Содержание
- 2. Learning Objectives Outline Basic network configurations Name kinds of applications that might use each Configuration
- 3. Network Configurations? Ways of organizing data processing Where to do processing Decision on “which configuration” depends
- 4. Basic configurations Terminal to mainframe computer Microcomputer to mainframe computer Microcomputer to local area network Microcomputer
- 5. Basic configurations Local area network to wide area network Wide Area network to Wide Area network
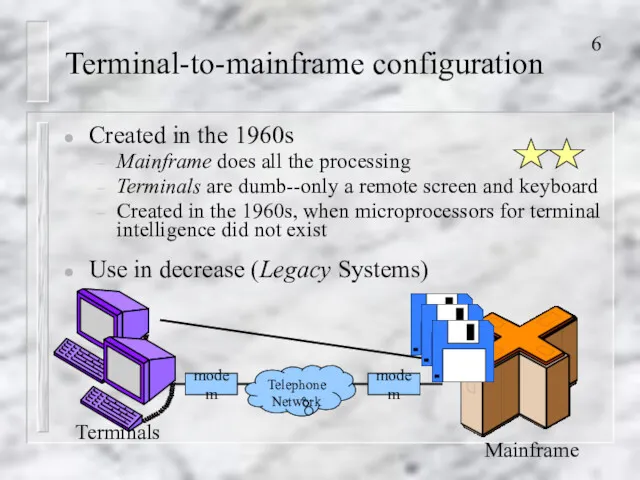
- 6. Terminal-to-mainframe configuration Created in the 1960s Mainframe does all the processing Terminals are dumb--only a remote
- 7. Terminal-to-mainframe configuration Usually, Mainframe Optimized for business uses--file access speed is more crucial than mathematical processing
- 8. Terminal-to-mainframe configuration Mainframe controls: Sending data to the terminals Receiving data from the terminals Require special
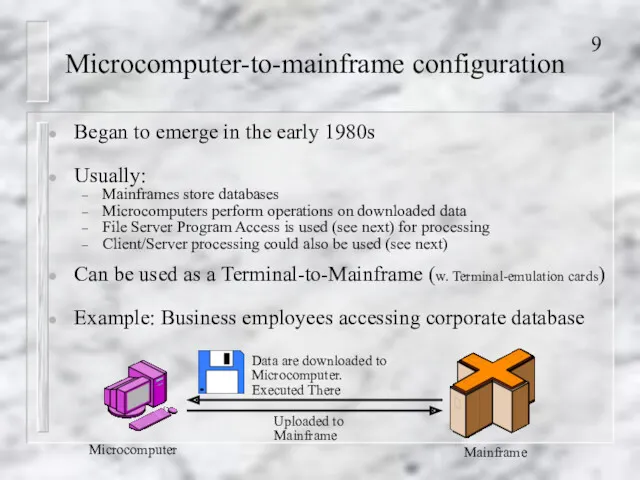
- 9. Microcomputer-to-mainframe configuration Began to emerge in the early 1980s Usually: Mainframes store databases Microcomputers perform operations
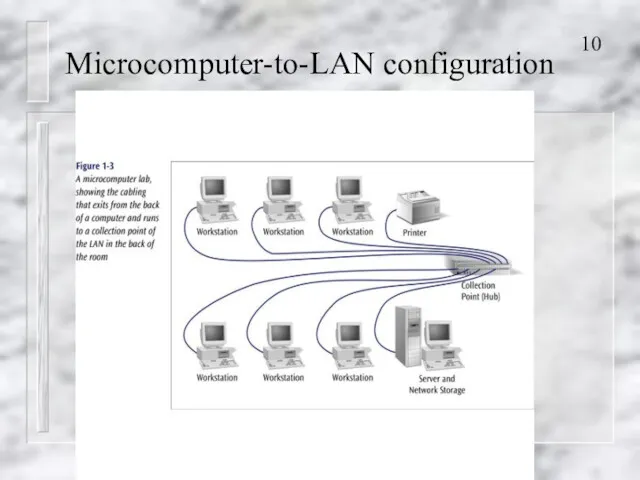
- 10. Microcomputer-to-LAN configuration
- 11. Microcomputer-to-LAN configuration Perhaps the most common Network configuration Very common in business and academic environments LAN
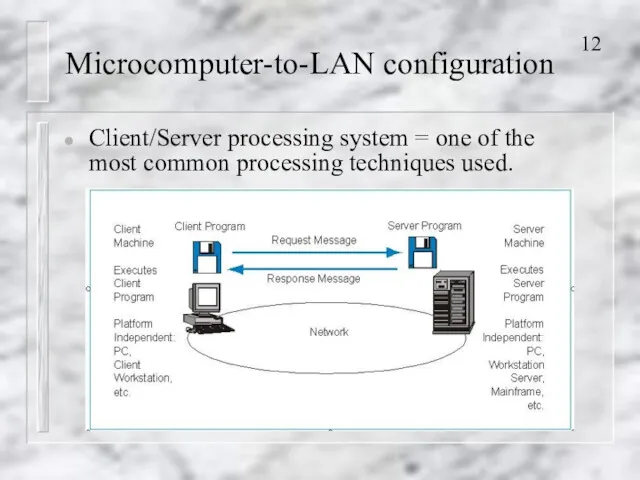
- 12. Microcomputer-to-LAN configuration Client/Server processing system = one of the most common processing techniques used.
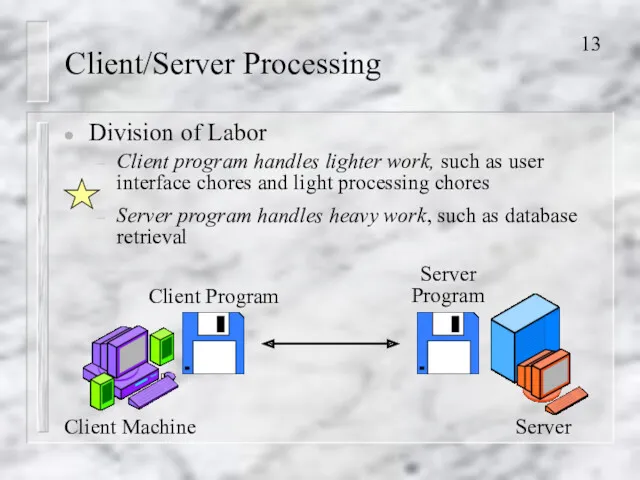
- 13. Client/Server Processing Division of Labor Client program handles lighter work, such as user interface chores and
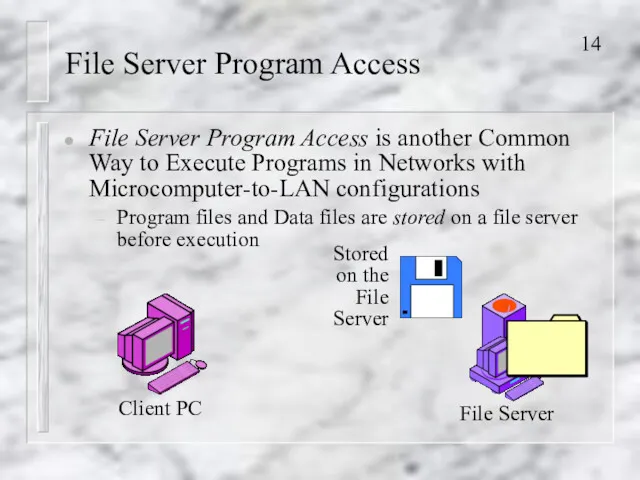
- 14. File Server Program Access File Server Program Access is another Common Way to Execute Programs in
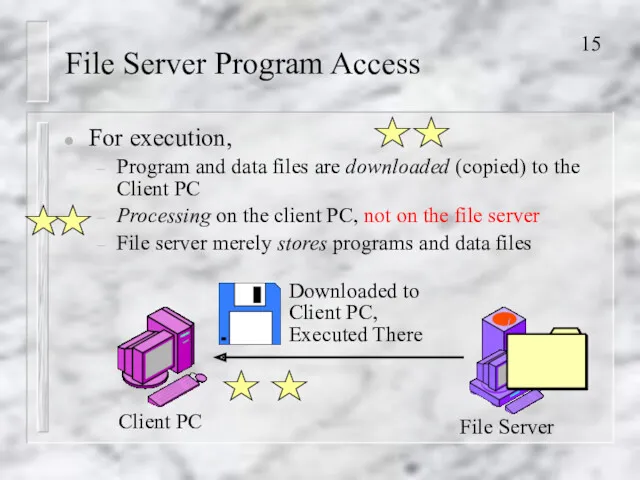
- 15. File Server Program Access For execution, Program and data files are downloaded (copied) to the Client
- 16. File Server Program Access PC processing power limits FSPA programs Client PCs do not get very
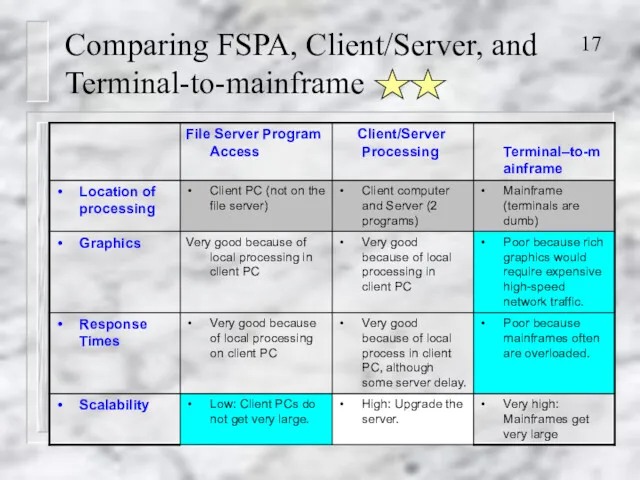
- 17. Comparing FSPA, Client/Server, and Terminal-to-mainframe
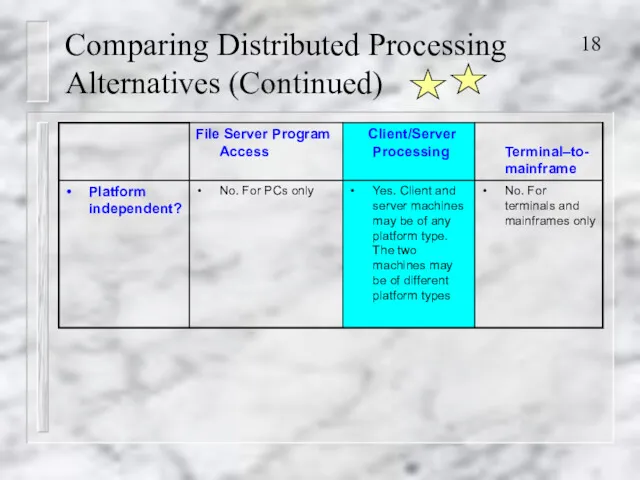
- 18. Comparing Distributed Processing Alternatives (Continued)
- 19. Summary Questions What kind of application might use: (a) a terminal-to-mainframe configuration, (b) a microcomputer-to-mainframe configuration,
- 20. Summary Questions (cont.) Which of the following may involve using a Terminal-to-Mainframe configuration? You are surfing
- 21. Summary Questions (cont.) Which of the following processing techniques is commonly used in schools’ LANs to
- 22. Other slides
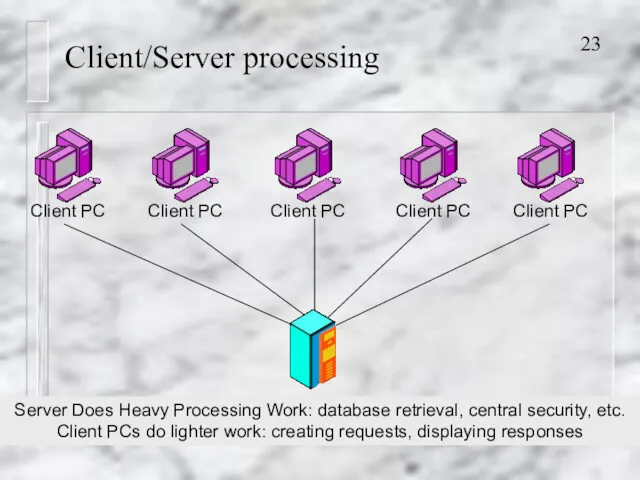
- 23. Client/Server processing Server Does Heavy Processing Work: database retrieval, central security, etc. Client PCs do lighter
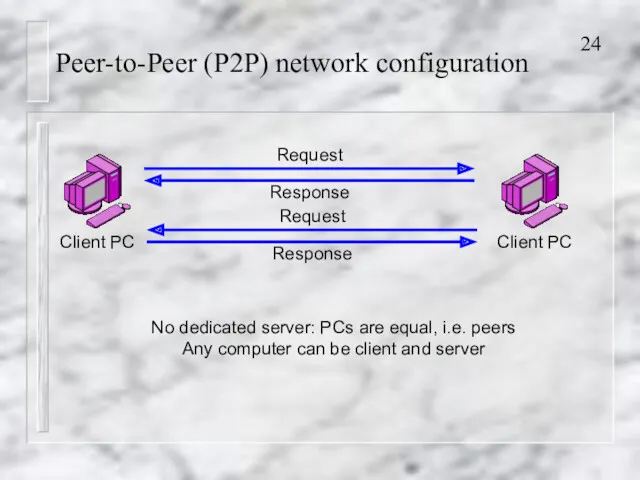
- 24. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) network configuration Request Response No dedicated server: PCs are equal, i.e. peers Any computer
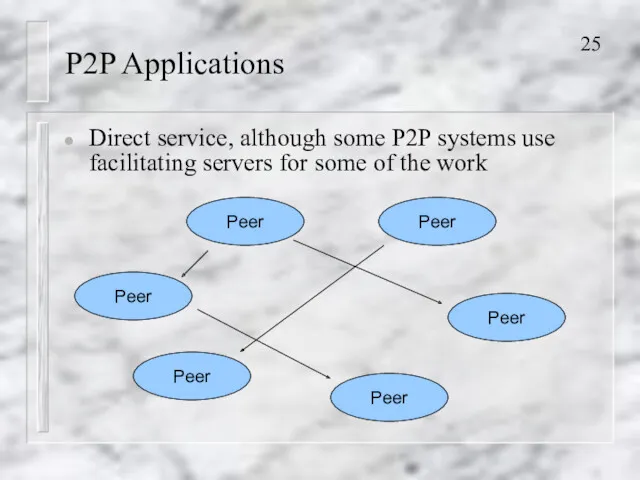
- 25. P2P Applications Direct service, although some P2P systems use facilitating servers for some of the work
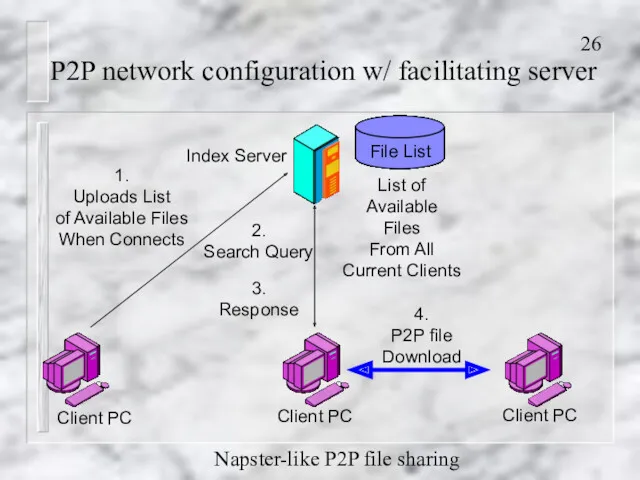
- 26. P2P network configuration w/ facilitating server Index Server 2. Search Query 3. Response 1. Uploads List
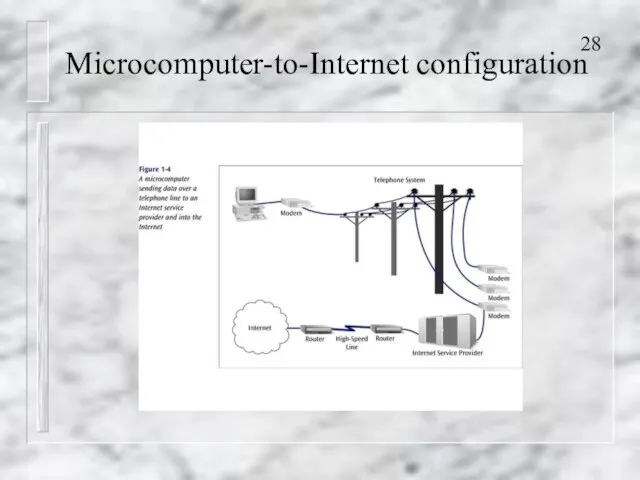
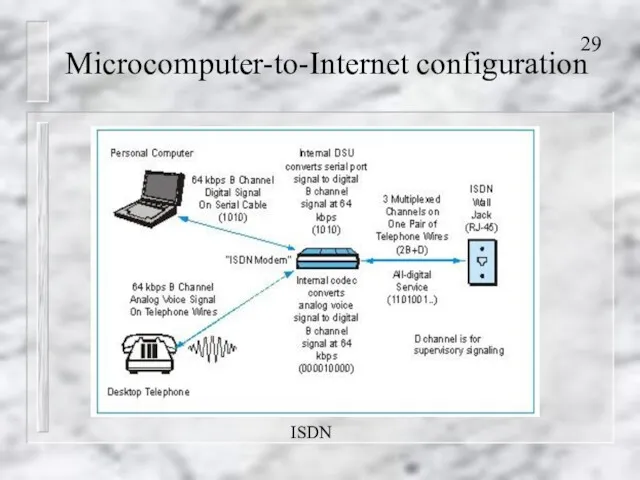
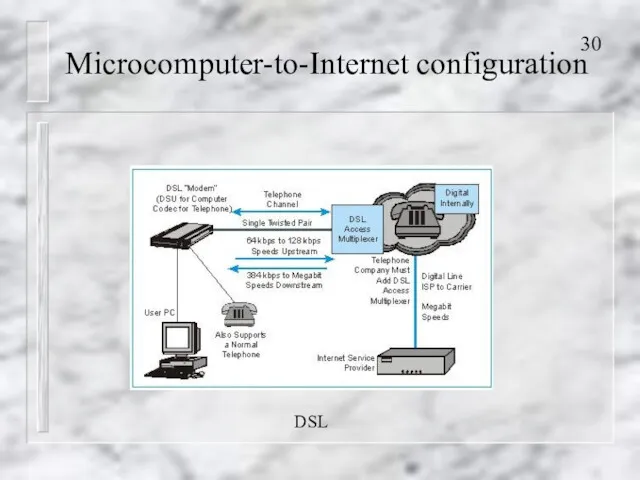
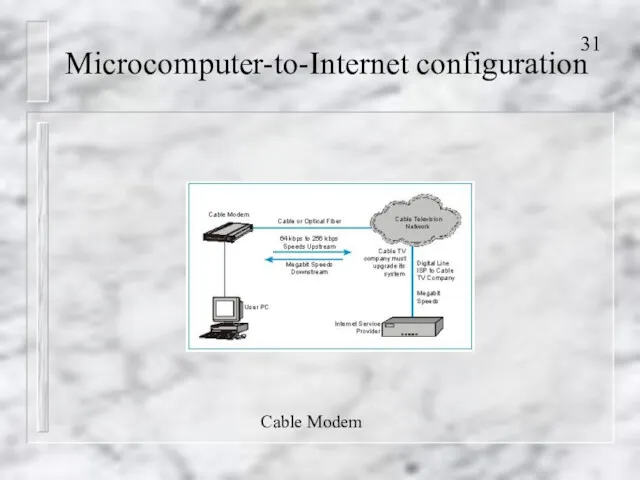
- 27. Microcomputer-to-Internet configuration Accessing the Internet using A modem and a dial-up telephone service ISDN (Integrated Services
- 28. Microcomputer-to-Internet configuration
- 29. Microcomputer-to-Internet configuration ISDN
- 30. Microcomputer-to-Internet configuration DSL
- 31. Microcomputer-to-Internet configuration Cable Modem
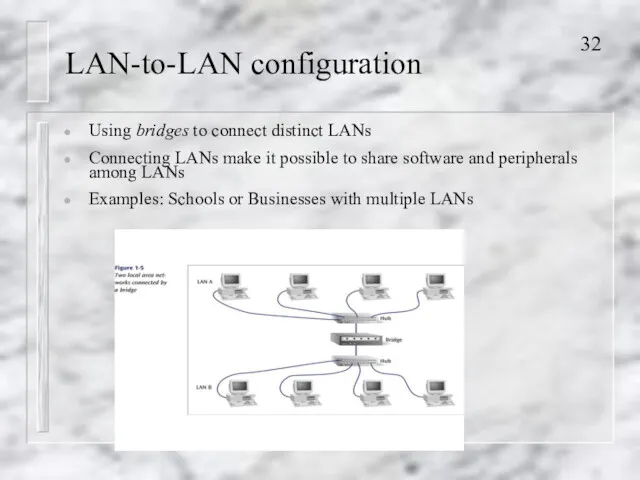
- 32. LAN-to-LAN configuration Using bridges to connect distinct LANs Connecting LANs make it possible to share software
- 34. Скачать презентацию











 Software. Operating system
Software. Operating system Информационно-технологический профиль
Информационно-технологический профиль C++ Network Programming Systematic Reuse with ACE & Frameworks
C++ Network Programming Systematic Reuse with ACE & Frameworks Компьютерные вирусы
Компьютерные вирусы Создание Web-страниц средствами языка HTML Пример веб-страницыH1>
Создание Web-страниц средствами языка HTML Пример веб-страницыH1> Сто к одному. Игра
Сто к одному. Игра SVG: Syntax Sprites Animation
SVG: Syntax Sprites Animation Библиография научной статьи: оформление ссылок и списка литературы
Библиография научной статьи: оформление ссылок и списка литературы Физический уровень модели OSI. Лекция 3
Физический уровень модели OSI. Лекция 3 Команды редактирования 3D чертежей. Алгоритмы визуализации. (Лекция 8)
Команды редактирования 3D чертежей. Алгоритмы визуализации. (Лекция 8) Разработка информационной системы Строительство жилых зданий
Разработка информационной системы Строительство жилых зданий Табличные данные
Табличные данные iOS
iOS Аффинные преобразования в компьютерной графике. (Тема 5)
Аффинные преобразования в компьютерной графике. (Тема 5) Таблицы, графики и диаграммы
Таблицы, графики и диаграммы Рефлексия типов и программирование с использованием атрибутов. Лекция #6
Рефлексия типов и программирование с использованием атрибутов. Лекция #6 Intro to databases database management system
Intro to databases database management system Создание диапазонов адресов. Лекция 5
Создание диапазонов адресов. Лекция 5 SQLite. Способы доступа СУБД к БД
SQLite. Способы доступа СУБД к БД Разработка программной платформы для создания и проведения квест-мероприятий
Разработка программной платформы для создания и проведения квест-мероприятий Введение в DIRECTUM (с чего надо было начинать знакомство). Лекция 2. Типовые маршруты
Введение в DIRECTUM (с чего надо было начинать знакомство). Лекция 2. Типовые маршруты Резиденция Деда Мороза в Великом Устюге
Резиденция Деда Мороза в Великом Устюге Программирование на языке Python
Программирование на языке Python Наступает новая реальность. СМИ: распространение информации для принятия решений
Наступает новая реальность. СМИ: распространение информации для принятия решений 1С:Управление нашей фирмой
1С:Управление нашей фирмой Нейронные сети
Нейронные сети Специалист по социальным сетям
Специалист по социальным сетям Создание зубчатых передач на Компас 3D
Создание зубчатых передач на Компас 3D