Содержание
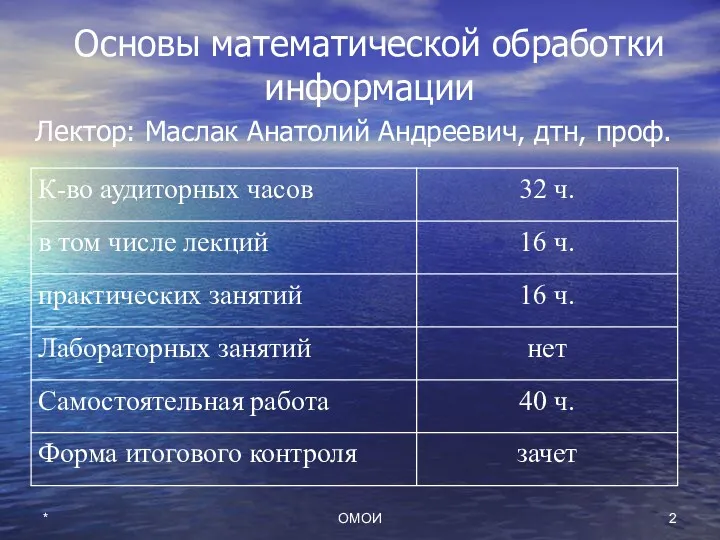
- 2. ОМОИ * Основы математической обработки информации Лектор: Маслак Анатолий Андреевич, дтн, проф.
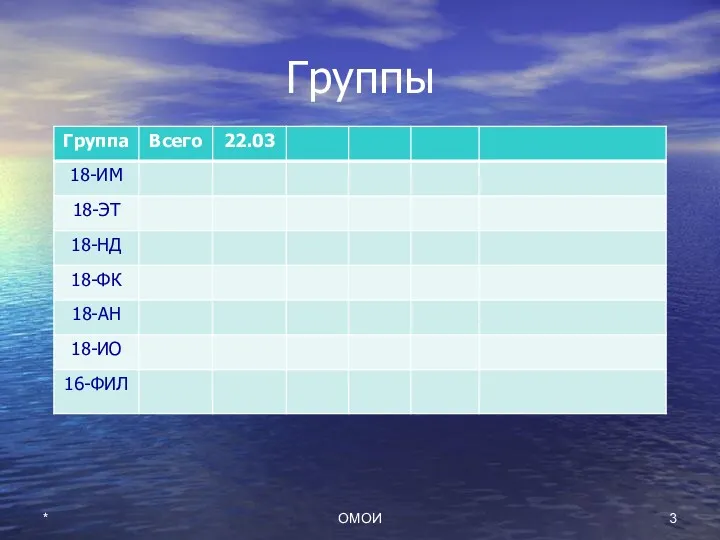
- 3. Группы * ОМОИ
- 4. * Роль математики Математические методы обработки информации давно уже востребованы не только в математических и естественнонаучных,
- 5. Взаимосвязь образования и науки? * ОМОИ
- 6. ОМОИ * Основные функции науки 1. Описание явлений и процессов (выявление значимых факторов) 2. Прогноз (выявление
- 7. * ОМОИ Роль математической статистики в прикладных и научных исследованиях В древности было три источника информации:
- 8. ОМОИ * Актуальность изучения статистических методов «Мы живем в вероятностном мире» «Жизнь – это школа вероятности»
- 9. * ОМОИ Роль математической статистики в прикладных и научных исследованиях Наличие ошибки – принципиально существенный компонент
- 10. * ОМОИ Разделы математической статистики 1. Описательная статистика 2. Теория статистического вывода 3. Планирование и анализ
- 11. Today's world is changing by the minute. So teachers have to prepare students for a world
- 12. Dimensions of innovation/change: new materials: e.g. computers, educational software, open source materials, etc., new teaching approaches:
- 13. Change is process, not an event! Not reasonable to expect schools and teachers to change at
- 14. In general, early questions are more self-oriented: What is it? And how will it affect me?
- 15. Did you know? The projected top ten in demand jobs in 2010 did not exist in
- 16. Lifelong learning skills: In new circumstances, people being able to generate and evaluate answers to open,
- 17. Demands Solve unforeseen problems Learning new things at work Able to choose or change methods at
- 18. ’21st Century’ skills I. Ways of thinking Creativity and Innovation Critical Thinking, Problem Solving, Decision Making
- 19. ’21st Century’ skills III. Tools for working 6. Information Literacy (includes research) 7. ICT Literacy IV.
- 20. ’21st Century’ skills Each skill elaborated in three categories: Knowledge: references to specific knowledge or understanding
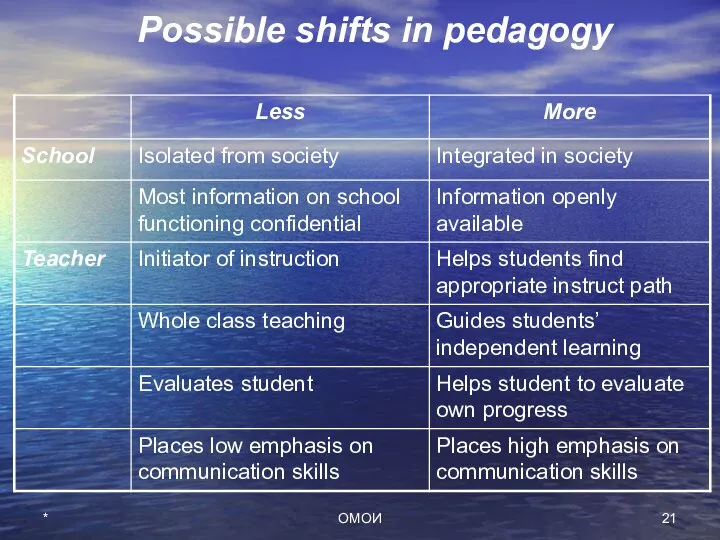
- 21. Possible shifts in pedagogy * ОМОИ
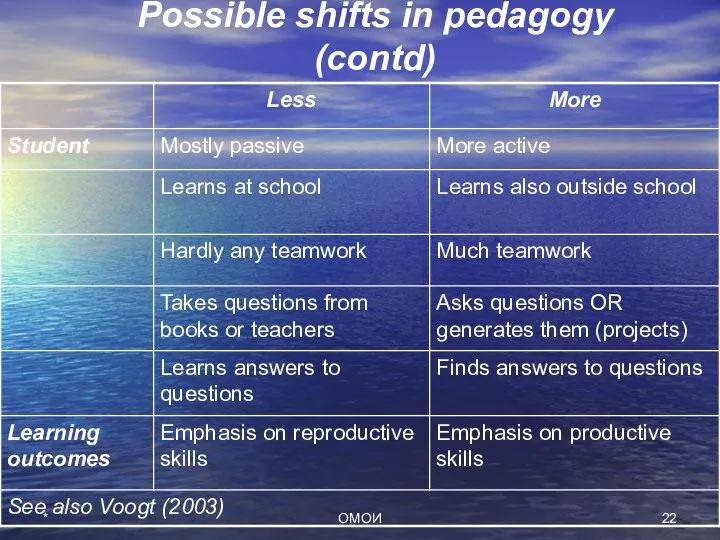
- 22. Possible shifts in pedagogy (contd) * ОМОИ
- 23. * ОМОИ
- 25. Скачать презентацию


















 Pravilnye_Mnogogranniki
Pravilnye_Mnogogranniki Дифференциальные уравнении (1)
Дифференциальные уравнении (1) презентация к уроку математики по теме Решение задач способом уравнения 4 класс Гармония
презентация к уроку математики по теме Решение задач способом уравнения 4 класс Гармония Сложение и вычитание обыкновенных дробей
Сложение и вычитание обыкновенных дробей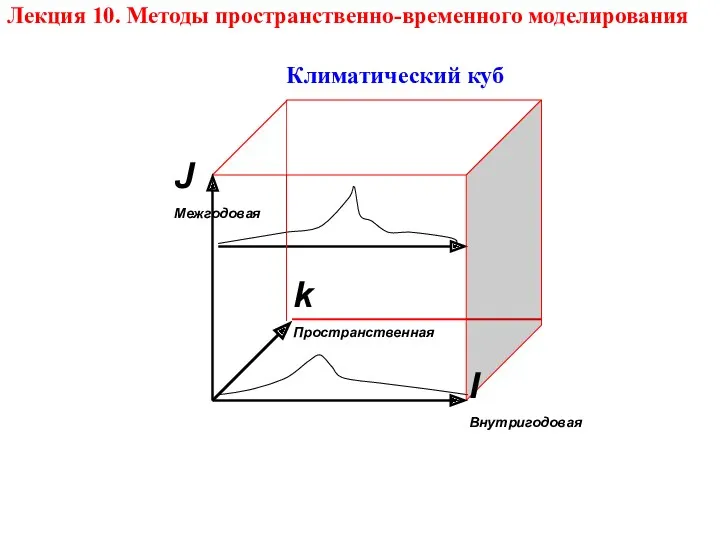 Методы пространственно-временного моделирования. Климатический куб. Лекция 10
Методы пространственно-временного моделирования. Климатический куб. Лекция 10 Методика ознакомления с долями и дробями
Методика ознакомления с долями и дробями Непараметрические критерии
Непараметрические критерии Функция. Область определения и область значений функции
Функция. Область определения и область значений функции Трапеция. 6 класс
Трапеция. 6 класс Графики функций y=ax2+n и y=a(x-m)2
Графики функций y=ax2+n и y=a(x-m)2 Занимательная математика для детей (устный счёт + учимся писать цифры)
Занимательная математика для детей (устный счёт + учимся писать цифры)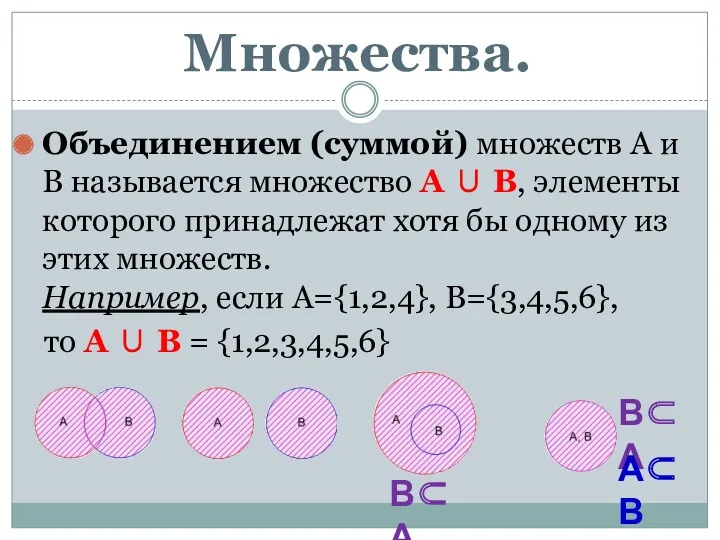 Множества. Комбинаторика
Множества. Комбинаторика Индексы. Группы индексов
Индексы. Группы индексов Моделирование в электронных таблицах. График и свойства квадратичной функции
Моделирование в электронных таблицах. График и свойства квадратичной функции Преподавание элементов теории вероятности и статистики в 5-9 классах. Система подготовки учащихся к итоговой аттестации
Преподавание элементов теории вероятности и статистики в 5-9 классах. Система подготовки учащихся к итоговой аттестации Линейные операторы
Линейные операторы Случайные процессы (лекция 15). Параметрические модели временных рядов. Сглаживание и фильтрация
Случайные процессы (лекция 15). Параметрические модели временных рядов. Сглаживание и фильтрация Похідна. Фізичний і геометричний зміст похідної
Похідна. Фізичний і геометричний зміст похідної Логарифмы вокруг нас
Логарифмы вокруг нас Считаем и играем
Считаем и играем Умножение единицы на число
Умножение единицы на число Ұзындық бірліктері
Ұзындық бірліктері Нужна ли математика в парикмахерской
Нужна ли математика в парикмахерской Площадь многоугольников. Теорема Пифагора. Решение задач
Площадь многоугольников. Теорема Пифагора. Решение задач Ряды Фурье. Семинар 30
Ряды Фурье. Семинар 30 Периметр 2 класс
Периметр 2 класс Вероятность и статистика. 7 класс
Вероятность и статистика. 7 класс Способи обчислення границь
Способи обчислення границь