Internal secretion. Basic concepts. Pituitary hormones and their control by the hypothalamus презентация
Содержание
- 2. Outline Types of Regulatory Molecules Endocrine Glands and Hormones Paracrine Regulation Hormones That Enter Cells Hormones
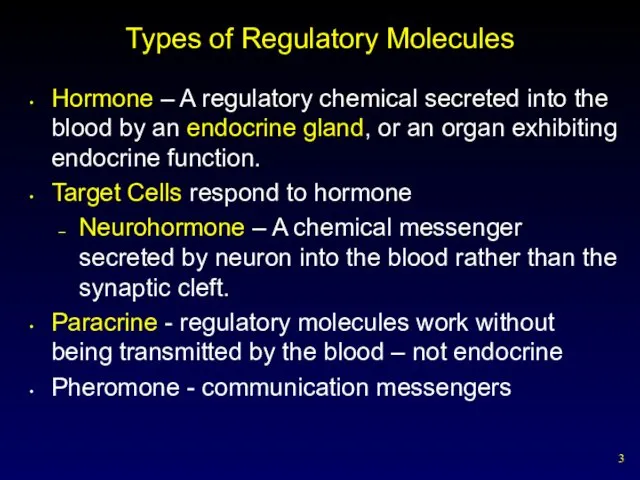
- 3. Types of Regulatory Molecules Hormone – A regulatory chemical secreted into the blood by an endocrine
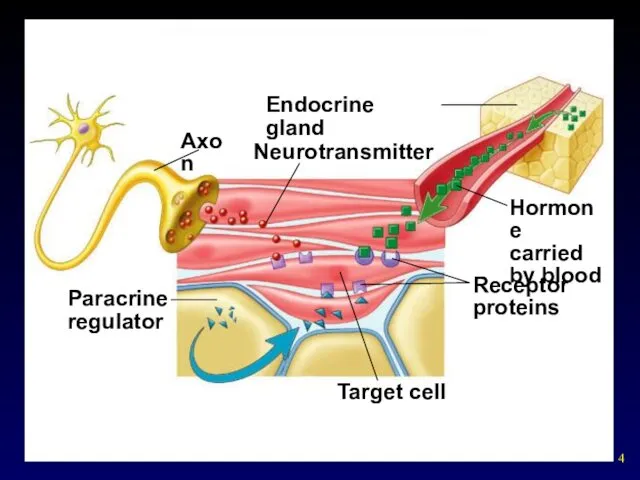
- 4. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Axon Neurotransmitter Endocrine gland
- 5. Endocrine Glands and Hormones Hormones secreted by the endocrine glands belong to four chemical categories: Polypeptides
- 6. Endocrine Glands and Hormones Neural and endocrine interactions Endocrine system also interacts and cooperates with the
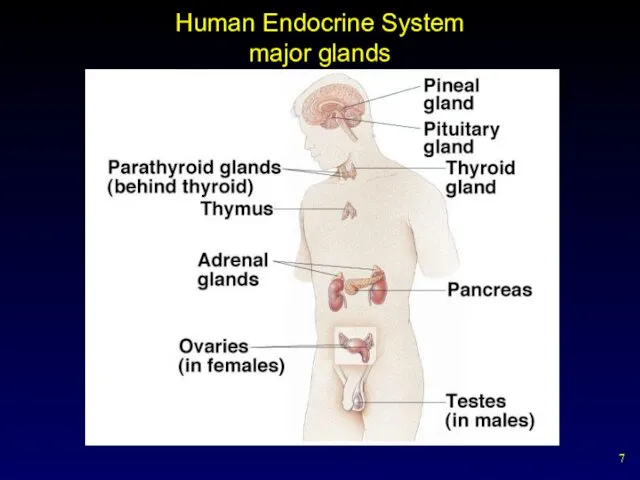
- 7. Human Endocrine System major glands
- 8. Paracrine Regulation Signaling between cells - Local effect and short-lived occurs in many organs Regulatory molecules
- 9. Paracrine Regulation Prostaglandins – most diverse group of paracrine regulators participate in regulation of: immune system
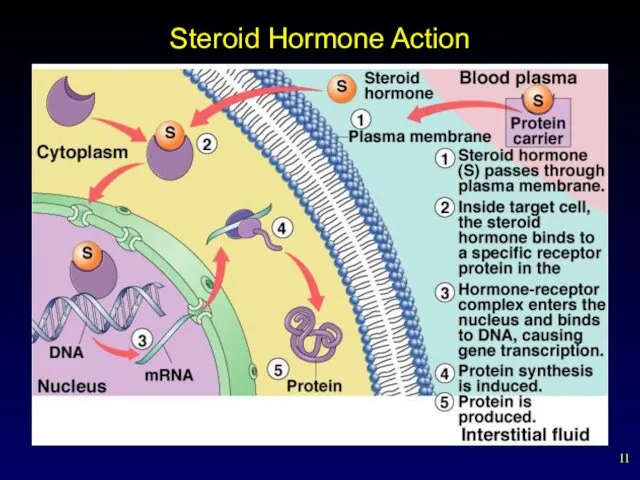
- 10. Hormones That Enter Cells Lipophilic hormones pass through the target cell’s plasma membrane and bind to
- 11. Steroid Hormone Action
- 12. Hormones That Do Not Enter Cells Hormones that are too large or too polar to cross
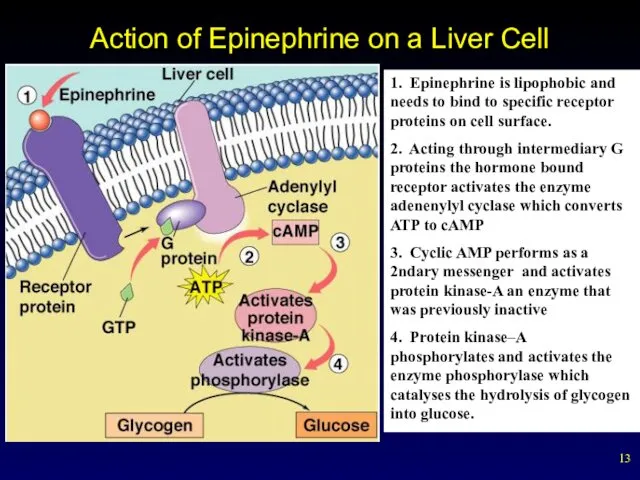
- 13. Action of Epinephrine on a Liver Cell 1. Epinephrine is lipophobic and needs to bind to
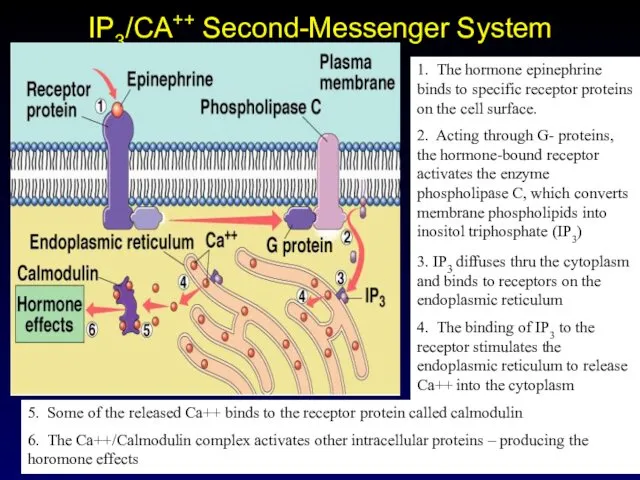
- 14. IP3/CA++ Second-Messenger System 1. The hormone epinephrine binds to specific receptor proteins on the cell surface.
- 15. Posterior Pituitary Gland Pituitary gland hangs by a stalk from the hypothalamus of the brain. anterior
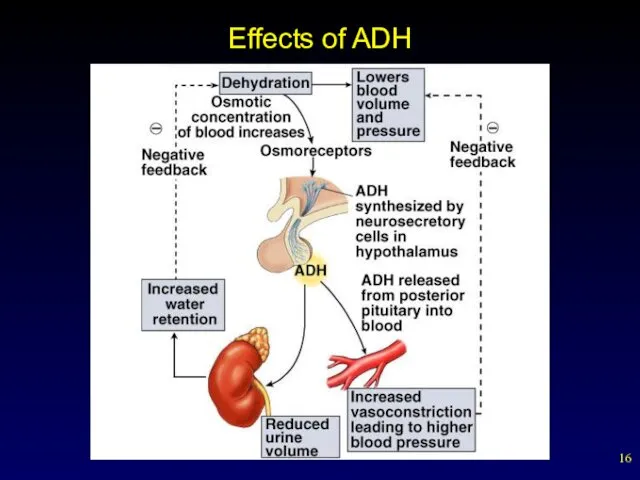
- 16. Effects of ADH
- 17. Anterior Pituitary Gland Develops from a pouch of epithelial tissue that pinches off the roof of
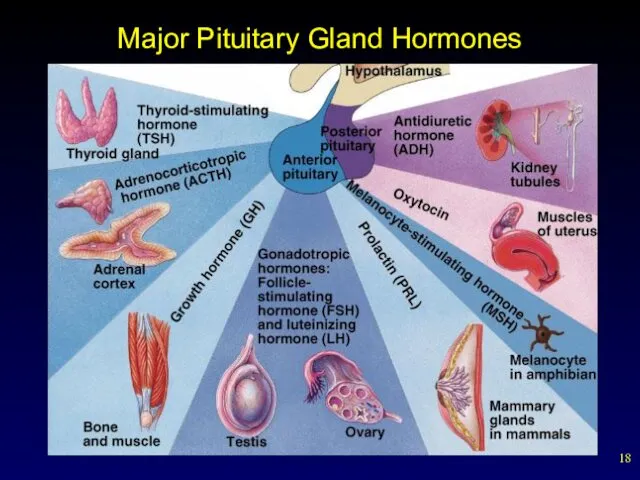
- 18. Major Pituitary Gland Hormones
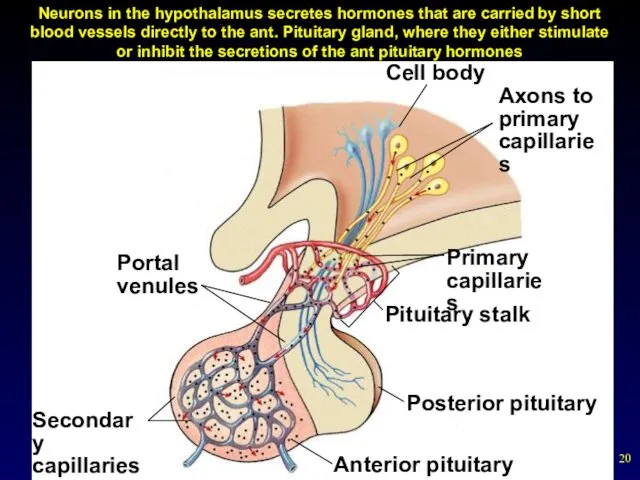
- 19. Anterior Pituitary Gland Hypothalamic control of anterior pituitary gland secretion Neurons in the hypothalamus secrete releasing
- 20. Neurons in the hypothalamus secretes hormones that are carried by short blood vessels directly to the
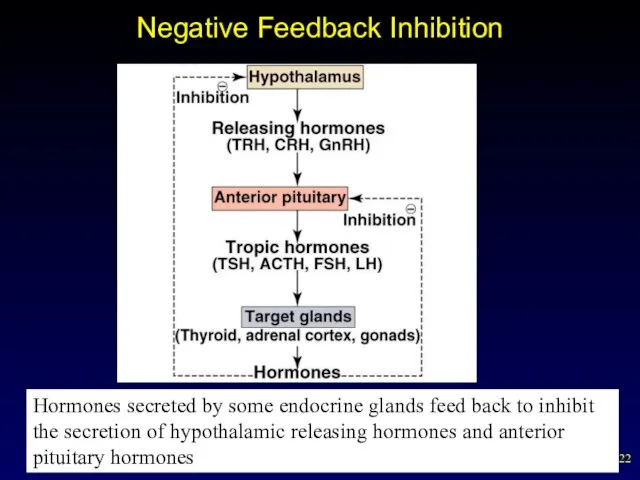
- 21. Anterior Pituitary Gland Negative feedback inhibition acts to maintain relatively constant levels of the target cell
- 22. Negative Feedback Inhibition Hormones secreted by some endocrine glands feed back to inhibit the secretion of
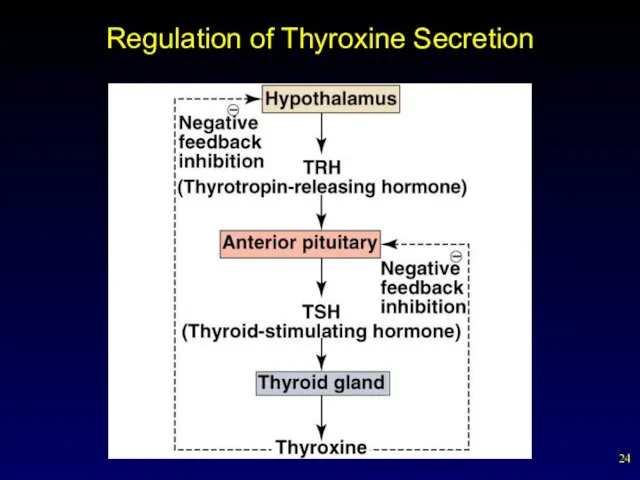
- 23. Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Thyroid gland Shaped like a shield and lies just below the Adam’s
- 24. Regulation of Thyroxine Secretion
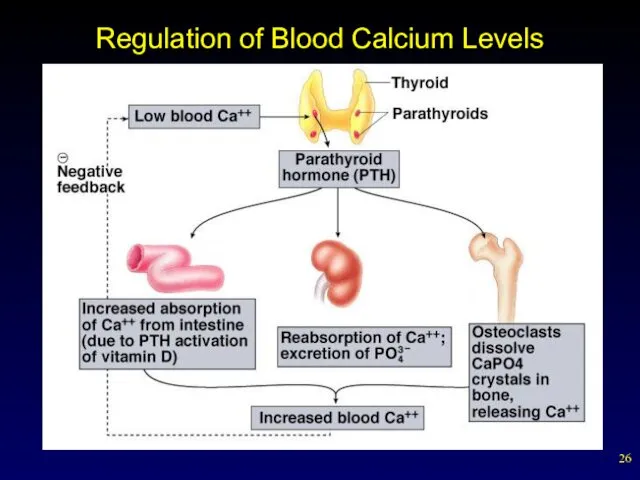
- 25. Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Parathyroid gland and calcium homeostasis four small glands attached to the thyroid
- 26. Regulation of Blood Calcium Levels
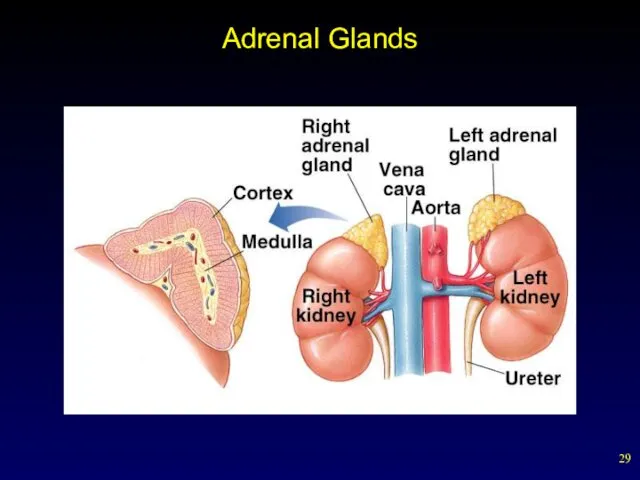
- 27. Adrenal Glands Adrenal glands are located above each kidney. Each gland composed of inner portion (adrenal
- 28. Adrenal Glands Adrenal cortex Hormones from adrenal cortex are collectively referred to as corticosteroids. Cortisol maintains
- 29. Adrenal Glands
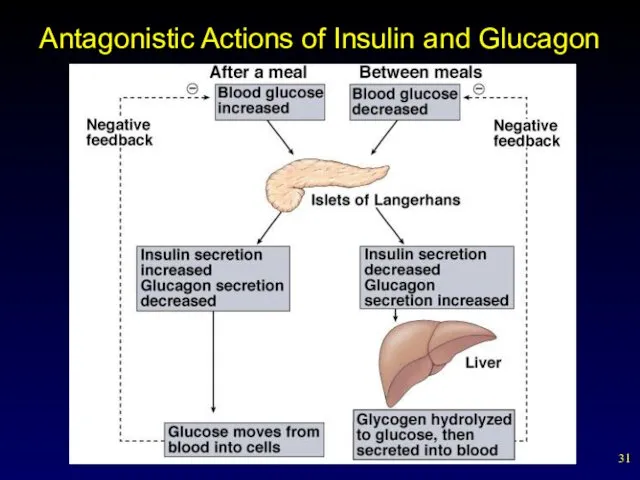
- 30. Pancreas Located adjacent to the stomach and is connected to the duodenum by the pancreatic duct.
- 31. Antagonistic Actions of Insulin and Glucagon
- 32. Other Endocrine Glands Ovaries and testes produce androgen secondary sexual characteristics Pineal gland secretes melatonin regulates
- 33. Other Endocrine Glands Molting and metamorphosis in insects Hormone secretions influence both molting and metamorphosis in
- 34. Other Endocrine Glands Endocrine disrupting chemicals chemicals that interfere with hormone function Any chemical that can
- 35. Summary Types of Regulatory Molecules Endocrine Glands and Hormones Paracrine Regulation Hormones That Enter Cells Hormones
- 37. Скачать презентацию




















 Билиарлы жүйенің және өт шығару жолдарының дисфункциясы
Билиарлы жүйенің және өт шығару жолдарының дисфункциясы Обеспечение безопасности при неблагоприятной экологической обстановке
Обеспечение безопасности при неблагоприятной экологической обстановке Қосымша аурулары бар науқастардың тістерін жұлуда қолданылатын жергілікті жансыздандырудың ерекшеліктері
Қосымша аурулары бар науқастардың тістерін жұлуда қолданылатын жергілікті жансыздандырудың ерекшеліктері Лицевой нерв
Лицевой нерв Харчові токсикоінфекції: сальмонельоз, ботулізм
Харчові токсикоінфекції: сальмонельоз, ботулізм Пароксизмальная тахикардия. Вид аритмии с частотой сердечных сокращений от 140 до 220 и более в минуту
Пароксизмальная тахикардия. Вид аритмии с частотой сердечных сокращений от 140 до 220 и более в минуту Алкогодьдің адам организміне зияны
Алкогодьдің адам организміне зияны Атрезия ануса и прямой кишки. Лечение аноректальных аномалий у детей
Атрезия ануса и прямой кишки. Лечение аноректальных аномалий у детей Особенности общего ухода за пациентами терапевтического профиля. Лекция 8
Особенности общего ухода за пациентами терапевтического профиля. Лекция 8 Технология гомеопатических таблеток. Викторина
Технология гомеопатических таблеток. Викторина Катаракта и современные методы лечения
Катаракта и современные методы лечения Пневмонии. Респираторный отдел
Пневмонии. Респираторный отдел Детский синдром Дауна
Детский синдром Дауна Ми қыртысының анатомиялық-гистологиялық құрылымы
Ми қыртысының анатомиялық-гистологиялық құрылымы Общая онкология
Общая онкология Сестринский процесс при нейрохирургических операциях, операциях на сосудах, урологических операций
Сестринский процесс при нейрохирургических операциях, операциях на сосудах, урологических операций Доказательная медицина. Систематические обзоры и мета-анализы
Доказательная медицина. Систематические обзоры и мета-анализы Тимостабилизаторы (нормотимики)
Тимостабилизаторы (нормотимики) Тиреотоксический криз. Алгоритм лечения
Тиреотоксический криз. Алгоритм лечения Grile de maxim 10
Grile de maxim 10 Хирургическая инфекция
Хирургическая инфекция Патогенные клостридии, возбудители инфекционных болезней животных. Лекция №2
Патогенные клостридии, возбудители инфекционных болезней животных. Лекция №2 Коленный сустав. Биомеханика, физиология
Коленный сустав. Биомеханика, физиология Атом энергетикасы өндірісі мен басқа да радиологиялық нысандардағы апаттардың себебінен жіктелуі және олардың салдарының маштабы
Атом энергетикасы өндірісі мен басқа да радиологиялық нысандардағы апаттардың себебінен жіктелуі және олардың салдарының маштабы Варикоцеле. Расширение вен семенного канатика
Варикоцеле. Расширение вен семенного канатика Он елі ішектің ойық жарасы кезіндегі емдік денешынықтыру шаралары
Он елі ішектің ойық жарасы кезіндегі емдік денешынықтыру шаралары Менингококковая инфекция у детей
Менингококковая инфекция у детей Жіті лейкоздар
Жіті лейкоздар