Слайд 2
Main Components Of An Operating System
Process Management
Disk And File Systems
Memory Management
Inter-process
communication (IPC)
Слайд 3

In the early days of electronic computing, two different processor/memory architectures
emerged:
Слайд 4
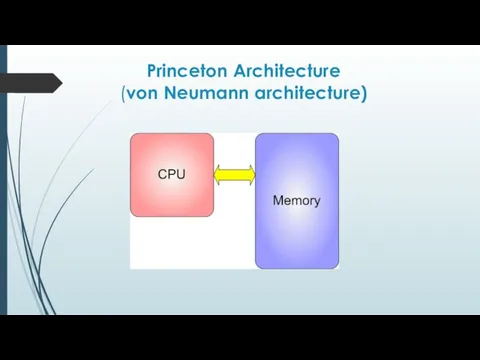
Princeton Architecture
(von Neumann architecture)
Слайд 5

The principles of von Neumann."
1. The principle of program control.
2. The
principle of one memory.
3. The principle of memory addressability.
Слайд 6
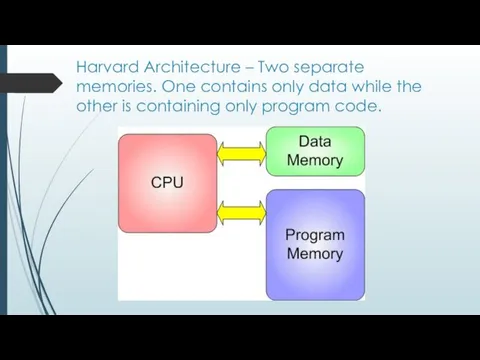
Harvard Architecture – Two separate memories. One contains only data while
the other is containing only program code.
Слайд 7

Which is better?
Each architecture has its advantages: All else being equal,
the Harvard model has the edge in performance. The Von Neumann model is more flexible.
Слайд 8
Types of memory
Automatic
static RAM
dynamic RAM
Слайд 9

MCB
The concept of a memory control block (MCB) was introduced in
MS-DOS, Version 2.0, as the operating system's basic method of tracking memory allocation for application programs and installable device drivers.
Слайд 10
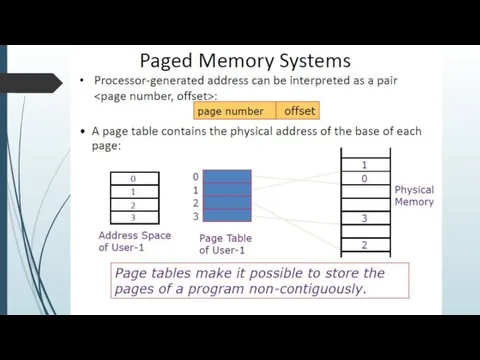
Слайд 11

Memory Technology Trade-offs
Слайд 12
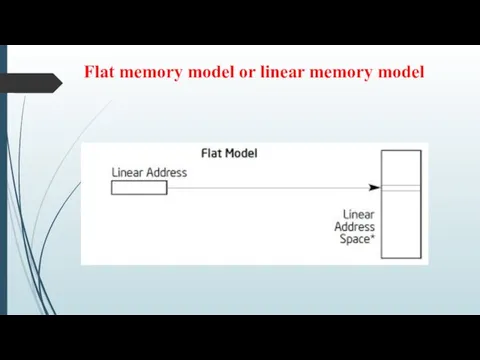
Flat memory model or linear memory model
Слайд 13
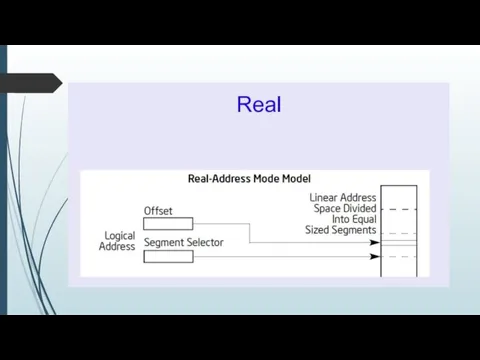
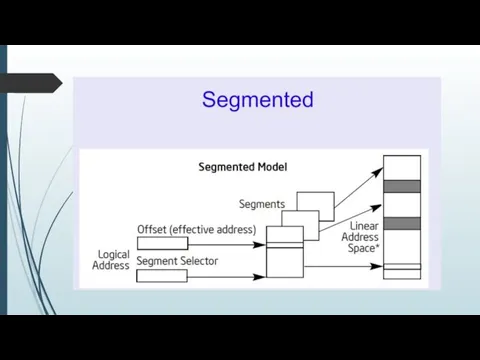
Слайд 14













 Linux и Windows. Сравнение двух операционных систем
Linux и Windows. Сравнение двух операционных систем Информационное обеспечение проектной деятельности (тема 2)
Информационное обеспечение проектной деятельности (тема 2) Технология Ethernet для сетей доступа и транспорта
Технология Ethernet для сетей доступа и транспорта Обеспечение информационной безопасности
Обеспечение информационной безопасности Разработка методов и алгоритмов для распознавания рукописных цифр с использованием нейронной сети
Разработка методов и алгоритмов для распознавания рукописных цифр с использованием нейронной сети Інтернет-магазин взуття. Технічне завдання
Інтернет-магазин взуття. Технічне завдання 5B070500 Mathematical and Computer Modeling Образовательные программы
5B070500 Mathematical and Computer Modeling Образовательные программы Створення потоку в Java
Створення потоку в Java Устройство компьютера
Устройство компьютера Литературный обзор
Литературный обзор Електронна пошта. Передача поштових повідомлень
Електронна пошта. Передача поштових повідомлень Глобальная сеть Интернет
Глобальная сеть Интернет Что такое программирование. Язык программирования java
Что такое программирование. Язык программирования java Цифровая обработка сигналов
Цифровая обработка сигналов Візуальна система формування набору об’єктів нерухомості на карті
Візуальна система формування набору об’єктів нерухомості на карті Виды информационно-поисковых тезаурусов
Виды информационно-поисковых тезаурусов Влияние эми компьютеров на память школьников
Влияние эми компьютеров на память школьников Алгоритмы и исполнители
Алгоритмы и исполнители Клавиатура – устройство ввода информации в память компьютера
Клавиатура – устройство ввода информации в память компьютера Детерминантты шекті автоматтар. Мур диаграммасы
Детерминантты шекті автоматтар. Мур диаграммасы Архитектурное проектирование и паттерны программирования
Архитектурное проектирование и паттерны программирования Классификация программного обеспечения
Классификация программного обеспечения Виды вторичного текста. Компрессия
Виды вторичного текста. Компрессия Personal Home Page (PHP)
Personal Home Page (PHP) Установка и настройка Apache и PHP
Установка и настройка Apache и PHP Передача, обработка и хранение информации
Передача, обработка и хранение информации Компьютерные сети
Компьютерные сети Рисуем мультфильм
Рисуем мультфильм