Содержание
- 2. Introduction MRP (Material Requirements Planning) Planning & scheduling technique used for batch production of assembled items
- 3. Dependent demand: Demand for materials which are derived from the build-plan of finished goods. Example: Wagon
- 4. Independent demand: Red Wagon Model #12 Dependent demand: The parts needed to make the wagon Handle
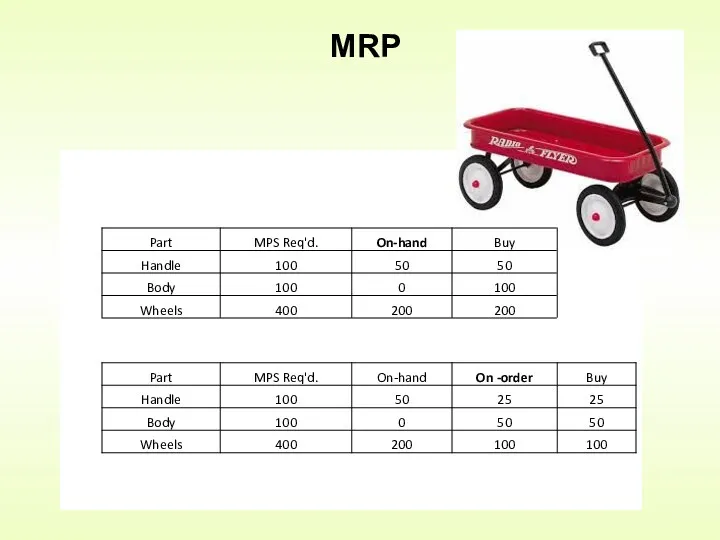
- 5. Build 100 wagons in May How many parts do I need? Handle 1 x 100 =
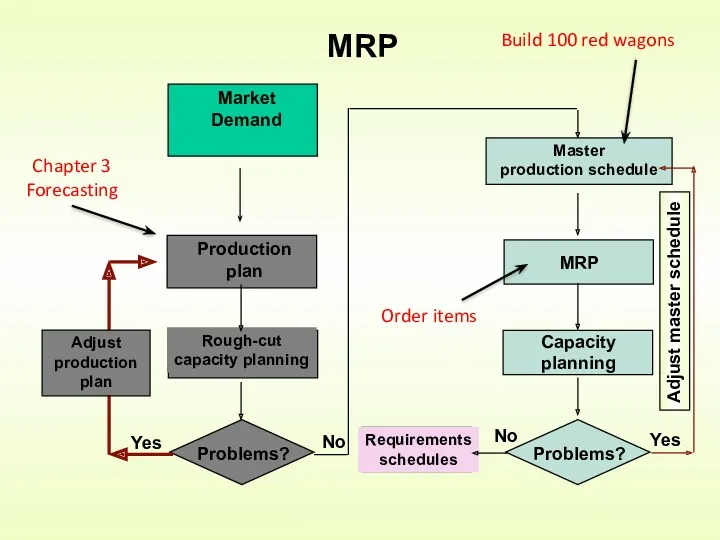
- 6. MRP
- 7. Build 100 wagons in May What if the supplier only sells wheels in cases of 500
- 8. MRP Build 100 red wagons Order items Chapter 3 Forecasting
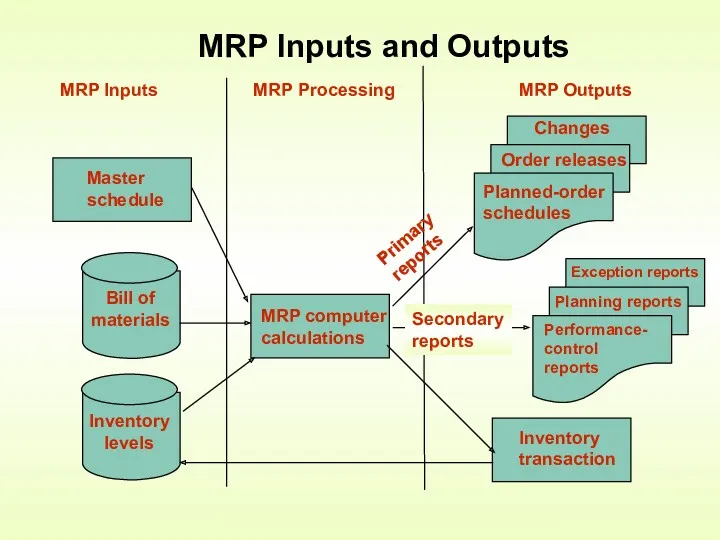
- 9. MRP Inputs and Outputs
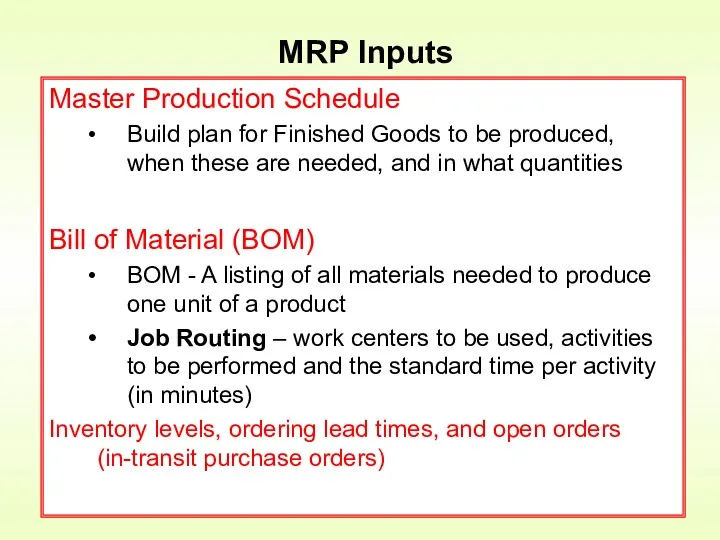
- 10. Master Production Schedule Build plan for Finished Goods to be produced, when these are needed, and
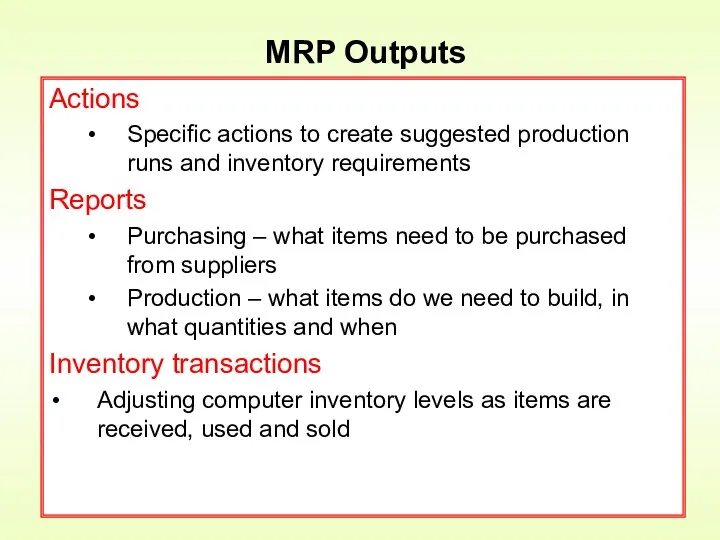
- 11. Actions Specific actions to create suggested production runs and inventory requirements Reports Purchasing – what items
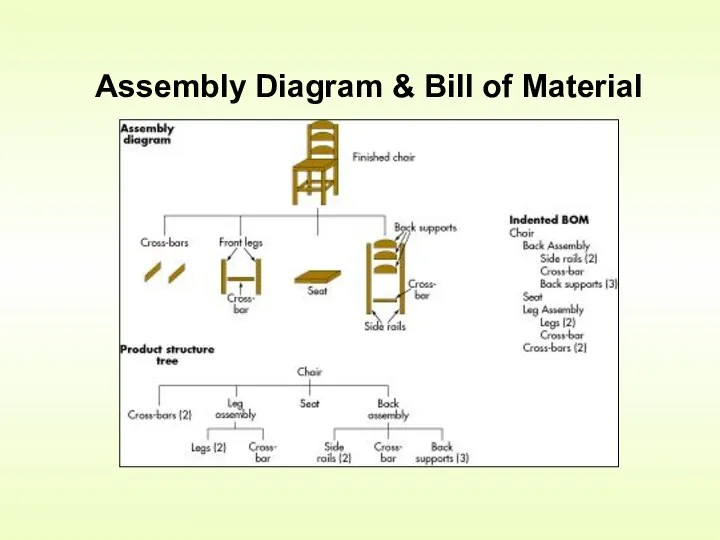
- 12. Assembly Diagram & Bill of Material
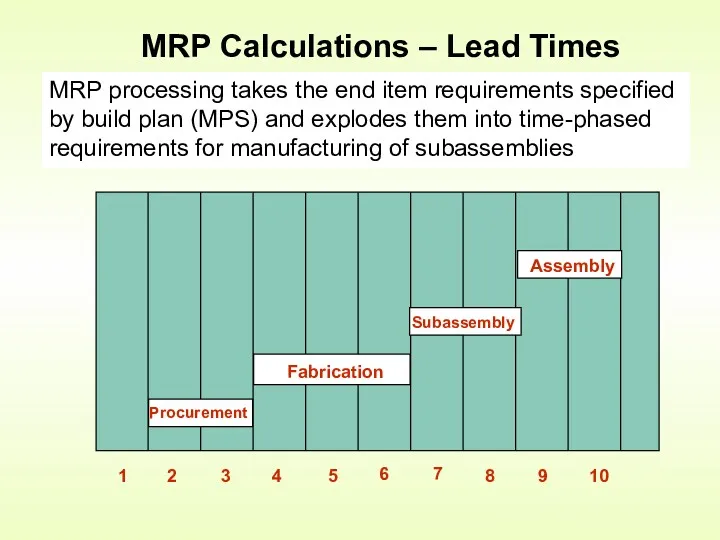
- 13. MRP Calculations – Lead Times MRP processing takes the end item requirements specified by build plan
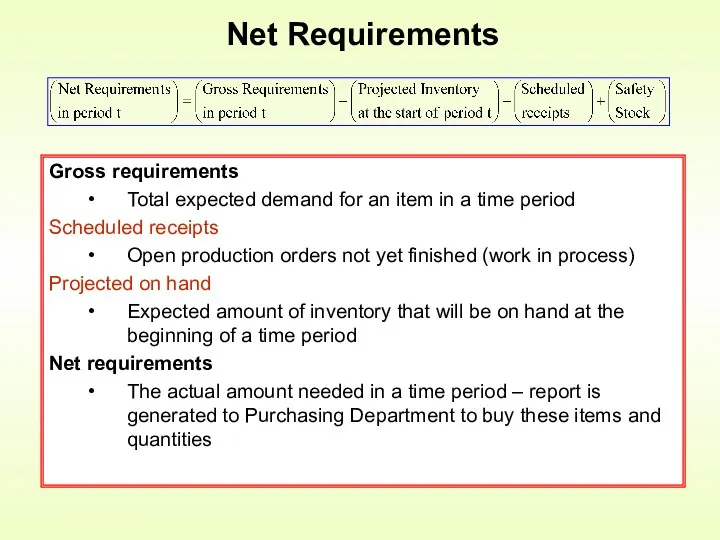
- 14. Net Requirements Gross requirements Total expected demand for an item in a time period Scheduled receipts
- 15. Net Requirements Planned order receipts Quantity expected to be received in the beginning of a time
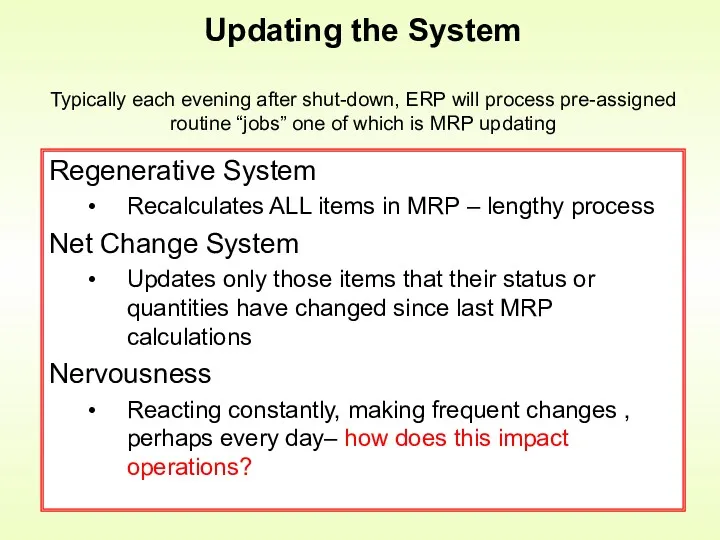
- 16. Regenerative System Recalculates ALL items in MRP – lengthy process Net Change System Updates only those
- 17. Other Considerations Safety Stock For or operations that are subject to variability in time (not consistent)
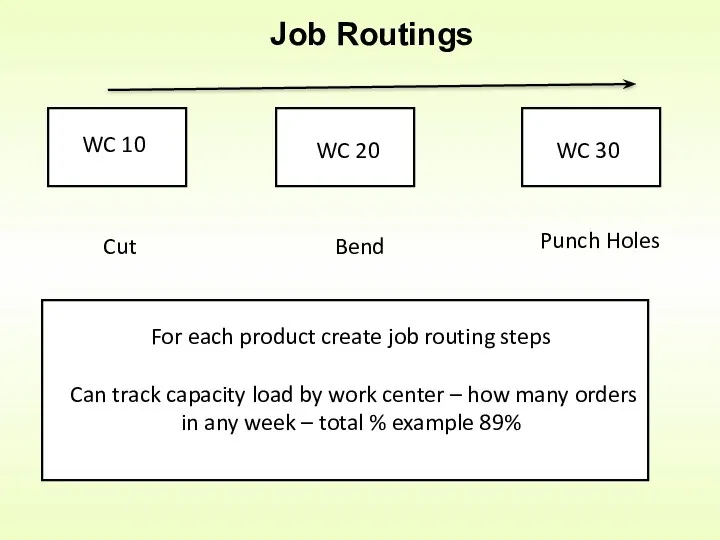
- 18. Job Routings WC 10 WC 20 WC 30 Cut Bend Punch Holes For each product create
- 20. Скачать презентацию






 Совершенствование закупочной логистики торговой компании. ООО БТ-КРАН
Совершенствование закупочной логистики торговой компании. ООО БТ-КРАН От лица компании МТС
От лица компании МТС Диагностика имиджа компании как работодателя
Диагностика имиджа компании как работодателя Психологическое сопровождение организации Арбат-фитнес
Психологическое сопровождение организации Арбат-фитнес Модуль Управление персоналом (Нuman Resources). Управление организационными структурами
Модуль Управление персоналом (Нuman Resources). Управление организационными структурами SuccessFactors User Guide
SuccessFactors User Guide Тьюториал. Управление организацией и персоналом. Власть, лидерство и изменения. (Книга 4)
Тьюториал. Управление организацией и персоналом. Власть, лидерство и изменения. (Книга 4) Понятие Экологического менеджмента
Понятие Экологического менеджмента Разработка системы качества для предприятия
Разработка системы качества для предприятия Управление знаниями. Knowledge Management. Знания в информационных системах
Управление знаниями. Knowledge Management. Знания в информационных системах Стратегическое управление организацией. Сущность стратегического управления и реализация стратегии
Стратегическое управление организацией. Сущность стратегического управления и реализация стратегии Основы финансового менеджмента
Основы финансового менеджмента Мотивация, как функция управления
Мотивация, как функция управления Умение крититковать в деятельности менеджера
Умение крититковать в деятельности менеджера Қонақ үй классификациясы
Қонақ үй классификациясы Деятельность менеджера
Деятельность менеджера Обзор литературы по проектной деятельности
Обзор литературы по проектной деятельности Структура службы Housekeeping: состав, основные функции и задачи
Структура службы Housekeeping: состав, основные функции и задачи Предприятия общественного питания
Предприятия общественного питания Виды организационных структур
Виды организационных структур Стандарты телефонного общения. Билайн
Стандарты телефонного общения. Билайн Навыки медицинского представителя. Тренинг
Навыки медицинского представителя. Тренинг Многомерный стиль руководства
Многомерный стиль руководства Этапы процесса проектирования туристско-рекреационного продукта
Этапы процесса проектирования туристско-рекреационного продукта Функции управления проектами
Функции управления проектами Модель сервиса. Руководство для тренера. (Модуль 1)
Модель сервиса. Руководство для тренера. (Модуль 1)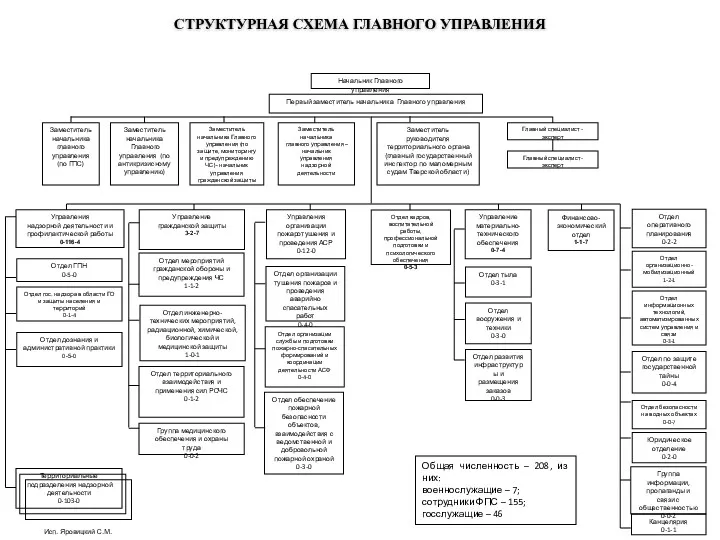 Структурная схема главного управления
Структурная схема главного управления Knowledge management in smes. Dr. Susanne Durst
Knowledge management in smes. Dr. Susanne Durst