Содержание
- 2. POSTGRESQL: UNION OPERATOR The UNION operator combines result sets of two or more SELECT statements into
- 3. THE FOLLOWING VENN DIAGRAM ILLUSTRATES HOW THE UNION WORKS:
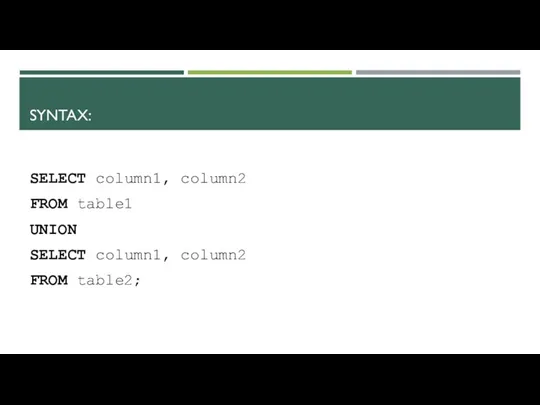
- 4. SYNTAX: SELECT column1, column2 FROM table1 UNION SELECT column1, column2 FROM table2;
- 5. POSTGRESQL: UNION ALL OPERATOR The UNION operator combines result sets of two or more SELECT statements
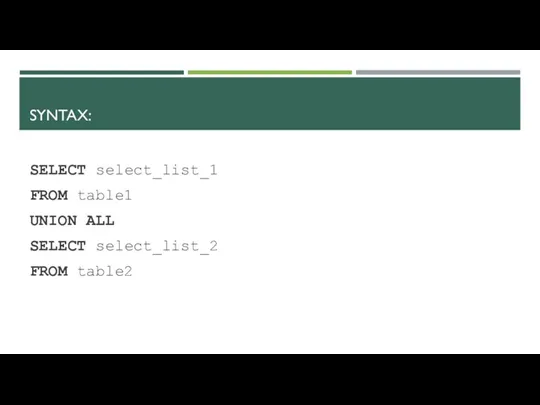
- 6. SYNTAX: SELECT select_list_1 FROM table1 UNION ALL SELECT select_list_2 FROM table2
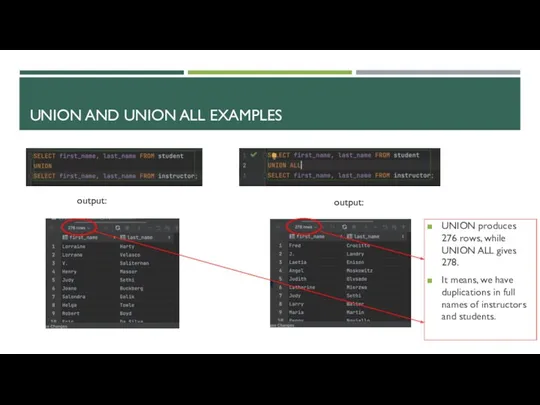
- 7. UNION AND UNION ALL EXAMPLES output: output: UNION produces 276 rows, while UNION ALL gives 278.
- 8. POSTGRESQL: INTERSECT OPERATOR Used to combine result set of two or more SELECT statement into a
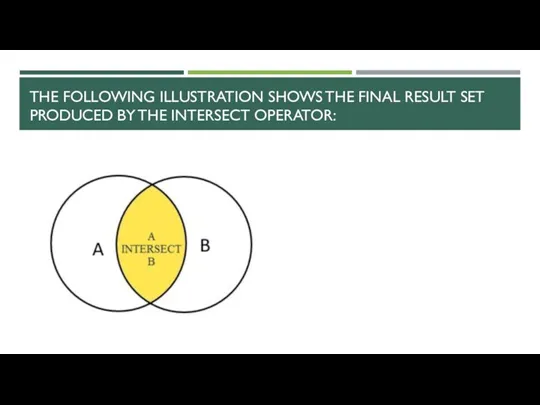
- 9. THE FOLLOWING ILLUSTRATION SHOWS THE FINAL RESULT SET PRODUCED BY THE INTERSECT OPERATOR:
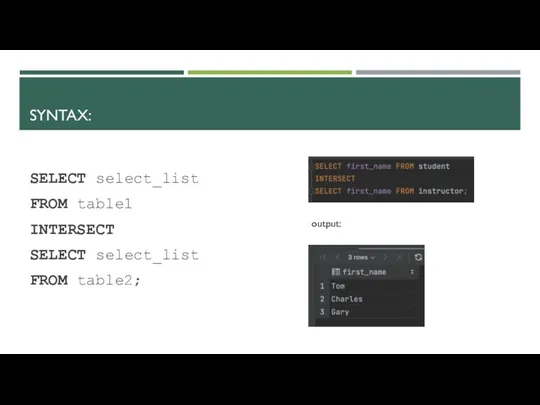
- 10. SYNTAX: SELECT select_list FROM table1 INTERSECT SELECT select_list FROM table2; output:
- 11. POSTGRESQL: EXCEPT OPERATOR Returns rows by comparing the result sets of two or more queries. Returns
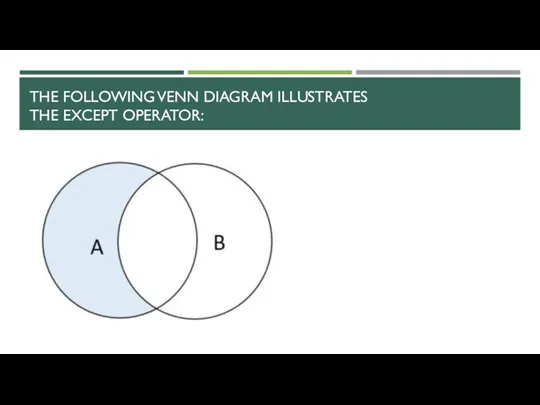
- 12. THE FOLLOWING VENN DIAGRAM ILLUSTRATES THE EXCEPT OPERATOR:
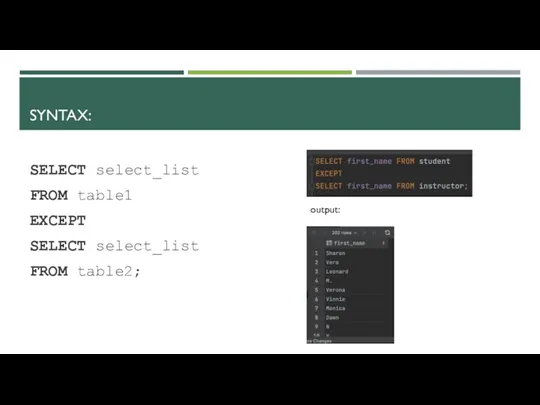
- 13. SYNTAX: SELECT select_list FROM table1 EXCEPT SELECT select_list FROM table2; output:
- 14. POSTGRESQL: GROUPING SETS A grouping set is a set of columns by which you group by
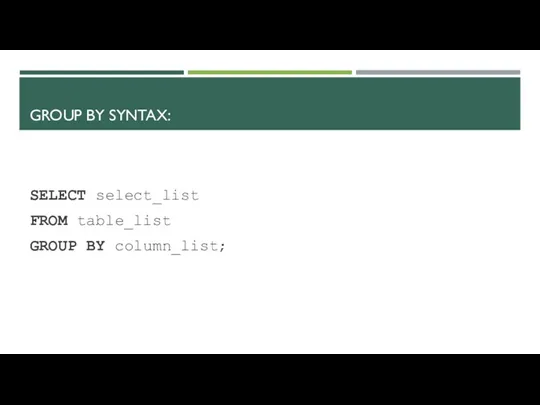
- 15. GROUP BY SYNTAX: SELECT select_list FROM table_list GROUP BY column_list;
- 16. POSTGRESQL GROUPING SETS PostgreSQL provides the GROUPING SETS clause which is the subclause of the GROUP
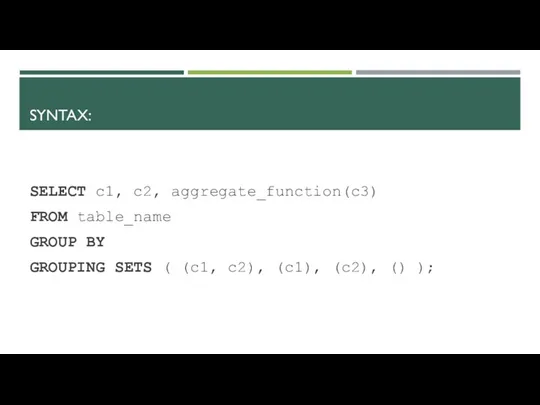
- 17. SYNTAX: SELECT c1, c2, aggregate_function(c3) FROM table_name GROUP BY GROUPING SETS ( (c1, c2), (c1), (c2),
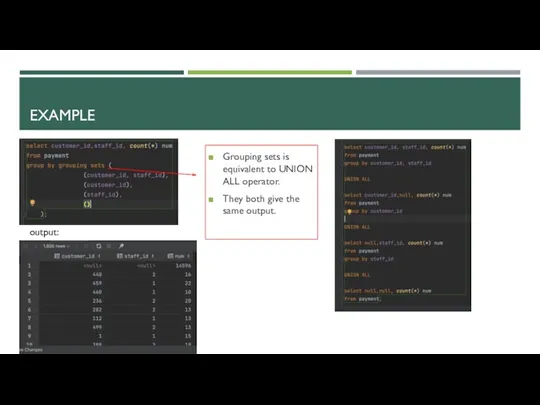
- 18. EXAMPLE output: Grouping sets is equivalent to UNION ALL operator. They both give the same output.
- 19. POSTGRESQL GROUPING SETS: CUBE. Grouping operations are possible with the concept of grouping sets. PostgreSQL CUBE
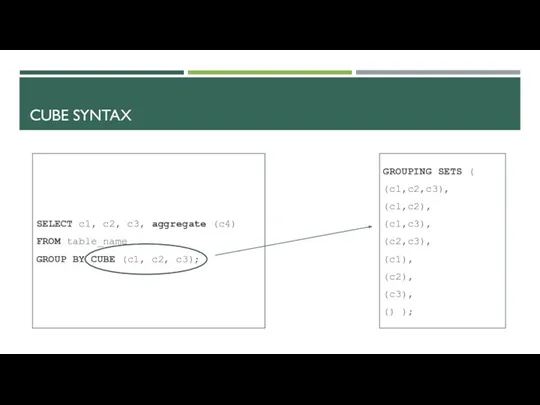
- 20. CUBE SYNTAX GROUPING SETS ( (c1,c2,c3), (c1,c2), (c1,c3), (c2,c3), (c1), (c2), (c3), () ); SELECT c1,
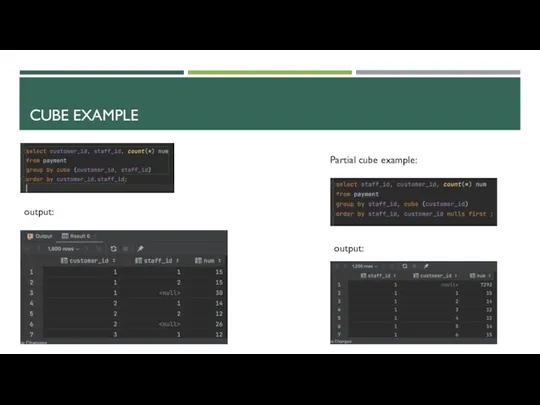
- 21. CUBE EXAMPLE output: output: Partial cube example:
- 22. POSTGRESQL GROUPING SETS: ROLLUP. PostgreSQL ROLLUP is a subclause of the GROUP BY clause. Different from
- 23. CUBE VS ROLLUP CUBE sets: (c1, c2, c3) (c1, c2) (c2, c3) (c1,c3) (c1) (c2) (c3)
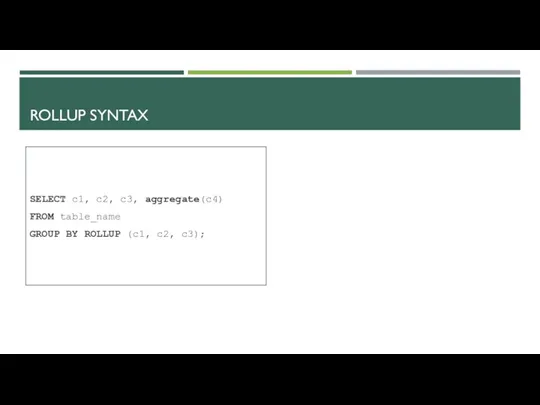
- 24. ROLLUP SYNTAX SELECT c1, c2, c3, aggregate(c4) FROM table_name GROUP BY ROLLUP (c1, c2, c3);
- 26. Скачать презентацию










 Bootstrap. Самые современные технологии CSS и HTML
Bootstrap. Самые современные технологии CSS и HTML Кодирование графической информации
Кодирование графической информации Самодельный робот-манипулятор с дистанционным управлением
Самодельный робот-манипулятор с дистанционным управлением Integrivideo. Automation framework
Integrivideo. Automation framework Android 6 Работа с базой данных SQLite
Android 6 Работа с базой данных SQLite Безпека в інтернеті
Безпека в інтернеті Элективный курсМатематика и компьютер. Mathcad: помощь в вычислениях
Элективный курсМатематика и компьютер. Mathcad: помощь в вычислениях Технические средства телекоммуникационных технологий
Технические средства телекоммуникационных технологий Программирование мобильных приложений. Сенсоры. Кубик
Программирование мобильных приложений. Сенсоры. Кубик OWASP – Web Spam Techniques
OWASP – Web Spam Techniques Системы счисления, или как считает компьютер
Системы счисления, или как считает компьютер Прототип мобильного приложения для обучения правильной технике свинга при помощи AI
Прототип мобильного приложения для обучения правильной технике свинга при помощи AI Школа развития Академия успеха
Школа развития Академия успеха Drugs. Online store
Drugs. Online store Использование программы ZOOM. Исламская онлайн-школа
Использование программы ZOOM. Исламская онлайн-школа Система управления цифровыми активами промышленного предприятия для обеспечения процесса технического обслуживания
Система управления цифровыми активами промышленного предприятия для обеспечения процесса технического обслуживания Разработка урока информатики Векторная графика
Разработка урока информатики Векторная графика Как пройти анкетирование в рамках НОКУООД ОО (пошаговая инструкция)
Как пройти анкетирование в рамках НОКУООД ОО (пошаговая инструкция) MS Access. Основные элементы главного окна Access
MS Access. Основные элементы главного окна Access СУБД. Microsoft Access
СУБД. Microsoft Access Установка операционной системы на ПК, серверах, а также правила настройки интерфейса пользователя
Установка операционной системы на ПК, серверах, а также правила настройки интерфейса пользователя Программирование циклов в Паскале
Программирование циклов в Паскале IP-адресация
IP-адресация Кодирование как изменение формы представления информации
Кодирование как изменение формы представления информации Интеграция информационной системы DPD
Интеграция информационной системы DPD Групповая сплоченность и конформное поведение
Групповая сплоченность и конформное поведение нформационные ресурсы общества Информационные услуги и продукты
нформационные ресурсы общества Информационные услуги и продукты Бағдарламалардың графикалық интерфейсін жасау технологиялары
Бағдарламалардың графикалық интерфейсін жасау технологиялары