Содержание
- 2. Introduction Projects are the New Way to Work Project Management is Keeping Pace with Global Change
- 3. The Art and Science of Project Leadership Agreement among the project team, customers, and management on
- 4. FUNDAMENTALS OF PROJECT MANAGEMENT Chapter 2 Project Management :Foundation Principles of Project Management 1-
- 5. Projects Require Project Management Every project has a beginning and an end Every project produces a
- 6. Additional Definitions “A project is a unique venture with a beginning and an end, conducted by
- 7. Elements of Projects Complex, one-time processes Limited by budget, schedule, and resources Developed to resolve a
- 8. Definition of Ongoing Operations An Insurance company processes thousands of claims every day A bank teller
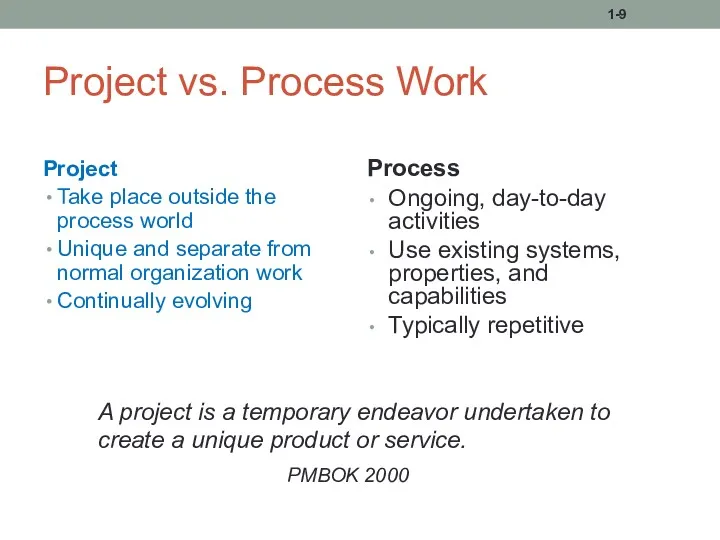
- 9. Project vs. Process Work Project Take place outside the process world Unique and separate from normal
- 10. Process & Project Management (Table 1.1) 1- Process Repeat process or product Several objectives Ongoing People
- 11. General Project Characteristics (1/2) Ad-hoc endeavors with a clear life cycle Building blocks in the design
- 12. General Project Characteristics (2/2) Entail crossing functional and organization boundaries Traditional management functions of planning, organizing,
- 13. Why are Projects Important? Shortened product life cycles Narrow product launch windows Increasingly complex and technical
- 14. Project Success Rates Software & hardware projects fail at a 65% rate Over half of all
- 15. The Challenge of Managing Projects Personnel Estimating Authority Controls Project Management in Industry –Independent-Project Managers Are
- 16. The Definition of Success On time On budget High quality 1) Scope 2) Performance The Cost
- 17. Project Management Functions According to the project definition there are two activities involved in this groundwork:
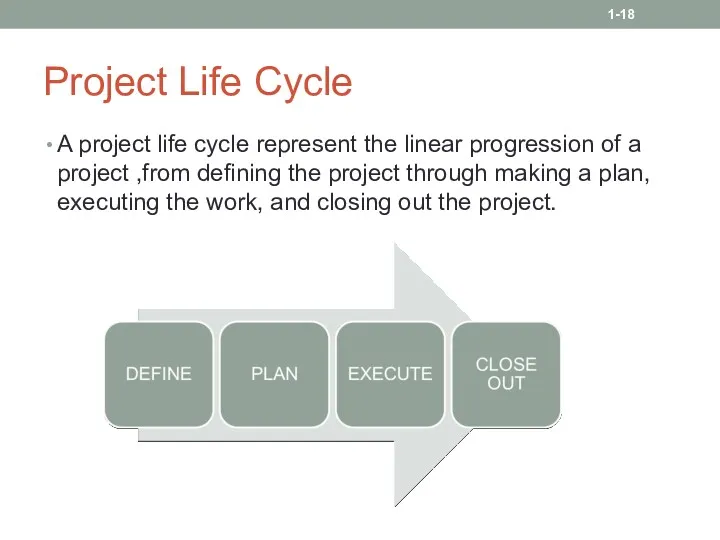
- 18. Project Life Cycle A project life cycle represent the linear progression of a project ,from defining
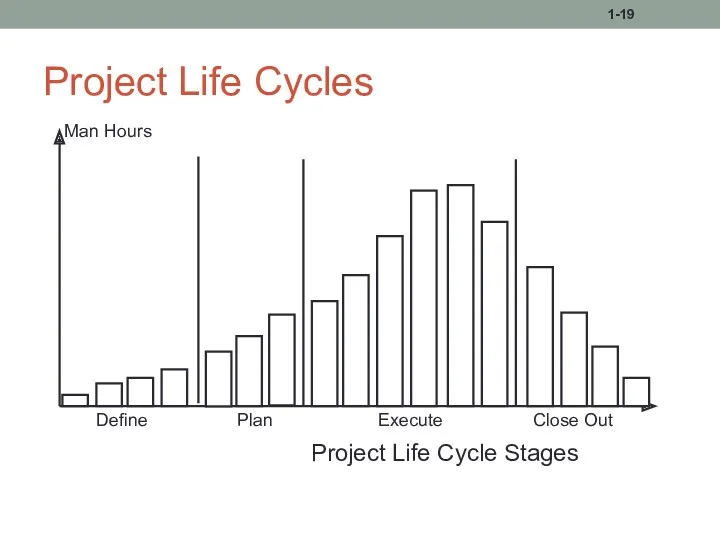
- 19. Project Life Cycles 1- Man Hours Define Plan Execute Close Out Project Life Cycle Stages
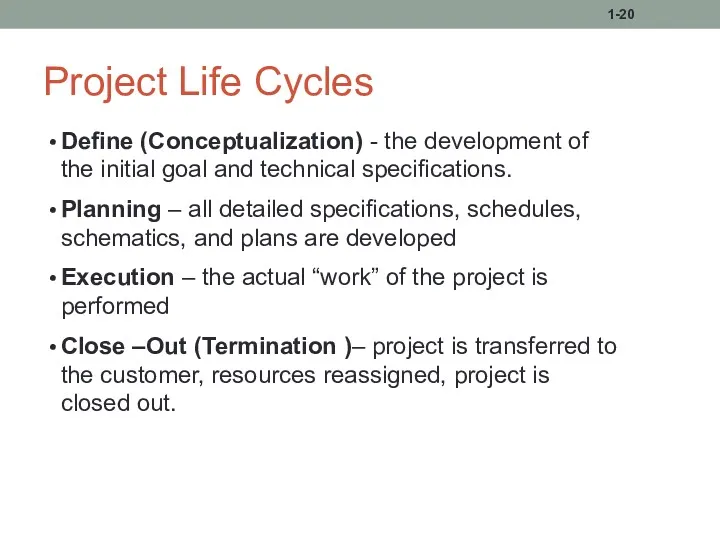
- 20. Project Life Cycles Define (Conceptualization) - the development of the initial goal and technical specifications. Planning
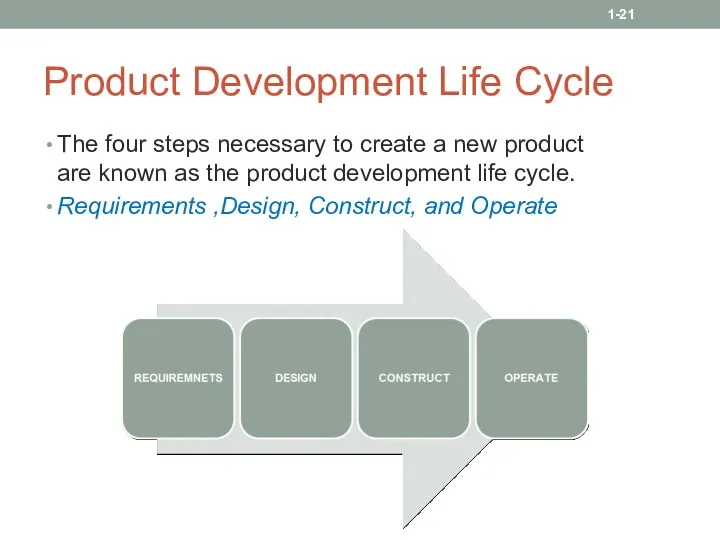
- 21. Product Development Life Cycle The four steps necessary to create a new product are known as
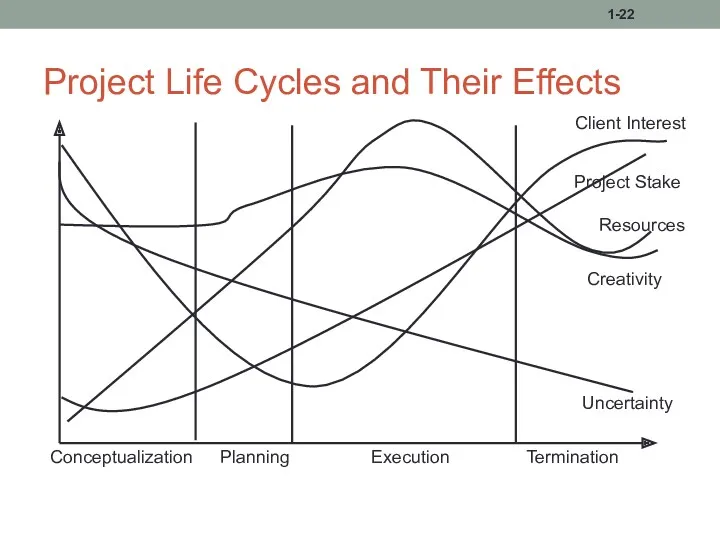
- 22. Project Life Cycles and Their Effects 1- Uncertainty Client Interest Project Stake Creativity Resources
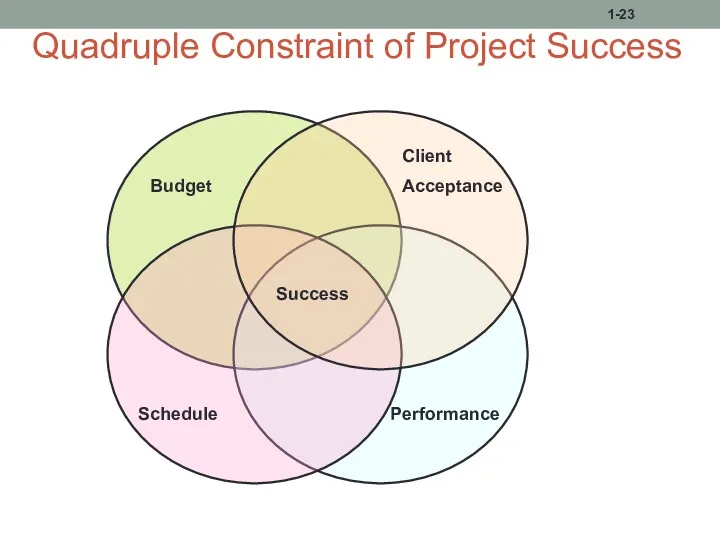
- 23. Quadruple Constraint of Project Success 1-
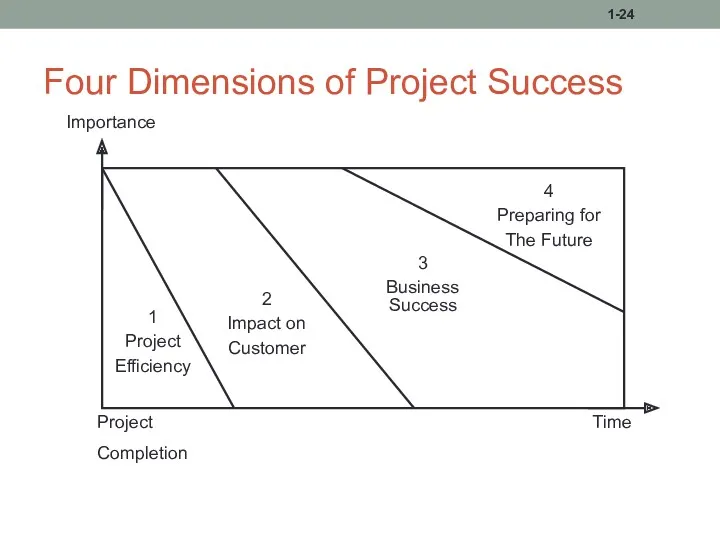
- 24. Four Dimensions of Project Success 1-
- 25. Product Life Cycle vs. Project Life Cycle The product life cycle describes the work required to
- 26. 2- Forms of Organizational Structure Functional organizations – group people performing similar activities into departments (page
- 27. Six Criteria for IT Project Success System quality Information quality Use User satisfaction Individual Impact Organizational
- 29. Скачать презентацию

















 Ethical decision-making in everyday work situations. (Part 2)
Ethical decision-making in everyday work situations. (Part 2) Boshlang‘ich ta’lim metod birlashmalari ishini samarali tashkil etish shakl va usullari
Boshlang‘ich ta’lim metod birlashmalari ishini samarali tashkil etish shakl va usullari Совершенствование методов оценки сотрудников государственного учреждения
Совершенствование методов оценки сотрудников государственного учреждения Рабочая программа курса закупочная логистика по специальности 1-26 02 05 логистика
Рабочая программа курса закупочная логистика по специальности 1-26 02 05 логистика Основы менеджмента
Основы менеджмента Управление проектами (часть 1)
Управление проектами (часть 1) Ұйымдастыру - бұл оның мақсаттарына бірге жету үшін адамдарға тиімді жұмыс істеуге мүмкіндік беретін кәсіпорынның құрылымын
Ұйымдастыру - бұл оның мақсаттарына бірге жету үшін адамдарға тиімді жұмыс істеуге мүмкіндік беретін кәсіпорынның құрылымын Система управления окружающей средой
Система управления окружающей средой Грузы, грузооборот и грузовые перевозки
Грузы, грузооборот и грузовые перевозки Виды туристской деятельности
Виды туристской деятельности Организационно-методические основы создания системы контроллинга в организации. (Тема 3.1)
Организационно-методические основы создания системы контроллинга в организации. (Тема 3.1) Профессиональная этика повара
Профессиональная этика повара Машинное обучение в электронной коммерции – практика использования и подводные камни
Машинное обучение в электронной коммерции – практика использования и подводные камни Разработка бизнес-плана по увеличению производственных мощностей предприятия
Разработка бизнес-плана по увеличению производственных мощностей предприятия Инновационные стратегии в деятельности современных организаций
Инновационные стратегии в деятельности современных организаций НБП-240-97. Противодымная защита зданий и сооружений. Методы приемо-сдаточных и периодических испытаний
НБП-240-97. Противодымная защита зданий и сооружений. Методы приемо-сдаточных и периодических испытаний Система управления человеческими ресурсами на предприятии
Система управления человеческими ресурсами на предприятии Менеджер по продажам
Менеджер по продажам Project to improve hr management of a chain of yamato restaurants
Project to improve hr management of a chain of yamato restaurants Организация труда на предприятии
Организация труда на предприятии Становление менеджмента. Школы менеджмента
Становление менеджмента. Школы менеджмента Личность и коллектив как объект управления
Личность и коллектив как объект управления Унификация и стандартизация документов
Унификация и стандартизация документов Основы организации производства
Основы организации производства Мотивація для продавців
Мотивація для продавців Моделирование вычислительных процессов в экономических процессах
Моделирование вычислительных процессов в экономических процессах Понятие качества в современной экономике. 14 принципов Деминга
Понятие качества в современной экономике. 14 принципов Деминга Делегирование полномочий в аптечных организациях
Делегирование полномочий в аптечных организациях