Содержание
- 2. STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Global E-Business and Collaboration What are
- 3. Why are systems for collaboration and teamwork so important and what technologies do they use? What
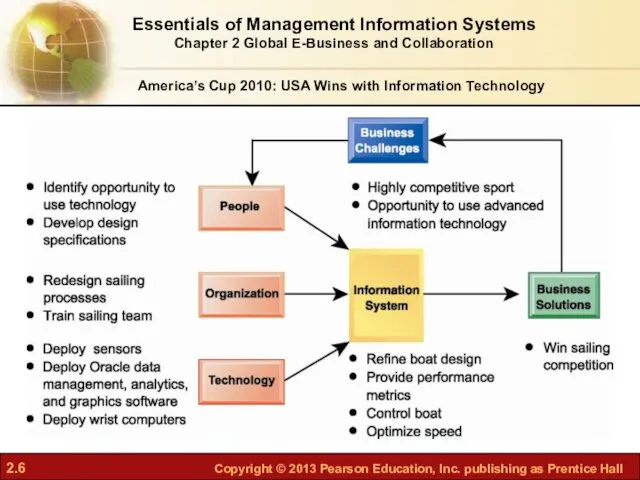
- 4. America’s Cup 2010: USA Wins with Information Technology Problem: Using IT to win the America’s Cup
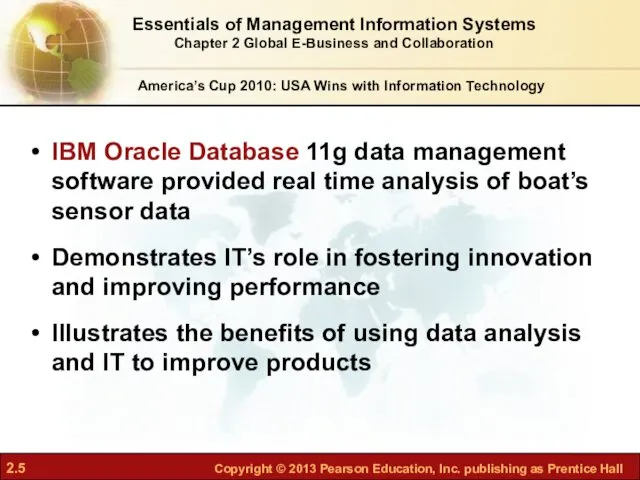
- 5. IBM Oracle Database 11g data management software provided real time analysis of boat’s sensor data Demonstrates
- 6. Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Global E-Business and Collaboration America’s Cup 2010: USA Wins
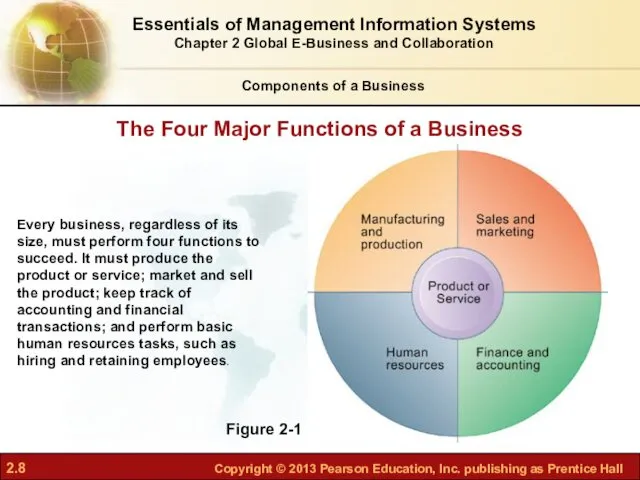
- 7. Components of a Business Four basic business functions Manufacturing and production Sales and marketing Finance and
- 8. Figure 2-1 Every business, regardless of its size, must perform four functions to succeed. It must
- 9. Components of a Business Suppliers Customers Employees Invoices/payments Products and services Five Basic Business Entities Essentials
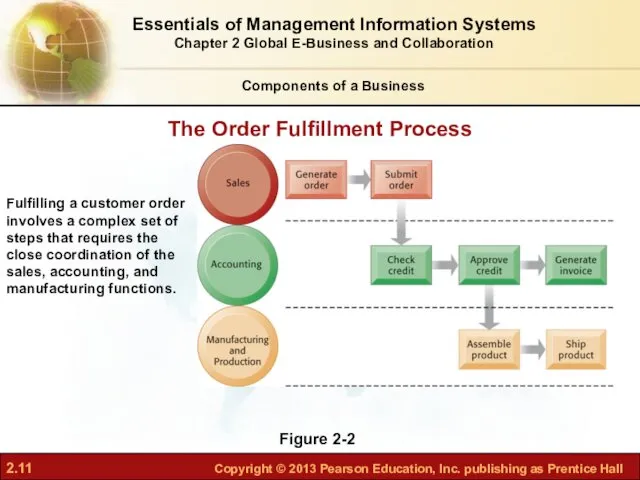
- 10. Logically related set of tasks that define how specific business tasks are performed The tasks each
- 11. Figure 2-2 Fulfilling a customer order involves a complex set of steps that requires the close
- 12. Managing a Business and Firm Hierarchies Firms coordinate work of employees by developing hierarchy in which
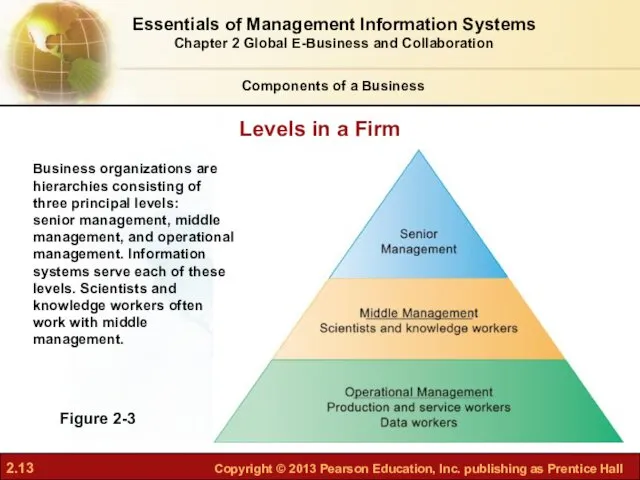
- 13. Figure 2-3 Business organizations are hierarchies consisting of three principal levels: senior management, middle management, and
- 14. The Business Environment Components of a Business Global environment factors Technology and science Economy Politics International
- 15. Figure 2-4 To be successful, an organization must constantly monitor and respond to—or even anticipate—developments in
- 16. Firms invest in information systems in order to: Achieve operational excellence Develop new products and services
- 17. Transaction processing systems (TPS) Keep track of basic activities and transactions of organization Systems for business
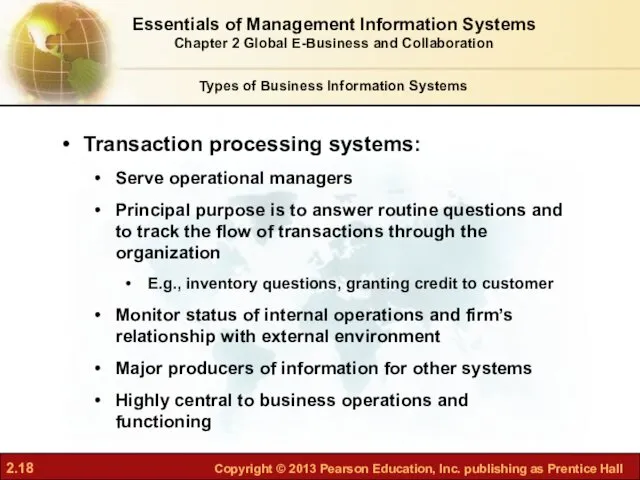
- 18. Transaction processing systems: Serve operational managers Principal purpose is to answer routine questions and to track
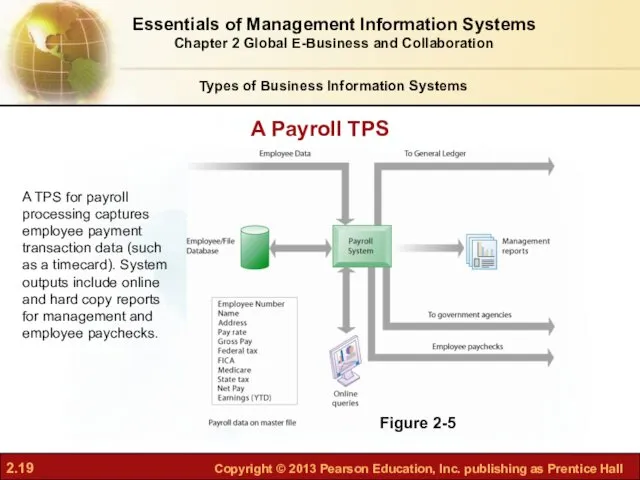
- 19. Figure 2-5 A TPS for payroll processing captures employee payment transaction data (such as a timecard).
- 20. Management information systems: Provide middle managers with reports on firm’s performance To monitor firm and help
- 21. Figure 2-6 How MIS Obtain Their Data from TPS Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 2
- 22. Sample MIS Report Figure 2-7 This report, showing summarized annual sales data, was produced by the
- 23. Read the Interactive Session and then discuss the following questions: What types of transactions do baggage
- 24. Decision support systems (DSS): Serve middle managers Support nonroutine decision making E.g., What is impact on
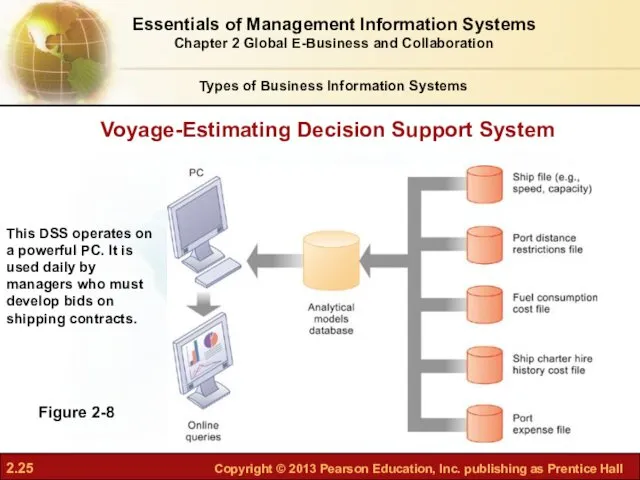
- 25. Voyage-Estimating Decision Support System Figure 2-8 This DSS operates on a powerful PC. It is used
- 26. Executive support systems (ESS): Serve senior managers Address strategic issues and long-term trends E.g., What products
- 27. Digital Dashboard A digital dashboard delivers comprehensive and accurate information for decision making often using a
- 28. Read the Interactive Session and then discuss the following questions: What people, organization, and technology issues
- 29. Enterprise applications Systems that span functional areas, focus on executing business processes across the firm, and
- 30. Enterprise Application Architecture Figure 2-9 Enterprise applications automate processes that span multiple business functions and organizational
- 31. Also called enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems Integrate data from key business processes into single system
- 32. Manage relationships with suppliers, purchasing firms, distributors, and logistics companies Manage shared information about orders, production,
- 33. Help manage relationship with customers Coordinate business processes that deal with customers in sales, marketing, and
- 34. Manage processes for capturing and applying knowledge and expertise Collect relevant knowledge and make it available
- 35. Intranets and Extranets Technology platforms that increase integration and expedite the flow of information Intranets: Internal
- 36. E-Business, E-Commerce, and E-Government E-business: Use of digital technology and Internet to drive major business processes
- 37. What Is Collaboration? Systems for Collaboration and Teamwork Growing Importance of collaboration: Changing nature of work
- 38. Business Benefits of Collaboration and Teamwork Systems for Collaboration and Teamwork Recent surveys find that investment
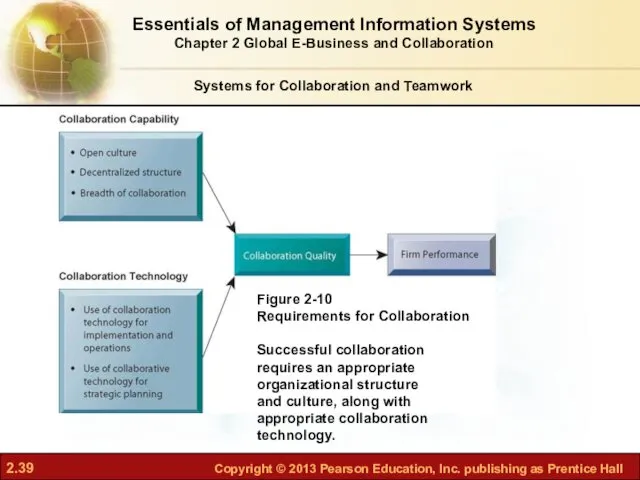
- 39. Systems for Collaboration and Teamwork Figure 2-10 Requirements for Collaboration Successful collaboration requires an appropriate organizational
- 40. Tools and Technologies for Collaboration and Teamwork Systems for Collaboration and Teamwork E-mail and instant messaging
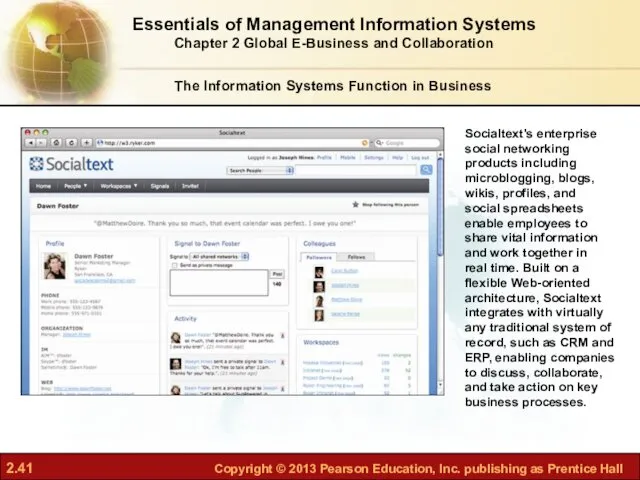
- 41. Socialtext's enterprise social networking products including microblogging, blogs, wikis, profiles, and social spreadsheets enable employees to
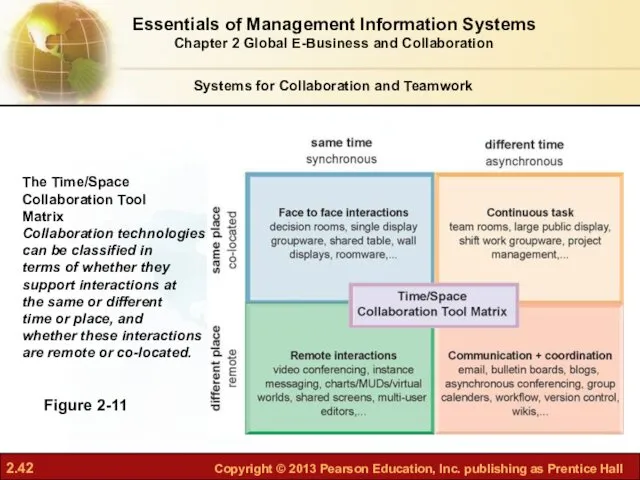
- 42. Systems for Collaboration and Teamwork The Time/Space Collaboration Tool Matrix Collaboration technologies can be classified in
- 43. Systems for Collaboration and Teamwork Evaluating and Selecting Collaboration Software Tools What are your firm’s collaboration
- 44. The Information Systems Department The Information Systems Function in Business Programmers Systems analysts Principle liaisons to
- 45. Information Systems Services The Information Systems Function in Business Computing services Telecommunications services Data management services
- 47. Скачать презентацию
































 Совершенствование закупочной логистики торговой компании. ООО БТ-КРАН
Совершенствование закупочной логистики торговой компании. ООО БТ-КРАН От лица компании МТС
От лица компании МТС Диагностика имиджа компании как работодателя
Диагностика имиджа компании как работодателя Психологическое сопровождение организации Арбат-фитнес
Психологическое сопровождение организации Арбат-фитнес Модуль Управление персоналом (Нuman Resources). Управление организационными структурами
Модуль Управление персоналом (Нuman Resources). Управление организационными структурами SuccessFactors User Guide
SuccessFactors User Guide Тьюториал. Управление организацией и персоналом. Власть, лидерство и изменения. (Книга 4)
Тьюториал. Управление организацией и персоналом. Власть, лидерство и изменения. (Книга 4) Понятие Экологического менеджмента
Понятие Экологического менеджмента Разработка системы качества для предприятия
Разработка системы качества для предприятия Управление знаниями. Knowledge Management. Знания в информационных системах
Управление знаниями. Knowledge Management. Знания в информационных системах Стратегическое управление организацией. Сущность стратегического управления и реализация стратегии
Стратегическое управление организацией. Сущность стратегического управления и реализация стратегии Основы финансового менеджмента
Основы финансового менеджмента Мотивация, как функция управления
Мотивация, как функция управления Умение крититковать в деятельности менеджера
Умение крититковать в деятельности менеджера Қонақ үй классификациясы
Қонақ үй классификациясы Деятельность менеджера
Деятельность менеджера Обзор литературы по проектной деятельности
Обзор литературы по проектной деятельности Структура службы Housekeeping: состав, основные функции и задачи
Структура службы Housekeeping: состав, основные функции и задачи Предприятия общественного питания
Предприятия общественного питания Виды организационных структур
Виды организационных структур Стандарты телефонного общения. Билайн
Стандарты телефонного общения. Билайн Навыки медицинского представителя. Тренинг
Навыки медицинского представителя. Тренинг Многомерный стиль руководства
Многомерный стиль руководства Этапы процесса проектирования туристско-рекреационного продукта
Этапы процесса проектирования туристско-рекреационного продукта Функции управления проектами
Функции управления проектами Модель сервиса. Руководство для тренера. (Модуль 1)
Модель сервиса. Руководство для тренера. (Модуль 1) Структурная схема главного управления
Структурная схема главного управления Knowledge management in smes. Dr. Susanne Durst
Knowledge management in smes. Dr. Susanne Durst