Содержание
- 2. Y=SS0+ SS1X1+ SS2X2+ SS3X3+ SS4X4+ SS5X5+ SS6X6+ SS7X7+ SS8X8+ SS9X9 THERE ARE: Y-your favorite shopping center
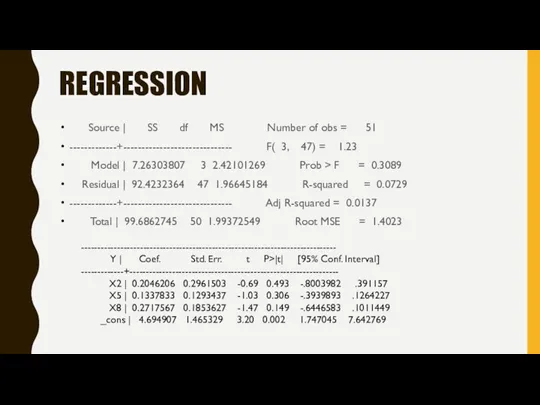
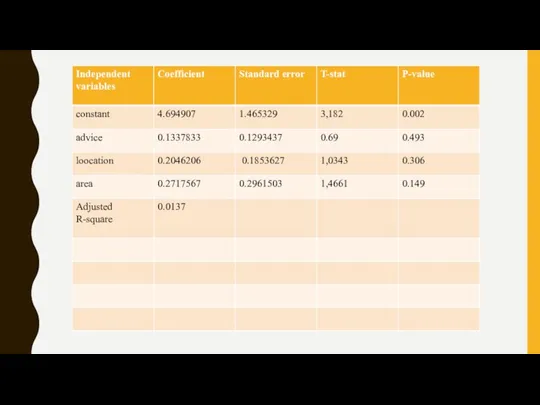
- 3. REGRESSION Source | SS df MS Number of obs = 51 -------------+------------------------------ F( 3, 47) =
- 4. Y= 4.694907 +0.204*X2+0,133*X5+0,271*X8 When all the independent variables are equal to zero, the intercept of the
- 5. T-TEST a)H0: β2=0 no linear relationship H1: β2≠0 linear relationship does exist between x and y
- 6. T-TEST b) H0: β5=0 no linear relationship H1: β3≠0 linear relationship does exist between xj and
- 7. T-TEST c) H0: β8=0 no linear relationship H1: β6≠0 linear relationship does exist between x and
- 8. F-TEST H0: β2=β5=β8=0 H1: at least one of the βi is not equal to zero f-statistics=1.23
- 9. R-SQUARE, R2. The value of R2 is 0,01 means that 1% of the variation in satisfaction
- 10. Auto Correlation Breusch-Godfrey LM test for autocorrelation --------------------------------------------------------------------------- lags(p) | chi2 df Prob > chi2 -------------+-------------------------------------------------------------
- 11. HETROCODECETICITY TEST Breusch-Pagan / Cook-Weisberg test for heteroskedasticity Ho: Constant variance Variables: fitted values of Y
- 12. DURBIN-WATSON TEST Durbin-Watson d-statistic( 4, 51) = 1.857508 0-----------------dl(1.206)---------------------du(1.537)------------4-du(2.463)--------------4-dl(2.79)--------------4 P ? Nope ? Negative No autocorrelation
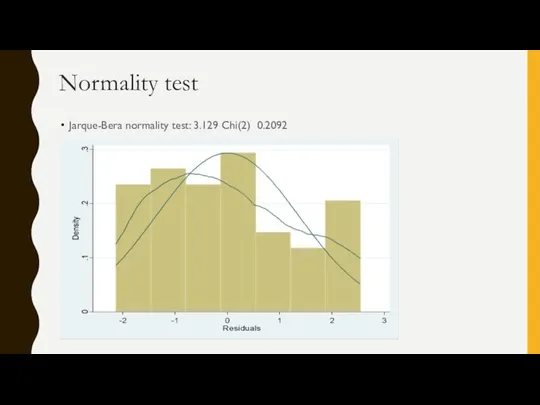
- 13. Normality test Jarque-Bera normality test: 3.129 Chi(2) 0.2092
- 14. MULTICOLENARITY TEST Variable | VIF 1/VIF -------------+---------------------- X5 | 1.07 0.937834 X2 | 1.04 0.957690 X8
- 15. RAMSEY TEST Ramsey RESET test using powers of the fitted values of Y Ho: model has
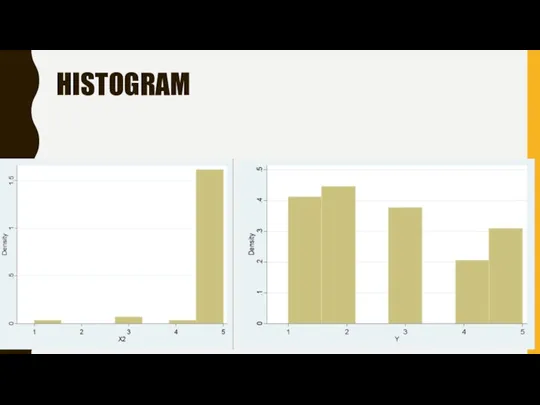
- 17. HISTOGRAM
- 19. Скачать презентацию












 Умножение чисел на 0 и на 1
Умножение чисел на 0 и на 1 Движение. Урок геометрии. 9 класс
Движение. Урок геометрии. 9 класс Паркеты из многоугольников
Паркеты из многоугольников Родительское собрание. Математика в школе (5 - 6 классы)
Родительское собрание. Математика в школе (5 - 6 классы) Решение иррациональных уравнений
Решение иррациональных уравнений Презентация Название компонентов при вычитании
Презентация Название компонентов при вычитании F-тест на качество оценивания
F-тест на качество оценивания Градиентные и генетические методы решения оптимизационных задач
Градиентные и генетические методы решения оптимизационных задач Статистичні помилки. Статистичні гіпотези та їх перевірка. Параметричні і непараметричні критерії перевірки
Статистичні помилки. Статистичні гіпотези та їх перевірка. Параметричні і непараметричні критерії перевірки Задачи оптимизации производства товаров и услуг
Задачи оптимизации производства товаров и услуг Показательная функция, ее свойства и график
Показательная функция, ее свойства и график Зеркальная симметрия
Зеркальная симметрия Сложение и вычитание алгебраических дробей
Сложение и вычитание алгебраических дробей Симметричные фигуры
Симметричные фигуры Состав чисел 6 и 7
Состав чисел 6 и 7 Десятичные дроби. 5 класс
Десятичные дроби. 5 класс Векторы в пространстве
Векторы в пространстве روش تحقیق پیشرفته .تدوین کننده.دکتر محمد صالحی
روش تحقیق پیشرفته .تدوین کننده.دکتر محمد صالحی Основные теоремы теории вероятностей
Основные теоремы теории вероятностей Обобщающий урок геометрии за курс 8 класса
Обобщающий урок геометрии за курс 8 класса Основные математические положения, применяемые для анализа и построения статистической модели
Основные математические положения, применяемые для анализа и построения статистической модели Разработка контрольно-диагностического материала по разделу математики Натуральные числа 5 класса
Разработка контрольно-диагностического материала по разделу математики Натуральные числа 5 класса Геометрические фигуры
Геометрические фигуры Урок - путешествие.
Урок - путешествие. Арифметична прогресія
Арифметична прогресія Математика. Поточная практика 7.5. Аналитическая геометрия. Поверхности второго порядка
Математика. Поточная практика 7.5. Аналитическая геометрия. Поверхности второго порядка Презентация Путешествие в страну вычесляйка 1 класс.
Презентация Путешествие в страну вычесляйка 1 класс. Отношения. Декартово произведение
Отношения. Декартово произведение