Содержание
- 2. What are Vectors? Vectors are pairs of a direction and a magnitude. We usually represent a
- 3. Vectors in Rn (R1-space can be represented geometrically by the x-axis) (R2-space can be represented geometrically
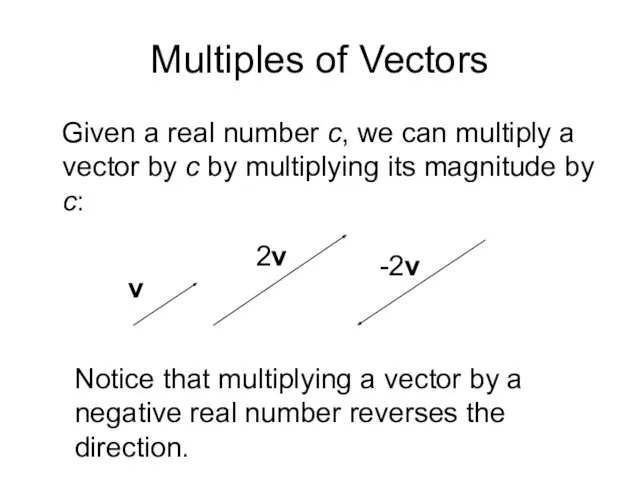
- 4. Multiples of Vectors Given a real number c, we can multiply a vector by c by
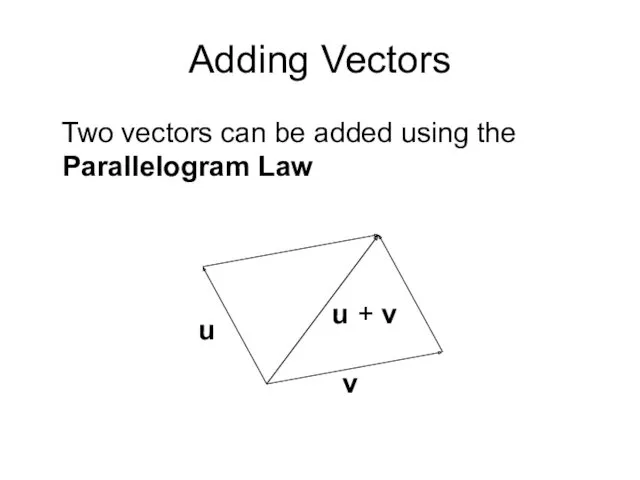
- 5. Adding Vectors Two vectors can be added using the Parallelogram Law u v u + v
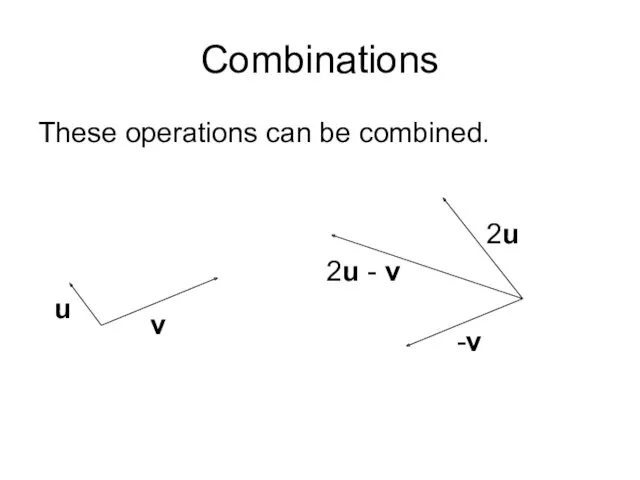
- 6. Combinations These operations can be combined. u v 2u -v 2u - v
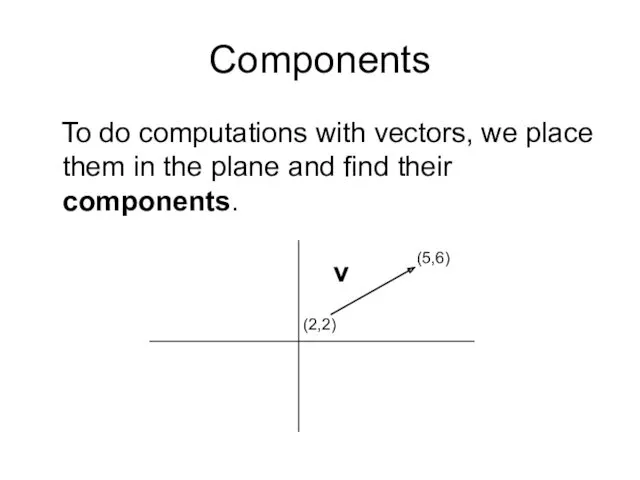
- 7. Components To do computations with vectors, we place them in the plane and find their components.
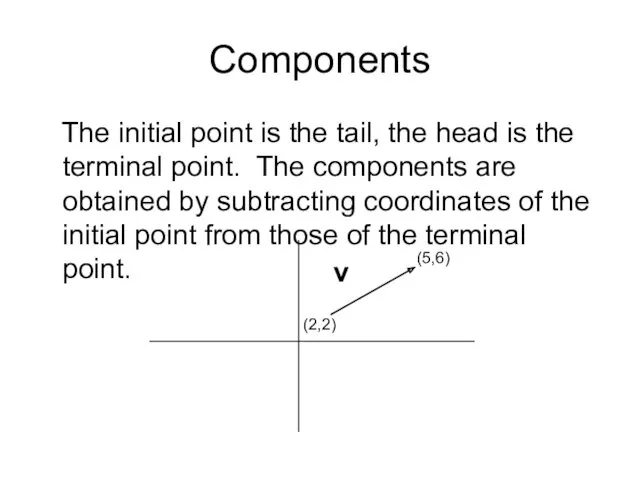
- 8. Components The initial point is the tail, the head is the terminal point. The components are
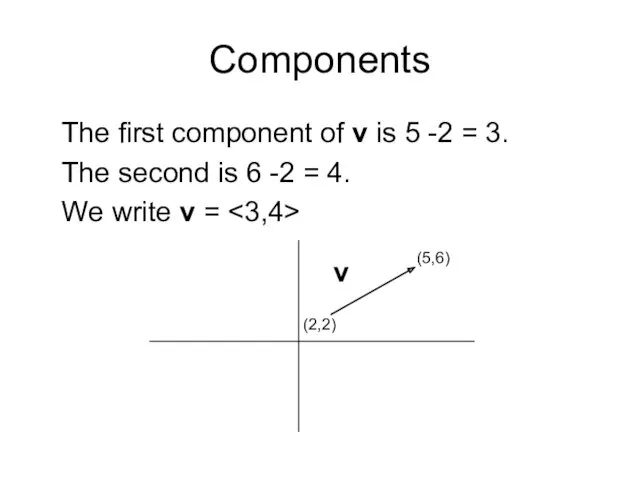
- 9. Components The first component of v is 5 -2 = 3. The second is 6 -2
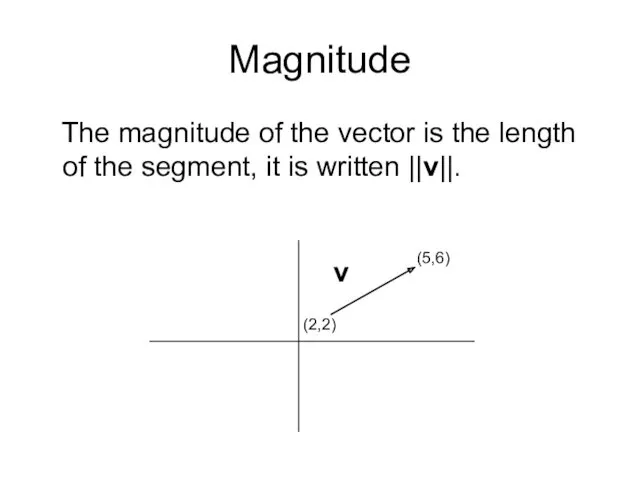
- 10. Magnitude The magnitude of the vector is the length of the segment, it is written ||v||.
- 11. Scalar Multiplication Once we have a vector in component form, the arithmetic operations are easy. To
- 12. Addition To add vectors, simply add their components. For example, if v = and w =
- 13. Unit Vectors A unit vector is a vector with magnitude 1. Given a vector v, we
- 14. Special Unit Vectors A vector such as can be written as 3 + 4 . For
- 17. Spanning Sets and Linear Independence Linear combination :
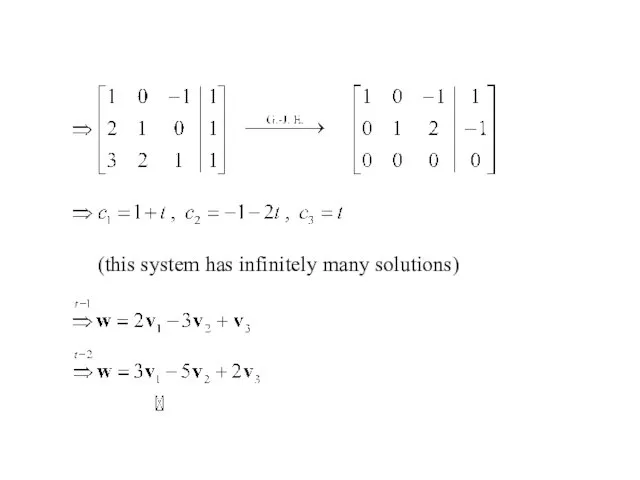
- 18. Ex : Finding a linear combination Sol:
- 21. If S={v1, v2,…, vk} is a set of vectors in a vector space V, then the
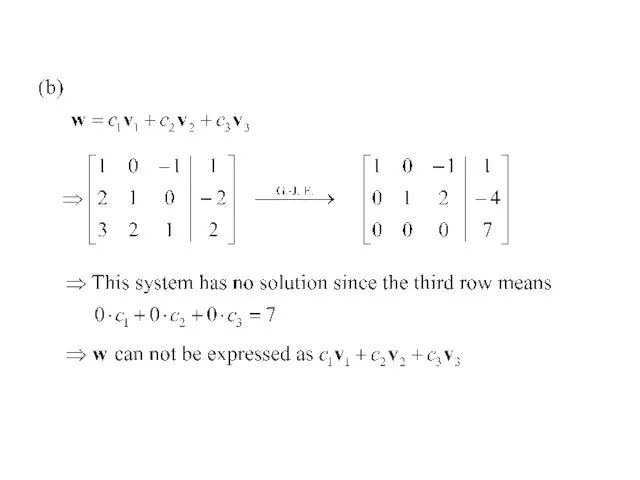
- 22. Note: The above statement can be expressed as follows Ex 4:
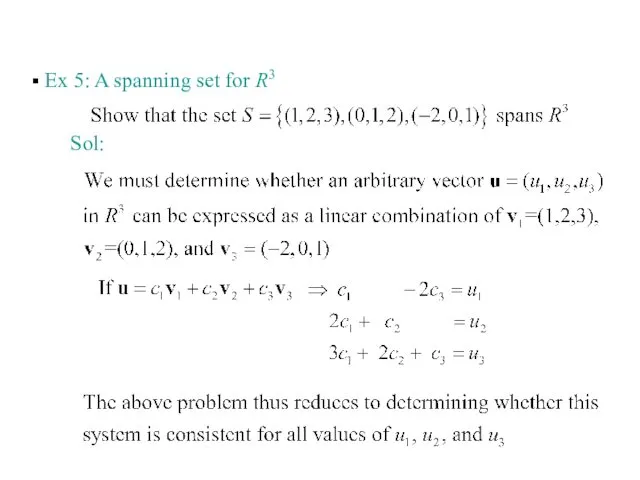
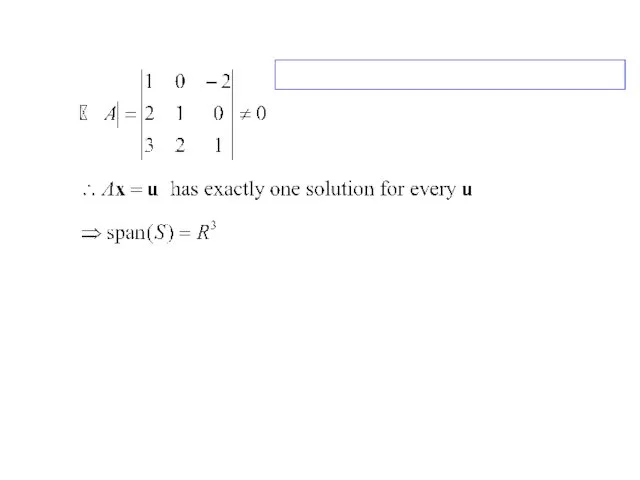
- 23. Ex 5: A spanning set for R3 Sol:
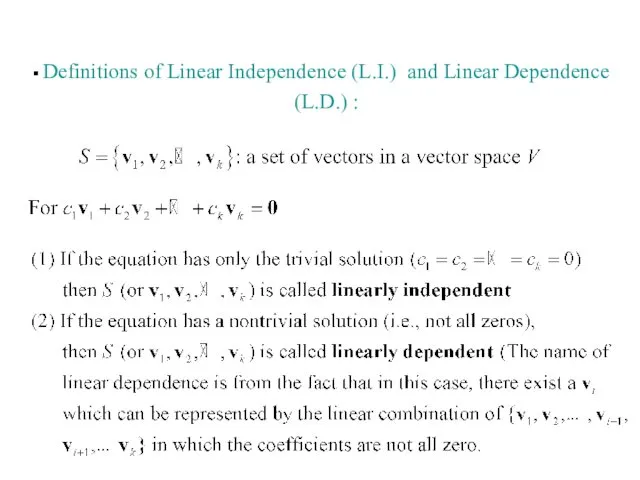
- 25. Definitions of Linear Independence (L.I.) and Linear Dependence (L.D.) :
- 26. Ex : Testing for linear independence Sol: Determine whether the following set of vectors in R3
- 27. EX: Testing for linear independence Determine whether the following set of vectors in P2 is L.I.
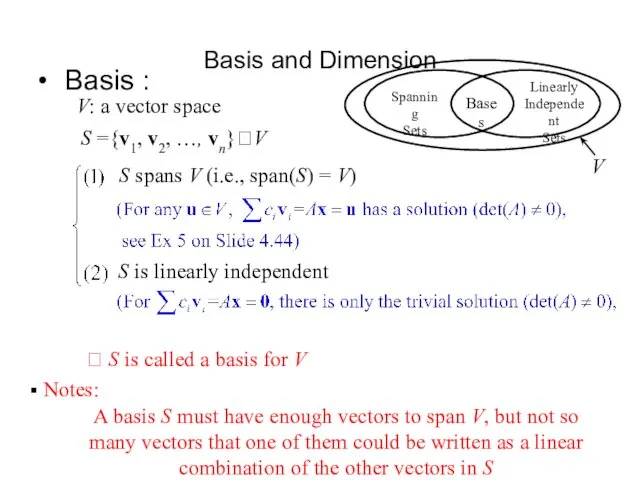
- 28. Basis and Dimension Basis : V: a vector space S spans V (i.e., span(S) = V)
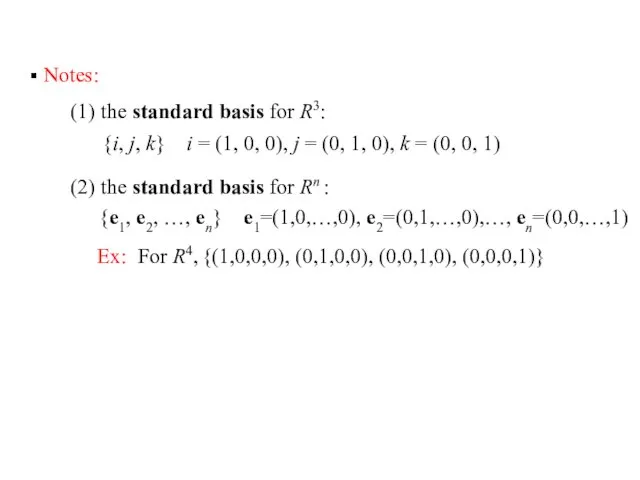
- 29. Notes: (1) the standard basis for R3: {i, j, k} i = (1, 0, 0), j
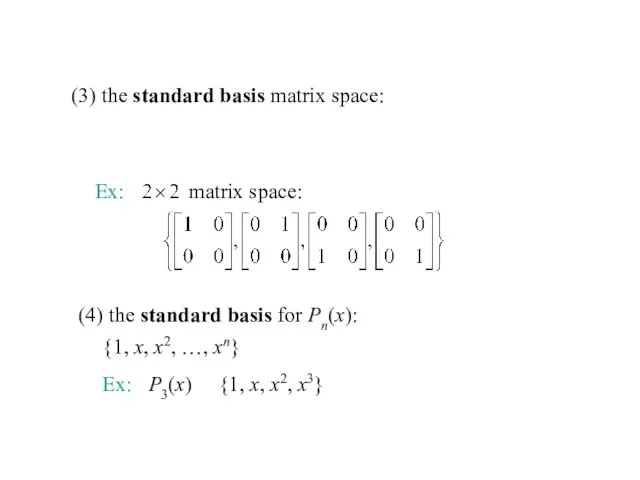
- 30. Ex: matrix space: (3) the standard basis matrix space:
- 32. Скачать презентацию












 Умножение целых чисел
Умножение целых чисел Замечательные кривые в математике
Замечательные кривые в математике Використання формул скороченого множення для розкладання многочлена на множники
Використання формул скороченого множення для розкладання многочлена на множники Познавательные математические цепочки
Познавательные математические цепочки Формулы разности и суммы кубов
Формулы разности и суммы кубов Решение задач на применение аксиом стереометрии и их следствий
Решение задач на применение аксиом стереометрии и их следствий Ряды динамики
Ряды динамики Ремонт кабинета с использованием математических формул
Ремонт кабинета с использованием математических формул Приближение десятичных дробей
Приближение десятичных дробей Старинные задачи по элементарной математике (Россия)
Старинные задачи по элементарной математике (Россия) Математическое описание линейных САУ. Дифференциальные уравнения, передаточная функция. Временные и частотные характеристики
Математическое описание линейных САУ. Дифференциальные уравнения, передаточная функция. Временные и частотные характеристики Свойства параллельных плоскостей
Свойства параллельных плоскостей В гости к царице Математике
В гости к царице Математике Математика. 1 класс. Урок 36. Числа 1-6 - Презентация
Математика. 1 класс. Урок 36. Числа 1-6 - Презентация Этапы расчета прогнозных значений методом прогнозной экспраполяции
Этапы расчета прогнозных значений методом прогнозной экспраполяции Как найти неизвестное вычитаемое
Как найти неизвестное вычитаемое Создание проблемных ситуаций через умышленно допущенные учителем ошибки
Создание проблемных ситуаций через умышленно допущенные учителем ошибки Основы теории вероятностей
Основы теории вероятностей Неопределённый интеграл, его свойства . Непосредственное интегрирование. Метод замены переменной в неопределенном интеграле
Неопределённый интеграл, его свойства . Непосредственное интегрирование. Метод замены переменной в неопределенном интеграле Замечательные пределы
Замечательные пределы Образование чисел из одного десятка и нескольких единиц
Образование чисел из одного десятка и нескольких единиц Численные методы оптимизации
Численные методы оптимизации Углы. Виды углов
Углы. Виды углов Таблица умножения достойна уважения.
Таблица умножения достойна уважения. Тела вращения
Тела вращения Екі түзудің ара қашықтығы
Екі түзудің ара қашықтығы Сложение и вычитание дробей с одинаковыми знаменателями
Сложение и вычитание дробей с одинаковыми знаменателями урок математики в 1 классе Числа 1 – 10 . Закрепление
урок математики в 1 классе Числа 1 – 10 . Закрепление