Слайд 2

Lecture’s topics
What is controlling?
What are the steps of the control process?
What
are the main types of control?
Слайд 3

Management functions
Planning
Organising
Leading
Controlling
the final link in the functional chain of management
Слайд 4

Controlling Function
Are activities going as planned? monitoring
If not, what can we
do about it? taking action
Слайд 5

Controlling Function
Controlling is the process of:
monitoring activities to ensure they are
being
accomplished as planned
acting to correct any significant variations
Слайд 6
Controlling Function
Frequent checks ensure that corrective action is
taken quickly to
avoid wasting effort and resources.
when?
Слайд 7
Controlling Function
All managers exercise control as they try to add
value
by transforming resources into outputs of
greater value.
by whom?
Слайд 8

Example 1
Volume of sales in November: 975 units.
Average monthly volume of
sales: 1000 units.
Variation = 1000-975 = 25 units.
Action: Do nothing (variation acceptable).
Слайд 9

Example 2
Volume of sales in November: 800 units.
Average monthly volume of
sales: 1000 units.
Variation = 1000-800 = 200 units.
Action: Identify cause of variation and correct performance.
Слайд 10

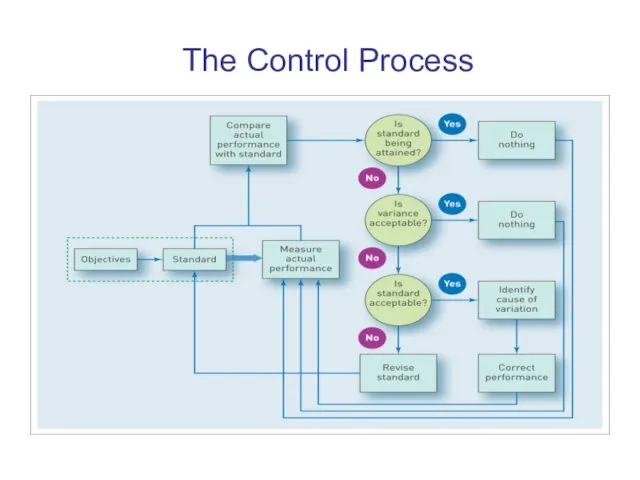
The Control Process
The control process involves four basic steps.
Слайд 11

The Control Process
Step 1 - Define objectives and set standards.
Слайд 12

Setting standards
The standard will itself have an effect on its
achievement.
standards seen as too high may be ignored as
unattainable
standards that are too low will lower performance
Слайд 13
The Control Process
Step 2 - Measure performance.
Слайд 14

Measuring performance
Quantifiable aspects of performance are relatively
easy to measure
whereas non-quantifiable aspects
of performance are more open to subjective
interpretations.
Слайд 15

The Control Process
Step 3 - Compare performance with standard.
Слайд 16

Comparing performance with standard
As some variation from the plan is
always to be
expected, managers need to determine the
acceptable range of variation.
Слайд 17

The Control Process
Step 4 - Take appropriate managerial action to correct
variations or inadequate standards.
Слайд 18

Taking action
Managers need to act on significant variations
from the
plan – either to correct future performance
or to revise inadequate standards.
Слайд 19

Taking action
Managers need to act on significant variations
from the
plan – either to correct future performance
or to revise inadequate standards.
Be careful – a constant lowering of standards can result in
employees blaming the standard as being too high rather
than accepting that their performance was inadequate!
Слайд 20
Слайд 21

Types of Control
Concurrent control
Feedback control
Слайд 22

Concurrent Control
Takes place while an activity is in progress.
Normally involves direct
supervision.
Main advantage: allows managers to correct problems
before they become too costly.
Слайд 23

Feedback Control
Takes place after the activity.
Does not require direct supervision.
Main advantage:
allows managers to provide feedback,
which can enhance employee motivation.
Слайд 24

Control & organisational size
Small organisations:
- informal & personal
- concurrent control through
direct supervision
Large organisations:
- formal & impersonal
- feedback control
Слайд 25

Control & position level
Low-level positions:
- performance easier to measure
High-level positions:
-
performance more difficult to measure
- many performance criteria
Слайд 26

Control & degree of decentralisation
Low decentralisation:
- reduced number of controls
High decentralisation:
-
increased number of controls

























 Стратегии поведения в конфликте
Стратегии поведения в конфликте Методики бизнес-инжиниринга и их применение в системе антикризисного управления. (Лекция 12)
Методики бизнес-инжиниринга и их применение в системе антикризисного управления. (Лекция 12) Контур логистика. Структуры КИС в которых имеется контур логистики. Система БЭСТ
Контур логистика. Структуры КИС в которых имеется контур логистики. Система БЭСТ Трудовой потенциал и трудовые ресурсы общества
Трудовой потенциал и трудовые ресурсы общества Концепция нового государственного менеджмента
Концепция нового государственного менеджмента Product Planning & Development
Product Planning & Development Планирование как важнейшая функция управления
Планирование как важнейшая функция управления Технология управленческого консультирования. Подготовка к консультированию и диагноз проблемы клиента
Технология управленческого консультирования. Подготовка к консультированию и диагноз проблемы клиента Менеджмент інформаційних систем. Лекція №1
Менеджмент інформаційних систем. Лекція №1 Корпоративный кодекс
Корпоративный кодекс Основные принципы работы системы продаж
Основные принципы работы системы продаж Американская модель управления качеством
Американская модель управления качеством Лидерство и руководство. Типы лидерства. Лидерство и власть. Стили лидерства и руководства. Командообразование
Лидерство и руководство. Типы лидерства. Лидерство и власть. Стили лидерства и руководства. Командообразование Секрет постоянного роста в Орифлэйм
Секрет постоянного роста в Орифлэйм Основні теорії та моделі організації
Основні теорії та моделі організації ИСО 14001-2016. Системы экологического менеджмента. Требования и руководство по применению
ИСО 14001-2016. Системы экологического менеджмента. Требования и руководство по применению Контроллинг бизнес процессов. Бизнес-процессы на предприятии
Контроллинг бизнес процессов. Бизнес-процессы на предприятии Управление коммуникациями и стейкхолдерами проекта. Лекция 8
Управление коммуникациями и стейкхолдерами проекта. Лекция 8 Мотивационное управление
Мотивационное управление Стратегии управления персоналом
Стратегии управления персоналом Функционирование редакционного коллектива. Системность, ритмичность, цикличность
Функционирование редакционного коллектива. Системность, ритмичность, цикличность Формирование эффективной команды
Формирование эффективной команды Management Decision Support and Intelligent Systems
Management Decision Support and Intelligent Systems Инициация проекта
Инициация проекта Методы принятия управленческих решений
Методы принятия управленческих решений Управление человеческими ресурсами организации
Управление человеческими ресурсами организации Managing Risk
Managing Risk Стратегический анализ внутренней и внешней среды организации
Стратегический анализ внутренней и внешней среды организации