Содержание
- 2. Cryptology is a branch of mathematics that studies the mathematical foundations of cryptographic methods.
- 3. Cryptography periods: 1. The first period (from about the 3rd millennium BC) is characterized by the
- 4. CEPHAR CAESAR (shift code, Caesar's shift) An example of a Caesar cipher (encryption using the key
- 5. An example of encryption using the key K = 3 in the Russian alphabet. Source Alphabet:
- 6. 2. The second period (chronological framework - from the 9th century in the Middle East (Al-Kindi)
- 7. For example, in the process of encryption, the Vigenère table is used, which is structured as
- 8. 3. The third period (from the beginning to the middle of the 20th century) is characterized
- 9. For example, the German Enigma machine was used to encrypt classified information during World War II.
- 10. Wehrmacht Enigma Cryptographic machine of the Third Reich. The code created using Enigma is considered one
- 11. 4. The fourth period - from the middle to the 70s of the XX century -
- 12. 5. The modern period of cryptography development (from the end of the 1970s to the present)
- 13. Cryptanalysis is the science of how to open an encrypted message, that is, how to extract
- 14. Interrelation of Algebra and Critology
- 15. Def. 1. Encryption is the reversible conversion of plaintext to ciphertext. It is defined by two
- 16. Def. 2. The role of the key k in the permutation cipher is played by an
- 17. Def. 3. The role of the key k in the replacement cipher is played by an
- 18. Example. 1. If you believe the story, then the first permutation cipher was used in Sparta.
- 19. Example 2. The first replacement code was invented by Julius Caesar. As a permutation of the
- 20. Example 3. The class of permutation ciphers includes route permutation ciphers. They have such an idea.
- 21. CHANGE WITH REPLACEMENT OF LETTERS TO NUMBERS for example :«LIFE» - «12 9 6 5»
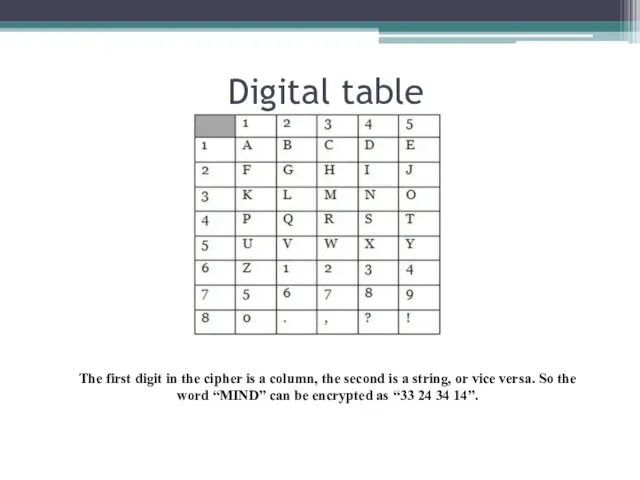
- 22. Digital table The first digit in the cipher is a column, the second is a string,
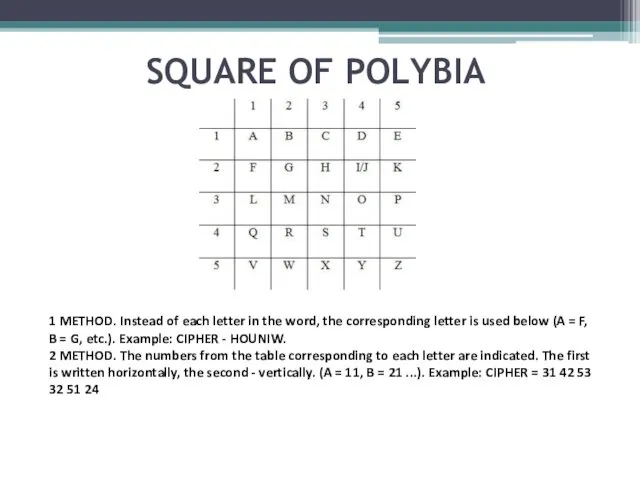
- 23. SQUARE OF POLYBIA 1 METHOD. Instead of each letter in the word, the corresponding letter is
- 24. Color chart The first color in the cipher is a row, the second is a column
- 25. Source text: The purpose of studying this topic is to familiarize students with the theory of
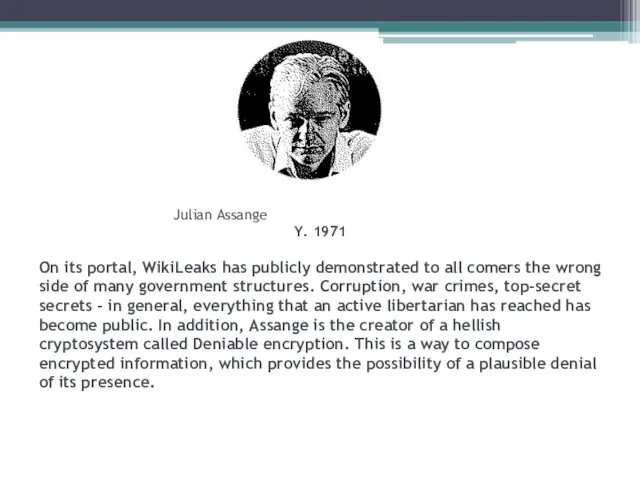
- 26. Julian Assange Y. 1971 On its portal, WikiLeaks has publicly demonstrated to all comers the wrong
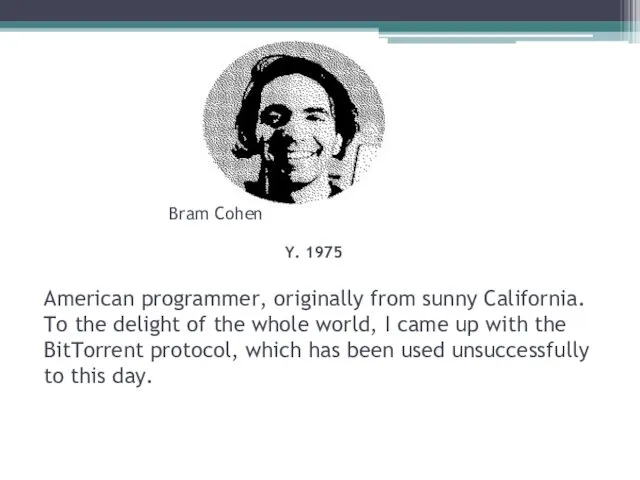
- 27. Bram Cohen Y. 1975 American programmer, originally from sunny California. To the delight of the whole
- 28. Фильмы Zodiac 2007 Y. The intense thriller of David Fincher, built on real events. For most
- 30. Скачать презентацию























 Частинні похідні вищих порядків. Змішані похідні. Теорема Шварца. Повний приріст і повний диференціал функції кількох змінних
Частинні похідні вищих порядків. Змішані похідні. Теорема Шварца. Повний приріст і повний диференціал функції кількох змінних Геометричні перетворення
Геометричні перетворення Планируемые результаты по математике в 1 классе по разделу Числа и величины
Планируемые результаты по математике в 1 классе по разделу Числа и величины Квадрат и куб (1 класс)
Квадрат и куб (1 класс) Призма, пирамида. Понятие и чертёж
Призма, пирамида. Понятие и чертёж Урок по математике Деление круглых чисел. 2 класс. Школа 2000... (автор учебника Л.Г. Петерсон)
Урок по математике Деление круглых чисел. 2 класс. Школа 2000... (автор учебника Л.Г. Петерсон) Мир чисел
Мир чисел Зачем нужны отрицательные числа? Примеры применения отрицательных чисел
Зачем нужны отрицательные числа? Примеры применения отрицательных чисел Презентация к уроку математики по теме: Таблица единиц времени
Презентация к уроку математики по теме: Таблица единиц времени Олимпиада по математике для 4класса
Олимпиада по математике для 4класса Отношения и пропорции
Отношения и пропорции Введение в теорию графов. Способы представления ориентированных и неориентированных графов
Введение в теорию графов. Способы представления ориентированных и неориентированных графов Математика - бизнесмен. Игра. 9 -11 классы
Математика - бизнесмен. Игра. 9 -11 классы Електронний альбом дидактичних матеріалів. Аналітична геометрія у просторі. (Частина 2)
Електронний альбом дидактичних матеріалів. Аналітична геометрія у просторі. (Частина 2) Применение математических методов в биологии и в медицине
Применение математических методов в биологии и в медицине Математический диктант. Уравнение окружности
Математический диктант. Уравнение окружности АА-деревья. Операции для работы с АА-деревом и алгоритмы их реализации
АА-деревья. Операции для работы с АА-деревом и алгоритмы их реализации Путешествие в мир геометрии. 5 класс
Путешествие в мир геометрии. 5 класс Подготовка к ЕГЭ. Задание 1. Задачи на вычисление
Подготовка к ЕГЭ. Задание 1. Задачи на вычисление Общие вопросы изучения нумерации
Общие вопросы изучения нумерации Корреляциялык анализ
Корреляциялык анализ Сложение и вычитание смешанных чисел
Сложение и вычитание смешанных чисел Великая Отечественная война
Великая Отечественная война Как правильно писать цифры
Как правильно писать цифры Умножение многозначных чисел на трёхзначное. Закрепление. 4 класс
Умножение многозначных чисел на трёхзначное. Закрепление. 4 класс Арифметические действия над числами.
Арифметические действия над числами. Урок математики по системе Л.В. Занкова 1 класс по теме Счёт,сравнение предметов Автор Смородинова Елена Эдуардовна МОУ гимназия №1 город Комсомольск- на - Амуре Хабаровский край
Урок математики по системе Л.В. Занкова 1 класс по теме Счёт,сравнение предметов Автор Смородинова Елена Эдуардовна МОУ гимназия №1 город Комсомольск- на - Амуре Хабаровский край Сложение и вычитание десятичных дробей. Урок 111
Сложение и вычитание десятичных дробей. Урок 111