Содержание
- 2. An equation that includes at least one derivative of a function is called a differential equation.
- 3. Differential equations are classified according to: type linearity homogenity
- 4. Differential equations according to their type can be ordinary or partial. Ordinary Differential Equation It is
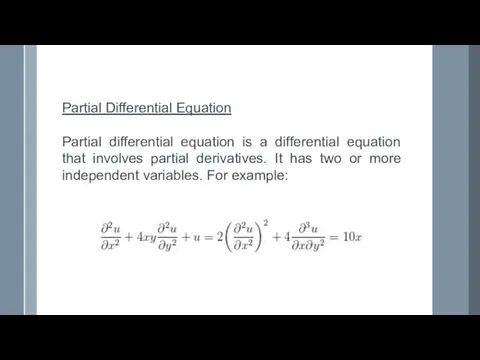
- 5. Partial Differential Equation Partial differential equation is a differential equation that involves partial derivatives. It has
- 6. Linear Differential Equation It is first degree with respect to the dependent variable(s) and its derivatives
- 7. Non-Linear Differential Equation It is second degree or higher with respect to dependent variables and its
- 8. Homogeneous Differential Equation It is first order differential equation which can be written as where, f
- 9. Non-Homogeneous Differential Equation It is a differential equation whose right-hand side is not equal to zero.
- 11. Скачать презентацию







 Средняя линия треугольника
Средняя линия треугольника Тригонометрия в ладони
Тригонометрия в ладони Задание плоскости на чертеже. Точка и прямая в плоскости. Положение плоскости в пространстве. Главные линии плоскости
Задание плоскости на чертеже. Точка и прямая в плоскости. Положение плоскости в пространстве. Главные линии плоскости Обратная пропорциональность. График функции
Обратная пропорциональность. График функции Натуральные числа. 7 класс
Натуральные числа. 7 класс Окружность, вписанная в правильный многоугольник
Окружность, вписанная в правильный многоугольник Уравнения. 5 класс
Уравнения. 5 класс Делим отрезки на равные части с помощью циркуля и линейки
Делим отрезки на равные части с помощью циркуля и линейки Презентация Секреты таблицы умножения
Презентация Секреты таблицы умножения Угол между векторами. Скалярное произведение векторов
Угол между векторами. Скалярное произведение векторов Нод и НОК и их практическое применение при решении текстовых задач в 5 классе
Нод и НОК и их практическое применение при решении текстовых задач в 5 классе Преобразование суммы тригонометрических функций в произведение и произведение в сумму
Преобразование суммы тригонометрических функций в произведение и произведение в сумму Математические задачки
Математические задачки Модуль Алгебра №12
Модуль Алгебра №12 Математика Тема: Маша и Медведь учатся считать
Математика Тема: Маша и Медведь учатся считать Урок повторения курса геометрии 7-9
Урок повторения курса геометрии 7-9 Столбчатые и круговые диаграммы
Столбчатые и круговые диаграммы Сумма углов треугольника. Тренировочные упражнения
Сумма углов треугольника. Тренировочные упражнения Прямоугольный параллелепипед
Прямоугольный параллелепипед Основное свойство дроби
Основное свойство дроби Координатная плоскость. Урок 17
Координатная плоскость. Урок 17 Измерение отрезков
Измерение отрезков Сравнение, сложение и вычитание дробей с разными знаменателями и смешанных чисел
Сравнение, сложение и вычитание дробей с разными знаменателями и смешанных чисел Ромашка.Презентация. Устный счёт.
Ромашка.Презентация. Устный счёт. Решето Эратосфена
Решето Эратосфена Понятие о доказательной медицине. Случайное событие. Определение вероятности. Лекция 2
Понятие о доказательной медицине. Случайное событие. Определение вероятности. Лекция 2 Задачи на нахождение значений параметра
Задачи на нахождение значений параметра Деление многозначных круглых чисел
Деление многозначных круглых чисел