Содержание
- 2. Main ideas What is navigation? What is navigation used for? ILS ; VOR/DME
- 3. What is navigation? The process or activity of accurately ascertaining one's position and planning and following
- 4. What is navigation used for? Navigation is the art and science of determining the position of
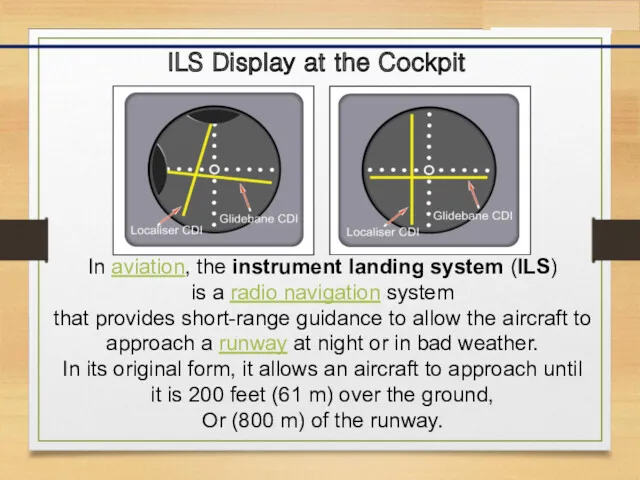
- 5. ILS Display at the Cockpit In aviation, the instrument landing system (ILS) is a radio navigation
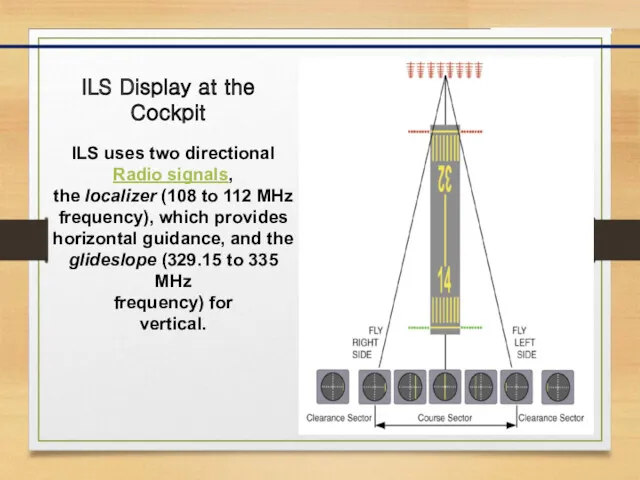
- 6. ILS Display at the Cockpit ILS uses two directional Radio signals, the localizer (108 to 112
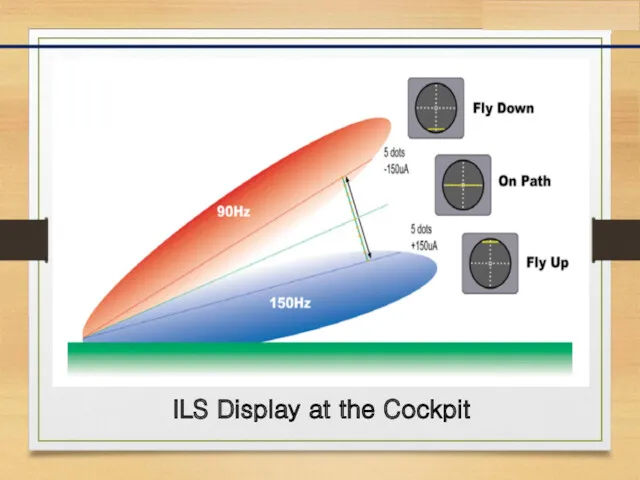
- 7. ILS Display at the Cockpit
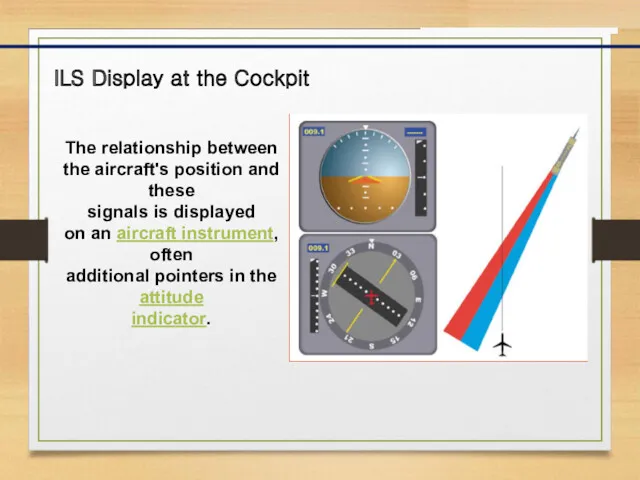
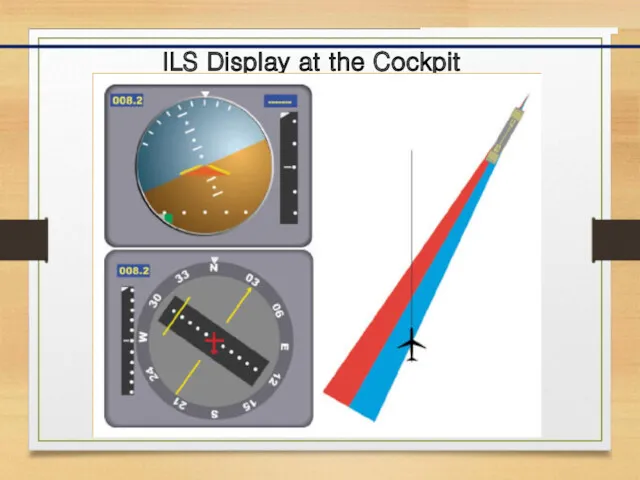
- 8. ILS Display at the Cockpit The relationship between the aircraft's position and these signals is displayed
- 9. ILS Display at the Cockpit
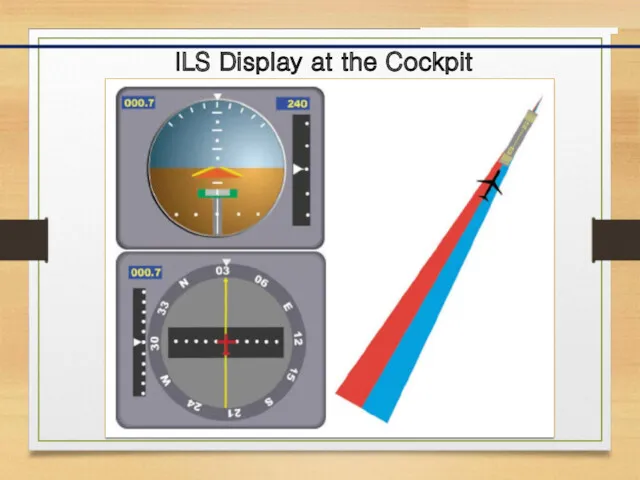
- 10. ILS Display at the Cockpit
- 11. ILS Display at the Cockpit
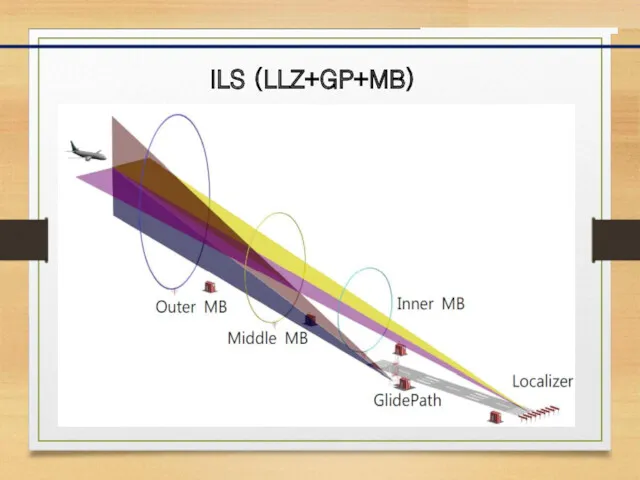
- 12. ILS (LLZ+GP+MB)
- 13. LLZ Antenna Array An instrument landing system operates as a ground-based instrument approach system that provides
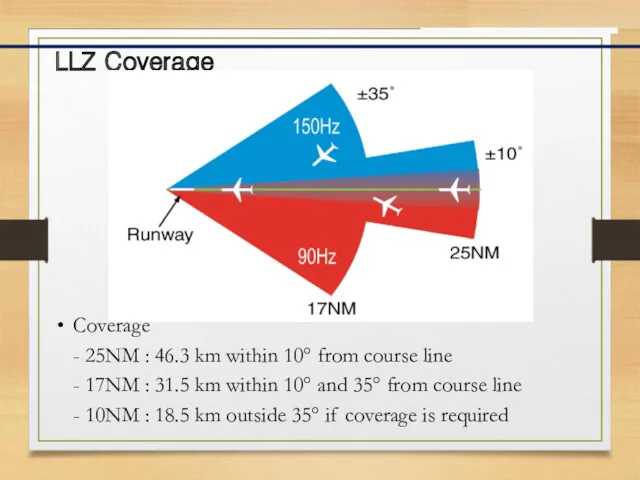
- 14. LLZ Coverage Coverage - 25NM : 46.3 km within 10° from course line - 17NM :
- 15. DVOR/DME In radio navigation, a VOR/DME is a radio beacon that combines a VHF omnidirectional range
- 16. VOR Display at the Cockpit
- 17. DVOR/DME The VOR system was first introduced in the 1930s, but didn't enter significant commercial use
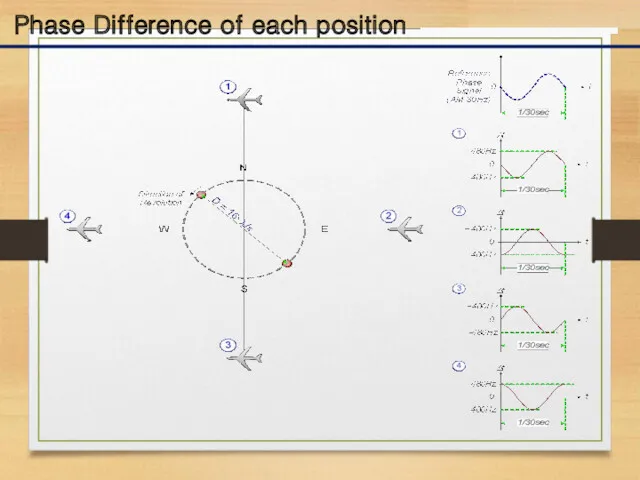
- 18. Phase Difference of each position
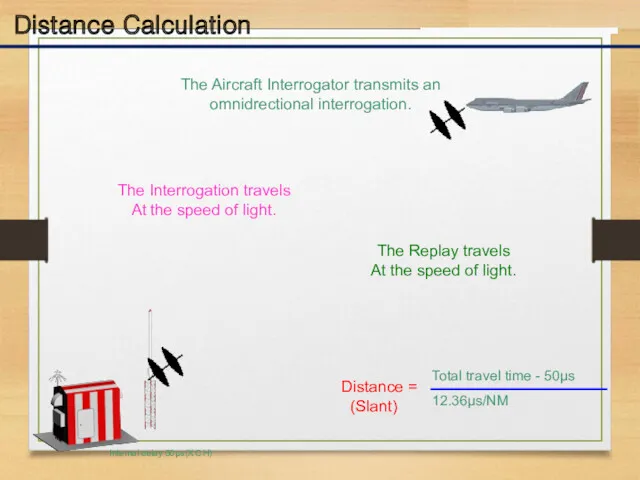
- 19. Distance Calculation The Aircraft Interrogator transmits an omnidrectional interrogation. The Interrogation travels At the speed of
- 21. Скачать презентацию








 Welcome To ZyXEL Router Customer Care Center. How to Install a ZyXEL Router
Welcome To ZyXEL Router Customer Care Center. How to Install a ZyXEL Router Доступы: гостевой и представительский доступ, настройка и управление
Доступы: гостевой и представительский доступ, настройка и управление NFT \ Non Fungible Token
NFT \ Non Fungible Token Компьютерные игры как современный вид хобби
Компьютерные игры как современный вид хобби Как найти пользователей ВКонтакте, которые действительно покупают товары?
Как найти пользователей ВКонтакте, которые действительно покупают товары? Характерные черты информационного общества
Характерные черты информационного общества Опасности в Интернете. Перечень опасностей
Опасности в Интернете. Перечень опасностей Описательная статистика. Группировка данных. Лекция 2
Описательная статистика. Группировка данных. Лекция 2 History of Cologne Digital Lexicons
History of Cologne Digital Lexicons Разработка сайта
Разработка сайта Компьютер – универсальная машина для работы с информацией
Компьютер – универсальная машина для работы с информацией Lersus. Основные задачи и возможности
Lersus. Основные задачи и возможности Организация вычислений в электронных таблицах. Обработка числовой информации в электронных таблицах. Информатика. 9 класс
Организация вычислений в электронных таблицах. Обработка числовой информации в электронных таблицах. Информатика. 9 класс Мы за интернет!
Мы за интернет! Проектная технология на уроках информатики
Проектная технология на уроках информатики Основные виды опасного и запрещённого контента в Интернете и его признаки, приёмы распознавания опасностей в Интернете
Основные виды опасного и запрещённого контента в Интернете и его признаки, приёмы распознавания опасностей в Интернете Создание мультфильмов средствами power point
Создание мультфильмов средствами power point Язык программирования Pascal. Линейные алгоритмы
Язык программирования Pascal. Линейные алгоритмы Монтаж видеороликов в Windows Movie Maker
Монтаж видеороликов в Windows Movie Maker Бейне жобаны әзірлеу және қорғау
Бейне жобаны әзірлеу және қорғау 1С:Управление автотранспортом
1С:Управление автотранспортом Поколения ЭВМ
Поколения ЭВМ Логика — это наука о формах и способах мышления
Логика — это наука о формах и способах мышления Компонентно-орієнтоване проектування. Основи розробки веб-застосувань за допомогою АSР.NЕТ. Керування станом у ASP.NET
Компонентно-орієнтоване проектування. Основи розробки веб-застосувань за допомогою АSР.NЕТ. Керування станом у ASP.NET Использование массивов и табличных формул. Операции с матрицами. Решение систем линейных уравнений. (Лекция 8)
Использование массивов и табличных формул. Операции с матрицами. Решение систем линейных уравнений. (Лекция 8) Современные возможности ES-2015
Современные возможности ES-2015 Компьютерные технологии. Версия Matlab R2013b
Компьютерные технологии. Версия Matlab R2013b Моделирование, как метод познания
Моделирование, как метод познания