Содержание
- 2. Managing Human Resources
- 3. Learning Objectives Explain the importance of the human resource management process and the external influences that
- 4. Why Is HRM Important? As a significant source of competitive advantage: People-oriented HR creates superior shareholder
- 5. Why Is HRM Important? (cont.) High – performance work practices – work practices that lead to
- 6. Exhibit 12-1 High-Performance Work Practices Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
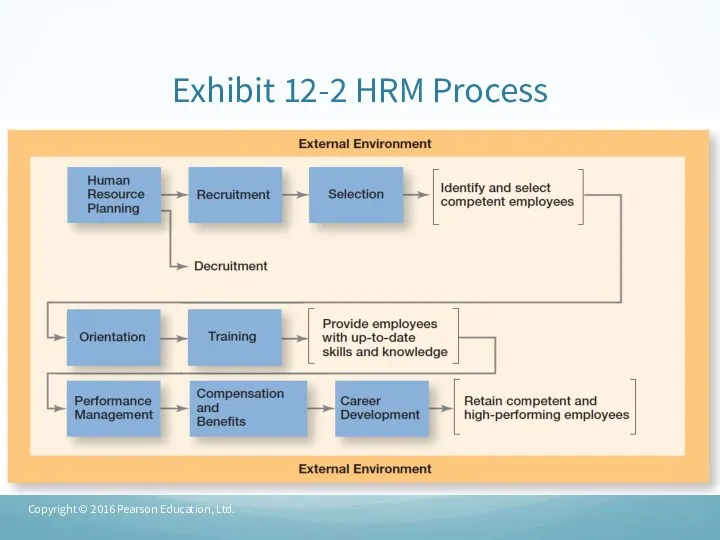
- 7. Exhibit 12-2 HRM Process Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 8. External Factors That Affect the HRM Process The Economy's Effect on HRM The global economic downturn
- 9. External Factors That Affect the HRM Process (cont.) Employee Labor Unions Labor union – an organization
- 10. External Factors That Affect the HRM Process (cont.) Legal Environment of HRM Affirmative action – organizational
- 11. Exhibit 12-3 Major HRM Laws Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 12. Exhibit 12-3 Major HRM Laws (cont.) Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 13. Exhibit 12-3 Major HRM Laws (cont.) Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 14. Global HRM Laws Work councils – groups of nominated or elected employees who must be consulted
- 15. External Factors That Affect the HRM Process (cont.) Demographic Trends The oldest, most experienced workers (those
- 16. Human Resource Planning Human resource planning – ensuring that the organization has the right number and
- 17. Human Resource Planning (cont.) Job description – a written statement that describes a job. Job specification
- 18. Recruitment and Decruitment Recruitment – locating, identifying, and attracting capable applicants. Decruitment – reducing an organization’s
- 19. Exhibit 12-4 Recruiting Sources Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 20. Exhibit 12-5 Decruitment Options Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 21. Selection Selection – screening job applicants to ensure that the most appropriate candidates are hired. A
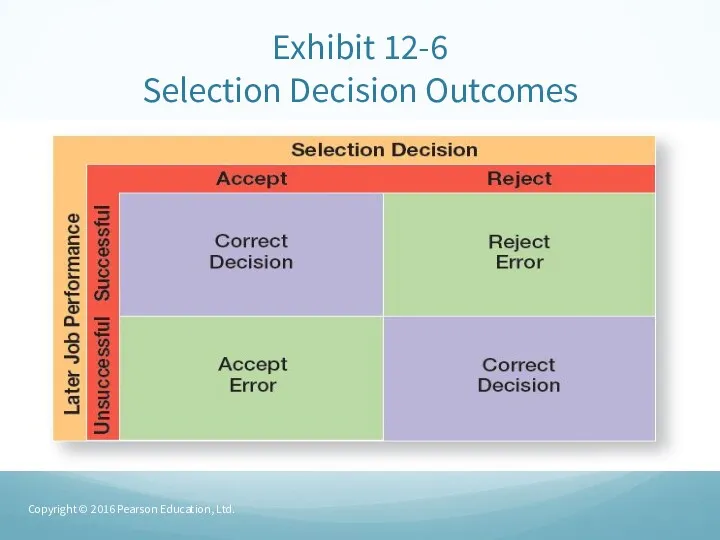
- 22. Exhibit 12-6 Selection Decision Outcomes Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 23. Exhibit 12-7 Selection Tools Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 24. Exhibit 12-7 Selection Tools (cont.) Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 25. Exhibit 12-7 Selection Tools (cont.) Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 26. Selection (cont.) Realistic Job Preview (RJP) – a preview of a job that provides both positive
- 27. Providing Employees with Needed Skills and Knowledge Orientation – introducing a new employee to his or
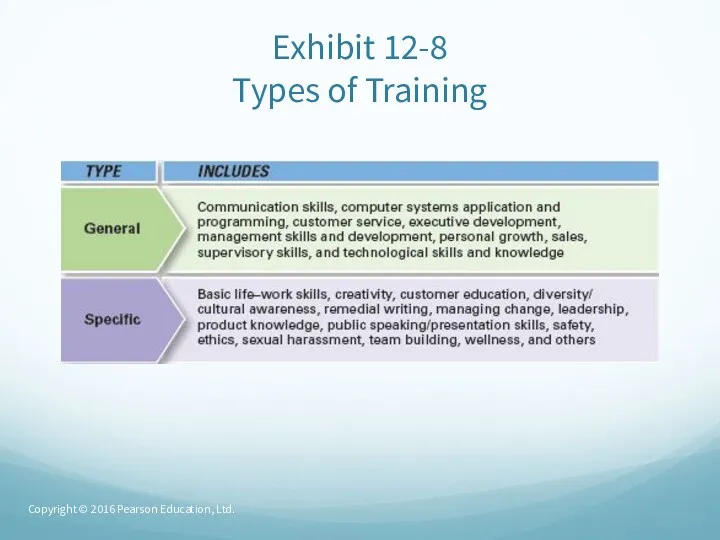
- 28. Exhibit 12-8 Types of Training Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 29. Exhibit 12-9 Traditional Training Methods Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 30. Exhibit 12-9 Traditional Training Methods (cont.) Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 31. Retaining Competent, High Performing Employees Performance management system – establishes performance standards used to evaluate employee
- 32. Exhibit 12-10 Performance Appraisal Methods Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 33. Exhibit 12-10: Performance Appraisal Methods (cont.) Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 34. Exhibit 12-11 What Determines Pay and Benefits Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 35. Contemporary Issues in Managing Human Resources Downsizing – the planned elimination of jobs in an organization.
- 36. Exhibit 12-12 Tips for Managing Downsizing Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 37. Contemporary Issues in Managing Human Resources (cont.) Family -friendly benefits – benefits that accommodate employees’ needs
- 38. Contemporary Issues in Managing Human Resources (cont.) Employee Health Care Costs – since 2002, health care
- 39. Creating and Managing Teams
- 40. Learning Objectives Define groups and the stages of group development. Describe the major components that determine
- 41. What Is a Group? Group – two or more interacting and interdependent individuals who come together
- 42. Exhibit 13-1 Examples of Formal Work Groups Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
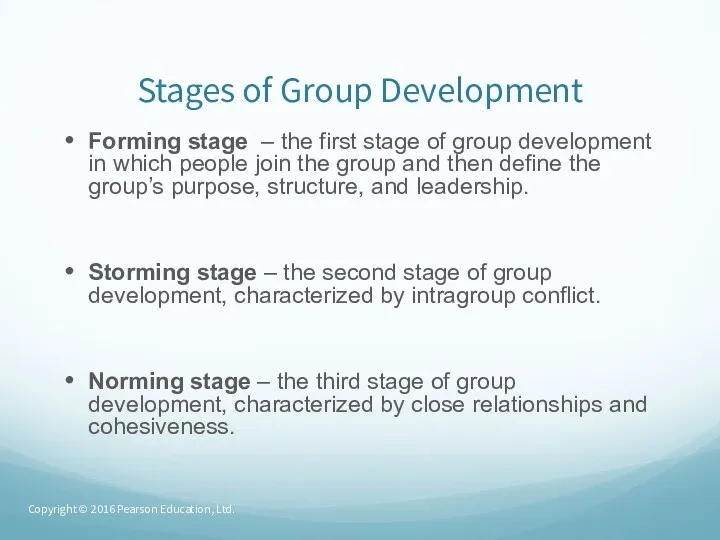
- 43. Stages of Group Development Forming stage – the first stage of group development in which people
- 44. Stages of Group Development (cont.) Performing stage – the fourth stage of group development when the
- 45. Exhibit 13-2 Stages of Group Development Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 46. Work Group Performance and Satisfaction Why are some groups more successful than others? The abilities of
- 47. Exhibit 13-3 Group Performance/Satisfaction Model Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 48. External Conditions Imposed on the Group Work groups are affected by the external conditions imposed on
- 49. Group Member Resources A group’s performance potential depends to a large extent on the resources each
- 50. Group Structure Role – behavior patterns expected of someone occupying a given position in a social
- 51. Group Structure (cont.) Status – a prestige grading, position, or rank within a group. Social loafing
- 52. Exhibit 13-5 Group Cohesiveness and Productivity Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 53. Group Structure (cont.) Group Size Small groups are faster than larger ones at completing tasks Large
- 54. Group Structure (cont.) Group Processes – processes that go on within a work group determines group
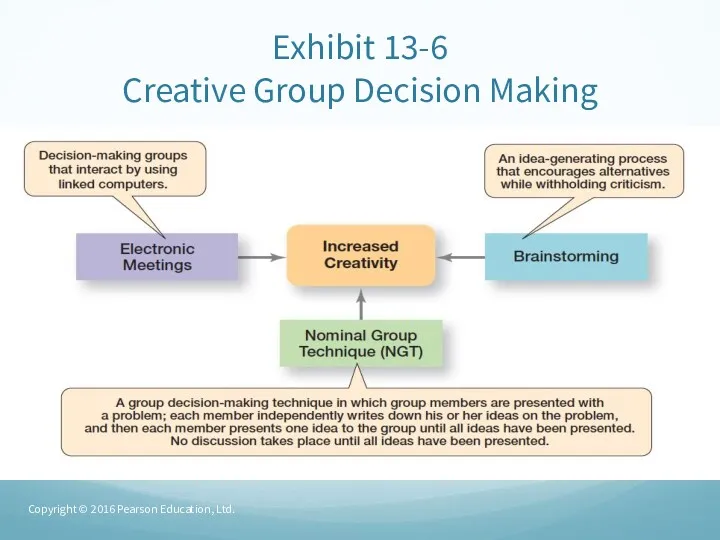
- 55. Group Structure (cont.) Group Decision-making – most organizations use groups to make decisions. Advantages of group
- 56. Exhibit 13-6 Creative Group Decision Making Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 57. Conflict Management Conflict – perceived incompatible differences that result in interference or opposition. Traditional view of
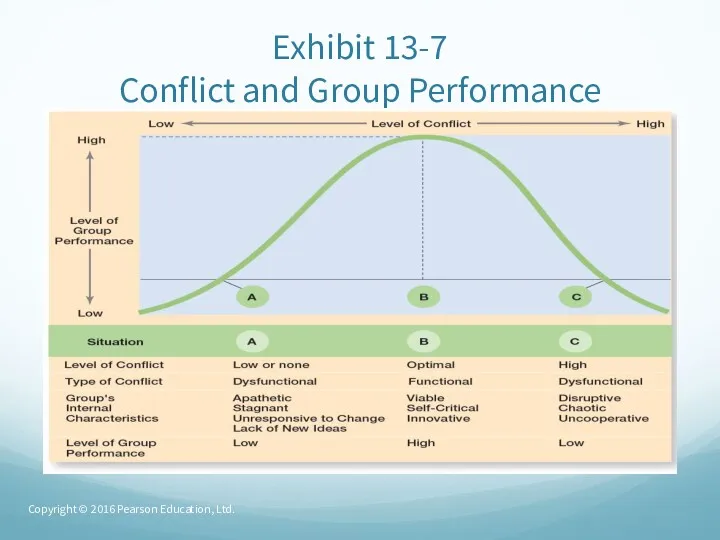
- 58. Conflict Management (cont.) Interactionist view of conflict – the view that some conflict is necessary for
- 59. Conflict Management (cont.) Task conflict – conflicts over content and goals of the work. Relationship conflict
- 60. Exhibit 13-7 Conflict and Group Performance Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
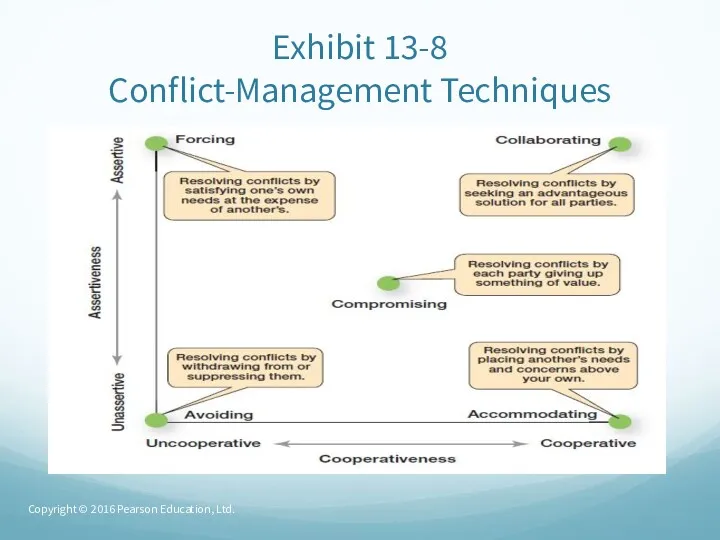
- 61. Exhibit 13-8 Conflict-Management Techniques Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 62. Turning Groups into Effective Teams Work teams – groups whose members work intensely on a specific,
- 63. Exhibit 13-9 Groups Versus Teams Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 64. Types of Work Teams Problem-solving team – a team from the same department or functional area
- 65. Types of Work Teams (cont.) Cross-functional team – a work team composed of individuals from various
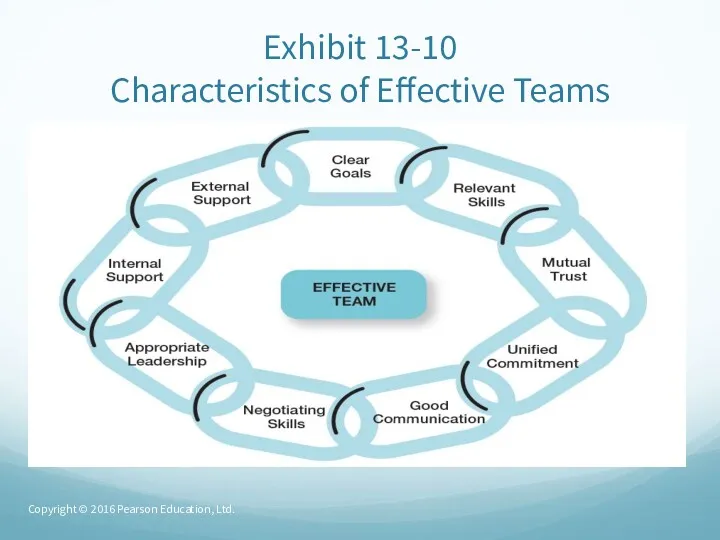
- 66. Creating Effective Work Teams Clear Goals – high-performance teams have a clear understanding of the goal
- 67. Creating Effective Work Teams (cont.) Good Communication – messages are clearly understood. Negotiating Skills – members
- 68. Exhibit 13-10 Characteristics of Effective Teams Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 69. Current Challenges in Managing Teams Group Member Resources in Global Teams – managers need to clearly
- 70. Exhibit 13-11 Global Teams Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd.
- 71. Understanding Social Networks Social Network The patterns of informal connections among individuals within groups. The Importance
- 73. Скачать презентацию






























































 Активные методы обучения
Активные методы обучения Статистическое управление процессами
Статистическое управление процессами Информационное, техническое и правовое обеспечение системы управления персоналом
Информационное, техническое и правовое обеспечение системы управления персоналом Индивидуальный план развития как инструмент управления развитием работника
Индивидуальный план развития как инструмент управления развитием работника Мотивация сотрудников Сектора обслуживания дебетовых карт, Чаты. Тинькофф
Мотивация сотрудников Сектора обслуживания дебетовых карт, Чаты. Тинькофф Основы проектной деятельности
Основы проектной деятельности Реструктуризация деятельности фирмы
Реструктуризация деятельности фирмы Варианты формирования логистических цепей
Варианты формирования логистических цепей Системный анализ, как методология решения проблем
Системный анализ, как методология решения проблем Анализ бизнес-этикета как составной части корпоративной культуры туристической фирмы
Анализ бизнес-этикета как составной части корпоративной культуры туристической фирмы Организационная структура управления
Организационная структура управления Автосервис — подсистема автомобильного транспорта (лекция № 1)
Автосервис — подсистема автомобильного транспорта (лекция № 1) Активные методы обучения
Активные методы обучения Формирование управленческих команд и управление командной работой
Формирование управленческих команд и управление командной работой Бережливое производство. Вводная часть
Бережливое производство. Вводная часть Административная (классическая) школа управления (1920-1950)
Административная (классическая) школа управления (1920-1950) Совершенствование безопасности в гостинице Дружба
Совершенствование безопасности в гостинице Дружба Основні теорії та моделі організації
Основні теорії та моделі організації Совершенствование методов обучения персонала
Совершенствование методов обучения персонала Анализ внутренней и внешний среды предприятия ООО Надежда
Анализ внутренней и внешний среды предприятия ООО Надежда Организация технической подготовки и сопровождения ремонтно-обслуживающего производства. Лекция 15
Организация технической подготовки и сопровождения ремонтно-обслуживающего производства. Лекция 15 Организация управления рисками на предприятии. (Лекция 7)
Организация управления рисками на предприятии. (Лекция 7) Гостеприимство. Основные понятия, объекты управления
Гостеприимство. Основные понятия, объекты управления Базисные условия поставки
Базисные условия поставки Человеческие ресурсы
Человеческие ресурсы Гостиничное дело. Основные службы гостиничного предприятия
Гостиничное дело. Основные службы гостиничного предприятия Риски и возможности. ISO 9000:2015 и руководство ISO 73:2009
Риски и возможности. ISO 9000:2015 и руководство ISO 73:2009 Система государственного регулирования инновационной деятельности
Система государственного регулирования инновационной деятельности