- Главная
- Информатика
- Lecture 6 Routing

Содержание
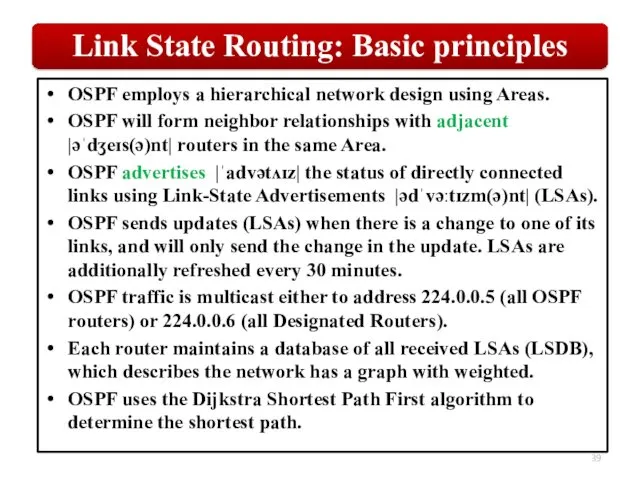
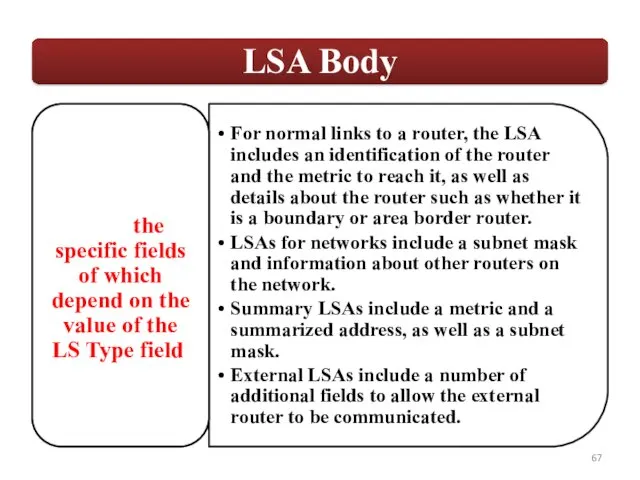
- 39. OSPF employs a hierarchical network design using Areas. OSPF will form neighbor relationships with adjacent |əˈdʒeɪs(ə)nt|
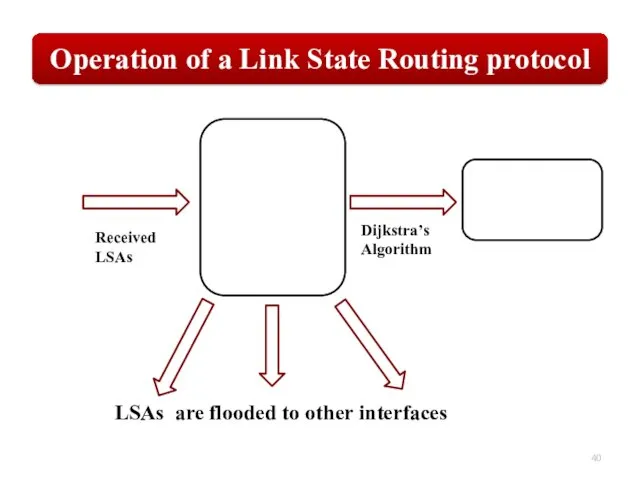
- 40. LSAs are flooded to other interfaces Received LSAs Dijkstra’s Algorithm
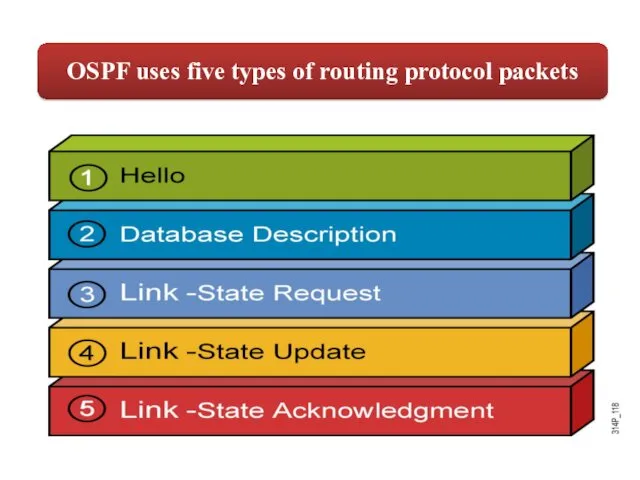
- 47. How OSPF Packet Processes Work
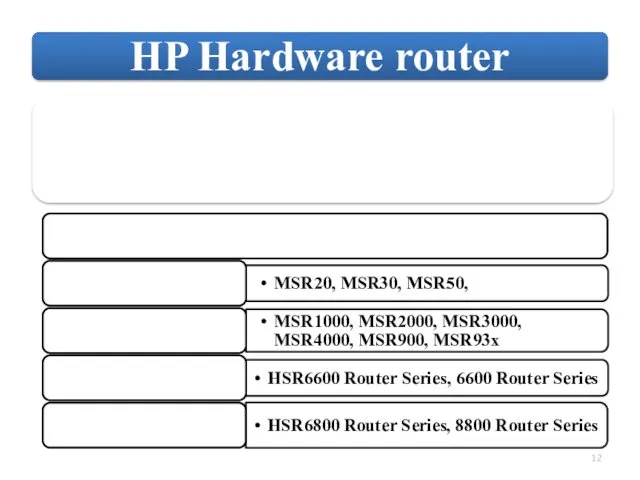
- 50. ABR BR Internal Routers.
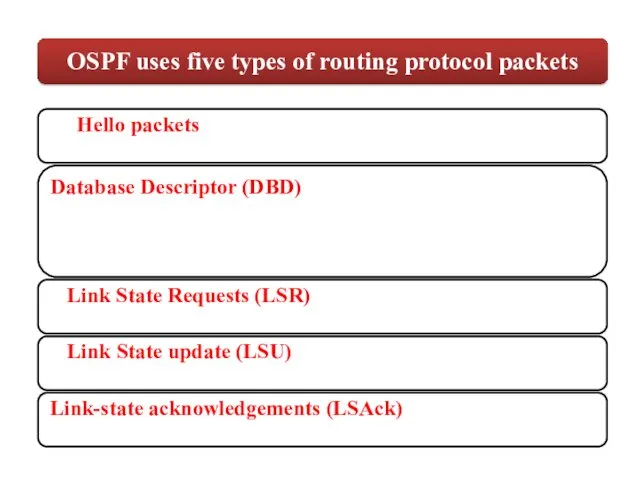
- 61. Database Descriptor (DBD)
- 63. Link State update (LSU) Link State Requests (LSR)
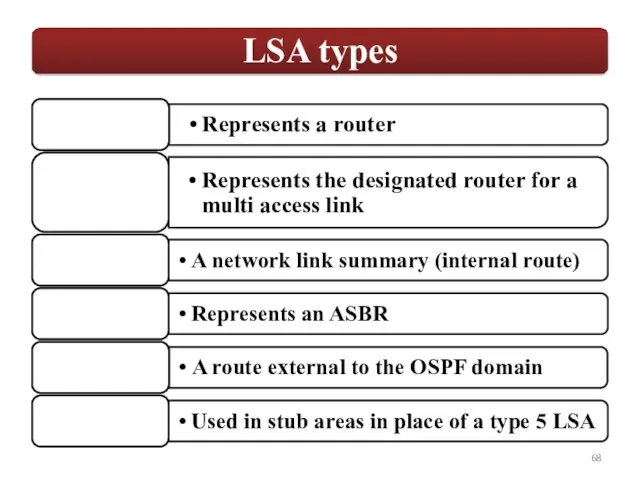
- 66. LS Age: By default an LSA has a maximum age of 3600 seconds. Options: (E-bit) -Indicates
- 74. Скачать презентацию
Слайд 2
Слайд 3
Слайд 4
Слайд 5
Слайд 6
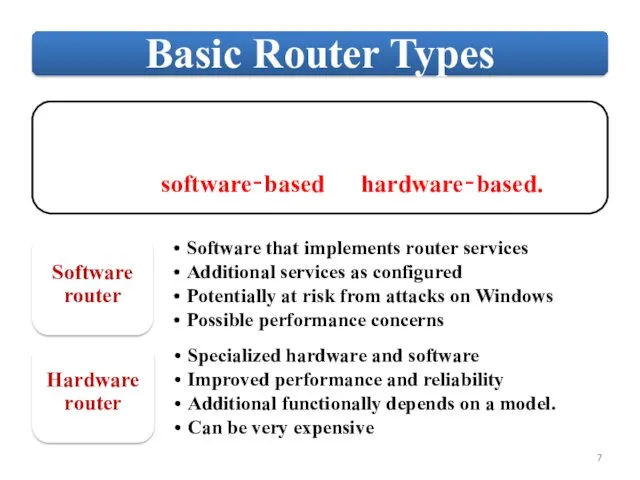
Слайд 7
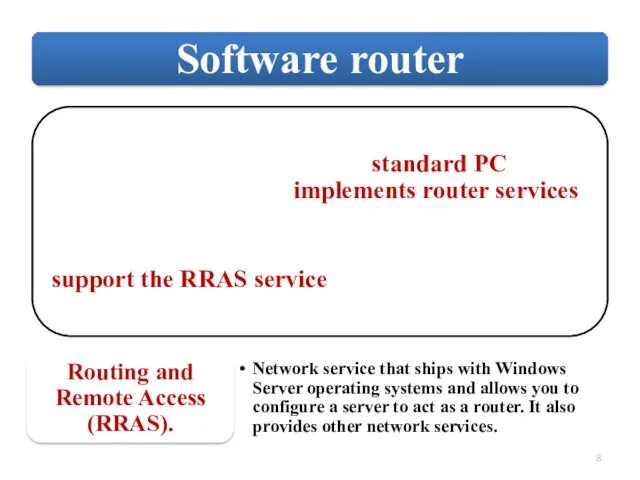
Слайд 8
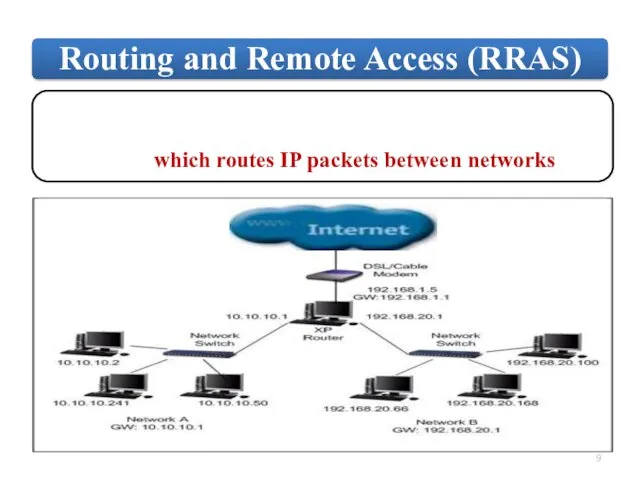
Слайд 9
Слайд 10
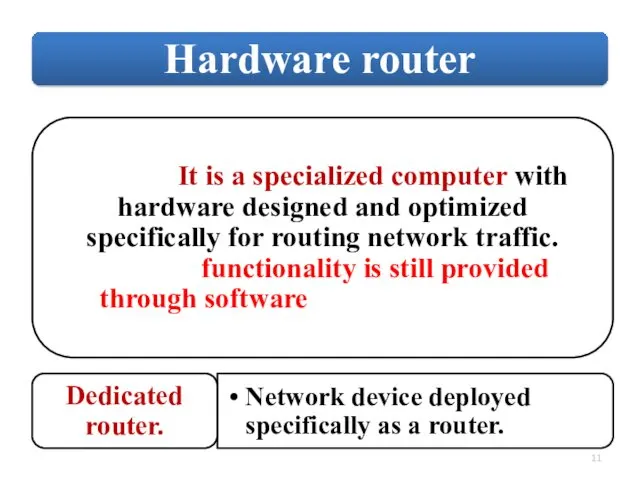
Слайд 11
Слайд 12
Слайд 13
Слайд 14
Слайд 15
Слайд 16
Слайд 17
Слайд 18
Слайд 19
Слайд 20
Слайд 21
Слайд 22
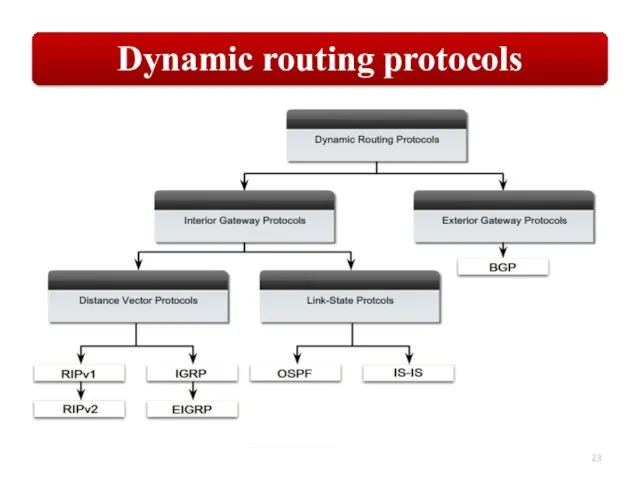
Слайд 23
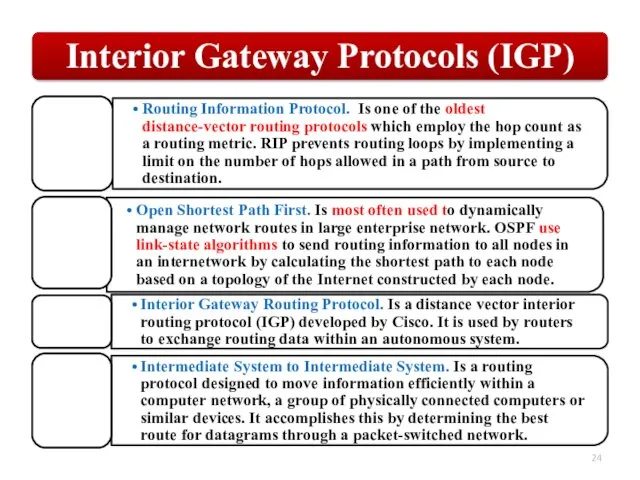
Слайд 24
Слайд 25
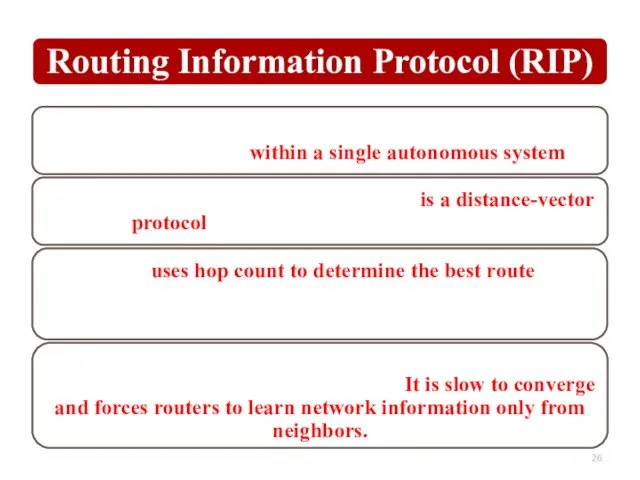
Слайд 26
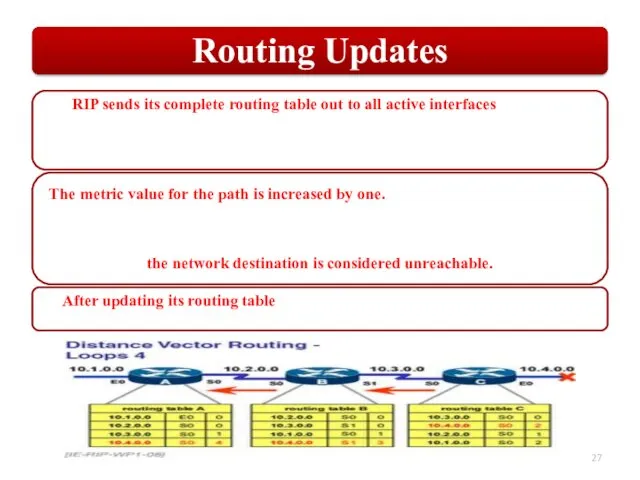
Слайд 27
Слайд 28
Слайд 29
Слайд 30
Слайд 31
Слайд 32
Слайд 33
Слайд 34
Слайд 35
Слайд 36
Слайд 37
Слайд 38
Слайд 39
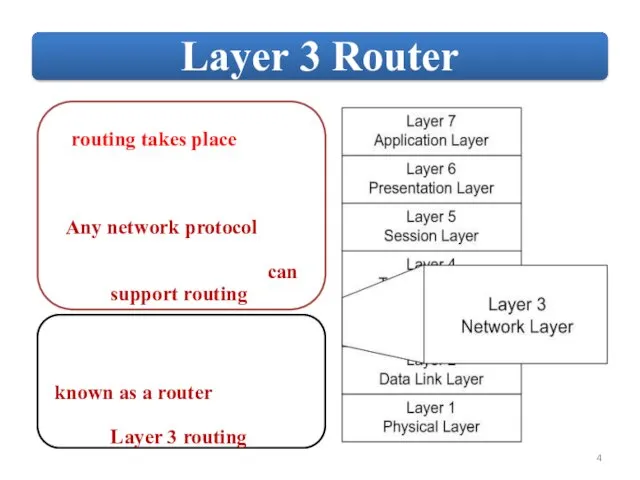
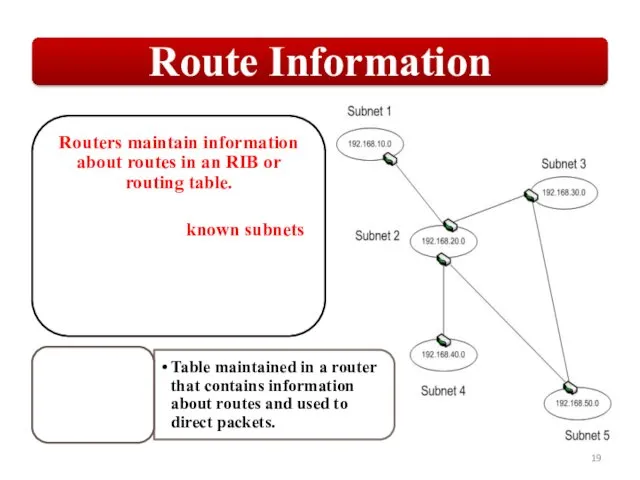
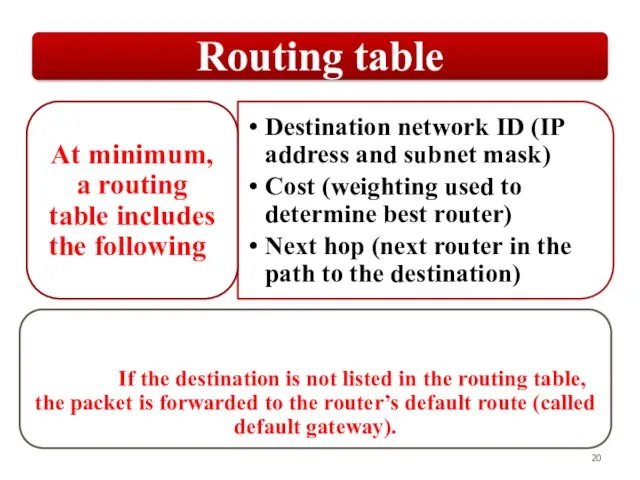
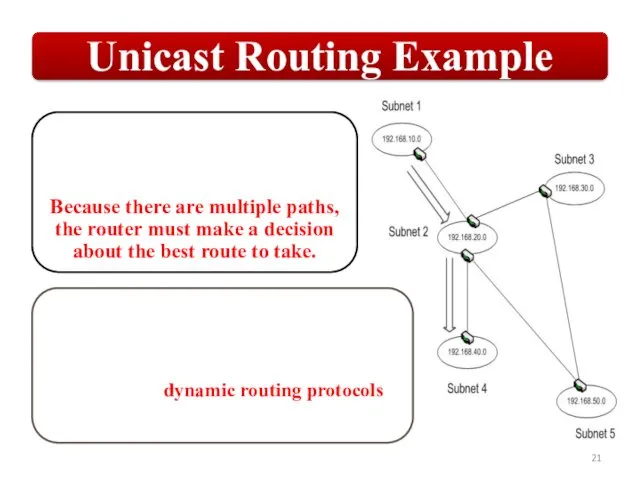
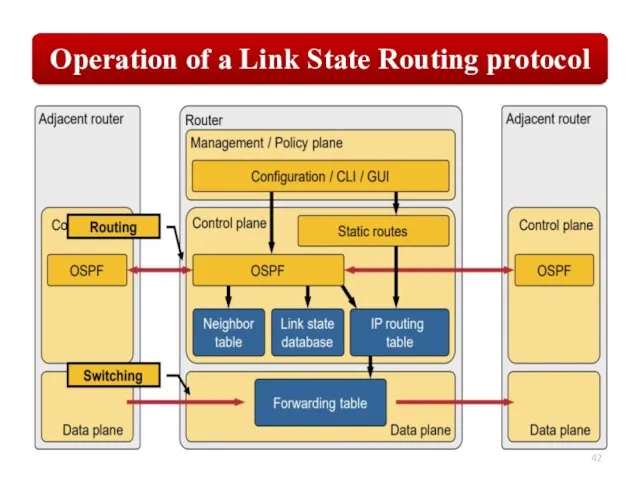
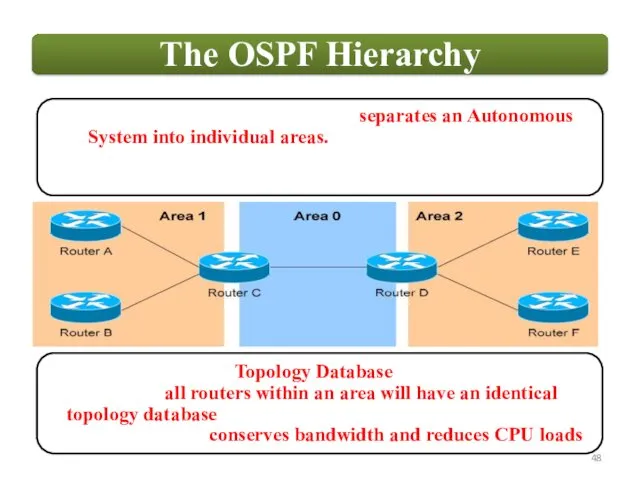
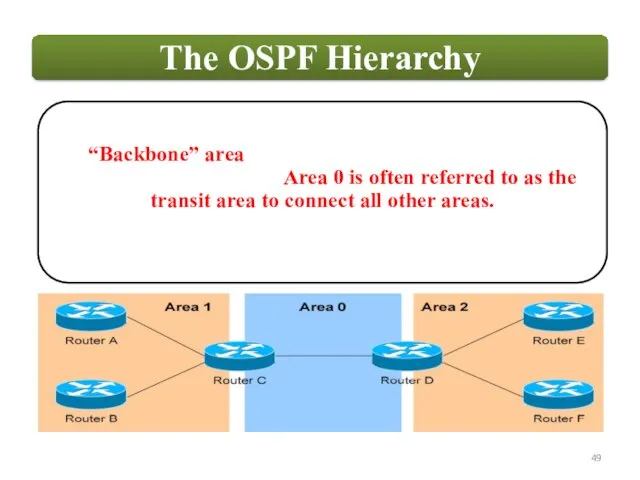
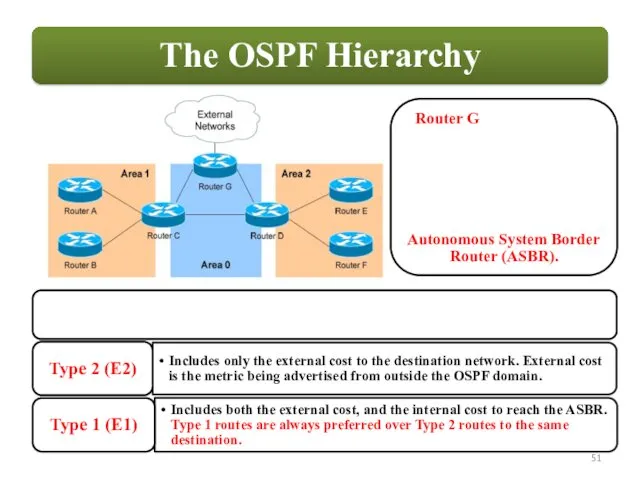
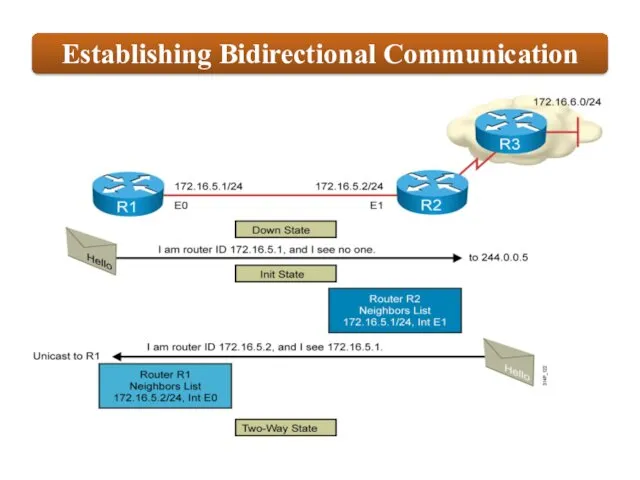
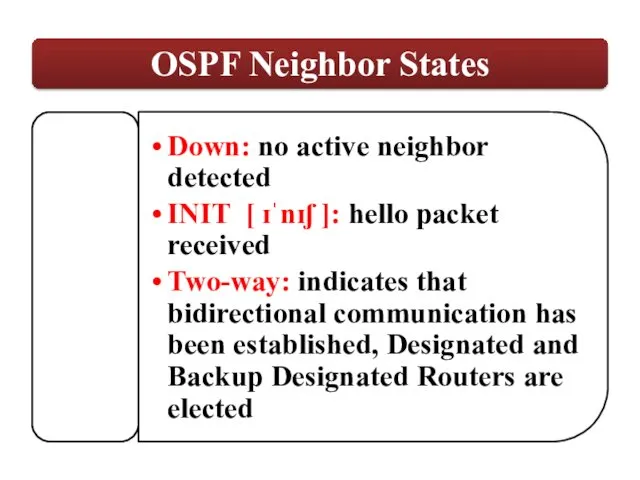
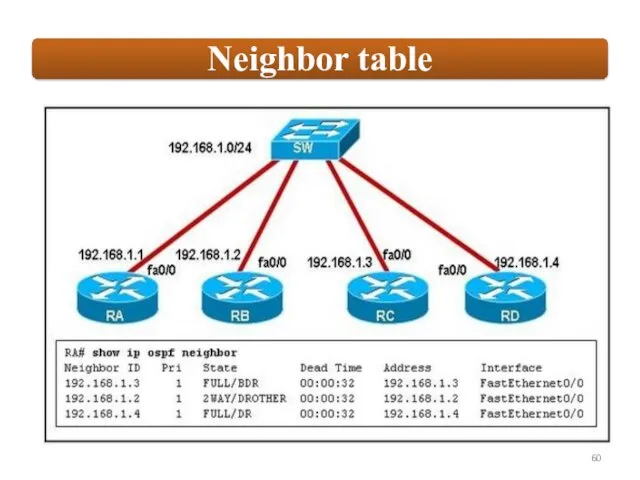
OSPF employs a hierarchical network design using Areas.
OSPF will form neighbor
OSPF employs a hierarchical network design using Areas.
OSPF will form neighbor
relationships with adjacent |əˈdʒeɪs(ə)nt| routers in the same Area.
OSPF advertises |ˈadvətʌɪz| the status of directly connected links using Link-State Advertisements |ədˈvəːtɪzm(ə)nt| (LSAs).
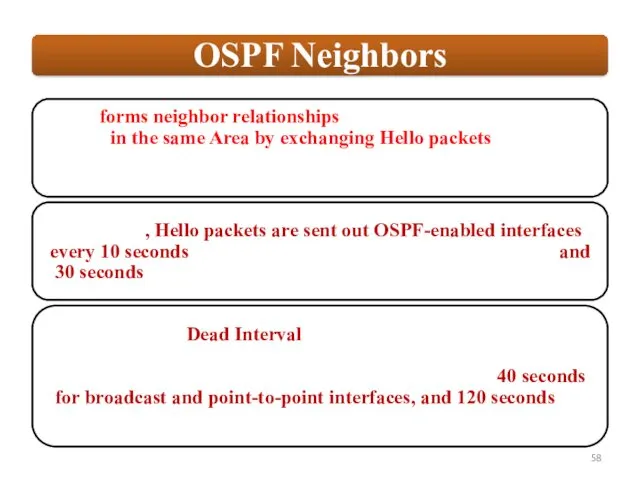
OSPF sends updates (LSAs) when there is a change to one of its links, and will only send the change in the update. LSAs are additionally refreshed every 30 minutes.
OSPF traffic is multicast either to address 224.0.0.5 (all OSPF routers) or 224.0.0.6 (all Designated Routers).
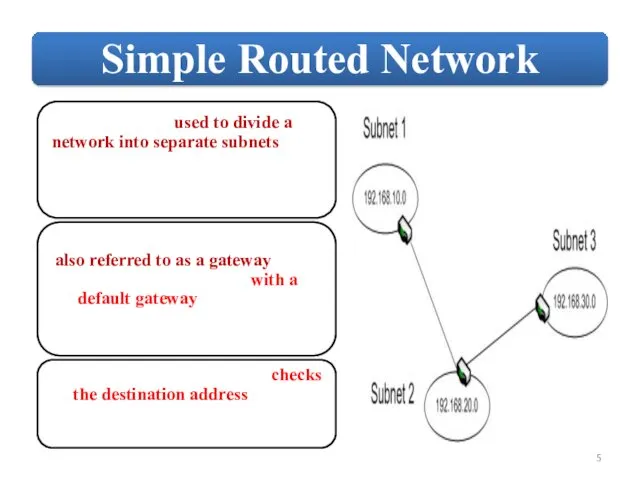
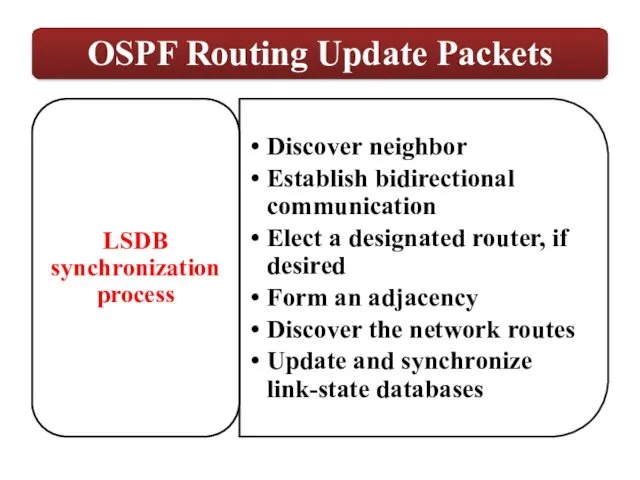
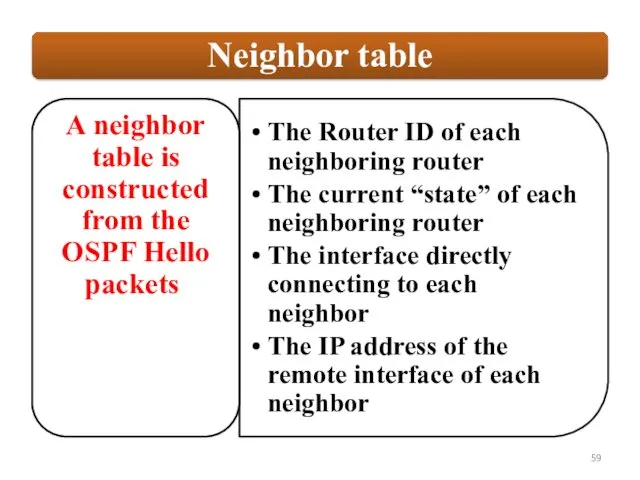
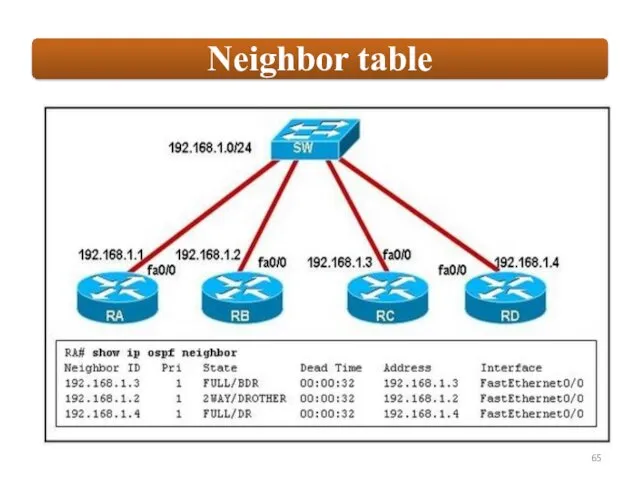
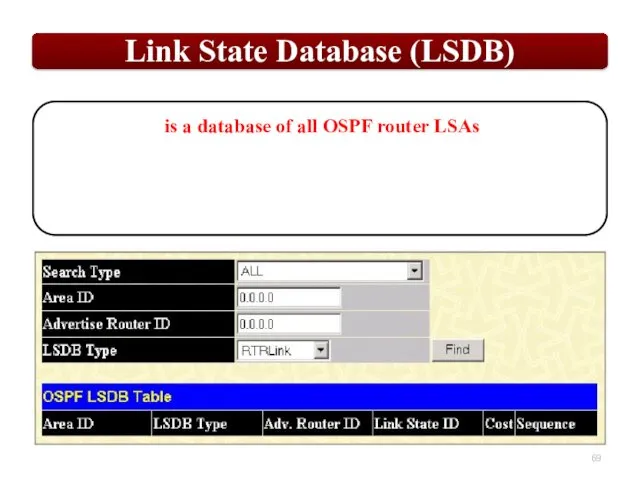
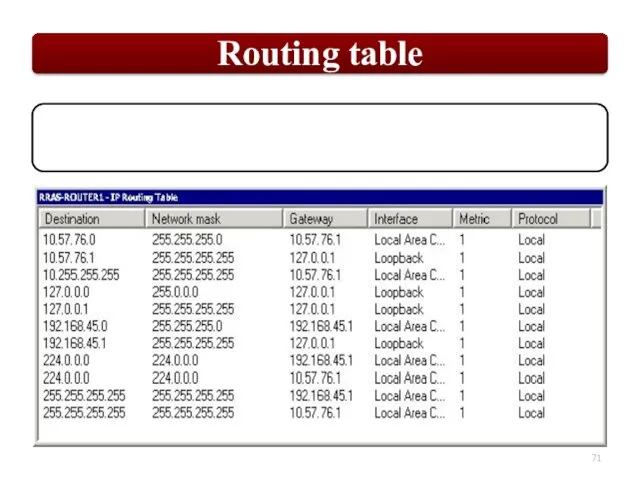
Each router maintains a database of all received LSAs (LSDB), which describes the network has a graph with weighted.
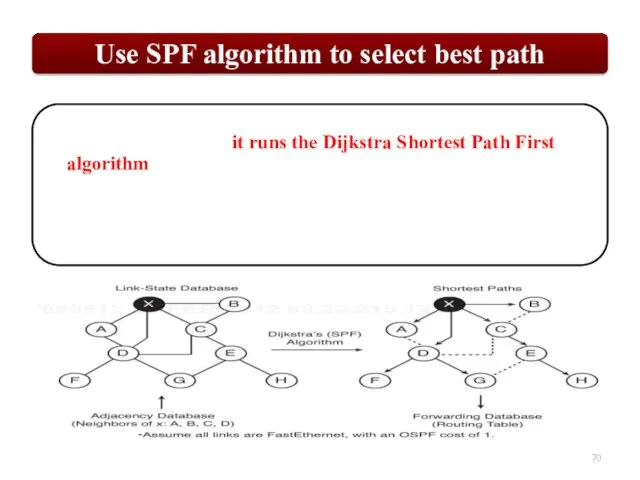
OSPF uses the Dijkstra Shortest Path First algorithm to determine the shortest path.
OSPF advertises |ˈadvətʌɪz| the status of directly connected links using Link-State Advertisements |ədˈvəːtɪzm(ə)nt| (LSAs).
OSPF sends updates (LSAs) when there is a change to one of its links, and will only send the change in the update. LSAs are additionally refreshed every 30 minutes.
OSPF traffic is multicast either to address 224.0.0.5 (all OSPF routers) or 224.0.0.6 (all Designated Routers).
Each router maintains a database of all received LSAs (LSDB), which describes the network has a graph with weighted.
OSPF uses the Dijkstra Shortest Path First algorithm to determine the shortest path.
Слайд 40
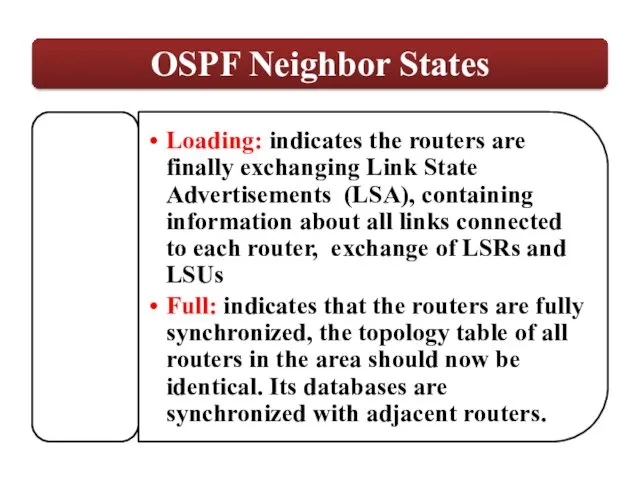
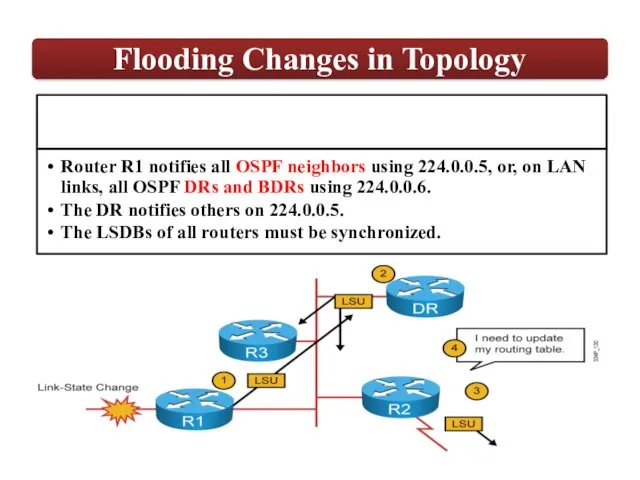
LSAs are flooded to other interfaces
Received
LSAs
Dijkstra’s
Algorithm
LSAs are flooded to other interfaces
Received
LSAs
Dijkstra’s
Algorithm
Слайд 41
Слайд 42
Слайд 43
Слайд 44
Слайд 45
Слайд 46
Слайд 47
How OSPF Packet Processes Work
How OSPF Packet Processes Work
Слайд 48
Слайд 49
Слайд 50
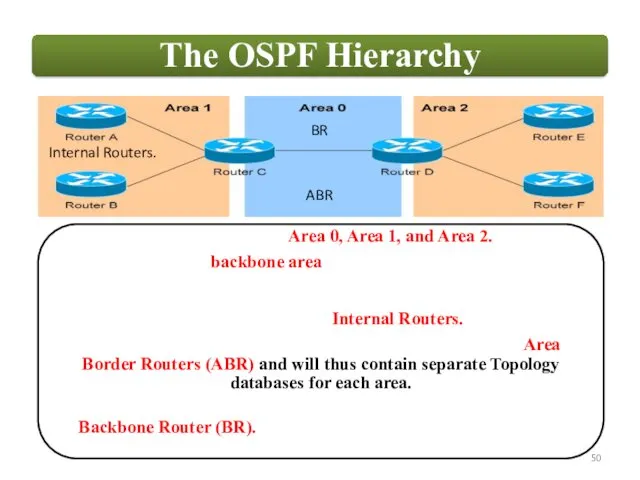
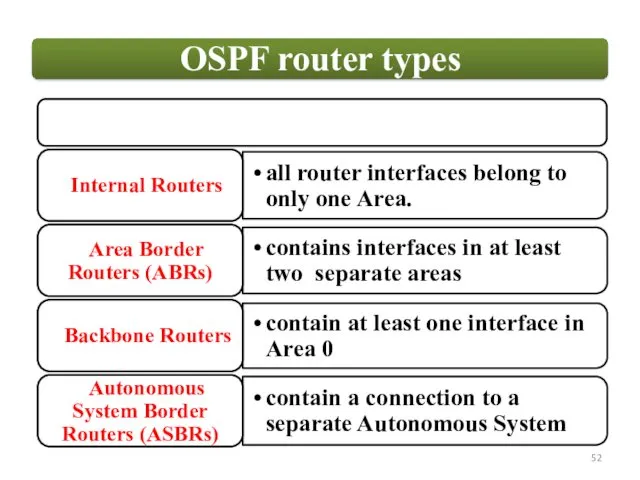
ABR
BR
Internal Routers.
ABR
BR
Internal Routers.
Слайд 51
Слайд 52
Слайд 53
Слайд 54
Слайд 55
Слайд 56
Слайд 57
Слайд 58
Слайд 59
Слайд 60
Слайд 61
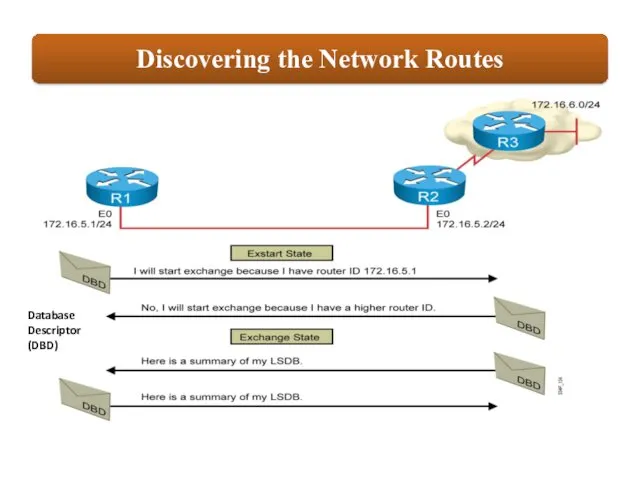
Database Descriptor
(DBD)
Database Descriptor
(DBD)
Слайд 62
Слайд 63
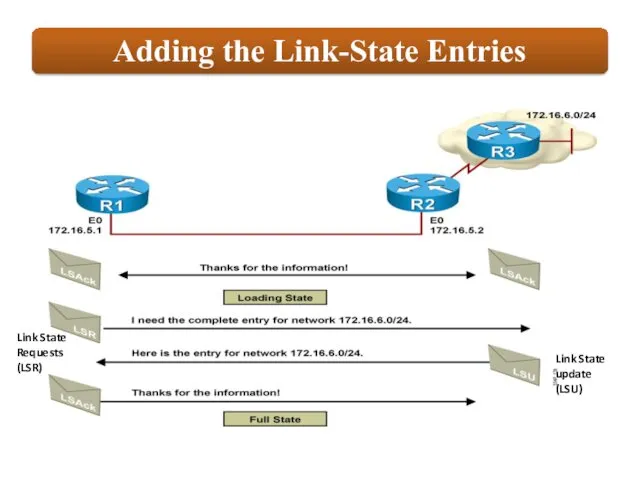
Link State update (LSU)
Link State Requests (LSR)
Link State update (LSU)
Link State Requests (LSR)
Слайд 64
Слайд 65
Слайд 66
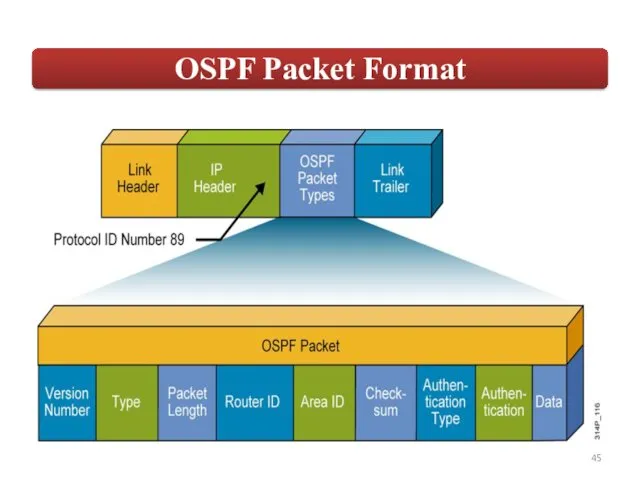
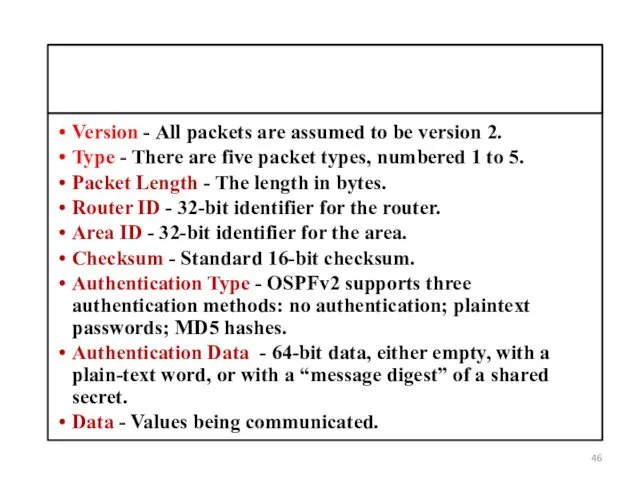
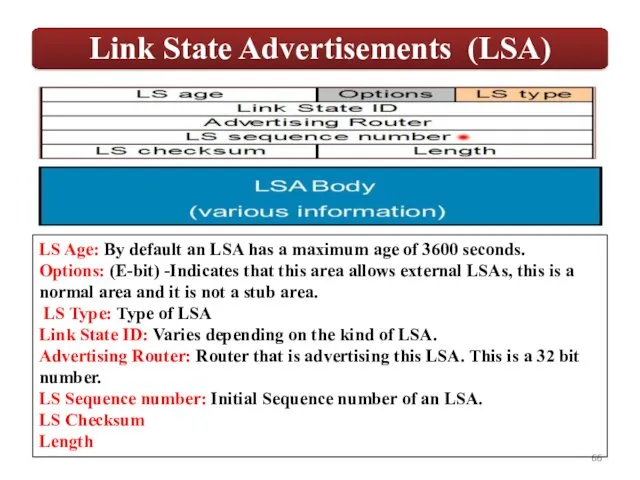
LS Age: By default an LSA has a maximum age of
LS Age: By default an LSA has a maximum age of
3600 seconds.
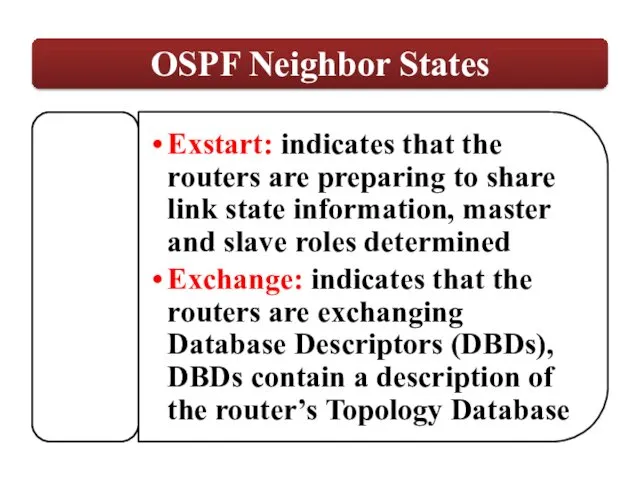
Options: (E-bit) -Indicates that this area allows external LSAs, this is a normal area and it is not a stub area.
LS Type: Type of LSA
Link State ID: Varies depending on the kind of LSA.
Advertising Router: Router that is advertising this LSA. This is a 32 bit number.
LS Sequence number: Initial Sequence number of an LSA.
LS Checksum
Length
Options: (E-bit) -Indicates that this area allows external LSAs, this is a normal area and it is not a stub area.
LS Type: Type of LSA
Link State ID: Varies depending on the kind of LSA.
Advertising Router: Router that is advertising this LSA. This is a 32 bit number.
LS Sequence number: Initial Sequence number of an LSA.
LS Checksum
Length
Слайд 67
Слайд 68
Слайд 69
Слайд 70
Слайд 71
Слайд 72













 Как создавать компьютерные игры?
Как создавать компьютерные игры? Персональный компьютер
Персональный компьютер Информационные технологии в государственном управлении. Тема 10
Информационные технологии в государственном управлении. Тема 10 От рисунка к анимации
От рисунка к анимации Understanding Databases
Understanding Databases Применение информационных технологий в преподавании русского языка и литературы
Применение информационных технологий в преподавании русского языка и литературы Личный кабинет отправителя
Личный кабинет отправителя Типичные ошибки работы в социальных сетях
Типичные ошибки работы в социальных сетях Знакомство с IDE
Знакомство с IDE Интерактивные тесты в Microsoft Office Excel
Интерактивные тесты в Microsoft Office Excel Создание таблиц SQL. Лекция 4
Создание таблиц SQL. Лекция 4 Занятие по познавательному развитию Волшебный песок
Занятие по познавательному развитию Волшебный песок Логические выражения и таблицы истинности. Логика
Логические выражения и таблицы истинности. Логика Обработка числовой информации
Обработка числовой информации Алгоритм работы с IPTV
Алгоритм работы с IPTV Спільна діяльність у мережі інтернет
Спільна діяльність у мережі інтернет Организация интернет-СМИ
Организация интернет-СМИ Разработка автоматизированной системы для центра управления паролями
Разработка автоматизированной системы для центра управления паролями Виды компьютерных вирусов. Антивирусные программы
Виды компьютерных вирусов. Антивирусные программы Методы программирования. Поиск в тексте. (Лекция 6)
Методы программирования. Поиск в тексте. (Лекция 6) Курс Програмування Kodu Game Lab
Курс Програмування Kodu Game Lab MS Word 2007
MS Word 2007 Электронная таблица EXCEL
Электронная таблица EXCEL Топ 5 самых удивительных достижений машинного обучения за 2018 год
Топ 5 самых удивительных достижений машинного обучения за 2018 год Основные правила и требования к созданию презентации
Основные правила и требования к созданию презентации Построение диаграмм и графиков в электронных таблицах
Построение диаграмм и графиков в электронных таблицах Электронная библиотечная система Лань
Электронная библиотечная система Лань Программирование. Оператор Mod в Visual Basic
Программирование. Оператор Mod в Visual Basic