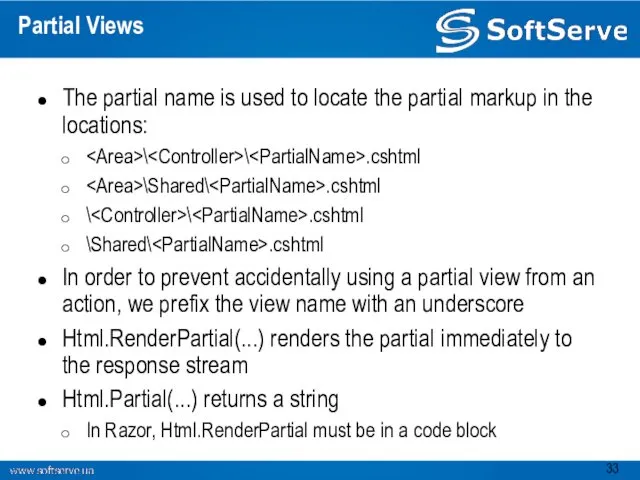
- 33. Partial Views The partial name is used to locate the partial markup in the locations: \
- 35. Скачать презентацию






 Game-Theoretic Methods in Machine Learning
Game-Theoretic Methods in Machine Learning Текстовые редакторы Sublime Text и Vim
Текстовые редакторы Sublime Text и Vim This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Особенности математики в Python. Задания
Особенности математики в Python. Задания Апробация технологий Silverlight/LINQ/WCF для создания web-приложений, ориентированных на интенсивную обработку данных
Апробация технологий Silverlight/LINQ/WCF для создания web-приложений, ориентированных на интенсивную обработку данных Интернет: вред и польза
Интернет: вред и польза Сравнительный анализ дизайна интернет-сайтов
Сравнительный анализ дизайна интернет-сайтов Функциональные подсистемы АИС
Функциональные подсистемы АИС Системы искусственного интеллекта
Системы искусственного интеллекта Как настроить контекст и не слить весь бюджет за один день
Как настроить контекст и не слить весь бюджет за один день Среда программирования Scratch. Урок 1
Среда программирования Scratch. Урок 1 Мультисервисная сеть на основе SoftSwitch
Мультисервисная сеть на основе SoftSwitch 4D-Printing
4D-Printing презентация урока информатики Устройство компьютера3-4 класс
презентация урока информатики Устройство компьютера3-4 класс Сетевые Операционные Системы
Сетевые Операционные Системы Угроза доступа к локальным файлам сервера при помощи URL
Угроза доступа к локальным файлам сервера при помощи URL Электронная почта
Электронная почта Конспект урока по теме Компьютерные презентации с использованием мультимедиа технологии
Конспект урока по теме Компьютерные презентации с использованием мультимедиа технологии Теоретические основы информатики
Теоретические основы информатики The Inverted Multi-Index
The Inverted Multi-Index Алгоритм с ветвящейся структурой
Алгоритм с ветвящейся структурой Statistical programming languages
Statistical programming languages Інформаційні системи та технології
Інформаційні системи та технології Введение. Беспроводные сети передачи данных
Введение. Беспроводные сети передачи данных Мастер-класс. Кодирование текстовой информации
Мастер-класс. Кодирование текстовой информации Путешествуя по клавиатуре
Путешествуя по клавиатуре Інструкція
Інструкція Оператор электронно-вычислительных и вычислительных машин. Отчет по производственной практике
Оператор электронно-вычислительных и вычислительных машин. Отчет по производственной практике