Содержание
- 2. Plan: Lecture 1. ICT role in key sectors of development of society. Standards in the field
- 3. Plan: Lecture 8. Cyber safety; Lecture 9. Internet technologies; Lecture 10. Cloud and mobile technologies; Lecture
- 4. ICT role in key sectors of development of society. Standards in the field of ICT
- 5. Contents: Definition of ICT; ICT subject and its objectives; ICT in key sectors of society; Advantages
- 6. ICT (information and communications technology - or technologies) is an common term that includes any communication
- 7. Definition of ICT (1) ICT is defined as an industry, i.e. as a set of enterprises
- 8. Information and communication technologies (ICT) are regarded as modern methods and means of communication of people
- 9. Definition of Development Program of Organization of United Nations in 2003 ICT is, mainly, a tool
- 10. Subject of ICT and purpose Discipline "ICT" is used for the formation of a particular ideology
- 11. Computers in society Home - Education - Small business - Industry – Government - Health care
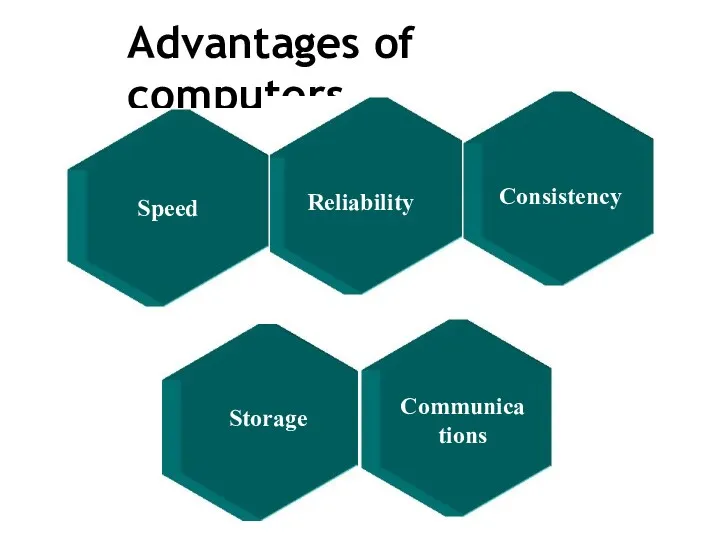
- 12. Advantages of computers Storage Communications Reliability Consistency Speed
- 13. Speed Up Work Efficiency This is by far the biggest advantage of using computers. They have
- 14. Large and Reliable Storage Capacity Computers can store huge volumes of data. To put this into
- 15. Connection with Internet The Internet is probably the most outstanding invention in history. Computers allow you
- 16. Consistency You always get the same result for the same process when using a computer. For
- 17. Disadvantages of computers Impact on Labor Force Violation of Privacy Health Risks Public Safety Impact on
- 18. Health Risk Improper and prolonged use of a computer might lead to disorders or injuries of
- 19. Violation of Privacy When using the Internet on your computer, you run the risk of leaking
- 20. Impact on Environment Manufacturing process of computers and computer waste are harmful to the environment. When
- 21. Data Security This is one of the most controversial aspects of computers today. The safety and
- 22. Other Unemployment - Different tasks are performed automatically by using computers. It reduces the need of
- 23. Data Representation
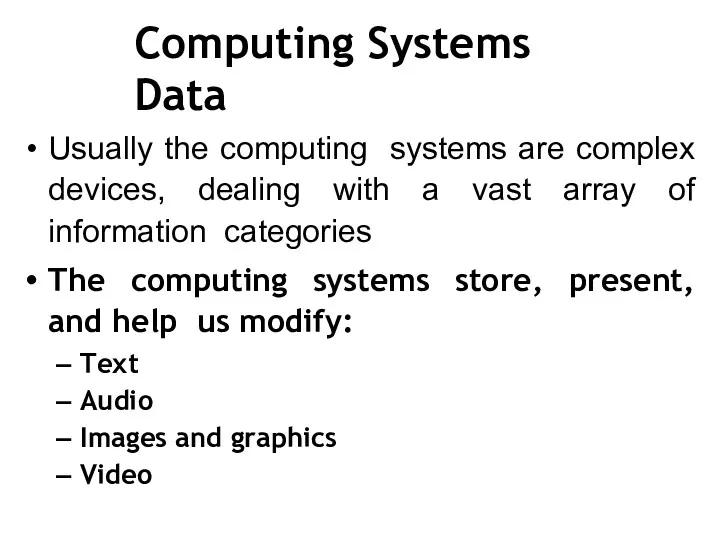
- 24. Computing Systems Data Usually the computing systems are complex devices, dealing with a vast array of
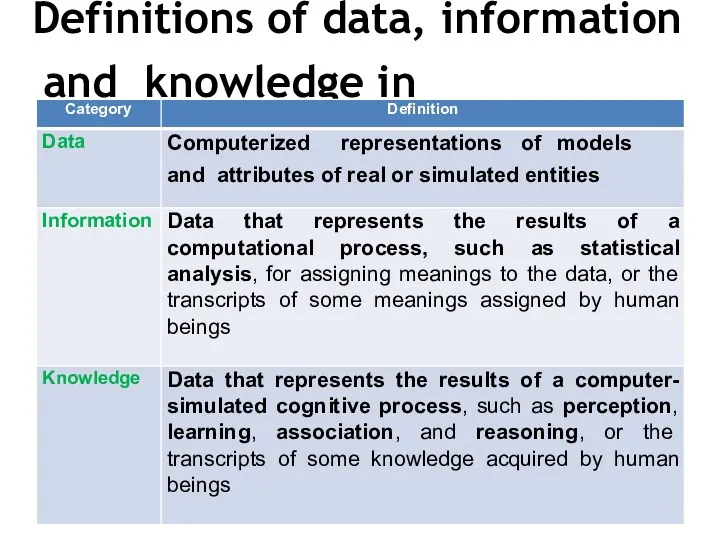
- 25. Definitions of data, information and knowledge in computational space
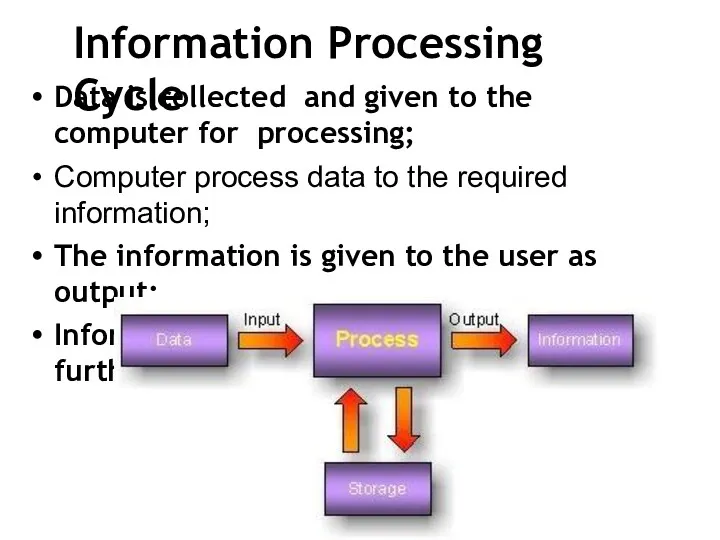
- 26. Information Processing Cycle Data is collected and given to the computer for processing; Computer process data
- 27. Digital versus Analog Computing systems are finite machines. They store a limited amount of information, even
- 28. Binary Representation Why binary representation (as suppose to decimal or octal, etc..)? Because the devices that
- 29. Binary Representation One bit can be either 0 or 1. Therefore, one bit can represent only
- 30. Standards in the field of ICT They exist because they: Allow communication and sharing of information
- 31. Standards Organizations ISO – International Standards Organization; IEEE – Institute for Electrical and Electronics Engineers; ANSI
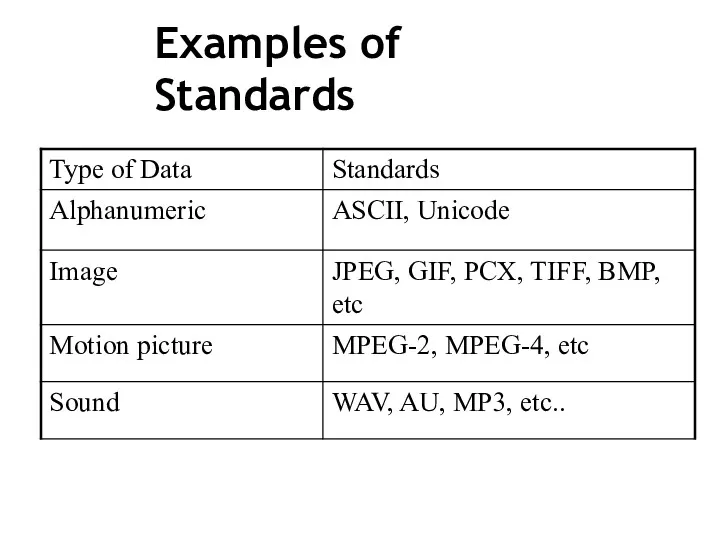
- 32. Examples of Standards
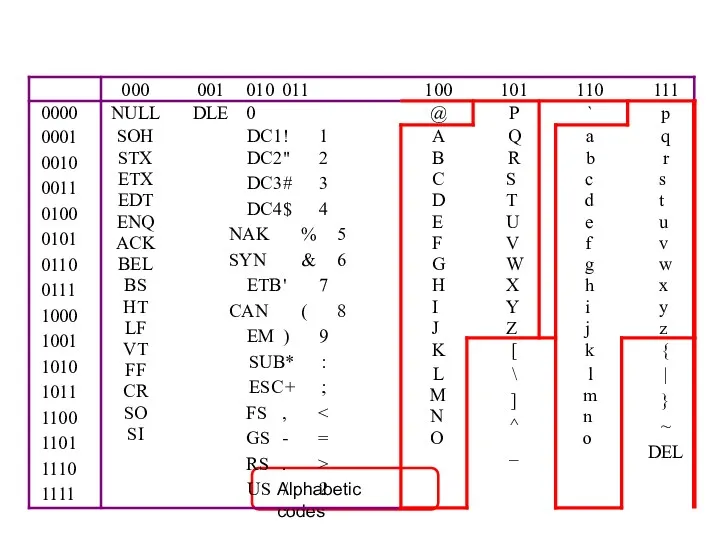
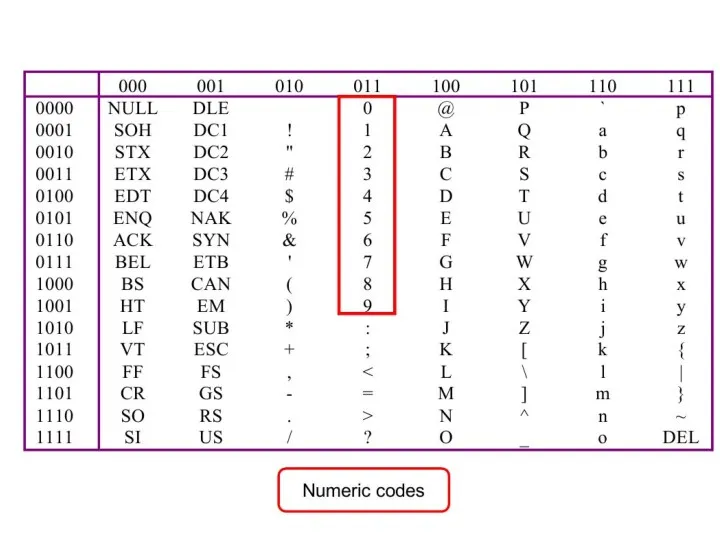
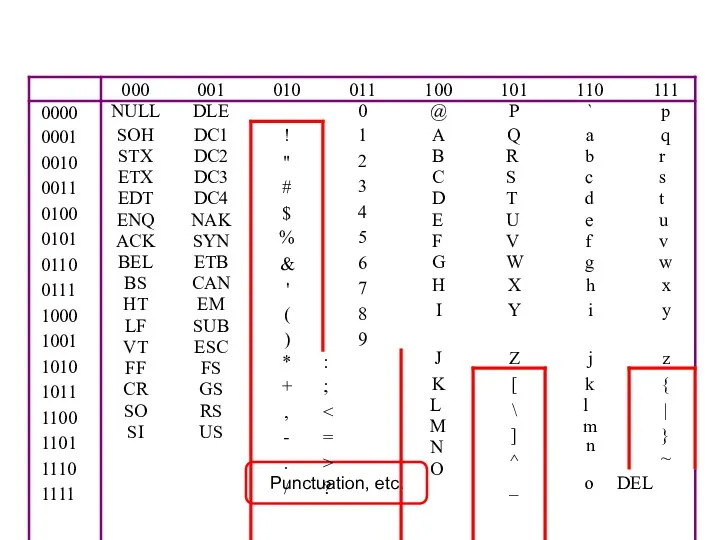
- 33. Alphanumeric Data (example) Three standards for representing letters (alpha) and numbers: ASCII – American Standard Code
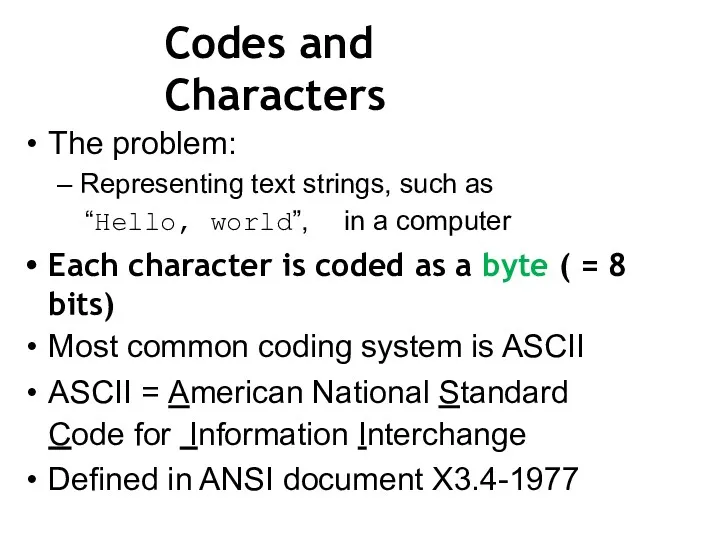
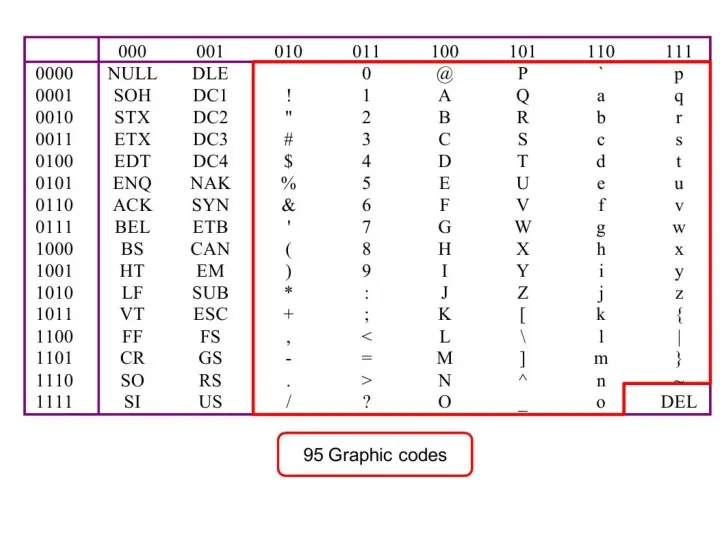
- 34. Codes and Characters The problem: – Representing text strings, such as “Hello, world”, in a computer
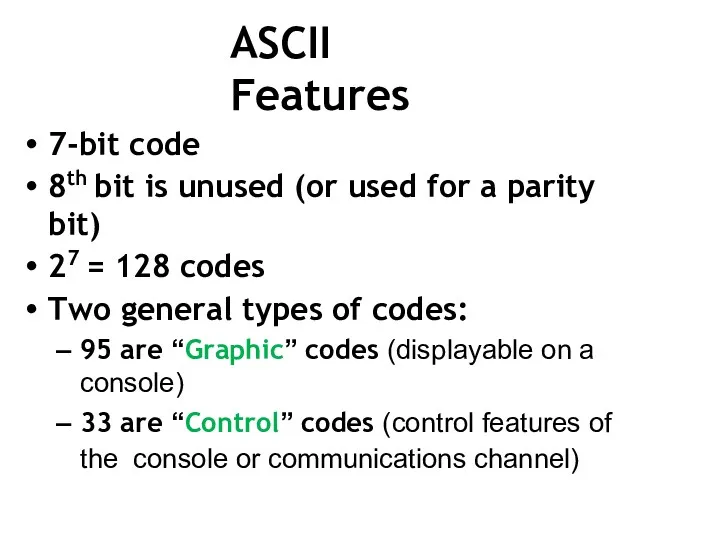
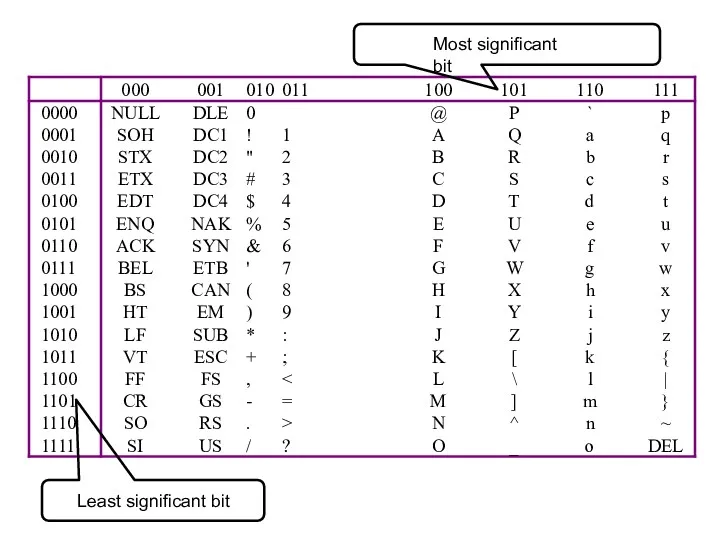
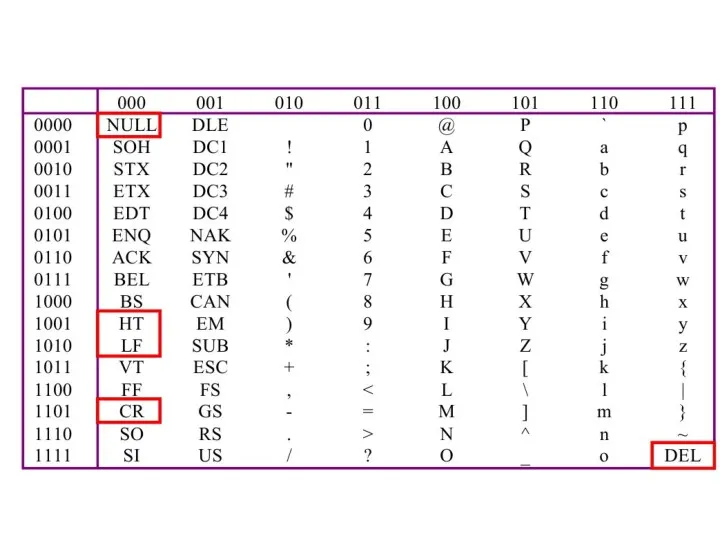
- 35. ASCII Features 7-bit code 8th bit is unused (or used for a parity bit) 27 =
- 36. Most significant bit Least significant bit
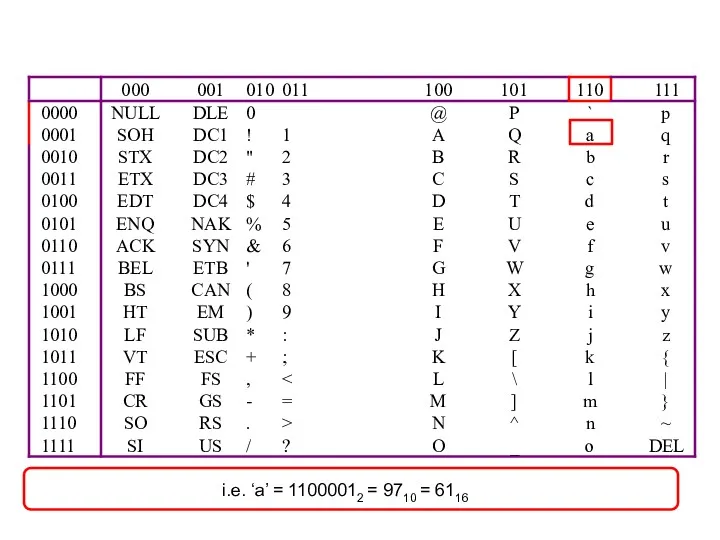
- 37. i.e. ‘a’ = 11000012 = 9710 = 6116
- 40. Alphabetic codes
- 43. “4+15” Example = = = = Hexadecimal 34 2B 31 35 Decimal 52 43 49 53
- 44. Punctuation, etc.
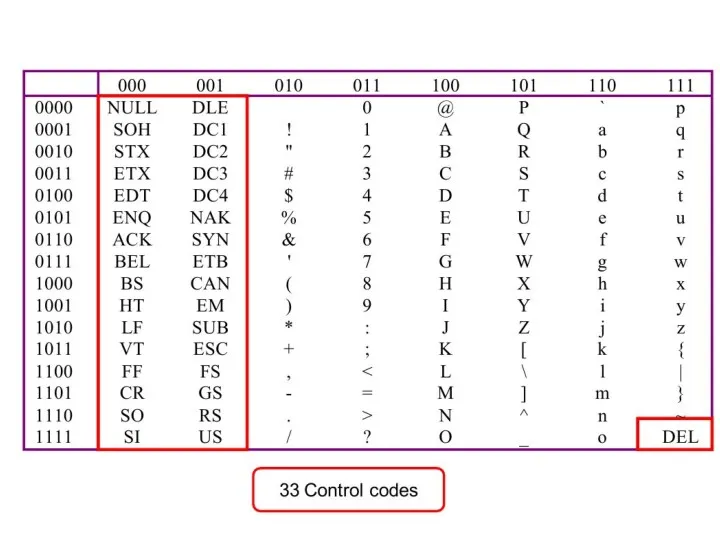
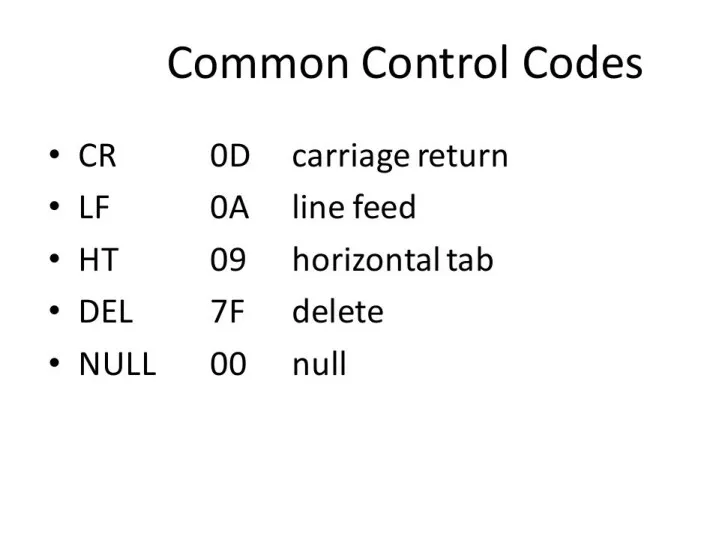
- 45. Common Control Codes
- 47. Unicode The extended version of the ASCII character set is not enough for international use. The
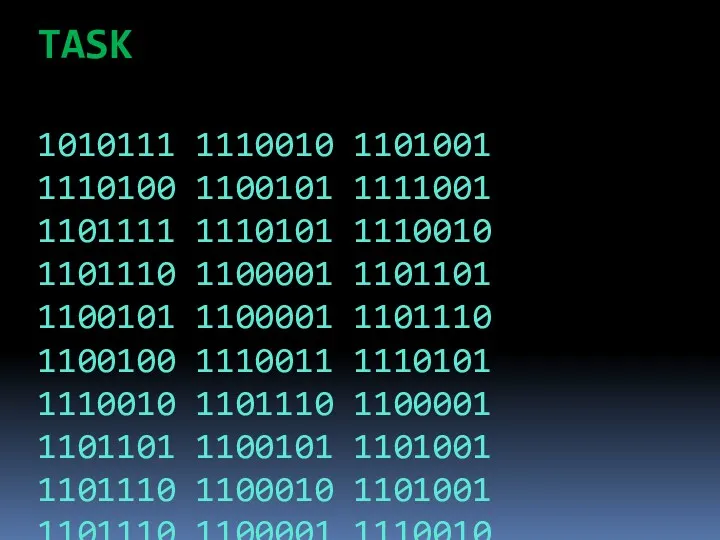
- 48. TASK 1010111 1110010 1101001 1110100 1100101 1111001 1101111 1110101 1110010 1101110 1100001 1101101 1100101 1100001 1101110
- 49. Communication between IKT and achievement of the objectives of a sustainable development
- 50. Human Resource Development Provide linkages, coordination and also providing accreditation between government and ICT firms. Promote
- 51. Electronic Government Provide stakeholders with enhanced access to government information. Facilitate enhanced citizen interaction with public
- 52. Infrastructure Development Provide leadership and vision to guide ICT infrastructure development. Provide equitable access to all
- 53. Education Re-engineer teaching and learning using ICT. Development of ICT education. Provision of adequate instructional materials,
- 54. Health Deploy and increase access to ICT within the National Health system to improve health delivery
- 55. Awareness, Popularization and Development Encourage ICT skills acquisition for all officers at all tiers of government.
- 56. Agriculture Use ICT tools such as Global positioning system (GPS), Geographic Information system (GIS) software to
- 57. Private sector development Develop an economy characterized by a large commercial services sector with a reasonably
- 58. Governance and Legislation Framework Facilitate electronic communication, governance and commerce. Promote and foster security in computer
- 59. National security and Law Enforcement Enhance national security and law enforcement. Ensure that ICT resources are
- 60. Research and Development Ease the difficulty in accessing relevant and up-to-date information on research in similar
- 61. Conclusion The world of ICT applications in all sectors offers great opportunities for gross national development;
- 63. Скачать презентацию










































 Створення таблиць у базі даних Access
Створення таблиць у базі даних Access Програмний засіб для адаптивного керування системою захисту інформації підприємства
Програмний засіб для адаптивного керування системою захисту інформації підприємства Решение логических задач с помощью нескольких таблиц
Решение логических задач с помощью нескольких таблиц Unit 02: Computer Systems
Unit 02: Computer Systems Содержание и объем понятий
Содержание и объем понятий История развития вычислительной техники
История развития вычислительной техники Презентация Количество информации как мера уменьшения неопределенности знания
Презентация Количество информации как мера уменьшения неопределенности знания Объекты окружающего мира. Объекты и множества. Объекты изучения в информатике. Признаки объектов
Объекты окружающего мира. Объекты и множества. Объекты изучения в информатике. Признаки объектов Коммуникационные технологии
Коммуникационные технологии Інтернет - навчання
Інтернет - навчання Тема №1 Архитектура системы команд. Занятие №2/2 Форматы команд
Тема №1 Архитектура системы команд. Занятие №2/2 Форматы команд Interesting Facts
Interesting Facts Statistical programming languages
Statistical programming languages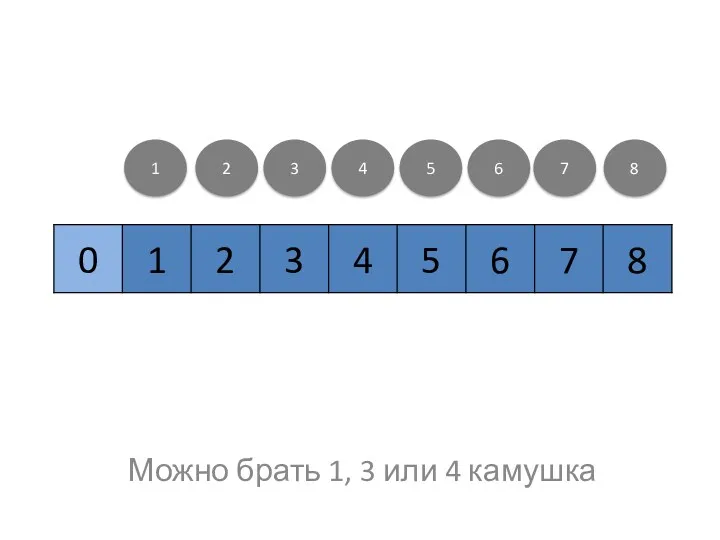 Игра Камушки, информатика, 4 класс. Тришина Е.М.
Игра Камушки, информатика, 4 класс. Тришина Е.М. Итоговый проект Комплексное тестирование платформы idemo.bspb.ru
Итоговый проект Комплексное тестирование платформы idemo.bspb.ru Безопасное сетевое взаимодействие. Протокол TLS/SSL
Безопасное сетевое взаимодействие. Протокол TLS/SSL Экскурсия по виртуальному музею Компьютерной графики (Office 2007)
Экскурсия по виртуальному музею Компьютерной графики (Office 2007) Нейронные сети
Нейронные сети Создание презентации в среде Microsoft PowerPoint
Создание презентации в среде Microsoft PowerPoint Интеллектуальная собственность в сети Интернет
Интеллектуальная собственность в сети Интернет Программирование линейных алгоритмов на языке Паскаль
Программирование линейных алгоритмов на языке Паскаль Операционные системы. Основные понятия. Классификация ОС
Операционные системы. Основные понятия. Классификация ОС Архитектура компьютера открытый урок
Архитектура компьютера открытый урок Информация
Информация Регистрация ККТ в электронном виде
Регистрация ККТ в электронном виде От простого шутера до киберспорта
От простого шутера до киберспорта Учебный курс Сетевое программное обеспечение. Сеть Н.323
Учебный курс Сетевое программное обеспечение. Сеть Н.323 Выставка в библиотеке
Выставка в библиотеке