Содержание
- 2. Course structure Semester 1 (4 weeks): 8 lectures, 8 practical classes (2 Labs) → exam 01.10
- 3. Information and computer sciences Information science is primarily concerned with gathering, storing, transmitting, sharing and protecting
- 4. Information vs Data Information can be thought of as the resolution of uncertainty. When you get
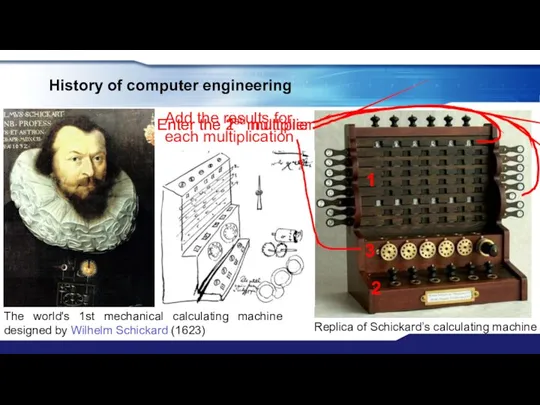
- 5. History of computer engineering Replica of Schickard’s calculating machine The world's 1st mechanical calculating machine designed
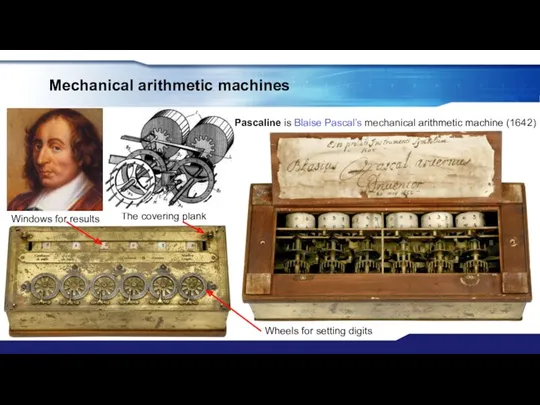
- 6. Mechanical arithmetic machines Pascaline is Blaise Pascal’s mechanical arithmetic machine (1642) Windows for results Wheels for
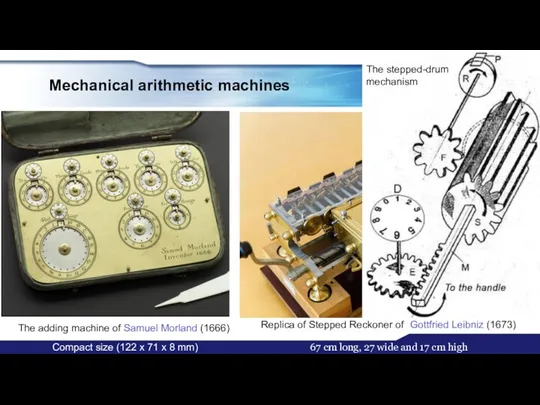
- 7. Mechanical arithmetic machines Replica of Stepped Reckoner of Gottfried Leibniz (1673) The adding machine of Samuel
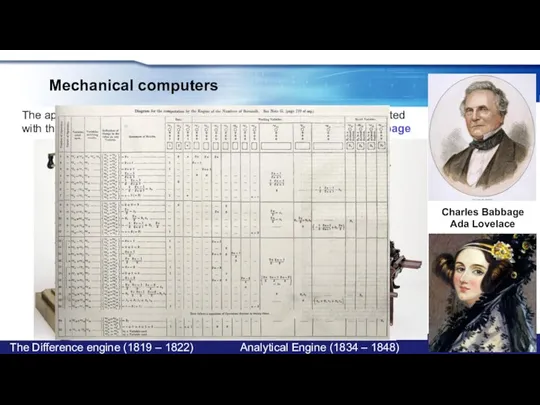
- 8. Mechanical computers The appearance of the first (mechanical) versions of computers is associated with the name
- 9. Mechanical computers After Babbage, a significant contribution to the development of computer technology was made by
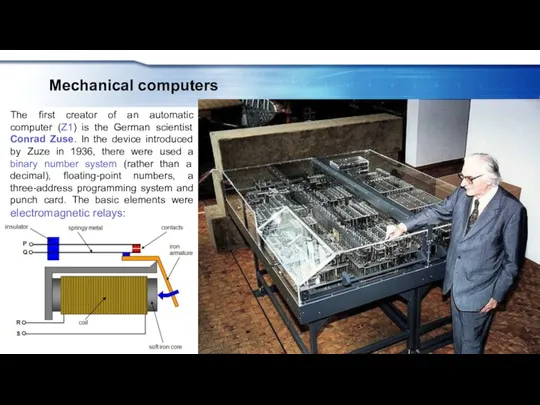
- 10. Mechanical computers The first creator of an automatic computer (Z1) is the German scientist Conrad Zuse.
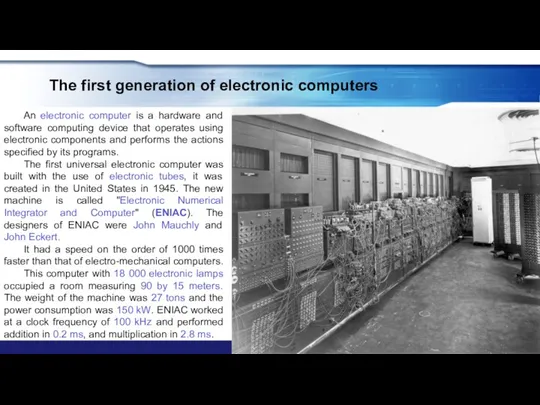
- 11. The first generation of electronic computers An electronic computer is a hardware and software computing device
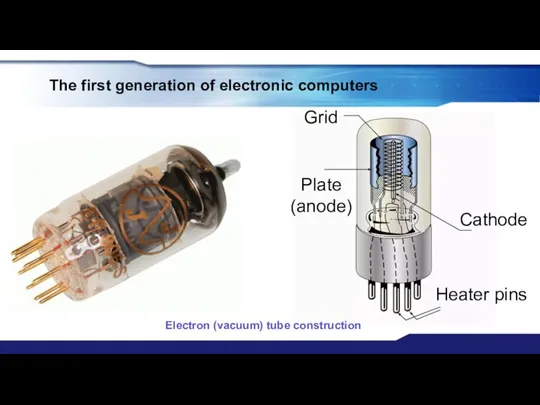
- 12. The first generation of electronic computers Cathode Heater pins Grid Plate (anode) Electron (vacuum) tube construction
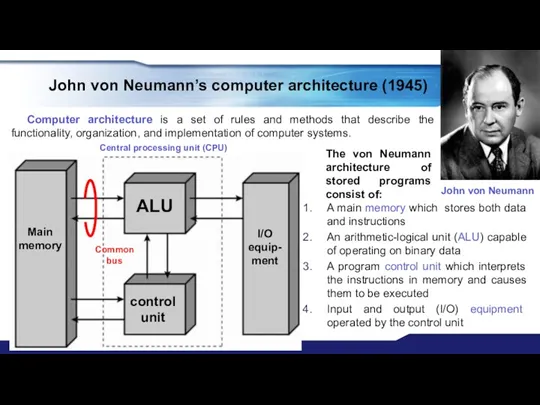
- 13. John von Neumann’s computer architecture (1945) Computer architecture is a set of rules and methods that
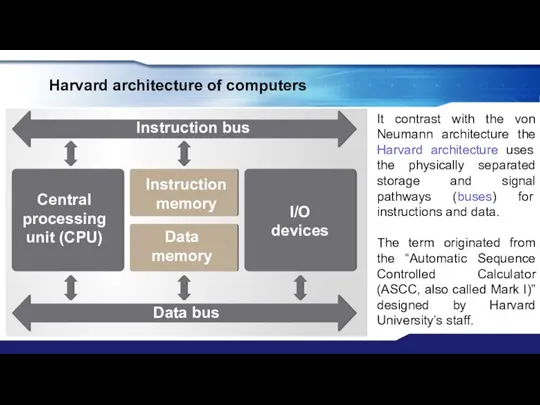
- 14. Harvard architecture of computers Central processing unit (CPU) I/O devices Instruction memory Data memory Instruction bus
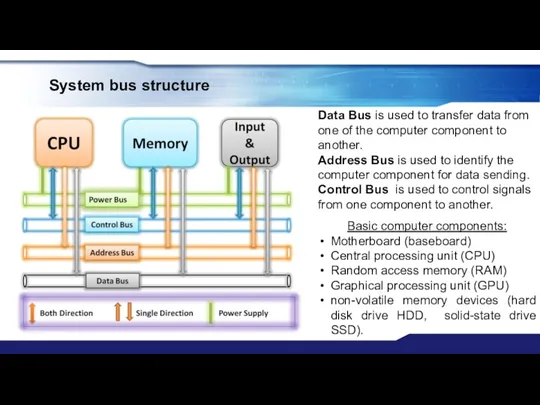
- 15. System bus structure Data Bus is used to transfer data from one of the computer component
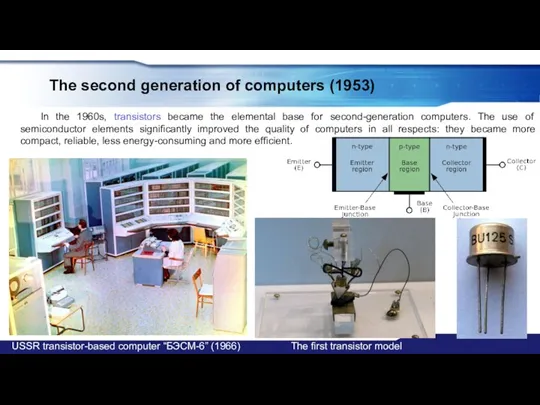
- 16. The second generation of computers (1953) In the 1960s, transistors became the elemental base for second-generation
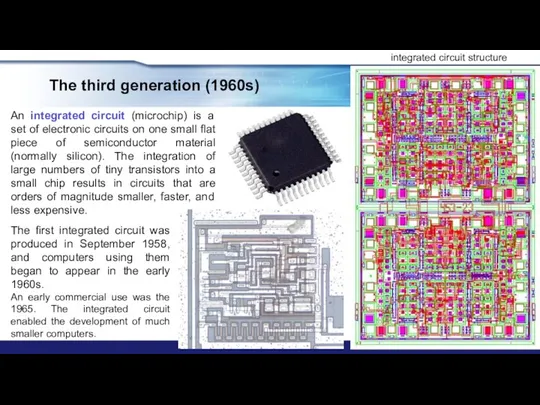
- 17. The third generation (1960s) An integrated circuit (microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one
- 18. The fourth generation (1970s) The development of microelectronics has led to the creation of the ability
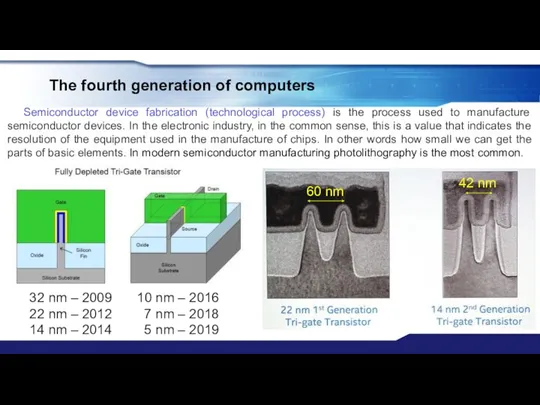
- 19. The fourth generation of computers Semiconductor device fabrication (technological process) is the process used to manufacture
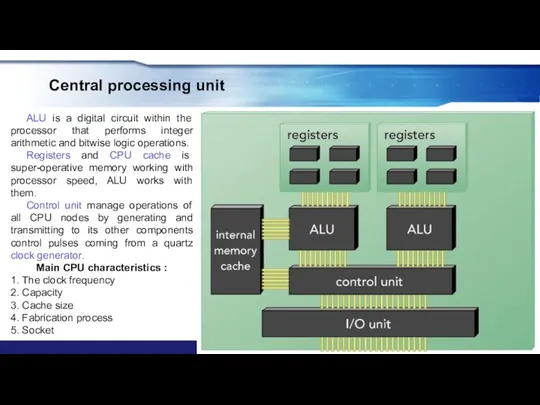
- 20. Central processing unit Simplified CPU block-diagram ALU is a digital circuit within the processor that performs
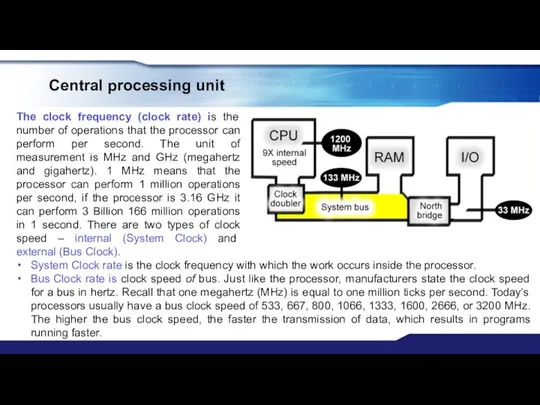
- 21. Central processing unit The clock frequency (clock rate) is the number of operations that the processor
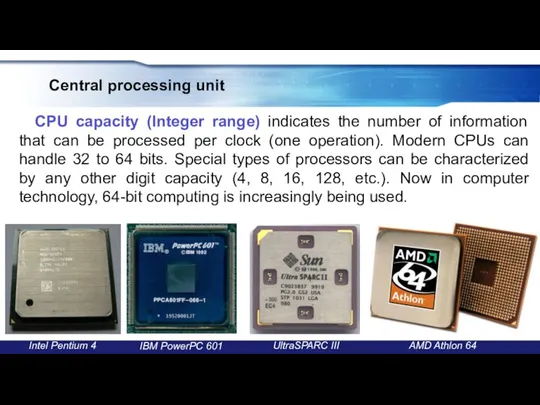
- 22. Central processing unit CPU capacity (Integer range) indicates the number of information that can be processed
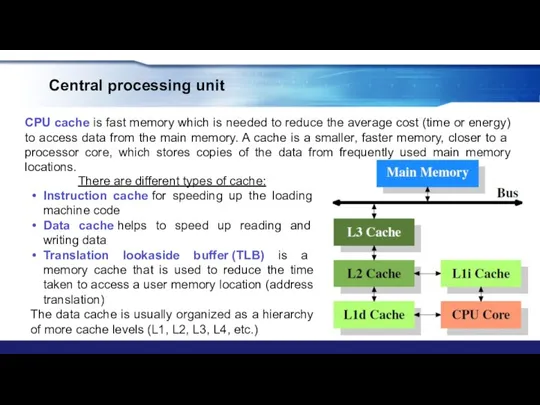
- 23. Central processing unit CPU cache is fast memory which is needed to reduce the average cost
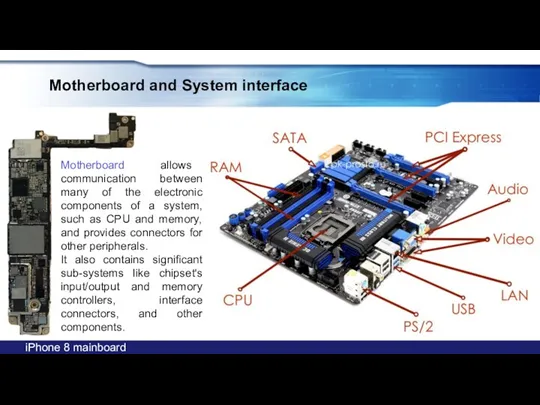
- 24. Motherboard and System interface Motherboard allows communication between many of the electronic components of a system,
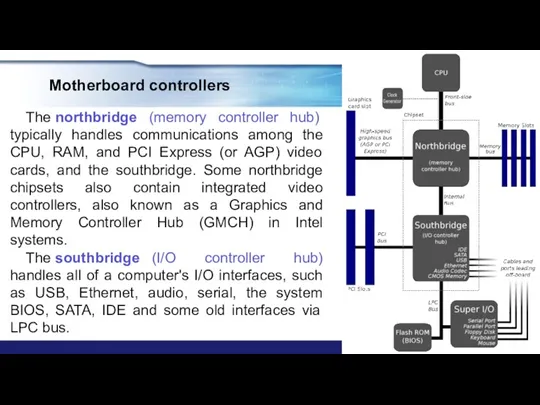
- 25. Motherboard controllers The northbridge (memory controller hub) typically handles communications among the CPU, RAM, and PCI
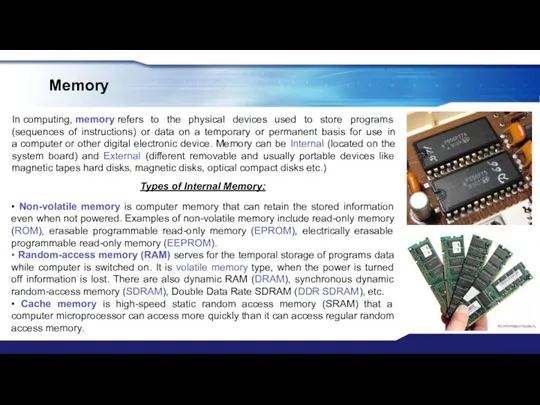
- 26. Memory In computing, memory refers to the physical devices used to store programs (sequences of instructions)
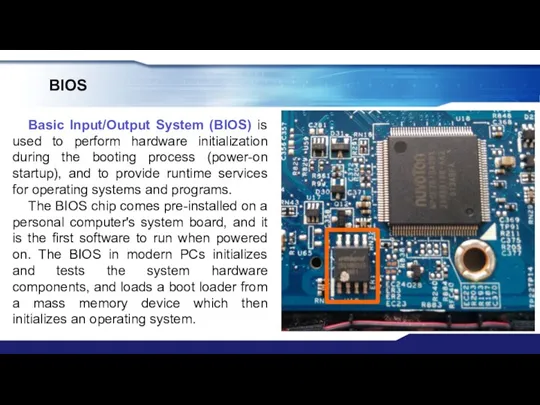
- 27. BIOS Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) is used to perform hardware initialization during the booting process (power-on
- 28. External memory Magnetic tape is a medium for magnetic recording, made of a thin, magnetizable coating
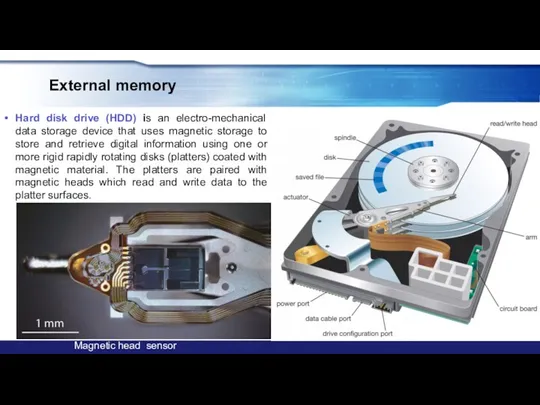
- 29. External memory Hard disk drive (HDD) is an electro-mechanical data storage device that uses magnetic storage
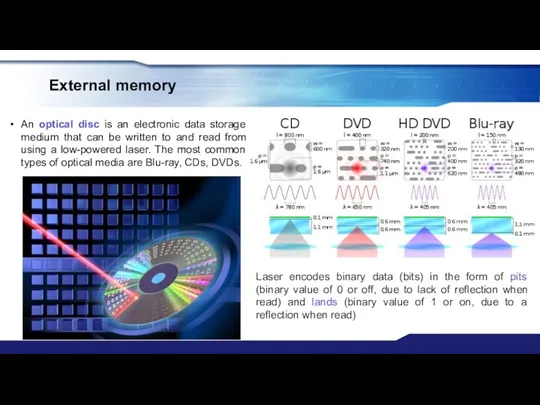
- 30. External memory An optical disc is an electronic data storage medium that can be written to
- 32. Скачать презентацию






 Разработка мобильного приложения к чемпионату мира по футболу 2018
Разработка мобильного приложения к чемпионату мира по футболу 2018 Задачи
Задачи Основы html/css
Основы html/css Проект Овощи в группе раннего возраста
Проект Овощи в группе раннего возраста Растровая графика
Растровая графика Рыцарский турнир по информатике
Рыцарский турнир по информатике Указатели и массивы (лекция 9 - 10)
Указатели и массивы (лекция 9 - 10) Разработка настольной игры
Разработка настольной игры Викторина Информ-бой. 10-11 класс
Викторина Информ-бой. 10-11 класс Моделювання бізнес-процесів лісозаготівлі
Моделювання бізнес-процесів лісозаготівлі Сети и системы телекоммуникаций
Сети и системы телекоммуникаций Алгоритмы. Свойства алгоритмов. Исполнители
Алгоритмы. Свойства алгоритмов. Исполнители 1С:Предприятие 8. Такси и аренда автомобилей
1С:Предприятие 8. Такси и аренда автомобилей Северная Африка. Журналистика, ислам, песок
Северная Африка. Журналистика, ислам, песок 1C:Предприятие 8. Автосервис
1C:Предприятие 8. Автосервис презентация Неделя безопасности Интернет
презентация Неделя безопасности Интернет Понятие информационной технологии
Понятие информационной технологии Осторожно! Цивилизация Безопасный Интернет ИГРА
Осторожно! Цивилизация Безопасный Интернет ИГРА Компьютерная безопасность
Компьютерная безопасность Построение диаграмм с помощью табличного процессора MS Excel
Построение диаграмм с помощью табличного процессора MS Excel Пресс-релиз
Пресс-релиз Creation of a simple network configuration
Creation of a simple network configuration Мониторинг сайтов образовательных организаций г.о. Самара
Мониторинг сайтов образовательных организаций г.о. Самара Международные организации по стандартизации. Основы стандартизации и сертификации ПО. Лекция 2
Международные организации по стандартизации. Основы стандартизации и сертификации ПО. Лекция 2 Использование Searchable DataStore для поиска закономерностей
Использование Searchable DataStore для поиска закономерностей Цифровое видеоизображение
Цифровое видеоизображение Графический редактор PAINT
Графический редактор PAINT Программы профессиональной переподготовки по информационной безопасности и технической защите информации
Программы профессиональной переподготовки по информационной безопасности и технической защите информации