Содержание
- 2. Definitions of Management The organization and coordinationThe organization and coordination of the activitiesThe organization and coordination
- 3. Definitions of Management Management in businesses in businesses and organizations in businesses and organizations is the
- 4. "Management is an art of knowing what is to be done and seeing that it is
- 5. "Management is that process by which managers create, direct, maintain and operate purposive organisation through systematic,
- 6. What are we working with? Organizations: People working together and coordinating their actions to achieve specific
- 7. Additional Key Concepts Resources are organizational assets and include: People, Machinery, Raw materials, Information, skills, Financial
- 8. Achieving High Performance Organizations must provide a good or service desired by its customers. Irene Rosenfeld
- 9. Organizational Performance Measures how efficiently and effectively managers use resources to satisfy customers and achieve goals.
- 10. Managerial Functions Henri Fayol was the first to describe the four managerial functions when he was
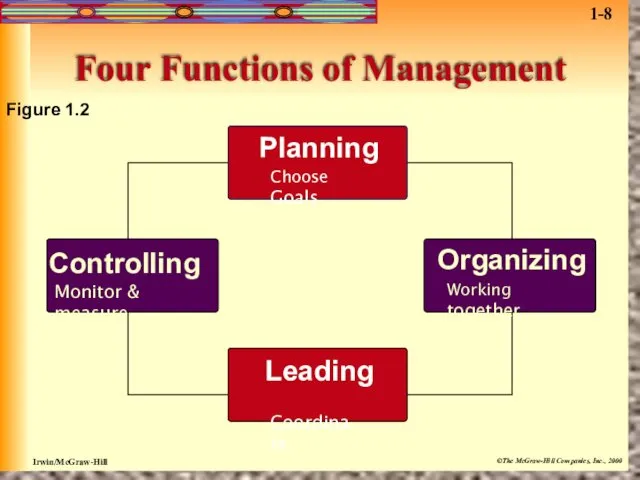
- 11. Four Functions of Management Figure 1.2 Planning Choose Goals Organizing Working together Leading Coordinate Controlling Monitor
- 12. Planning Planning is the process used by managers to identify and select appropriate goals and courses
- 13. Organizing In organizing, managers create the structure of working relationships between organizational members that best allows
- 14. Leading In leading, managers determine direction, state a clear vision for employees to follow, and help
- 15. Controlling In controlling, managers evaluate how well the organization is achieving its goals and takes corrective
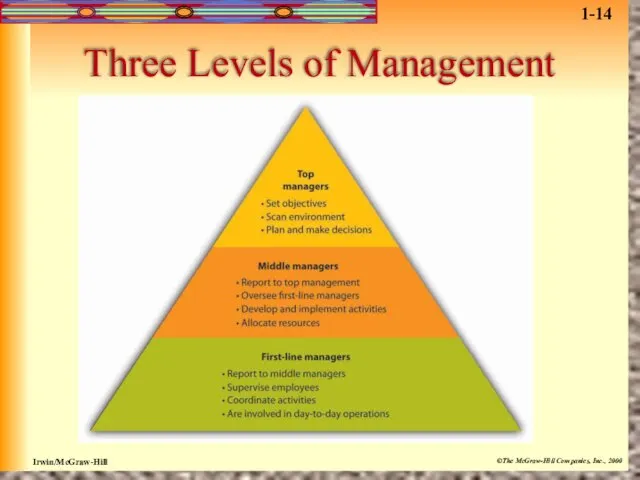
- 16. Management Levels Organizations often have 3 levels of managers: First-line Managers: responsible for day-to-day operation. They
- 17. Three Levels of Management 1-14
- 19. Restructuring Restructuring is the corporate management term for the act of reorganizing the legal, ownership, operational,
- 20. Management Trends Empowerment: expand the tasks and responsibilities of workers. Supervisors might be empowered to make
- 21. Management Trends New work tools increase transparency In the past, managers have typically determined how employees
- 25. Managerial Roles Described by Mintzberg. A role is a set of specific tasks a person performs
- 26. Interpersonal Roles Roles managers assume to coordinate and interact with employees and provide direction to the
- 27. Informational Roles Associated with the tasks needed to obtain and transmit information for management of the
- 28. Decisional Roles Associated with the methods managers use to plan strategy and utilize resources to achieve
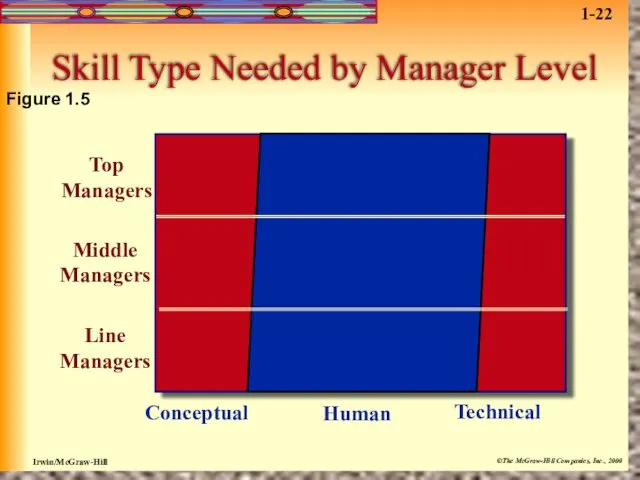
- 29. Managerial Skills There are three skill sets that managers need to perform effectively. 1. Conceptual skills:
- 30. Skill Type Needed by Manager Level Top Managers Middle Managers Line Managers Conceptual Human Technical Figure
- 31. Management Challenges Increasing number of global organizations. Building competitive advantage through superior efficiency, quality, innovation, and
- 33. Скачать презентацию

























 Управление цепями поставок
Управление цепями поставок Internal control and deontology - Chapter 4 Internal audit and auditcommittee
Internal control and deontology - Chapter 4 Internal audit and auditcommittee Планирование. Цель планирования. Примеры миссий. Этапы планирования
Планирование. Цель планирования. Примеры миссий. Этапы планирования Подбор сотрудников. Собеседование на рядовые позиции
Подбор сотрудников. Собеседование на рядовые позиции Scheduling and lot sizing
Scheduling and lot sizing Управление человеческими ресурсами. Динамика численности населения и трудовая миграция. (Тема 4)
Управление человеческими ресурсами. Динамика численности населения и трудовая миграция. (Тема 4) Performance Measurement
Performance Measurement Коучинг әдісі
Коучинг әдісі Психология мотивации персонала
Психология мотивации персонала Программа повышения лояльности посетителей ресторанов и заказчиков еды на дом
Программа повышения лояльности посетителей ресторанов и заказчиков еды на дом Istota zarządzania
Istota zarządzania Описание архивных документов
Описание архивных документов Факторы успешного трудоустройства
Факторы успешного трудоустройства Зонирование склада
Зонирование склада Оценка деятельности персонала
Оценка деятельности персонала Automatic decision development 2016 - 2017
Automatic decision development 2016 - 2017 Самоменеджмент, как условие личного и профессионального успеха
Самоменеджмент, как условие личного и профессионального успеха Стили руководства. Определение стилей. Классические стили. Многомерные стили
Стили руководства. Определение стилей. Классические стили. Многомерные стили Группа компаний РyссОйл
Группа компаний РyссОйл Жизненный цикл проекта
Жизненный цикл проекта Учет реализации и прочего выбытия товаров в аптечных организациях. (Тема 4)
Учет реализации и прочего выбытия товаров в аптечных организациях. (Тема 4) Загальна характеристика управління проектами в туризмі
Загальна характеристика управління проектами в туризмі Место исследования в деятельности и развитии организации
Место исследования в деятельности и развитии организации Метод мозгового штурма
Метод мозгового штурма Общая характеристика стратегического менеджмента
Общая характеристика стратегического менеджмента Основные отличия миссии от целей
Основные отличия миссии от целей Работа системы управление рисками в таможенных органах Республики Узбекистан
Работа системы управление рисками в таможенных органах Республики Узбекистан Годовые переговоры с поставщиком РК
Годовые переговоры с поставщиком РК